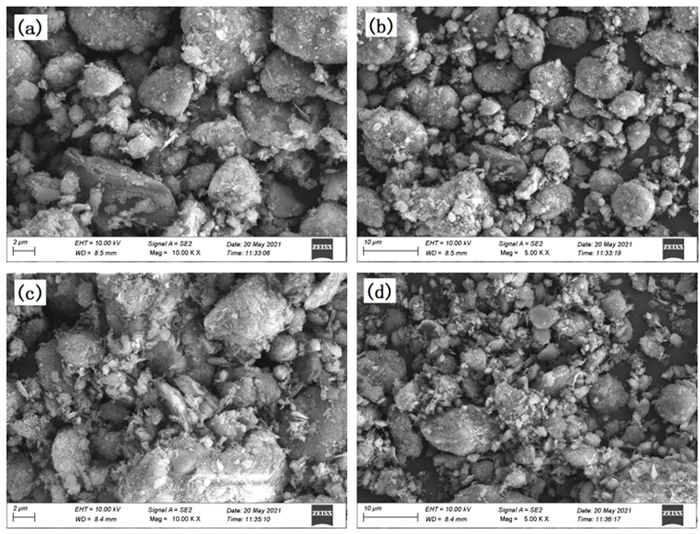
Study on Effects of Acid Modification or Heat Treatment on Formaldehyde Adsorption of Sepiolite in Air and the Related Mechanisms
-
摘要:
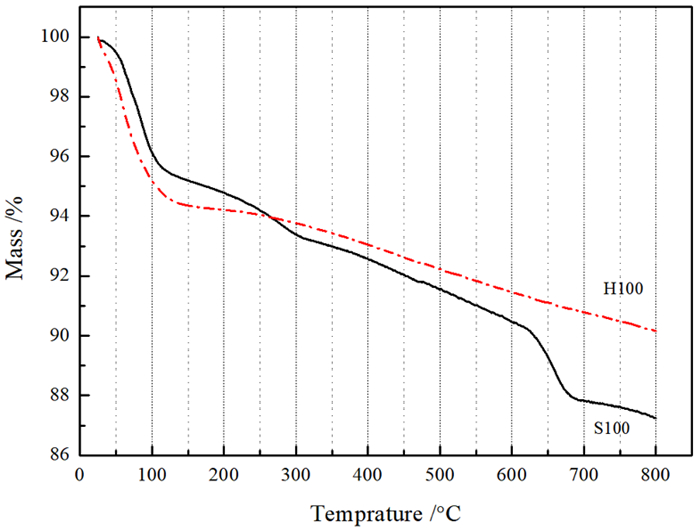
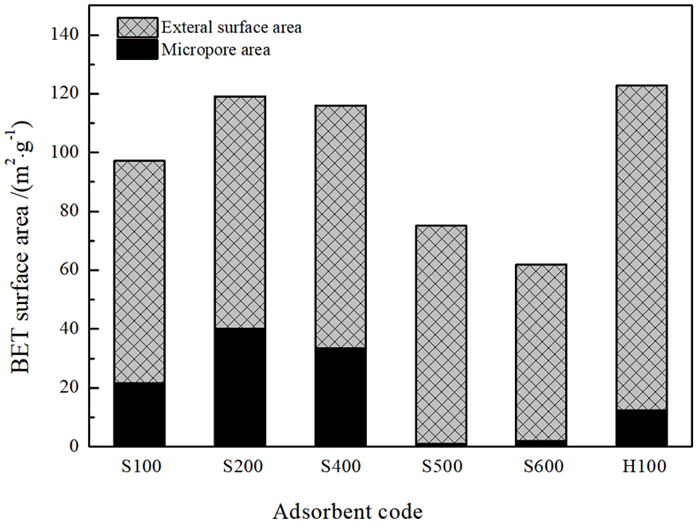
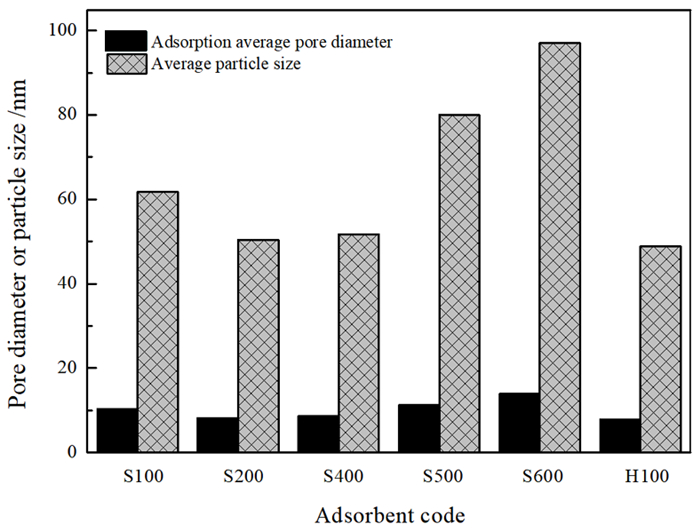
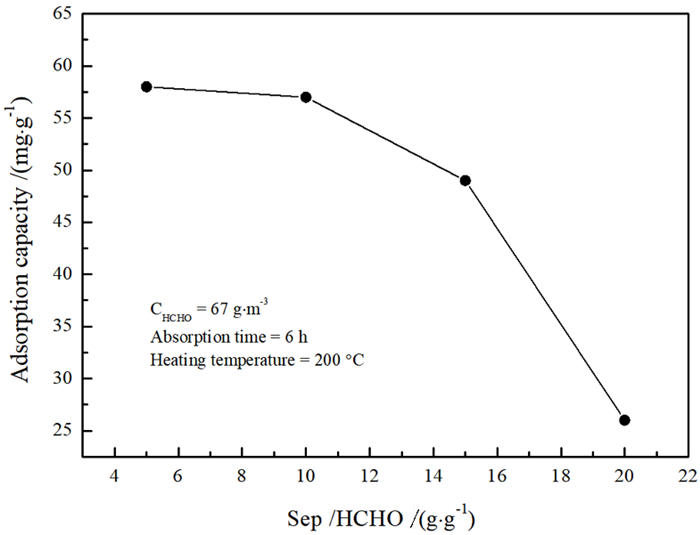
为再生海泡石的甲醛吸附能力,分别对经质量分数15%盐酸于60 ℃搅拌8.5 h和于100~600 ℃热处理5 h的海泡石进行甲醛静态吸附研究,并结合X射线衍射、红外吸收光谱、热重、BET比表面积和扫描电镜分析研究吸附机理。结果表明: 经≤450 ℃热处理的海泡石基本保持良好的甲醛吸附性能,但酸处理和≥500 ℃热处理均显著降低海泡石的甲醛吸附性能。推测海泡石相的结晶水对甲醛形成化学吸附,而其沸石孔洞为主的结构微孔有利于物理吸附的甲醛占位。酸处理使海泡石中大量的Al3+和Mg2+被H+取代,使原本与Mg2+结合的结晶水脱失,结构层拆解,其微孔面积则因结构微孔坍塌而显著减少,从而严重降低其甲醛吸附量; 而经≥500 ℃热处理后,海泡石相的全部结晶水不可逆脱出,全部结构微孔坍塌消失,甲醛吸附能力消失。该研究支持海泡石通过合理温度的热处理消除吸附的甲醛并再生吸附功能持续去除空气中的甲醛。
Abstract:In order to regenerate HCHO adsorption, both types of sepiolite stirred at 15% HCl for 8.5 h or heated at 100~600 ℃ for 5 h were applied to static adsorption experiments in high concentration HCHO to research the HCHO adsorption effects, and X-ray diffraction, infrared adsorption spectroscopy, thermogravimetry, BET specific surface area analysis and scanning electronic microscopy were adopted to research the adsorption mechanisms. The results revealed that the sepiolite heated at ≤450 ℃ held favorable HCHO adsorption capacities, while those modified by acid or heated at ≥500 ℃ had significantly reduced HCHO adsorption capacities. It is inferred that the crystalliferous water in sepiolite could chemically absorb HCHO and the structural microhole, basically composed of zeolite holes, could be occupied by HCHO through physical adsorption. Subjected to acid modification, large part of Al3+ and Mg2+ in the sepiolite structure were replaced by H+, then the crystalliferous water bonded with Mg2+ lost and the structural layers were dismantled. The micropore area significantly reduced due to the structural microhole collapsed, and the HCHO absorption capacity drastically declined. The sepiolite heated at ≥500 ℃ lost its HCHO adsorption ability for the sepiolite phase was decomposed with the crystalliferous water completely lost and the structural microhole collapsed also. The research affirmed continuously removing HCHO in the air with sepiolite by heating at reasonable temperature that could not only eliminate the absorbed HCHO and regenerate the adsorption capacity.
-
Key words:
- sepiolite /
- HCHO adsorption /
- heat treatment /
- acid modification /
- adsorption mechanism
-

-
表 1 海泡石其及酸化样的化学组成
Table 1. Chemical analysis of sepiolite and the acidized sepiolite
/% 样品性质 LOI (灼减) Al2O3 SiO2 Fe2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O TiO2 海泡石 11.43 4.70 58.28 1.44 4.18 19.14 0.29 0.09 0.14 酸化海泡石 8.70 2.22 79.47 0.23 0.11 8.53 0.29 0.06 0.19 -
[1] 崔维怡, 王希越, 谭乃迪. 甲醛催化氧化反应机理的研究进展[J]. 精细化工, 2020, 37(10): 1978-1985. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXHG202010004.htm
CUI W Y, WANG X Y, TAN N D. Research progress in the mechanism of catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2020, 37(10): 1978-1985. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXHG202010004.htm
[2] 张永航. 空气中甲醛净化处理的研究进展[J]. 广州化工, 2020, 48(22): 24-27+89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZHA202022011.htm
ZHANG Y H. Research progress on formaldehyde purification in air[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2020, 48(22): 24-27+89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZHA202022011.htm
[3] 黄慧娟, 尚莉莉, 马建锋, 等. 锰氧化物催化分解室内甲醛的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33: 521-525. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB2019S2105.htm
HUANG H J, SHANG L L, MA J F, et al. Advances on catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde by manganese oxide[J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33: 521-525. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB2019S2105.htm
[4] 王濮, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝, 等. 系统矿物学(中册)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987: 419-421.
WANG P, PAN Z L, WEN L B, et al. Systemic Mineralogy(middle volume)[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 1987: 419-421.
[5] CORUH S, GEYIKEI F, ELEVLI S. Adsorption of neutral red dye from an aqueous solution onto natural sepiolite using full factorial design[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 2011, 59(6): 617-625. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.2011.0590607
[6] 鲁旖, 仇丹, 章凯丽. 海泡石吸附剂的应用研究进展[J]. 宁波工程学院学报, 2016, 28(1): 17-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LBGS201601004.htm
LU Y, QIU D, ZHANG K L. Research progress on application of sepiolite absorbent[J]. Journal of Ningbo University of Technology, 2016, 28(1): 17-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LBGS201601004.htm
[7] 贺洋. 低品质海泡石提纯及吸附性能研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2019, 42(4): 56-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJSK201904017.htm
HE Y. Purification of low quality sepiolite and adsorption capacity research[J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 2019, 42(4): 56-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJSK201904017.htm
[8] 周鹏. 改性海泡石制备及其对甲醛的吸附行为研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2019.
ZHOU P. Preparation of modified sepiolite and adsorption behavior to formaldehyde[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2019.
[9] 宋公保, 彭同江, 董发勤, 等. 海泡石的红外光谱研究[J]. 矿物学报, 1998, 18(4): 525-532. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1998.04.019
SONG G B, PENG T J, DONG F Q, et al. Infrared spectrometric study of sepiolite[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1998, 18(4): 525-532. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1998.04.019
[10] 王艳, 王多君, 易丽. 空气气氛中滑石的热分解动力学试验研究[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2015, 32(1): 70-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB201501013.htm
WANG Y, WANG D J, YI L. Experimental study on thermal decomposition kinetics of talc under the condition of air[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015, 32(1): 70-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB201501013.htm
[11] 聂利华, 刘德忠, 姚守拙. 海泡石的物化特性[J]. 湖南大学学报, 1990, 17(1): 106-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDX199001015.htm
NIE L H, LIU D Z, YAO S C. Physichemieal Properties of sepiolite of Liuyang County in Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Hunan University, 1990, 17(1): 106-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDX199001015.htm
[12] 梁伟朝. 海泡石改性及其吸附挥发性有机物机理与过程研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2016.
LIANG W C. Adsorption mechanism and process of VOCs on Modified sepiolite[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2016.
-



 下载:
下载: