Study on Photodegradation of Organic Depressants in Wastewater from Molybdenum-lead Separation and Wastewater Recycle
-
摘要:
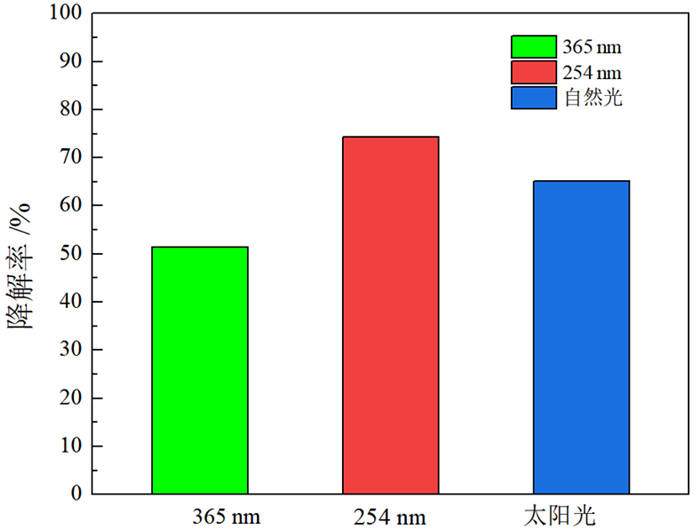
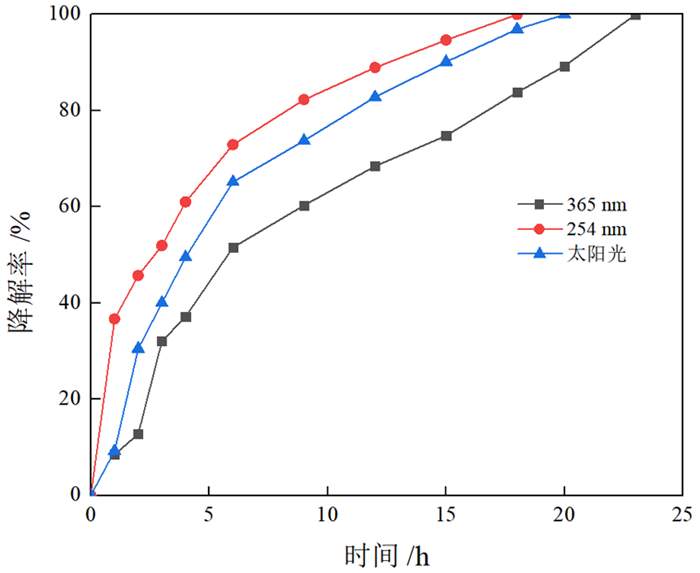
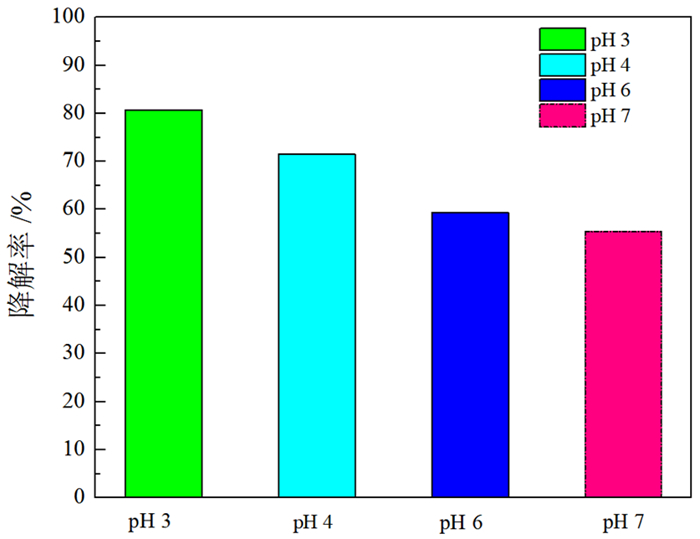
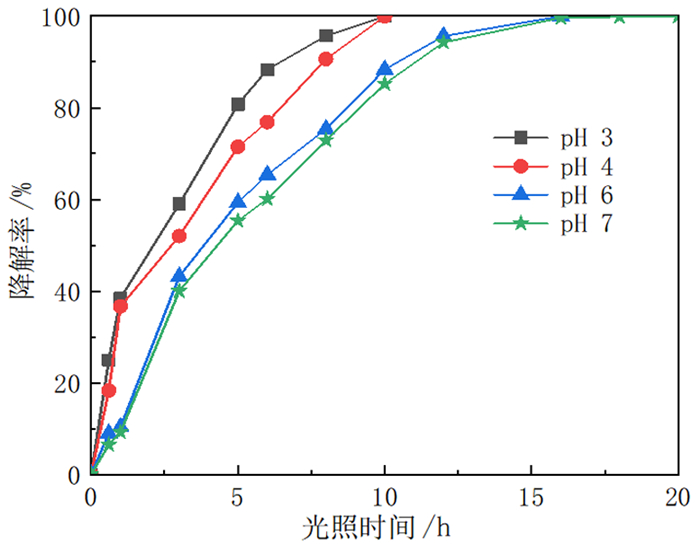
针对钼铅分离抑制剂在废水中残留导致回水利用困难的问题,将光敏感型抑制剂LM应用于钼铅分离,并进行了分离废水中抑制剂的降解动力学研究。采用光照降解,分别研究了太阳光照射、紫外光照射等不同光源对降解率的影响。结果表明,太阳光与紫外光光源均能激发LM抑制剂的分解程序,最终降解率均能达到99.9%以上。进一步研究了不同pH值对钼铅分离废水中LM抑制剂的降解影响,结果表明酸性环境下降解率加快。经过浮选试验验证,与清水相比,光降解后的选矿废水钼铅分离指标基本一致,因此可以直接回用,采用该抑制剂有利于钼铅分离的清洁生产与节能减排。
Abstract:The undecomposed residue of molybdenum-lead separation inhibitors remain in wastewater stream makes it difficult to be recycled. To tackle this issue, photodegradable inhibitor LM was used for molybdenum-lead separation, and the degradation kinetics of inhibitor in molybdenum-lead separation wastewater was also studied. The degradation method was photodegradation, and the effects of different light sources such as sunlight irradiation and ultraviolet light irradiation on the degradation rate were studied respectively. The results show that both sunlight and ultraviolet light sources can accelerate the decomposition process of LM, and the final degradation rate can reach more than 99.9%. The effect of different pH values on the degradation of LM in molybdenum-lead separation wastewater stream was further studied, which indicates that, the degradation rate was accelerated in an acidic environment. The verification flotation tests were conducted, the results of which suggest the molybdenum-lead separation wastewater after photodegradation can be directly reused. It is beneficial to clean production, energy saving and emission reduction.
-
Key words:
- molybdenum-lead separation /
- photodegradation depressant /
- wastewater recycling /
- flotation /
-

-
表 1 原料化学多元素分析结果
Table 1. Multi-elements analysis results of raw ores
/% 成分 Mo Fe Cu Pb Zn K2O Na2O 含量 16.61 8.00 1.04 0.21 0.23 2.39 0.38 成分 P S CaO MgO Ti SiO2 Al2O3 含量 0.052 18.21 2.32 1.24 0.24 40.25 7.97 表 2 采用清水与光照降解后的钼铅分离尾水钼铅分离试验结果
Table 2. Molybdenum-lead separation test results
/% 试验用水 产品名称 作业产率 品位 作业回收率 Mo Pb Mo Pb 清水 钼精矿 49.08 31.81 0.25 97.32 56.11 尾矿 50.92 0.84 0.19 2.68 43.89 钼粗精矿 100.00 16.04 0.22 100.00 100.00 365 nm波长紫外光降解20 h后的尾水 钼精矿 49.54 31.78 0.25 97.54 55.98 尾矿 50.46 0.79 0.19 2.46 44.02 钼粗精矿 100.00 16.14 0.22 100.00 100.00 254 nm波长紫外光降解20 h后的尾水 钼精矿 49.29 31.76 0.24 97.51 55.71 尾矿 50.71 0.79 0.19 2.49 44.29 钼粗精矿 100.00 16.05 0.21 100.00 100.00 太阳光降解20 h后的尾水 钼精矿 49.69 31.87 0.25 97.33 56.31 尾矿 50.31 0.86 0.19 2.67 43.69 钼粗精矿 100.00 16.27 0.22 100.00 100.00 -
[1] 林春元. 钼矿选矿与深加工[M]. 北京: 北京冶金出版社, 1997: 1-65.
LIN C Y. Beneficiation of molybdenum and its intensive processing[M]. Beijing Metallurgical Press, 1997: 1-65.
[2] 张文钲, 徐秋生. 提高钼精矿质量的探讨[J]. 矿业快报, 2006(12): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB200612000.htm
ZHANG W Z, XU Q S. Discussion on increasing quality of molybdenum concentrate[J]. Express information of mining industry, 2006(12): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYKB200612000.htm
[3] 王漪靖. 钼精矿铅高原因分析及对策[J]. 中国钼业, 2002, 26(6): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2602.2002.06.002
WANG Y J. Cause analysis and countermeasures of high-lead in molybdenum concentrate[J]. China Molydenum Industry, 2002, 26(6): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2602.2002.06.002
[4] TANRIVERDI M, OZTURK E. Use of sodium metabisulphide as an alternative depressant in selective notation of lead and copper[J]. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 2012, 24(8): 3579-3581.
[5] PIAO Z J, WEI D Z, LIU Z L, et al. Selective depression of galena and chalcopyrite by O, O-bis(2, 3-dihydroxypropyl) dithiophosphate[J]. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2013(23): 3063-3067.
[6] PIAO Z J, WEI D Z, LIU Z L. Influence of sodium 2, 3-dihydroxypropyl dithiocarbonate on floatability of chalcopyrite and galena[J]. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2014(24): 3343-3347.
[7] 王德海. 某复杂钼铅多金属矿浮选试验研究[J]. 甘肃冶金, 2017, 39(1): 1-4+14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2017.01.001
WANG D H. Research on flotation of a complex molybdenum-lead polymetallic ore[J]. Gangsu Metallurgy, 2017, 39(1): 1-4+14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4461.2017.01.001
[8] 温晓婵, 殷志刚, 刘建东. 新型组合抑制剂在钼铅浮选分离中的应用[J]. 中国钼业, 2016, 40(2): 26-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMY201602010.htm
WEN X C, YIN Z G, LIU J D. The application of new type of depressant on separation of molybdenite from galena[J]. China Molybdenum Industry, 2016, 40(2): 26-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMY201602010.htm
[9] 陈代雄. 新型组合抑制剂对微细粒方铅矿抑制机理研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2020(2): 105-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS202002003.htm
CHEN D X. Study on the inhibition mechanism of new combination inhibitors on fine galena[J]. Metal Mine, 2020(2): 105-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS202002003.htm
[10] 程新朝, 孙志健. 中国钼精矿降铅研究进展[J]. 矿冶, 2017, 26(5): 1-4+10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ201705001.htm
CHENG X C, SUN Z J. The research development on reducing lead from molybdenite concentrate in China[J]. Mining & Metallurgy, 2017, 26(5): 1-4+10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ201705001.htm
[11] 北京市环境保护科学研究院. 污水综合排放标准: GB 8978—1996[S]. 北京: 国家环境保护局, 1996.
Beijing Research Institute of Environmental Protection State. Integrated wastewater discharge Standard: GB 8978—1996[S]. Beijing: Department of Environmental Conservation, 1996.
[12] 胡鞍钢. 中国实现2030年前碳达峰目标及主要途径[J]. 北京工业大学学报(社会科学版), 2021, 21(3): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BGYS202103001.htm
HU A G. China's goal of achieving carbon peak by 2030 and its main approaches[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology (Social science edition), 2021, 21(3): 1-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BGYS202103001.htm
[13] 朱小米, 石文艳. 光降解-超声波耦合处理磺胺类药物废水的研究[J]. 化工时刊, 2018, 32(5): 24-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJS201807007.htm
ZHU X M, SHI W Y. Study on photodegration-ultrasonic coupling treatment of the wastewater sulfadiazine[J]. Chemical Industry Times, 2018, 32(5): 24-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGJS201807007.htm
[14] 马佳麟, 王恩革, 张雪洁, 等. 光催化氧化在难降解废水处理中的应用进展[J]. 山东化工, 2021, 50: 266-268+271. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG202108113.htm
MA J L, WANG E G, ZHANG X J and etc. Application of photocatalytic oxidation in refractory wastewater treatment[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2021, 50: 266-268+271. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG202108113.htm
[15] ALI S. ALKORBI, HAFIZ MUHAMMAD ASIF JAVED, SHAHID HUSSAIN, et al. Solar light-driven photocatalytic degradation of methyl blue by carbon-doped TiO2 nanoparticles[J]. Optical Materials, 2022, 127: 1-5.
[16] 王明晖, 聂晶, 李静. 光催化技术在水处理中的研究进展[J]. 能源与环境, 2012(2): 51-52+57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9064.2012.02.024
WANG M H, NIE J, LI J. Research progress of photocatalytic technologies in area of wastewater treatment[J]. Energy and Environment, 2012(2): 51-52+57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9064.2012.02.024
[17] 梅光军, 李佩悦, 雷绍民. 水杨羟肟酸捕收剂光催化降解研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2010(7): 157-160+187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201007050.htm
MEI G J, LI P Y, LEI S M. Study on photocatalytic degradation of flotation collector of salicylic hydroxamic acid[J]. Metal Mine, 2010(7): 157-160+187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201007050.htm
[18] 鄢恒珍, 龚文琪, 梅光军, 等. 共代谢条件下丁基黄药的生物降解试验研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2010, 32(4): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2010.04.001
YAN H Z, GONG W Q, MEI G J, et al. Study on co-metabolism biodegradation of butyl xanthate[J]. Environmental pollution and Prevention, 2010, 32(4): 1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2010.04.001
[19] XU M Y, ZENG G Q, CAI X W, et al. Screening of high efficient paracetamolum degrading bacterial strains and the effect of their biorugmentative use[J]. Acta Sci Circumst, 2003, 23(5): 391-395.
[20] 丁惠平. 微生物法处理苯胺工业废水[J]. 广东化工, 2005(12): 20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2005.12.006
DING H P. Microorganism treatment industrial aniline sewage[J]. Guangdong Chemical, 2005(12): 20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2005.12.006
[21] 袁芳. 多效唑在水体中光化学降解的研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2007.
YUAN F. Research on photochemical degradation of paclobutrazol in aqueous solution[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultral University, 2007.
-




 下载:
下载: