Calcium-Aluminum Composite Material Prepared by Mechanochemical Method for Deep Defluorination
-
摘要:
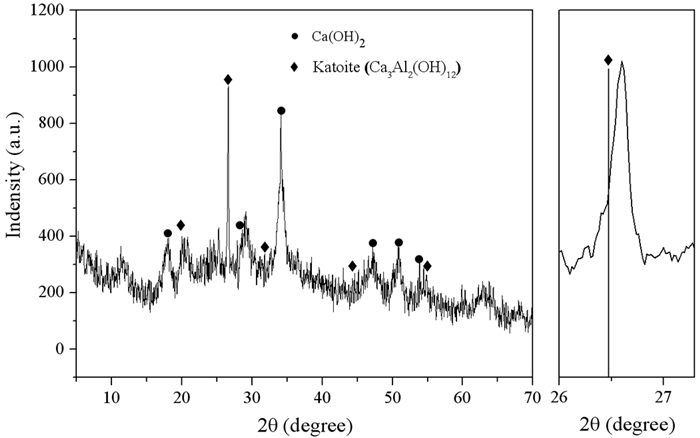
水体中氟化物含量超标一直是全球关注的环境问题之一,使用含钙物质生成氟化钙沉淀法,出水浓度一般在8~9 mg/L,不能满足饮用水中含氟低于1.5 mg/L的世卫标准。为此,本文基于机械力活化的概念,使用行星磨球磨钙铝氢氧化物合成加藤石材料[Ca3Al2(OH)12],通过OH-与F-离子交换的新脱氟机理,实现了饮水达标的深度脱氟。在Ca:Al摩尔比为3:2、球磨1 h、转速为500 r/min的条件下,制备的材料可将氟离子浓度从10 mg/L降到0.32 mg/L。用高岭石代替氢氧化铝也能实现类似的深度脱氟,为含氟废水的高度净化提供了新的思路和可行性。
Abstract:Excessive fluoride content in water has always been one of the environmental issues of global concern. The calcium fluoride precipitation method produced by calcium-containing substances with the effluent concentration of 8-9 mg/L cannot meet the WHO standard that the fluorine content in drinking water is less than 1.5 mg/L. Based on the concept of mechanochemical activation, the goal of deep defluoridation of drinking water up to standard has been achieved by the Ca3Al2(OH)12 synthesized by grinding calcium aluminum hydroxide using planetary milling balls, which is based on a new defluorination mechanism of OH- and F- exchange. The prepared material can reduce the fluoride ion concentration from 10mg/L to 0.32 mg/L under the condition of the molar ratio of Ca: Al being 3:2, grinding time of 1h and the stirred speed of 500 r/min. Substituting kaolinite for aluminum hydroxide can also achieve similar deep defluorination, which provides new ideas and feasibility for the high purification of fluorine-containing wastewater.
-
Key words:
- mechanochemistry /
- deep defluorination /
- fluoride ions /
- katoite /
- kaolinite
-

-
表 1 高岭土样品的主要化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical compositions of kaolin sample
Composition Na2O MgO Al2O3 SiO2 P2O5 SO3 Mass/% 0.14 0.19 36.91 45.50 0.16 0.86 Composition K2O CaO TiO2 Fe2O3 LOI Mass/% 0.24 0.44 1.15 0.59 13.82 -
[1] MEENAKSHI, MAHESHWARI R C. Fluoride in drinking water and its removal[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 137: 456-463. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.024
[2] MEENAKSHI S, VISWANATHAN N. Identification of selective ion-exchange resin for fluoride sorption[J]. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 2007, 308: 438-450. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2006.12.032
[3] DWIVEDI A D, DUBEY S P, GOPAL K, et al. A comparative investigation for strengthening the adsorptive phenomenon by activated natural minerals and plant waste-carbon for defluoridation in water milieu[J]. Desalination, 2010, 263: 189-199. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.06.059
[4] 张小磊, 何宽, 马建华. 氟元素对人体健康的影响[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2006(6): 69-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WYJK200606028.htm
[5] MEENAKSHI, MAHESHWARI R C. Fluoride in drinking water and its removal[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 137: 456-463. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.02.024
[6] KIMAMBO V, BHATTACHARYA P, MTALO F, et al. Fluoride occurrence in groundwater systems at global scale and status of defluoridation-State of the art[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 2019, 9: 100223. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100223
[7] MOHAPATRA M, ANAND S, MISHRA B K, et al. Review of fluoride removal from drinking water[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2009, 91: 67-77. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20103203651.html
[8] 姜华, 刘佳, 苏国栋. 含氟废水的处理[J]. 化工生产与技术, 2012(6): 8-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGSC201206007.htm
[9] 闫秀芝, 王淑芬. CaCl2+磷酸盐法处理含氟废水的探讨[J]. 环境保护科学, 1998(2): 13-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJBH802.004.htm
[10] 张其武. 碳酸钙矿物材料用于环境治理的新概念[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2018(4): 93-96. http://kcbh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKD/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=5a6a6059-3a3f-4898-8bcd-fd7c59e48b85
[11] ZHIWU LEI, GIOVANNI CAGNETTA, XUEWEI LI, Jet al. Enhanced adsorption of potassium nitrate with potassium cation on H3PO4 modified kaolinite and nitrate anion into Mg-Al layered double hydroxide[J]. Applied Clay Sci., 2018, 154: 10-16. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.12.040
[12] YUJIE LI, YUJIE LI, XIAOMAN HE, et al. Enhanced phosphate removal from wastewater by using in situ generated fresh trivalent Fe composition through the interaction of Fe(Ⅱ) on CaCO3[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2018, 221: 38-44. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29793208
-




 下载:
下载: