Application of Iolite in Data Reduction of Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry Line-scan Analysis
-
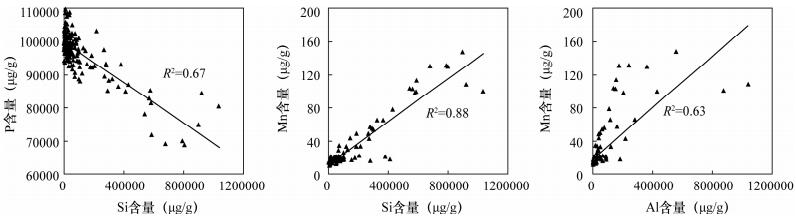
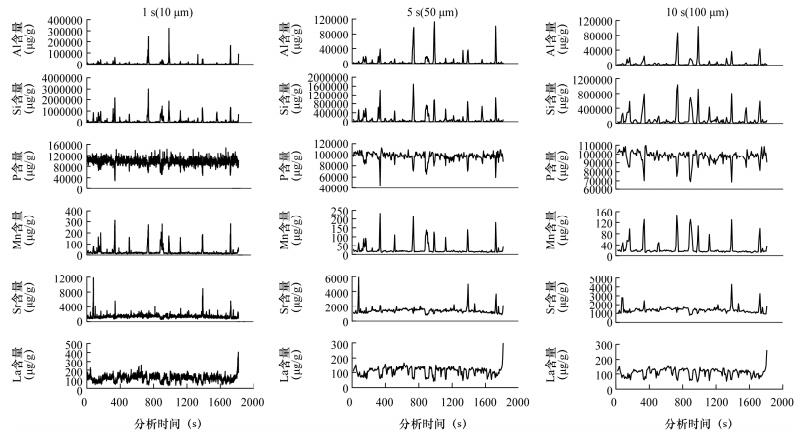
摘要: LA-ICP-MS分析技术是获取矿物/岩石内部的元素和同位素成分变化的重要手段。在利用该技术对地质样品进行线/面扫描时,仪器输出的初始数据量远远大于点分析,数据的处理和计算是一个关键问题。本文以磷质结核样品为例,阐述了利用Iolite软件进行元素线扫描数据计算的主要过程,包括背景信号的扣除、标准物质信号的拟合、线分析数据的导出等。借助软件自带的分段导出功能,对不同时间和空间分辨率下采集数据得到的结果进行了比较。研究表明Iolite能有效处理线分析数据,分析结果与前人用传统化学全岩法测定得到的元素含量范围相当。对比不同空间分辨率下(10 μm、50 μm、100 μm)获取的数据发现:相对于选用的束斑直径(40 μm),在分辨率过小(10 μm)或过大(100 μm)的条件下获得的数据存在数据波动大以及细节不足等缺陷;而当分辨率(50 μm)与选用的束斑直径接近时,数据质量得到最大优化。本研究展示了Iolite软件在处理线扫描数据方面具有很好的应用前景,通过分辨率的选取可实现数据的优化。Abstract: Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) serves as an important tool for assessing variations in elemental/isotopic compositions of rocks and minerals. During LA-ICP-MS analysis, as spectrometric data acquired via mapping/line analysis are much more than those by single spot analysis, reduction and processing of the obtained data are critical. In this study, Iolite was used to handle LA-ICP-MS data acquired by line analysis on a phosphate nodule. The reduction processes include baseline subtraction, data correction using the interpolation method, and data output. The results obtained using different temporal (spatial) resolution were compared by the section output function of the software. Data reduction of line analysis using Iolite yields results similar to those obtained using wet-chemical analysis. Comparison of different temporal (spatial) resolution (10 μm, 50 μm, 100 μm) for data processing indicates that the results are best optimized when the chosen resolution (50 μm) approximates the spot size (40 μm) during analysis (in Fig.3 and Fig.4). By contrast, results obtained using lower (10 μm) or higher (100 μm) spatial resolution are either fluctuate more or lack detail. These observations indicate that Iolite is a promising tool for LA-ICP-MS data reduction. The results also emphasis the importance of using appropriate temporal (spatial) resolution for data reduction.
-
Key words:
- LA-ICP-MS /
- Iolite software /
- line analysis /
- phosphate nodule /
- spatial resolution
-

-
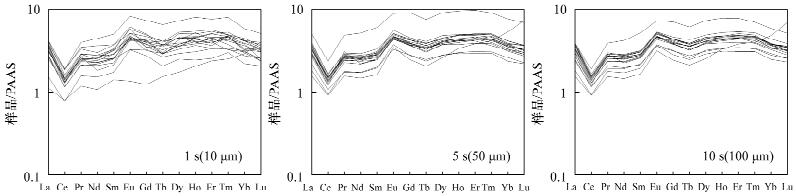
图 3 稀土元素PAAS标准化配分曲线图解 (PAAS数据引自文献[37])
Figure 3.
表 1 仪器分析参数
Table 1. Working parameters of instrument measurement
电感耦合等离子体质谱 激光剥蚀系统 工作参数 设定值 工作参数 设定值 RF功率 1350 W 能量密度 22 J/cm2 冷却气流量 15.00 L/min 输出比例 90% 辅助气流量 1.00 L/min 束斑大小 40 μm 载气流量 1.02 L/min He气流量 0.85 L/min 数据模式 TRA 检测器模式 双重模式 测试元素 27Al, 29Si, 43Ca, 51V, 55Mn, 57Fe,
88Sr, 89Y, 95Mo, REEs (139La~175Lu),
208Pb, 238U积分时间 Al、Si、P、Fe、Mn、Sr均为1 ms;
其他元素为1.5 ms -
[1] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Li M, et al.Applications of LA-ICP-MS in the elemental analyses of geological samples[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58:3863-3878. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-5901-4
[2] 李秋立, 杨蔚, 刘宇, 等.离子探针微区分析技术及其在地球科学中的应用进展[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013:32(3):310-327. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201303004.htm
Li Q L, Yang W, Liu Y, et al.Ion microprobe microanalytical techniques and their applications in earth sciences[J].Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2013, 32(3):310-327. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201303004.htm
[3] 李金华, 潘永信.透射电子显微镜在地球科学研究中的应用[J].中国科学 (地球科学), 2015, 45(9):1359-1382. doi: 10.1360/zd2015-45-09-1359
Li J H, Pan Y X.Applications of transmission electron microscopy in the earth sciences[J].Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2015, 45(9):1359-1382. doi: 10.1360/zd2015-45-09-1359
[4] 秦玉娟, 张天付, 胡圆圆, 等.电子探针背散射电子图像在碳酸盐岩微区分析中的意义[J].电子显微学报, 2013, 32(6):479-484. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXV201306006.htm
Qin Y J, Zhang T F, Hu Y Y, et al.The significance of a back-scattered electron image (of EPMA) in micro-area analyses of carbonate rocks[J].Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2013, 32(6):479-484. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXV201306006.htm
[5] 李冰, 周剑雄, 詹秀春.无机多元素现代仪器分析技术[J].地质学报, 2011, 85(11):1878-1916. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201111009.htm
Li B, Zhou J X, Zhan X C.Modern instrumental analysis of inorganic multi-elements[J].Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(11):1878-1916. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201111009.htm
[6] 梁述廷, 刘玉纯, 刘瑱, 等.X射线荧光光谱微区分析在铜矿物类质同象鉴定中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 2015, 34(2):201-206. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150208&flag=1
Liang S T, Liu Y C, Liu Z, et al.Application of in-situ micro-XRF spectrometry in the identification of copper minerals[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(2):201-206. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150208&flag=1
[7] 王坤阳, 徐金沙, 饶华文, 等.扫描电镜-X射线能谱仪在丹巴地区铂族矿物物相特征分析中的应用[J].岩矿测试, 2013, 32(6):924-930. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130615&flag=1
Wang K Y, Xu J S, Rao H W, et al.Application of SEM and EDS for phase characteristics analysis of platinoid mineral in the Danba area[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(6):924-930. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/ykcs/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130615&flag=1
[8] Agangi A, Przybyłowicz W, Hofmann A.Trace element mapping of pyrite from Archean gold deposits-A comparison between PIXE and EPMA[J].Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research, 2015, 348:302-306.
[9] 李献华, 柳小明, 刘勇胜, 等.LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb定年的准确度:多实验室对比分析[J].中国科学 (地球科学), 2015, 45(9):1294-1303. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201509004.htm
Li X H, Liu X M, Liu Y S, et al.Accuracy of LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb age determination:An inter-laboratory comparison[J].Science China (Earth Sciences), 2015, 45(9):1294-1303. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201509004.htm
[10] Woodhead J D, Hellstrom J, Hergt J M, et al.Isotopic and elemental imaging of geological materials by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2007, 31(4):331-343.
[11] Jackson S E, Pearson N J, Griffin W L, et al.The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J].Chemical Geology, 2004, 211(1-2):47-69. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.06.017
[12] Halter W E, Pettke T, Heinrich C A, et al.Major to trace element analysis of melt inclusions by laser-ablation ICP-MS:Methods of quantification[J].Chemical Geology, 2002, 183(1-4):63-86. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00372-2
[13] 徐伟彪.离子探针测试方法及其在矿物微区微量元素和同位素分析中的应用[J].高校地质学报, 2005, 11(2):239-252. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200502011.htm
Xu W B.Ion microprobe:Techniques and applications in cosmochemistry and geochemistry[J].Geological Journal of China Universities, 2005, 11(2):239-252. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200502011.htm
[14] Riches A J V, Ickert R B, Pearson D G, et al.In situ oxygen-isotope, major-, and trace-element constraints on the metasomatic modification and crustal origin of a diamondiferous eclogite from roberts victor, Kaapvaal craton[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2016, 174(4):345-359.
[15] Liu Y, Li Q L, Tang G Q, et al.Towards higher precision SIMS U-Pb zircon geochronology via dynamic multi-collector analysis[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2015, 30(4):979-985. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00459K
[16] 袁静, 罗立强.同步辐射微区X射线荧光和吸收谱技术在大气、土壤和动植物分析中的应用[J].核技术, 2014, 37(8):1-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJSU201408001.htm
Yuan J, Luo L Q.Synchrotron P-XRF and XAFS in element distribution and speciation of air, soil and biological samples[J].Nuclear Techniques, 2014, 37(8):1-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJSU201408001.htm
[17] Chang Z, Vervoort J D, Mcclelland W C, et al.U-Pb dating of zircon by LA-ICP-MS[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7(5):145-162.
[18] Yuan H L, Gao S, Dai M N, et al.Simultaneous determinations of U-Pb age, Hf isotopes and trace element compositions of zircon by excimer laser-ablation quadrupole and multiple-collector ICP-MS[J].Chemical Geology, 2008, 247(1-2):100-118. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.003
[19] Frei D, Gerdes A.Precise and accurate in situ U-Pb dating of zircon with high sample throughput by automated LA-SF-ICP-MS[J].Chemical Geology, 2009, 261(3-4):261-270. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.07.025
[20] Solari L A, Gómez-Tuena A, Bernal J P, et al.U-Pb zircon geochronology with an integrated LA-ICP-MS microanalytical workstation:Achievements in precision and accuracy[J].Geostandards & Geoanalytical Research, 2010, 34(34):5-18. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/230412526_U-Pb_Zircon_Geochronology_with_an_Integrated_LA-ICP-MS_Microanalytical_Workstation_Achievements_in_Precision_and_Accuracy
[21] Woodhead J, Hergt J, Meffre S, et al.In situ Pb-isotope analysis of pyrite by laser ablation (multi-collector and quadrupole) ICPMS[J].Chemical Geology, 2009, 262(3-4):344-354. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.02.003
[22] Lee S, Bi X, Reed R B, et al.Nanoparticle size detection limits by single particle ICP-MS for 40 elements[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(17):10291-10300.
[23] George L, Cook N J, Ciobanu C L, et al.Trace and minor elements in galena:A reconnaissance LA-ICP-MS study[J].American Mineralogist, 2015, 100(2-3):548-569. doi: 10.2138/am-2015-4862
[24] Liu P P, Zhou M F, Chen W T, et al.In-situ LA-ICP-MS trace elemental analyses of magnetite:Fe-Ti-(Ⅴ) oxide-bearing mafic-ultramafic layered intrusions of the Emeishan large igneous province, SW China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65(4):853-871. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/272182954_In-situ_LA-ICP-MS_trace_elemental_analyses_of_magnetite_Fe-Ti-V_oxide-bearing_mafic-ultramafic_layered_intrusions_of_the_Emeishan_Large_Igneous_Province_SW_China
[25] Wohlgemuth-Ueberwasser C C, Viljoen F, Petersen S, et al.Distribution and solubility limits of trace elements in hydrothermal black smoker sulfides:An in-situ LA-ICP-MS study[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2015, 159:16-41. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2015.03.020
[26] Chen L, Li X H, Li J W, et al.Extreme variation of sulfur isotopic compositions in pyrite from the Qiuling sediment-hosted gold deposit, West Qinling orogen, Central China:An in situ SIMS study with implications for the source of sulfur[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2015, 50(6):643-656. doi: 10.1007/s00126-015-0597-9
[27] Chirinos J R, Oropeza D D, Gonzalez J J, et al.Simultaneous 3-dimensional elemental imaging with Libs and LA-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29(7):1292-1298. doi: 10.1039/c4ja00066h
[28] Gao J F, Jackson S E, Dubé B, et al.Genesis of the Canadian Malartic, Côté Gold, and Musselwhite Gold Deposits:Insights from LA-ICP-MS Element Mapping of Pyrite[M].Targeted Geoscience Initiative 4:Contributions to the Understanding of Precambrian Iode Gold Deposits and Implications for Exploration (Dubé B, Mercier-Langevin P), Natural Resources Canada/Ressources naturelles Canada, 2015:157-175.
[29] Becker J S, Matusch A, Bei W.Bioimaging mass spectro-metry of trace elements-Recent advance and applications of LA-ICP-MS:A review[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2014, 835(16):1-18.
[30] Liu Y, Hu Z, Gao S, et al.In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J].Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1-2):34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
[31] Rittner M, Müller W.2D mapping of LA-ICPMS trace element distributions using R[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2012, 42:152-161.
[32] Paton C, Hellstrom J, Paul B, et al.Iolite:Freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2011, 26(12):2508-2518. doi: 10.1039/c1ja10172b
[33] Paul B, Paton C, Norris A, et al.Cellspace:A module for creating spatially registered laser ablation images within the iolite freeware environment[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2012, 27(4):700-706. doi: 10.1039/c2ja10383d
[34] Zhu B, Jiang S Y, Yang J H, et al.Rare earth element and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of phosphate nodules from the lower Cambrian niutitang formation, NW Hunan Province, South China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2014, 398(3):132-143.
[35] Jiang S Y, Zhao H X, Chen Y Q, et al.Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of phosphate nodules from the lower Cambrian black shale sequence in the Mufu Mountain of Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, China[J].Chemical Geology, 2007, 244(3):584-604.
[36] Bian X P, Yang T, Lin A J, et al.Rapid and high-precision measurement of sulfur isotope and sulfur concentration in sediment pore water by multi-collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2015, 132:8-14. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2014.08.053
[37] Mclennan S M.Rare-earth elements in sedimentary rocks:Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[J].Reviews in Mineralogy, 1989, 21(8):169-200.
[38] 赵伦山, 张本仁编著.地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1987:41-43.
Zhao L S, Zhang B R.Geochemistry[M].Beijing:Geology Publishing House, 1987:41-43.
[39] Woodhead J D, Hellstrom J, Hergt J M, et al.Isotopic and elemental imaging of geological materials by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Geostandards & Geoanalytical Research, 2007, 31(4):331-343.
[40] Zhu Z, Cook N, Yang T, et al.Mapping of sulfur isotopes and trace elements in sulfides by LA-(MC)-ICP-MS:Potential analytical problems, improvements and implications[J].Minerals, 2016, 6(4):110. doi: 10.3390/min6040110
-




 下载:
下载: