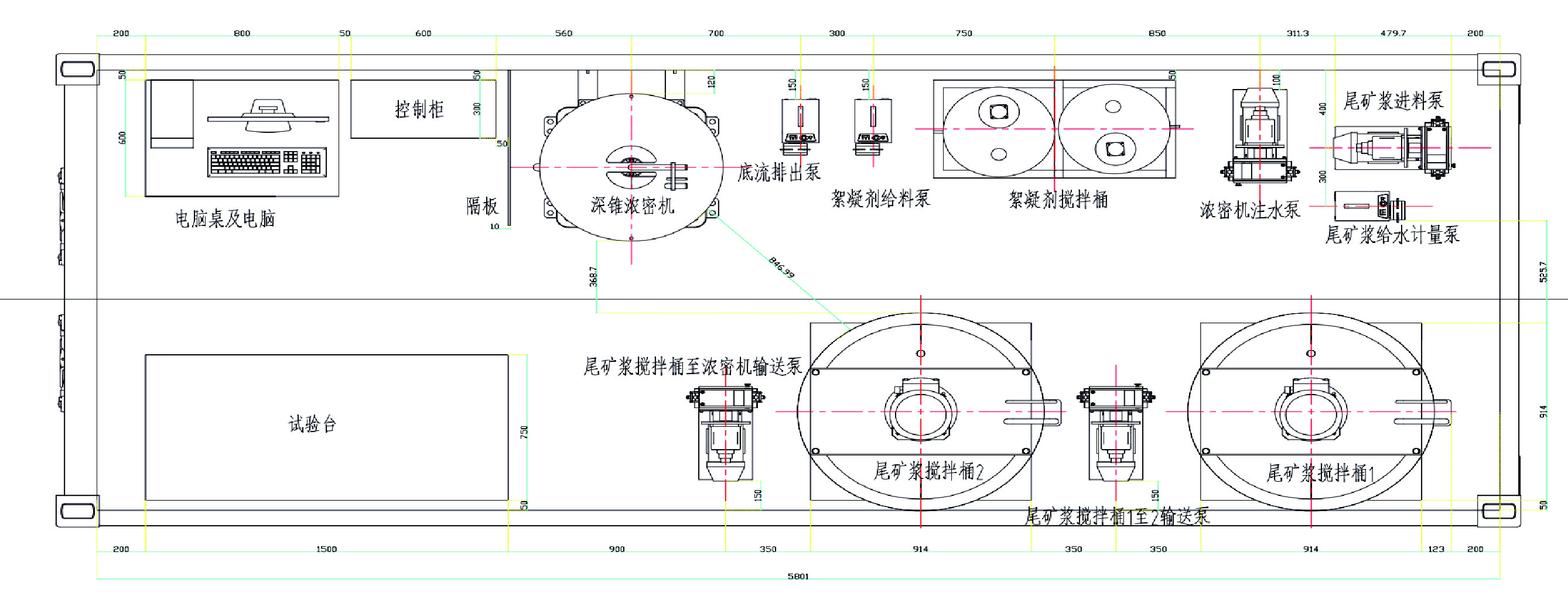
Semi−industrial Experiment of Dynamic Thickening of Tailings Based on NSGA−II Algorithm and Its Multi−objective Optimization
-
摘要:
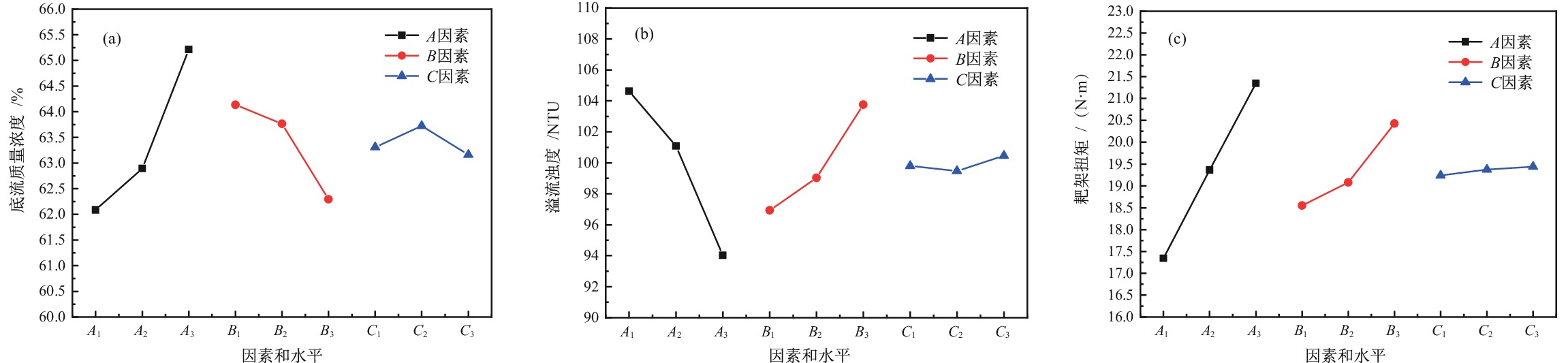
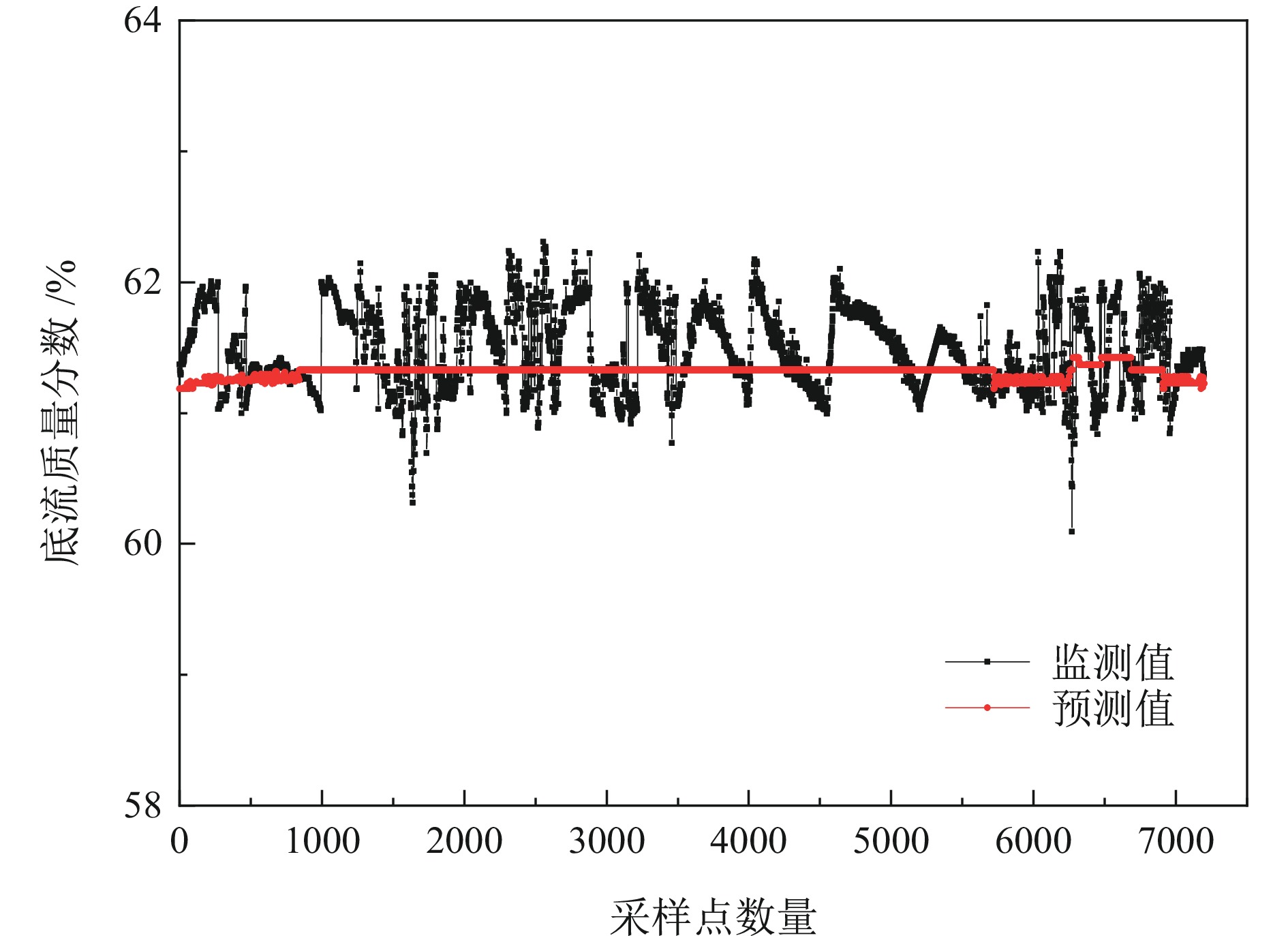
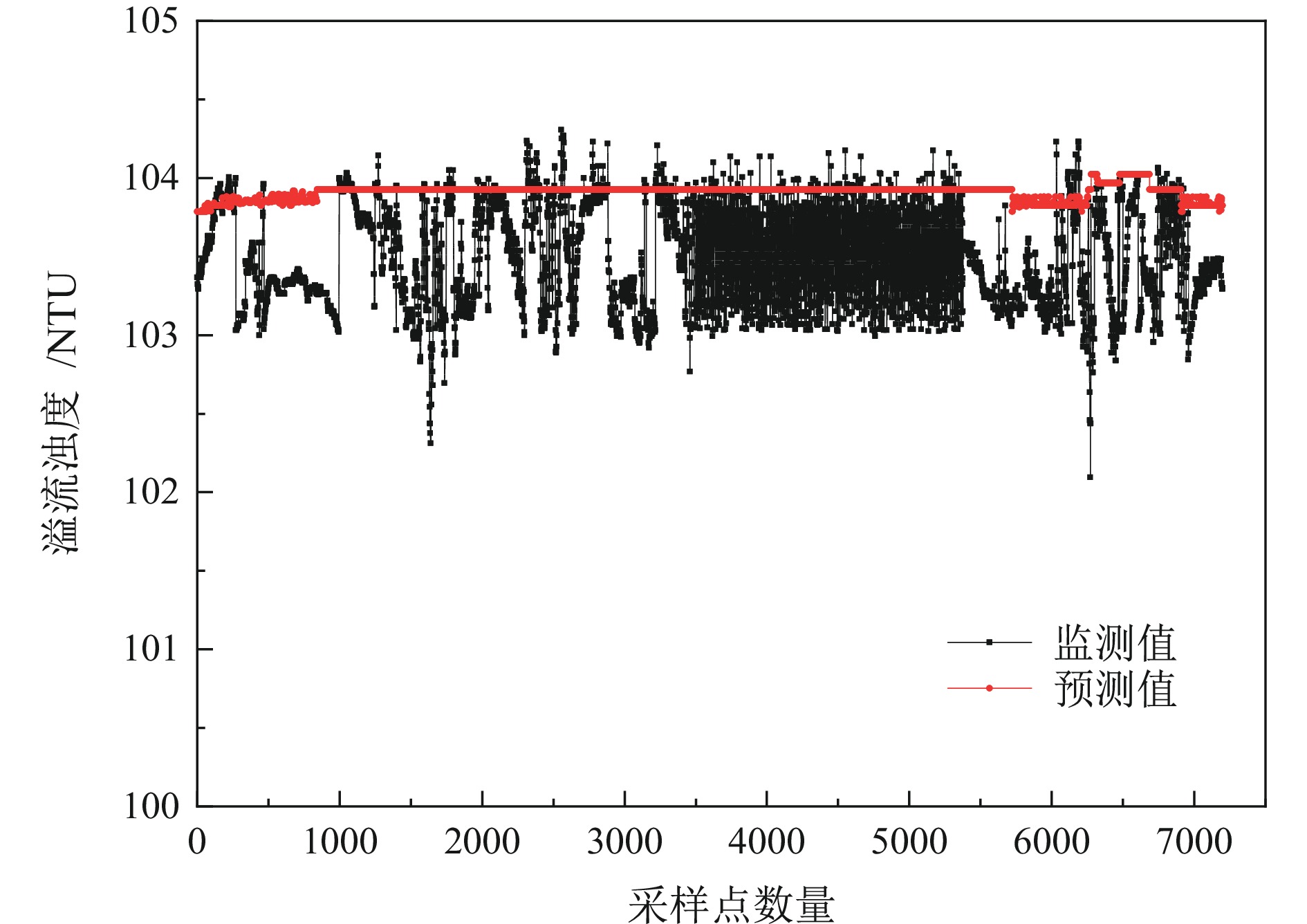
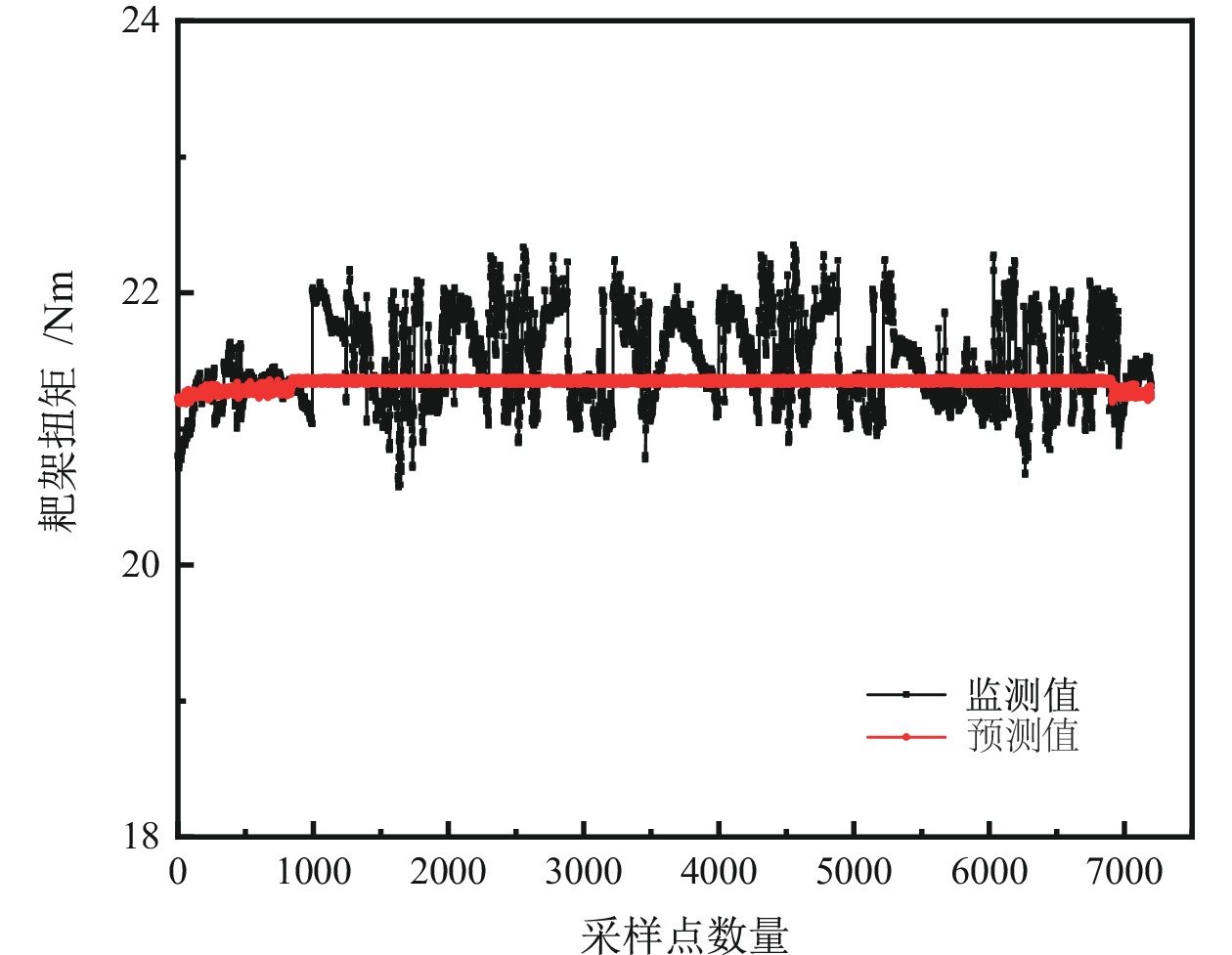
尾砂浓密工艺是一种多输入、多输出、高时滞的复杂系统,探究不同因素影响下尾砂浓密多目标优化问题具有重要意义,为推进尾砂浓密工艺的精准控制和智能化发展提供参考。研制了一套尾砂动态浓密半工业智能实验装置,开展了尾砂动态浓密正交实验,考察泥层高度、进料流量和耙架转速对尾砂浓密多目标的影响;结合尾砂动态浓密半工业正交实验结果,建立了底流质量浓度、溢流浊度和耙架扭矩的多元回归模型,利用MATLAB 软件的通讯模块,实现了对尾砂动态浓密半工业实验效果的实时预测;结合矿山对尾砂浓密的实际需求,构建了基于NSGA−Ⅱ算法的尾砂动态浓密多目标优化模型,获得了优化后的尾砂动态浓密参数和浓密效果。研究结果表明:泥层高度和进料流量对尾砂浓密效果具有显著影响,泥层高度是影响浓密效果的最主要因素;尾砂浓密多元回归模型的预测差异在4.53%以内,模型拟合效果良好;多目标优化后的尾砂动态浓密参数为泥层高度0.30 m、进料流量0.91 m3/h、耙架转速3.80 r/min,优化后的尾砂浓密效果为底流质量浓度69.57%,溢流浊度40.41 NTU、耙架扭矩11.53 N·m。
Abstract:The tailings thickening process is a complex system with multiple inputs, multiple outputs, and high time delay. Exploring the multi−objective optimization problem of tailings thickening under different factors is of great significance, which provides reference for promoting precise control and intelligent development of tailings thickening process. A semi−industrial intelligent testing device for dynamic thickening of tailings was developed to conduct orthogonal experiments on dynamic thickening of tailings, and investigate the effects of mud layer height, feed flow rate, and rake speed on the multi−objective thickening of tailings; A multiple regression model was established for underflow concentration, overflow turbidity, and rake torque based on the results of semi−industrial orthogonal experiments for dynamic thickening of tailings. Using the communication module of MATLAB software, the real−time prediction of the semi−industrial test effect of dynamic thickening of tailings was achieved; Taking into account the actual demand of mines for tailings thickening, a multi−objective optimization model for dynamic tailings thickening based on NSGA−II algorithm was constructed. The optimized parameters and thickening effects of dynamic tailings thickening were obtained. The research results indicate that the height of the mud layer and the feed flow rate had a significant impact on the thickening effect of tailings. The height of the mud layer was the most important factor affecting the thickening effect. The prediction difference of the multiple regression model for tailings thickening process was within 4.53%, and the model fitting effect was good; The optimized parameters for tailings thickening after multi−objective optimization were mud layer height of 0.30 m, feed flow rate of 0.91 m3/h, and rake speed of 3.80 r/min. The optimized tailings thickening effect parameters were underflow mass concentration of 69.57%, overflow turbidity of 40.41 NTU, and rake torque of 11.53 N·m.
-

-
表 1 正交实验因素水平
Table 1. Factor levels of orthogonal experiments
水平 因素 A泥层高度/m B进料流量/(m3·h−1) C耙架转速/(r·min−1) 1 0.15 0.97 1.50 2 0.20 1.08 2.00 3 0.30 1.19 2.50 表 2 尾砂动态浓密半工业正交实验结果
Table 2. Results of semi−industrial orthogonal test for dynamic thickening of tailings
编号 因素 指标 泥层
高度/m进料
流量
/(m3·h−1)耙架
转速
/(r·min−1)底流
质量
浓度/%溢流
浊度
/NTU耙架
扭矩
/(N·m)1 0.15 0.97 1.50 62.95 100.71 16.19 2 0.15 1.08 2.00 62.73 102.24 17.18 3 0.15 1.19 2.50 60.58 110.91 18.66 4 0.20 0.97 2.00 63.79 99.57 18.74 5 0.20 1.08 2.50 63.24 99.93 18.94 6 0.20 1.19 1.50 61.65 103.75 20.41 7 0.30 0.97 2.50 65.66 90.52 20.72 8 0.30 1.08 1.50 65.33 94.93 21.12 9 0.30 1.19 2.00 64.65 96.62 22.21 表 3 正交实验的方差分析
Table 3. Analysis of variance in orthogonal experiments
指标 方差来源 离差平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 底流质量浓度 A 15.81 2 7.90 69.23 0.01 B 5.69 2 2.85 24.92 0.04 C 0.51 2 0.26 2.24 0.31 D空白 0.23 2 0.11 溢流浊度 A 174.64 2 87.32 10.75 0.08 B 73.35 2 36.68 4.52 0.18 C 1.49 2 0.74 0.09 0.92 D空白 16.24 2 8.12 耙架扭矩 A 24.08 2 12.04 91.16 0.01 B 5.62 2 2.81 21.26 0.04 C 0.06 2 0.03 0.24 0.81 D空白 0.26 2 0.13 -
[1] CAI M, LI P, TAN W, et al. Key engineering technologies to achieve green, intelligent, and sustainable development of deep metal mines in China[J]. Engineering, 2021, 7(11): 1513−1517. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2021.07.010
[2] 吴爱祥, 杨莹, 程海勇, 等. 中国膏体技术发展现状与趋势[J]. 工程科学学报, 2018, 40(5): 517−525.
WU A X, YANG Y, CHENG H Y, et al. Status and prospects of paste technology in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2018, 40(5): 517−525.
[3] 吴爱祥, 张晋军, 王贻明, 等. 膏体充填: 金属矿绿色开采的变革性技术[J/OL]. 中国有色金属学报, 1−19[2024−02−05]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/43.1238.TG.20240123.1128.001.html.
WU A X, ZHANG J J, WANG Y M, et al. Cemented paste backfill: a transformative technology for green mining in metal mines[J/OL]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1−19[2024−02−05]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/43.1238.TG.20240123.1128.001.html.
[4] QI C, FOURIE A. Cemented paste backfill for mineral tailings management: review and future perspectives[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2019, 144(9): 106025.
[5] 阮竹恩, 吴爱祥, 焦华喆, 等. 我国全尾砂料浆浓密研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2022, 32(1): 286−301.
RUAN Z E, WU A X, JIAO H Z, et al. Advances and trends on thickening of full−tailings slurry in China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2022, 32(1): 286−301.
[6] 王洪江, 彭青松, 杨莹, 等. 金属矿尾砂浓密技术研究现状与展望[J]. 工程科学学报, 2022, 44(6): 971−980.
WANG H J, PENG Q S, YANG Y, et al. Research status and prospect of thickening technology for metal tailings[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2022, 44(6): 971−980.
[7] 王辉镜. 基于静动态浓密试验的全尾砂絮凝沉降规律研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2023, 39(2): 84−87+91.
WANG H J. Study on flocculation and sedimentation law of unclassified tailings based on static and dynamic thickening test[J]. Modern Mining, 2023, 39(2): 84−87+91.
[8] 肖崇春. 基于全尾砂深度浓密演绎机理的智能预测模型研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2022.
XIAO C C. Research on intelligent prediction model based on depth thickening deductive mechanism of unclassed tailings[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2022.
[9] 诸利一, 杨鹏, 吕文生. 全尾砂絮凝沉降与浓密影响因素试验研究[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2021, 41(8): 59−64.
ZHU L Y, YANG P, LYU W S. Experimental study on influencing factors of flocculation sedimentation and thickening of unclassified tailings[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2021, 41(8): 59−64.
[10] 王贤情, 万文, 王刚, 等. 金矿全尾砂浆动静态絮凝沉降规律研究[J]. 地下空间与工程学报, 2023, 19(4): 1358−1366.
WANG X Q, WAN W, WANG G, et al. Study on flocculation and sedimentation characteristics of unclassified tailings in gold mine[J]. Chinese Journal of Underground Space and Engineering, 2023, 19(4): 1358−1366.
[11] 杨纪光, 吴再海, 寇云鹏, 等. 某金矿两段分级超细尾砂静态沉降与半工业浓密试验研究[J]. 金属矿山, 2022(9): 37−42.
YANG J G, WU Z H, KOU Y P, et al. Experimental study on static settlement and semi industrial thickening of two−stage classification ultrafine tailings in a gold mine[J]. Metal Mine, 2022(9): 37−42.
[12] 张钦礼, 王石, 王新民. 絮凝剂单耗对全尾砂浆浑液面沉速的影响规律[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(2): 318−324.
ZHANG Q L, WANG S, WANG X M. Influence rules of unit consumptions of flocculants oninterface sedimentation velocity of unclassified tailings slurry[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2017, 27(2): 318−324.
[13] 张钦礼, 刘奇, 赵建文. 全尾砂絮凝沉降参数预测模型研究[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 37(6): 875−879. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.06.024
ZHANG Q L, LIU Q, ZHAO J W. Study on the parameters prediction model of flocculating sedimentation of crude tailings[J]. Journal of Northeastern University(Natural Science), 2016, 37(6): 875−879. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3026.2016.06.024
[14] 王晓军, 马晓霞, 孙燕飞, 等. 基于RSM−BBD的全尾砂絮凝沉降效果多因素耦合分析[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2023, 43(6): 62−67.
WANG X J, MA X X, SUN Y F, et al. Multi−factor coupling analysis on flocculation and sedimentation effect of whole tailings based on RSM−BBD[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2023, 43(6): 62−67.
[15] 吴再海. 基于超细尾砂絮凝沉降浓密试验及应用分析[J]. 有色金属工程, 2022, 12(10): 117−125.
WU Z H. Study and application of flocculation sedimentation thickening experiment based on ultrafine tailings[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2022, 12(10): 117−125.
[16] 张美道, 饶运章, 徐文峰, 等. 全尾砂膏体充填配比优化正交试验[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2021, 29(5): 740−748.
ZAHNG M D, RAO Y Z, XUN W F, et al. Orthogonal experiment for optimizing the filling ratio of unclassified tailings paste[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2021, 29(5): 740−748.
[17] 黄仁东, 李哲. 基于正交试验的细尾砂−分级尾砂充填体强度研究[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2021, 29(2): 256−265.
HUANG R D, LI Z. Research on the strength of fine tailings−graded tailings filling body based on orthogonal experiment[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2021, 29(2): 256−265.
[18] 李志强, 张轩硕, 卜娜蕊, 等. 基于正交实验金尾矿砂再生混凝土实验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(6): 73−78+83.
LI Z Q, ZHANG X S, BU N R, et al. Research on orthogonal test of mixture ratio of gold tailings recycled concrete[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(6): 73−78+83.
[19] 袁士宝, 白玉, 蒋海岩, 等. 基于遗传算法的割缝衬管防砂多目标优化[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2021, 51(2): 113−119.
YUAN S B, BAI Y, JIANG H Y, et al. Multi−objective optimization of sand control for slotted lining pipes based on genetic algorithm[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2021, 51(2): 113−119.
[20] 高峰, 艾浩泉, 梁耀东, 等. 基于NSGA−Ⅱ算法的废石及尾砂混合充填料配比优化[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2022, 30(1): 46−53.
GAO F, AI H Q, LIANG Y D, et al. Optimization of proportioning of waste rock and tailings mixed filling materials based on NSGA−Ⅱ algorithm[J]. Gold Science and Technology, 2022, 30(1): 46−53.
-



 下载:
下载: