Regulation and Evaluation of Selenium Availability in Se-rich Soils in Southern China
-
摘要: 多目标区域地球化学调查发现中国南方酸性土壤的硒含量普遍较高,但其生物有效性一般较低,土壤硒有效性直接关系到富硒土地资源的可利用性,而土壤酸碱度是影响土壤硒生物有效性的重要因素。本文选取福建、海南富硒红壤(pH为3.91~4.98)、富硒水稻土(pH为4.33~5.75),以生石灰、燃煤炉渣为改良剂,分别设置6个实验处理以调控土壤硒生物有效性。结果表明:添加生石灰和燃煤炉渣均能提升南方酸性土壤的pH,上升幅度在1~2个pH单位,从而有利于土壤中硒元素的活化,显著提高了土壤中硒元素的生物有效性;燃煤炉渣用量与其10倍的生石灰对提升土壤硒有效度的效果相当,而燃煤炉渣作为调控物料更为经济、实用,既可以实现炉渣的有效利用,又可以改善土壤结构、提高土壤硒有效度。Abstract: The multi-purpose regional geochemical survey showed that the concentration of selenium in acid soil in Southern China is generally high, but the bio-availability of selenium in soil is relatively low, which affects the usage of selenium-rich soil. The pH values of soils are an important factor affecting the bio-availability. Se-rich red soil samples with pH of 3.91-4.98 and Se-rich paddy soil samples with pH of 4.33-5.75 were collected from Fujian Province and Hainan Island. Six experiments were conducted using lime and coal slag as the modifier to improve the bio-availability of selenium in soil. The results show that soil pH can be significantly elevated by 1 to 2 units by using the modifiers, which advances the mobility of Se in soils and improves selenium bio-availability in soils. Coalcinder and 10 times weights of quicklime have the same effect to promote selenium availability. The coalcinder as a regulation material is more economical and practical. It can not only realize the effective utilization of cinder, but also improve the soil structure and increase the soil selenium availability.
-
Key words:
- Se availability /
- regulation experiment /
- quicklime /
- coalcinder /
- selenium-rich soil in Southern China
-

-
表 1 实验土壤样品理化性质
Table 1. Physico-chemical properties of soil samples for the experiment
样品编号 采样地区 地质成因 土地利用 土壤类型 全硒含量
(10-6)有机碳含量(%) pH CEC
[cmol(+)/kg]S1 龙海市角美镇 冲-洪积 旱地 水稻土 0.66 2.31 5.75 10.9 S2 龙海市颜厝镇 残坡积 果园 红壤 0.86 1.30 4.39 5.74 S3 龙海华侨农场 残坡积 果园 红壤 0.77 1.33 4.46 9.81 S4 龙海市东泗乡 残坡积 林地 红壤 0.42 1.11 4.91 7.43 S5 龙海市海澄镇 残积土 林地 红壤 1.11 0.85 4.41 7.99 S6 诏安县红星乡 残坡积 果园 红壤 0.60 2.41 3.91 12.3 S7 万宁市横岭村 冲洪积 水田 水稻土 1.25 1.30 4.33 9.97 S8 万宁市横岭村 残坡积 果园 红壤 2.48 0.48 4.50 6.69 S9 海口市琼山区 残坡积 旱地 红壤 2.72 0.82 4.98 10.6 表 2 生石灰及炉渣添加量对土壤pH的影响
Table 2. Effect of the amount of quicklime and cinder added on pH of soil
处理
编号生石灰添加量
(g/100g土)pH S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 T1 0 5.75 4.39 4.46 4.91 4.41 3.91 4.33 4.50 4.98 T2 0.0208 5.74 4.47 4.52 5.03 4.27 4.70 4.57 4.56 5.07 T3 0.0417 5.78 4.81 4.64 5.13 4.55 4.95 4.68 4.68 5.15 T4 0.0833 5.92 5.08 5.20 5.97 5.05 4.60 5.01 4.94 5.46 T5 0.1667 6.11 5.51 5.48 6.30 5.45 5.14 6.03 5.44 5.95 T6 0.3333 6.58 6.36 5.97 7.00 6.53 5.74 6.81 5.95 6.31 最大提升单位 0.83 1.97 1.51 2.09 2.12 1.83 2.48 1.45 1.33 处理编号 炉渣添加量
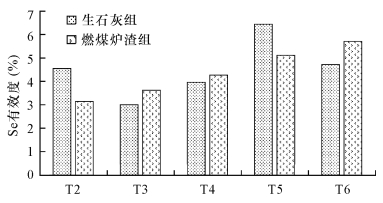
(g/100g土)pH S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 T1 0 5.72 4.41 4.55 4.80 4.15 4.01 4.14 4.48 4.99 T2 0.2083 5.76 4.79 4.60 5.11 4.62 4.24 4.65 4.59 5.05 T3 0.4167 5.86 4.85 4.73 5.50 4.61 4.43 4.85 4.76 5.28 T4 0.8333 6.00 5.32 5.17 6.18 4.94 4.70 5.40 5.05 5.49 T5 1.6667 6.26 5.69 5.60 7.10 5.41 5.62 6.35 5.61 5.91 T6 3.3333 6.92 6.44 6.38 7.60 6.24 5.39 6.82 6.41 6.25 最大提升单位 1.20 2.03 1.83 2.80 2.09 1.38 2.68 1.93 1.26 表 3 添加生石灰对土壤硒有效度的影响
Table 3. Effect of quicklime added on the bio-availability of selenium in soil
样品编号 处理编号 总硒含量
(10-6)硒有效量
(10-6)硒有效度
(%)S1 T1 0.507 0.015 2.98 T2 0.487 0.0076 1.56 T3 0.487 0.014 2.85 T4 0.494 0.012 2.47 T5 0.507 0.023 4.53 T6 0.506 0.013 2.56 S2 T1 0.654 0.031 4.68 T2 0.620 0.041 6.56 T3 0.630 0.039 6.16 T4 0.627 0.040 6.42 T5 0.624 0.041 6.62 T6 0.656 0.034 5.23 S3 T1 0.659 0.050 7.52 T2 0.658 0.024 3.65 T3 0.621 0.0074 1.20 T4 0.646 0.040 6.17 T5 0.681 0.045 6.68 T6 0.673 0.032 4.72 S4 T1 0.320 0.029 9.00 T2 0.329 0.028 8.43 T3 0.322 0.016 4.82 T4 0.328 0.034 10.38 T5 0.328 0.044 13.30 T6 0.311 0.033 10.73 S5 T1 0.810 0.028 3.45 T2 0.796 0.038 4.74 T3 0.835 0.019 2.27 T4 0.831 0.019 2.24 T5 0.805 0.039 4.86 T6 0.851 0.041 4.77 S6 T1 0.487 0.052 10.68 T2 0.469 0.044 9.38 T3 0.477 0.064 13.42 T4 0.476 0.059 12.41 T5 0.508 0.057 11.18 T6 0.498 0.056 11.20 S7 T1 1.490 0.024 1.61 T2 1.682 0.037 2.18 T3 1.838 0.036 1.95 T4 1.985 0.030 1.50 T5 1.677 0.027 1.63 T6 1.750 0.058 3.32 S8 T1 1.117 0.033 2.95 T2 1.092 0.050 4.55 T3 1.077 0.052 4.82 T4 1.088 0.043 3.95 T5 1.055 0.068 6.42 T6 1.171 0.037 3.13 S9 T1 2.538 0.057 2.24 T2 2.527 0.038 1.51 T3 2.575 0.077 2.99 T4 2.363 0.089 3.76 T5 2.512 0.058 2.30 T6 2.465 0.055 2.24 表 4 添加炉渣对土壤硒有效度的影响
Table 4. Effect of cinder added on the bio-availability of selenium in soil
样品编号 处理编号 总硒含量
(10-6)硒有效量
(10-6)硒有效度
(%)S1 T1 0.499 0.018 3.51 T2 0.515 0.016 3.14 T3 0.506 0.013 2.54 T4 0.481 0.023 4.70 T5 0.452 0.033 7.39 T6 0.457 0.018 4.01 S2 T1 0.648 0.0047 0.73 T2 0.660 0.013 1.97 T3 0.623 0.039 6.18 T4 0.631 0.013 2.10 T5 0.638 0.012 1.81 T6 0.630 0.061 9.67 S3 T1 0.686 0.044 6.36 T2 0.683 0.029 4.17 T3 0.709 0.060 8.51 T4 0.669 0.053 7.93 T5 0.651 0.044 6.70 T6 0.683 0.042 6.13 S4 T1 0.315 0.015 4.78 T2 0.316 0.033 10.51 T3 0.314 0.027 8.48 T4 0.311 0.039 12.65 T5 0.299 0.036 11.89 T6 0.322 0.032 9.92 S5 T1 0.845 0.032 3.73 T2 0.854 0.041 4.80 T3 0.874 0.032 3.61 T4 0.856 0.037 4.27 T5 0.861 0.044 5.11 T6 0.854 0.049 5.69 S6 T1 0.501 0.063 12.61 T2 0.517 0.039 7.62 T3 0.494 0.039 7.87 T4 0.490 0.051 10.37 T5 0.490 0.046 9.36 T6 0.489 0.068 13.83 S7 T1 1.902 0.052 2.75 T2 1.727 0.021 1.23 T3 1.702 0.049 2.85 T4 1.768 0.028 1.59 T5 1.725 0.0070 0.40 T6 1.769 0.0045 0.25 S8 T1 1.167 0.044 3.80 T2 1.132 0.032 2.86 T3 1.518 0.030 2.01 T4 1.325 0.015 1.10 T5 1.167 0.024 2.07 T6 1.167 0.021 1.82 S9 T1 2.436 0.047 1.94 T2 2.490 0.046 1.87 T3 2.476 0.069 2.80 T4 2.476 0.039 1.59 T5 2.370 0.037 1.55 T6 2.358 0.042 1.76 -
[1] 谭见安, 李日邦.环境硒与健康[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1989.
Tan J A, Li R B.Environmental Selenium and Health[M].Beijing:People's Medical Publishing House, 1989.
[2] 杨琼, 侯青叶, 顾秋蓓, 等.广西武鸣县典型土壤剖面Se的地球化学特征及其影响因素研究[J].现代地质, 2016, 30(2):455-462. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201602022.htm
Yan Q, Hou Q Y, Gu Q B, et al.Study of geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium in the typical soil profiles in Wuming country of Guangxi[J].Geoscience, 2016, 30(2):455-462. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201602022.htm
[3] 杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等.海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J].现代地质, 2012, 26(5):837-849. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201205000.htm
Yang Z F, Yu T, Hou Q Y, et al.Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan Island[J].Geoscience, 2012, 26(5):837-849. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201205000.htm
[4] 吴永尧, 彭振坤, 罗泽民.硒的多重生物学功能与人和动物的健康[J].湖南农业大学学报, 1997, 23(3):294-300. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNND199703022.htm
Wu Y Y, Peng Z K, Luo Z M.Multi-biological functions of selenium to the health of human beings and animals[J].Journal of Hunan Agricultural University, 1997, 23(3):294-300. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNND199703022.htm
[5] 张东威.中国土壤中硒及其土壤环境质量标准研究(简报)[J].水土保持研究, 1994(增刊):112. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY4S1.025.htm
Zhang D W.Study on Se and its soil environmental quality standards in China (brief)[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 1994(Supplement):112. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY4S1.025.htm
[6] Yu T, Yang Z F, Lü Y Y, et al.The origin and geo-chemical cycle of soil selenium in a Se-rich area of China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 139:97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.09.006
[7] 徐文, 唐文浩, 邝春兰, 等.海南省土壤中硒含量及影响因素分析[J].安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(6):3026-3027. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHNY201006105.htm
Xu W, Tang W H, Kang C L, et al.Analysis on content of Se in soil of Hainan Province and its influencing factors[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(6):3026-3027. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHNY201006105.htm
[8] 宋明义, 刘建新, 黄春雷.浙北富硒土壤地球化学特征与生物学效应[J].广东微量元素科学, 2012, 19(3):32-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYS201203008.htm
Song M Y, Liu J X, Huang C L.Geochemistic charactristics and biological effects of selenium-rich soil in northern Zhejiang[J].Guangdong Trace Elements Science, 2012, 19(3):32-38. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYS201203008.htm
[9] Stroud J L, McGrath S P, Zhao F J.Selenium speciation in soil extracts using LC-ICP-MS[J]. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 92(2):222-236. doi: 10.1080/03067310903111661
[10] 于世举.石灰改良酸性土壤的效果[J].现代农业科技, 2012(1):277-278. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ANHE201201178.htm
Yu S J.Effect of lime improved acid soil[J].Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2012(1):277-278. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ANHE201201178.htm
[11] 王文军, 朱宏斌, 武际, 等.不同土壤改良剂在皖南酸性红黄壤油菜上的效应[J].安徽农业科学, 2002, 30(4):529-530. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHNY200204025.htm
Wang W J, Zhu H B, Wu J, et al.Study on the different soil ameliorations on rapeseed in acid soils in southern Anhui[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2002, 30(4):529-530. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHNY200204025.htm
[12] 敖俊华, 黄振瑞, 江永, 等.石灰施用对酸性土壤养分状况和甘蔗生长的影响[J].中国农学通报, 2010, 26(15):266-269. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201015057.htm
Ao J H, Huang Z R, Jiang Y, et al.Effects of applying lime on the properties of acid soil and the growth of sugarcane[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(15):266-269. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201015057.htm
[13] 廖敏, 黄昌勇, 谢正苗.施加石灰降低不同母质土壤中镉毒性的机理研究[J].农业环境保护, 1998, 17(3):101-103. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH803.001.htm
Liao M, Huang C Y, Xie Z M.Study on the decrease of mechanism of cadmium toxicity after liming in different soils[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 1998, 17(3):101-103. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH803.001.htm
[14] 张青, 李菊梅, 徐明岗, 等.改良剂对复合污染红壤中镉锌有效性的影响及机理[J].农业环境科学学报, 2006, 25(4):861-865. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200604007.htm
Zhang Q, Li J M, Xu M G, et al.Effects of amendments on bioavailability of cadmium and zinc in compound contaminated red soil[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2006, 25(4):861-865. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH200604007.htm
[15] 杨金辉, 陈思光, 虢青伟, 等.煤渣对水中氨氮和总磷吸附的试验研究[J].铀矿冶, 2011, 30(4):221-224. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKYI201104021.htm
Yang J H, Chen S G, Guo Q W, et al.Experimental study of adsorbing ammonia nitrogen and phosphorus in water by cinders[J].Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2011, 30(4):221-224. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKYI201104021.htm
[16] 马万征, 赵光雷, 何会民, 等.煤渣对废水中氨氮吸附效果的影响因素研究[J].环境与健康杂志, 2013, 30(4):346-348. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJYJ201304021.htm
Ma W Z, Zhao G L, He H M, et al.Ammonia nitrogen adsorption efficiency by cinder and influencing factors in wastewater treatment[J].Journal of Environment and Health, 2013, 30(4):346-348. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJYJ201304021.htm
[17] 黄泽辉, 韩宝军, 邓登飞, 等.煤渣过滤调酸钨冶炼废水的研究[J].赣南师范学院学报, 2014(6):46-48. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GNSY201406013.htm
Huang Z H, Han B J, Deng D F, et al.Investigation on coal cinder filtering acid adjusting tungsten smelting waste water[J].Journal of Gannan Normal University, 2014(6):46-48. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GNSY201406013.htm
[18] 赵娜, 李鹏飞, 林德华, 等.炉渣对调节稻田土壤pH和盐度的有效性分析[J].亚热带农业研究, 2010, 6(4):264-266. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZZZ201004012.htm
Zhao N, Li P F, Lin D H, et al.Effect of slag on pH and salinity of paddy soil[J].Subtropical Agriculture Research, 2010, 6(4):264-266. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZZZ201004012.htm
[19] 蔡东, 肖文芳, 李国怀, 等.施用石灰改良酸性土壤的研究进展[J].中国农学通报, 2010, 26(9):206-213. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201009044.htm
Cai D, Xiao W F, Li G H, et al.Advance on study of liming on acid soils[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(9):206-213. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNTB201009044.htm
[20] 胡德春, 李贤胜, 尚健, 等.不同改良剂对棕红壤酸性的改良效果[J].土壤, 2006, 38(2):206-209. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA200602016.htm
Hu D C, Li X S, Shang J, et al.Influences of various modifiers on acidity of brown red soil[J].Soils, 2006, 38(2):206-209. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA200602016.htm
[21] 王腾云, 周国华, 孙彬彬, 等.福建沿海地区土壤-稻谷重金属含量关系与影响因素研究[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(3):295-301. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160312&flag=1
Wang T Y, Zhou G H, Sun B B, et al.The relationship between heavy metal contents of soils and rice in coastal areas, Fujian Province, including influencing factors[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(3):295-301. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160312&flag=1
[22] 陈志慧, 孙洛新, 钟莅湘, 等.快速催化极谱法测定土壤中的有效态钼[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(4):584-588. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140422&flag=1
Chen Z H, Sun L X, Zhong L X, et al.Determination of available molybdenum in soil by rapid catalytic polarography[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(4):584-588. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140422&flag=1
[23] 鲁如坤.土壤-植物营养学原理和施肥[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 1998.
Lu R K.Principles of Soil Plant Nutrition and Fertilization[M].Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 1998.
[24] 邹宇, 于俊林, 徐晶.硒及微生物富硒研究进展[J].食品研究与开发, 2006, 27(9):171-173. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPYK200609055.htm
Zou Y, Yu J L, Xu J.Research advance of the selenium and concentrating selenium of microbe[J].Food Research and Development, 2006, 27(9):171-173. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPYK200609055.htm
[25] Dhillon K S.Adsorption-desorption reactions of selenium in some soils of India[J]. Geoderma, 1999, 93:19-31. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7061(99)00040-3
-



 下载:
下载: