Determination of Steroid Estrogens in Different Water Samples Using SPE-derivatization Coupled with GC-MS
-
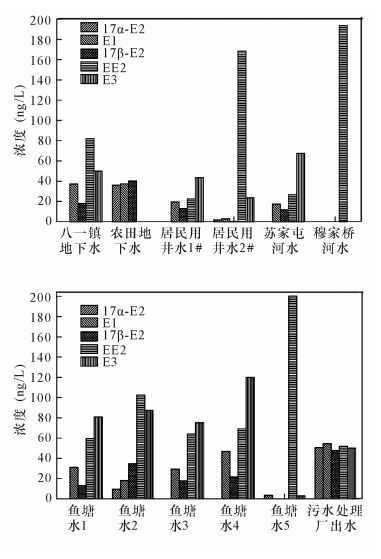
摘要: 针对地下水及地表水体样品中痕量类固醇雌激素(SEs)污染问题,本文建立了固相萃取-衍生化-气相色谱-质谱联用(SPE-GC-MS)同时测定不同水体中5种SEs:雌酮(E1)、17α-雌二醇(17α-E2)、17β-雌二醇(17β-E2)、17α-乙炔基雌二醇(EE2)、雌三醇(E3)的分析检测方法。通过优化固相萃取过程和衍生化条件以及复杂样品的二次净化过程,发现用Oasis HLB柱萃取,用乙酸乙酯洗脱,40℃条件衍生化20 min可以达到最佳效果,并且经甲醇活化过的Generik NAX柱对复杂样品的二次净化效果较好。本方法对E1、17α-E2、17β-E2和EE2、E3检测的线性范围分别为5~1000 ng/L和10~1000 ng/L;方法检出限和定量限分别为2~3 ng/L和6.5~10 ng/L;对水样的加标回收率范围为80%~120%;该方法测定SEs峰面积的日内相对标准偏差为6.8%~10%。应用此方法对鱼塘水、河水、地下水、污水处理厂二级出水进行了SEs污染水平检测,结果表明该检测技术可以有效应用于不同水质地表及地下水体类固醇雌激素化学风险识别与评估。Abstract: In order to solve trace-level steroid estrogen pollution in groundwater and surface water, a SPE-GC-MS approach to determine five steroid estrogens (SEs), E1, 17α-E2, 17β-E2, EE2 and E3, by optimizing of solid phase extraction (SPE), derivatization conditions and the secondary purification process of complex samples has been developed. The results show that Oasis HLB column, ethyl acetate elution and derivatizing at 40℃ for 20 min can achieve the best results for extraction. Moreover, the Generik NAX column activated by methyl is suitable for the secondary purification of complex samples. The linear ranges of E1, 17α-E2, and 17β-E2 are 5-1000 ng/L, whereas those of EE2 and E3 are 10-1000 ng/L. The detection and quantitation limits are 2-3 ng/L and 6.5-10 ng/L, respectively. The standard solution added recoveries of water samples range from 80% to 120%. The relative standard deviations of daily peak areas in the SEs determination range from 6.8% to 10%. This method was used to determine the SEs pollution levels of waters from pond, river, groundwater and sewage treatment plant effluent and results show that this detection technique can be effectively applied to the identification and evaluation of estrogen risk in surface water and groundwater samples.
-

-
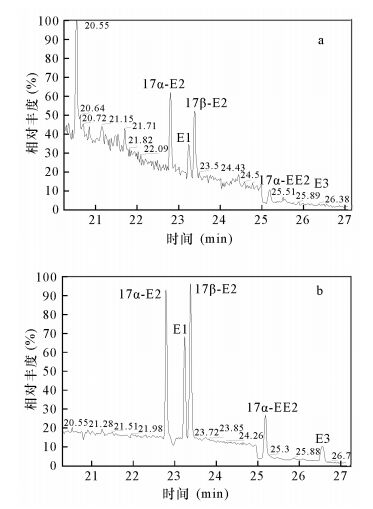
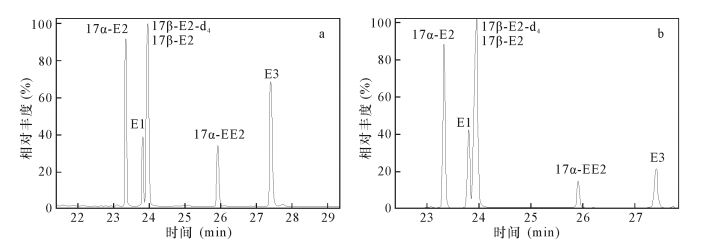
表 1 目标SEs的保留时间及其特征离子
Table 1. Retention times and characteristic ions of the target steroid estrogens
化合物 保留时间
(min)定性离子
(m/z)定量离子
(m/z)E1 23.24 342,218,257 342 17α-E2 22.81 285,326,416 285 17β-E2 23.40 285,326,416 285 17β-E2-d4 23.40 285,129,416 285 EE2 25.19 425,232,285 425 E3 26.56 311,386 311 表 2 衍生化时间和温度对目标化合物回收率的影响
Table 2. The effects of derivatization time and temperature on recoveries of the target compounds
化合物 回收率(%)±标准偏差(%) 20℃ 40℃ 60℃ 80℃ 40℃ 60℃ 80℃ 40℃ 60℃ 80℃ 20 min 40 min 60 min E1 88.8±2.8 98.4±2.9 101.2±3.4 101.3±3.1 100.2±3.7 103.1±3.9 96.7±5.0 105.5±3.4 105.6±6.1 108.1±4.3 17α-E2 90.7±2.9 98.2±2.9 95.8±7.0 98.2±5.0 99.3±3.2 99.2±4.5 93.9±8.6 100±3.4 102.8±3.6 99.1±5.8 17β-E2 90.5±7.0 98.8±5.0 98.1±3.4 98.5±2.6 96.1±6.4 98.9±4.5 93.8±5.8 99.8±4.4 103±8.2 100.6±3.1 EE2 86.8±4.3 99.9±5.2 99.8±5.4 96.5±8.8 101.3±3.3 97±7.6 95.9±8.8 108±4.2 100.6±7.0 100.3±8.4 E3 88.7±6.1 102.3±2.4 103.4±4.1 109.5±5.3 103.4±2.8 111.8±5.3 86.8±8.4 111.8±5.3 109.4±4.1 109.7±4.8 表 3 五种类固醇雌激素的线性方程、相关系数、线性范围、检出限和定量限
Table 3. Linear equation, correlation coefficient, linear range, LOD and LOQ of five estrogens
化合物回归方程 相关系数
(R2)线性范围
(ng/L)检出限
(S/N=3,ng/L)定量限
(S/N=10,ng/L)E1 Y=-3987.67+1312.43X 0.9984 5~1000 2 6.5 17-α E2 Y=-32075.1+1541.75X 0.9982 5~1000 2 6.5 17-β E2 Y=-36461.6+1694.59X 0.9981 5~1000 2 6.5 EE2 Y=-7596.5+291.442X 0.9963 10~1000 3 10 E3 Y=-5898.03+425.589X 0.9986 10~1000 3 10 -
[1] Chowdhury R R, Charpentier P A, Ray M B.Photode-gradation of 17β-estradiol in aquatic solution under solar irradiation:Kinetics and infiuencing water parameters[J].Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A:Chemistry, 2011, 219:67-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2011.01.019
[2] Chambers K B, Casey F X, Hakk H, et al.Potential bioactivity and association of 17β-estradiol with the dissolved and colloidal fractions of manure and soil[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 494-495:58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.121
[3] Zheng W, Zou Y, Li X, et al.Fate of estrogen conjugate 17α-estradiol-3-sulfate in dairy wastewater:Comparison of aerobic and anaerobic degradation and metabolite formation[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 258-259:109-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.04.038
[4] Liu Z H, Lu G N, Yin H, et al.Removal of natural estro-gens and their conjugates in municipal wastewater treatment plants:A critical review[J].Environment Science & Technology, 2015, 49:5288-5300. http://www.academia.edu/25264382/Occurrence_fate_and_removal_of_synthetic_oral_contraceptives_SOCs_in_the_natural_environment_A_review
[5] 都韶婷, 金崇伟, 刘越.水体SEs污染现状研究进展[J].环境科学, 2013, 34(9):3358-3365. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201309003.htm
Du S T, Jin C W, Liu Y.A review on current situations of steroid estrogen in the water system[J].Environmental Science, 2013, 34(9):3358-3365. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201309003.htm
[6] Sun W L, Zhou K.Adsorption of 17β-estradiol by multi-walled carbon nanotubes in natural waters with or without aquatic colloids[J].Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 258:185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.087
[7] D'Alessio M, Vasudevan D, Lichwa J, et al.Fate and transport of selected estrogen compounds in Hawaii soils:Effect of soil type and macropores[J].Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2014, 166:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2014.07.006
[8] Combalbert S, Hernandez-raquet G.Occurrence, fate and biodegradation of estrogens in sewage and manure[J].Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2010, 86(6):1671-1692. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2547-x
[9] Jiang J Q, Yin Q, Zhou J L, et al.Occurrence and treatment trials of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) in wastewaters[J].Chemosphere, 2005, 61(4):544-550. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.02.029
[10] Shrestha S L, Casey F X, Hakk H, et al.Fate and transformation of an estrogen conjugate and its metabolites in agricultural soils[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46:11047-11053. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22967238
[11] Bai X L, Shrestha S L, Francis X M, et al.Modeling coupled sorption and transformation of 17β-estradiol-17-sulfate in soil-water systems[J].Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2014, 168:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2014.09.001
[12] Lee J, Bartelthunt S L, Li Y, et al.Effect of 17β-estradiol on stability and mobility of TiO2 rutile nanoparticles[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 511:195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.054
[13] Goeppert N, Dror I, Berkowitz B.Fate and transport of free and conjugated estrogens during soil passage[J].Environmental Pollution, 2015, 206:80-87. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.06.024
[14] Singh R, Cabrera M L, Radcliffe D E, et al.Laccase me-diated transformation of 17β-estradiol in soil[J].Environmental Pollution, 2015, 197:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.11.023
[15] Postigo C.Synthetic organic compounds and their trans-formation products in groundwater:Occurrence, fate and mitigation[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 503-504:32-47. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.019
[16] Schuh M C, Casey F X, Hakk H, et al.Effects of field-manure applications on stratified 17β-estradiol concentrations[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192:748-752. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.05.080
[17] Lucci P, Núñ nez O, Galceran M T.Solid-phase extraction using molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction of natural and synthetic estrogens from aqueous samples[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218(30):4828-4833. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.02.007
[18] Zheng M, Wang L, Bi Y, et al.Improved method for analyzing the degradation of estrogens in water by solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet detection[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(4):693-698. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60439-1
[19] Fredj S B, Nobbs J, Tizaoui C, et al.Removal of estrone (E1), 17β-estradiol (E2), and 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) from wastewater by liquid-liquid extraction[J].Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 262:417-426. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.007
[20] Naing N N, Li S F Y, Lee H K.Evaluation of graphene-based sorbent in the determination of polar environmental contaminants in water by micro-solid phase extraction-high performance liquid chromatography[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2016, 1427:29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.12.012
[21] Wang J, Chen Z, Li Z, et al.Magnetic nanoparticles based dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction as a novel technique for the determination of estrogens in pork samples[J].Food Chemistry, 2016, 204:135-140. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.02.016
[22] Luo S, Fang L, Wang X, et al.Determination of octyl-phenol and nonylphenol in aqueous sample using simultaneous derivatization and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2010, 1217(43):6762-6768. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2010.06.030
[23] Wang P, Xiao Y, Liu W, et al.Vortex-assisted hollow fibre liquid-phase microextraction technique combined with high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection for the determination of oestrogens in milk samples[J].Food Chemistry, 2015, 172:385-390. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.092
[24] González A, Avivar J, Cerdà V.Estrogens determination in wastewater samples by automatic in-syringe dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction prior silylation and gas chromatography[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2015, 1413:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.08.031
[25] Manickum T, John W.The current preference for the immuno-analytical ELISA method for quantitation of steroid hormones (endocrine disruptor compounds) in wastewater in South Africa[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2015, 407(17):4949-4970. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-8546-0
[26] 王硕, 陈双, 方国臻, 等.分子印迹技术在环境雌激素检测中的应用[J].食品与生物技术学报, 2008, 26(6):99-104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WXQG200706025.htm
Wang S, Chen S, Fang G Z, et al.Determination of environmental estrogens by molecular imprinting technique[J].Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2008, 26(6):99-104:99-104. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WXQG200706025.htm
[27] Bai X, Casey F X, Hakk H, et al.Sorption and degra-dation of 17β-estradiol-17-sulfate in sterilized soil-water systems[J].Chemosphere, 2015, 119:1322-1328. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.016
[28] Kumar V, Johnson A C, Nakada N, et al.De-conjugation behavior of conjugated estrogens in the raw sewage, activated sludge and river water[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 227-228:49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.04.078
[29] Ronan J M, Mchugh B.A sensitive liquid chromatogra-phy/tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of natural and synthetic steroid estrogens in seawater and marine biota, with a focus on proposed Water Framework Directive Environmental Quality Standards[J].Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 2013, 27:738-746. doi: 10.1002/rcm.6505
[30] Atapattu S N, Rosenfeld J M.Solid phase analytical derivatization of anthropogenic and natural phenolic estrogen mimics with pentafluoropyridine for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2011, 1218:9135-9141. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2011.10.060
[31] 余方, 潘学军, 王彬, 等.固相萃取-羟基衍生化-气相色谱/质谱联用测定滇池水体中酚类内分泌干扰物[J].环境化学, 2010, 29(4):744-748. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201004040.htm
Yu F, Pan X J, Wang B, et al.Determination of phenols in surface water of dianchi lake by solid extraction-hydroxyl derivatization-GC-MS[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2010, 29(4):744-748. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201004040.htm
[32] 廖涛, 吴晓翠, 王少华, 等.固相萃取-气相色谱/质谱联用法同时检测水体中9种环境雌激素[J].分析化学, 2013, 41(3):422-426. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201303021.htm
Liao T, Wu X C, Wang S H, et al.Simultaneous detection of nine kinds of estrogens in water by solid phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(3):422-426. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201303021.htm
[33] 黄成, 姜理英, 陈建孟, 等.固相萃取-衍生化气相色谱/质谱法测定制药厂污水中的环境雌激素[J].色谱, 2008, 26(5):618-621. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPZZ200805021.htm
Huang C, Jiang L Y, Chen J M, et al.Determination of environmental estrogens in pharmacy wastewater using solid-phase extraction-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry with derivatization[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2008, 26(5):618-621. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPZZ200805021.htm
[34] Quintana J B, Carpinteiro J, Rodríguez I, et al.Deter-mination of natural and synthetic estrogens in water by gas chromatography with mass spectrometric detection[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2004, 1024:177-185. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2003.10.074
[35] Nie Y F, Qiang Z M, Zhang H Q, et al.Determination of endocrine-disrupting chemicals in the liquid and solid phases of activated sludge by solid phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2009, 1216(42):7071-7080. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2009.08.064
[36] Liu R, Zhou J L, Wilding A.Simultaneous determination of endocrine disrupting phenolic compounds and steroids in water by solid-phase extraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2004, 1022(1):179-189. http://www.academia.edu/33653534/Simultaneous_determination_of_endocrine_disrupting_phenolic_compounds_and_steroids_in_water_by_solid-phase_extraction_gas_chromatography_mass_spectrometry
[37] 黄斌, 潘学军, 万幸, 等.固相萃取衍生化气相色谱/质谱测定水中类固醇类环境内分泌干扰物[J].分析化学, 2011, 39(4):449-454. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201104003.htm
Huang B, Pan X J, Wan X, et al.Simultaneous determination of steroid endocrine disrupting chemicals in water by solid phase extraction-derivatization-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 39(4):449-454. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201104003.htm
[38] 张宏, 毛炯, 孙成均, 等.气相色谱-质谱法测定尿及河底泥中的环境雌激素[J].色谱, 2003, 21(5):451-455. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPZZ200305003.htm
Zhang H, Mao J, Sun C J, et al.Determination of environmental estrogens in urine and bed mud by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2003, 21(5):451-455. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SPZZ200305003.htm
[39] Delaune P B, Jr M P.17β-estradiol in runoff as affected by various poultry litter application strategies[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2013, 444:26-31. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.054
[40] Zhang H, Shi J, Liu X, et al.Occurrence and removal of free estrogens, conjugated estrogens, and bisphenol A in manure treatment facilities in East China[J].Water Research, 2014, 58:248-257. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2014.03.074
[41] Bevacqua C E, Rice C P, Torrents A, et al.Steroid hor-mones in biosolids and poultry litter:A comparison of potential environmental inputs[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2011, 409:2120-2126. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.02.007
[42] Caron E, Farenhorst A, Mcqueen R, et al.Mineralization of 17β-estradiol in 36 surface soils from Alberta, Canada[J].Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2010, 139:534-545. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2010.09.014
[43] Lee B, Kullman S W, Yost E E, et al.Predicting charac-teristics of rainfall driven estrogen runoff and transport from swine AFO spray fields[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 532:571-580. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.06.051
-



 下载:
下载: