Studies on Lead Isotope Analysis and Composition in Soils and Near-surface Atmospheric Aerosols of the Ruoergai High Altitude Plateau, and Lead Sources Identification
-
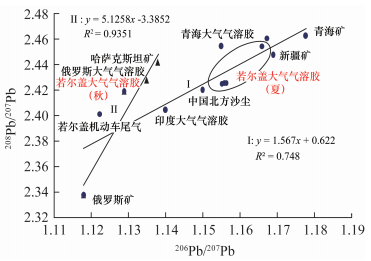
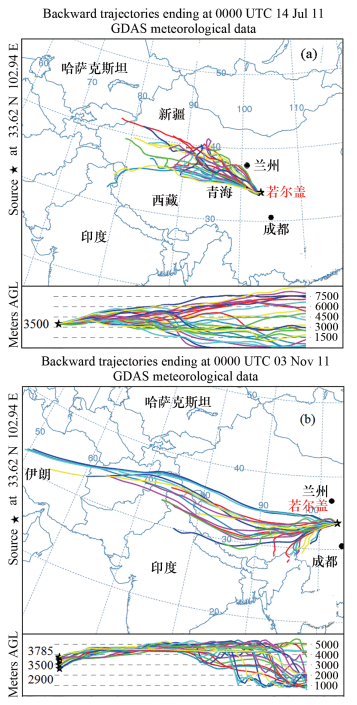
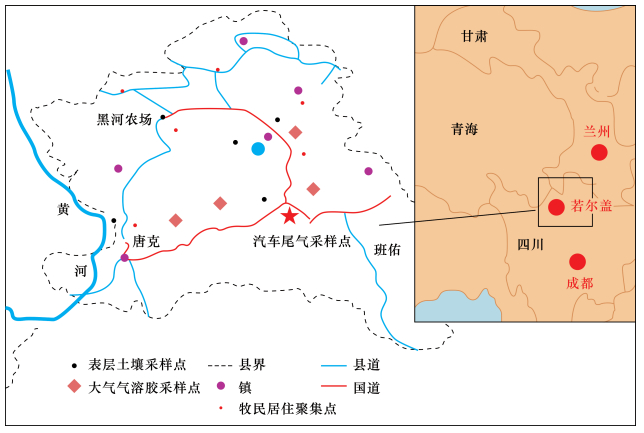
摘要: 若尔盖高原牧场处于中国偏远洁净高海拔地区,大气沉降是污染物主要来源途径之一。由于季风的影响,污染源的辨析较为困难。本文通过多点大气气溶胶不同季节同时采样方式,利用热电离固体同位素质谱仪可有效校正质谱分析中同位素分馏效应的优点,对若尔盖地区土壤和大气气溶胶的铅同位素比值进行精确分析,并结合季风特征对该地区污染物的来源进行解析。结果表明:土壤的 208Pb/204Pb比值变化范围为38.79059±0.00194~38.94461±0.00135,206Pb/207Pb为1.18551±0.00002~1.19362±0.00002;大气气溶胶的208Pb/204Pb比值变化范围为37.49571±0.00117~38.48980±0.00105,206Pb/207Pb为1.12894±0.00001~1.16734±0.00001。该地区土壤铅同位素的特征是放射成因铅高,来自于自身天然存在的岩石矿物,与大气污染关系不大;大气气溶胶的铅同位素组成与土壤差异较大,显示为多元混合模式,受到了天然物质和人类活动来源的混合影响,机动车尾气及来自北部(兰州)和西北部(青海、新疆、哈萨克斯坦、俄罗斯)的大气远程运移是若尔盖大气气溶胶及污染物质的主要来源。Abstract: The Ruoergai highland pasture is located in the remote, high altitude area of China. Atmospheric transport and precipitation is one of the major routes of pollutants to this area, but pollution source identification is difficult due to the monsoon. Atmospheric aerosol samples were taken in different seasons at multiple sites in Ruoergai. High precision Pb isotope analysis for soils and atmospheric aerosols was performed by using Thermal Ionization Mass Spectrometry (TIMS), which has the advantage of effectively removing the isotope fractionation effect in mass analysis. The sources of the aerosols were analyzed in association with the characteristics of the monsoon. The range of 208Pb/204Pb ratio is 38.79059±0.00194-38.94461±0.00135 and 206Pb/207Pb 1.18551±0.00002-1.19362±0.00002, 208Pb/204Pb in the atmo-spheric aerosol is 37.49571±0.00117-38.48980±0.00105 and 206Pb/207Pb 1.12894±0.00001-1.16734±0.00001. The Pb isotopic composition of soil in Ruoergai is characterized by high radiogenic Pb, mainly from local rock and minerals. The Pb isotopic composition of aerosols differs from that of soil, showing a multiple mode of mixing of natural and anthropogenic sources. Automobile exhaust gas and long-range atmospheric transport mainly from the north (Lanzou) and northwest (Qinghai, Xinjiang, Kazakhstan and Russia) are possible sources of aerosols and pollutants.
-

-
表 1 若尔盖地区土壤、大气气溶胶铅同位素组成(原子数比)及与兰州、成都比较
Table 1. Composition of lead isotope ratio (atomic ratio) of soil and aerosol in Ruoergai and data comparison with Lanzhou and Chengdu
样品类型 采样地点 采样季节 208Pb/204Pb 207Pb/204Pb 206Pb/204Pb 208Pb/207Pb 206Pb/207Pb 表层土壤 若尔盖 秋 38.79059±0.00194 15.65379±0.00073 18.55763±0.00080 2.478032±0.000028 1.18551±0.00002 表层土壤 若尔盖 秋 38.94461±0.00135 15.66181±0.00045 18.69384±0.00055 2.486597±0.000018 1.19362±0.00002 表层土壤 若尔盖 秋 38.83947±0.00139 15.64258±0.00046 18.60041±0.00067 2.482932±0.000019 1.18908±0.00003 表层土壤 若尔盖 秋 38.88189±0.00224 15.65591±0.00057 18.66972±0.00107 2.483530±0.000027 1.19255±0.00004 平均值 若尔盖 秋 38.86414±0.00173 15.65352±0.00055 18.63041±0.00077 2.482773±0.000023 1.19020±0.00003 汽车尾气 若尔盖 秋 37.34677±0.00225 15.55149±0.00085 17.4529±0.00094 2.401491±0.000034 1.12236±0.00005 大气 若尔盖 夏 37.77733±0.00357 15.57383±0.00122 18.00227±0.00138 2.419284±0.000018 1.15589±0.00002 大气 若尔盖 秋 37.49571±0.00117 15.49868±0.00046 17.49700±0.00046 2.425693±0.000051 1.12894±0.00001 大气 若尔盖 夏 37.76873±0.00263 15.57417±0.00099 17.99150±0.00110 2.425088±0.000039 1.15522±0.00002 大气 若尔盖 夏 37.78468±0.00211 15.57632±0.00089 18.01242±0.00097 2.425777±0.000033 1.15641±0.00001 大气 若尔盖 秋 38.48980±0.00105 15.64171±0.00039 18.25889±0.00042 2.460716±0.000015 1.16734±0.00001 大气 若尔盖 秋 38.38435±0.00099 15.63828±0.00038 18.23290±0.00042 2.454512±0.000014 1.16592±0.00001 平均值 若尔盖 - 37.95010±0.00192 15.58383±0.00072 17.99916±0.00079 2.435178±0.000028 1.15495±0.00001 大气 成都 夏 38.45013±0.00151 15.64558±0.00058 18.27440±0.00054 2.457571±0.000022 1.16803±0.00002 大气 成都 夏 38.44478±0.00147 15.63987±0.00037 18.25394±0.00059 2.458127±0.000018 1.16720±0.00003 大气 成都 夏 38.44479±0.00154 15.64533±0.00047 18.25746±0.00064 2.457269±0.000020 1.16694±0.00003 大气 成都 夏 38.50391±0.00143 15.65974±0.00040 18.31912±0.00072 2.458783±0.000018 1.16985±0.00005 大气 成都 夏 38.48133±0.00229 15.65578±0.00081 18.29963±0.00110 2.457963±0.000032 1.16891±0.00006 大气 成都 秋 38.46083±0.00288 15.64490±0.00092 18.31102±0.00121 2.458362±0.000039 1.17042±0.00006 大气 成都 秋 38.47638±0.00159 15.64845±0.00055 18.31136±0.00060 2.458798±0.000022 1.17019±0.00001 平均值 成都 - 38.46602±0.00182 15.64852±0.00059 18.28956±0.00077 2.458125±0.000025 1.16879±0.00004 大气 兰州 夏 37.56235±0.00305 15.50344±0.00049 17.52090±0.00142 2.422840±0.000036 1.13011±0.00008 大气 兰州 夏 36.68900±0.00172 15.48831±0.00077 16.93649±0.00082 2.368819±0.000029 1.09350±0.00002 大气 兰州 夏 37.57728±0.00127 15.50712±0.00048 17.52217±0.00051 2.423228±0.000019 1.12995±0.00001 大气 兰州 秋 37.33754±0.00086 15.47206±0.00036 17.31269±0.00036 2.413224±0.000014 1.11896±0.00001 大气 兰州 秋 37.73698±0.00133 15.53288±0.00050 17.71074±0.00060 2.429490±0.000020 1.14020±0.00001 大气 兰州 秋 37.50364±0.00107 15.50118±0.00035 17.50012±0.00047 2.419405±0.000015 1.12890±0.00001 平均值 兰州 - 37.40113±0.00155 15.50083±0.00049 17.41719±0.00070 2.412834±0.000022 1.12361±0.00002 -
[1] 胡恭任, 于瑞莲, 胡起超, 等.铅同位素示踪在大气降尘重金属污染来源解析中的应用[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(5):1520-1526. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201605024.htm
Hu G R, Yu R L, Hu Q C, et al.Application of stable lead isotope in tracing heavy metal sources in the atmospheric dustfall[J].Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science), 2016, 46(5):1520-1526. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201605024.htm
[2] 张棕巍, 胡恭任, 于瑞莲, 等.泉州市大气降尘中金属元素污染特征及来源解析[J].环境科学, 2016, 37(8):2881-2888. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201608008.htm
Zhang Z W, Hu G R, Yu R L, et al.Characteristics and source apportionment of metals in the dustfall of Quanzhou city[J].Environmental Science, 2016, 37(8):2881-2888. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201608008.htm
[3] 闫雨龙, 郭丽丽, 张桂香, 等.太原市大气PM2.5中铅同位素特征研究[J].地球与环境, 2015, 43(3):279-283. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201503002.htm
Yan Y L, Guo L L, Zhang G X, et al.Isotope characteristics of lead in PM2.5 of Taiyuan city, China[J].Earth and Environment, 2015, 43(3):279-283. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201503002.htm
[4] Widory D, Liu X, Dong S.Isotopes as tracers of sources of lead and strontium in aerosols (TSP & PM2.5) in Beijing[J].Atmosphere Environment, 2010, 44:3679-3687. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.06.036
[5] Cheng H, Hu Y.Lead isotopic fingerprinting and its applications in lead pollution studies in China:A review[J].Environmental Pollution, 2010, 158:1134-1148. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.12.028
[6] Sen I S, Bizimis M, Tripathi S N, et al.Lead isotopic fingerprinting of aerosols to characterize the sources of atmospheric lead in an industrial city of India[J].Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 129:27-33. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.01.005
[7] Cheng H, Zhang G, Jiang X, et al.Organochlorine pesti-cides, polybrominated biphenyl ethers and lead isotopes during the spring time at the Waliguan baseline observatory, Northwest China:Implication for long-range atmospheric transport[J].Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 41:4734-4747. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.03.023
[8] 朱赖民, 张海生, 陈立奇.铅稳定同位素在示踪环境污染中的应用[J].环境科学研究, 2002, 15(1):27-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200201007.htm
Zhu L M, Zhang H S, Chen L Q.Application of stable lead isotopes in tracing environmental pollution[J].Research of Environmental Sciences, 2002, 15(1):27-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKX200201007.htm
[9] 郝春莉, 林奇, 张远辉, 等.南极大气气溶胶中铅同位素比值的研究[J].中国环境监测, 2012, 28(4):41-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB201204010.htm
Hao C L, Lin Q, Zhang Y H, et al.The lead isotope ratios study of aerosols in Antarctica[J].Environmental Monitoring in China, 2012, 28(4):41-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB201204010.htm
[10] Tserenpil S, Sapkota A, Liu C Q, et al.Lead isotope and trace element composition of urban soils in Mongolia[J].Eurasian Soil Science, 2016, 49(8):879-889. doi: 10.1134/S1064229316080147
[11] Zhang H, Luo Y.Endogenous and exogenous lead in soils of Yangtze River delta region, China:Identified by lead isotopic compositions and multi-elemental approaches[J].Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 62(5):1109-1115. doi: 10.1007/s12665-010-0599-y
[12] Kylander M E, Klaminder J, Bindler R, et al.Natural lead isotope variations in the atmosphere[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 290:44-53. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2009.11.055
[13] Tessalina S G, Herrington R J, Taylor R N, et al.Lead isotopic systematics of massive sulfide deposits in the Urals:Applications for geodynamic setting and metal sources[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72:22-36. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.06.016
[14] Francov A, Chrastn V, Sillerov H, et al.Evaluating the stability of different environmental samples for tracing atmospheric pollution in Industrial areas[J].Environmental Pollution, 2017, 220:286-298. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.09.062
[15] 尚英男, 杨波, 尹观, 等.成都市近地表大气气溶胶铅分布特征及源解析[J].物探与化探, 2006, 30(2):104-107. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200602002.htm
Shang Y N, Yang B, Yin G, et al.Distribution characteristics and sources of lead in air dust near the ground surface of Chengdu city[J].Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 30(2):104-107. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200602002.htm
[16] 丰成友, 张德全, 李大新, 等.青海东昆仑造山型金矿硫、铅同位素地球化学[J].地球学报, 2003, 24(6):593-598. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ200311002024.htm
Feng C Y, Zhang D Q, Li D X, et al.Sulfur and lead isotope geochemistry of the orogenic gold deposits in east Kunlun area, Qinghai Province[J].Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2003, 24(6):593-598. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ200311002024.htm
[17] Mukai H, Machida T, Tanaka A, et al.Lead isotope ratios in the urban air of Eastern and Central Russia[J].Atmospheric Environment, 2001, 35:2783-2793. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(00)00341-1
[18] Bollhofer A, Rosman K J R.Isotopic source signatures for atmospheric lead:The northern hemisphere[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2001, 65(11):1727-1740. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00630-X
[19] Zhu B.The mapping of geochemical provinces in China based on Pb isotopes[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1995, 55:171-181. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(95)00011-9
[20] 李锋.中国北方沙尘源区铅同位素分布特征及其示踪意义的初步研究[J].中国沙漠, 2007, 27(5):738-744. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS200705004.htm
Li F.Distribution characteristics of lead isotope in dust source areas and it trace significance in the north of China[J].Journal of Desert Research, 2007, 27(5):738-744. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS200705004.htm
[21] 何阳阳, 温春齐, 刘显凡.西藏多不杂铜矿床硫铅同位素地球化学示踪[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2016, 35(5):855-862. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201605008.htm
He Y Y, Wen C Q, Liu X F.Sulfur and lead isotope geochemical tracing of the Duobuza copper deposit, Tibet[J].Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2016, 35(5):855-862. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW201605008.htm
-



 下载:
下载: