Observation of Surface Microstructure of HPHT Synthetic Diamond Crystals and Genesis Discussion
-
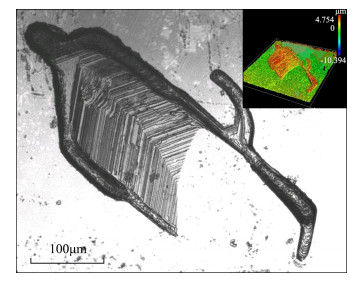
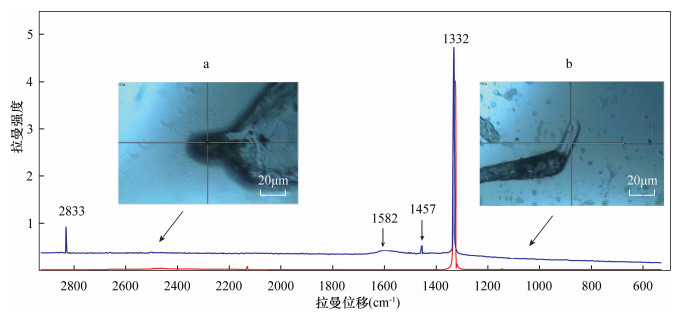
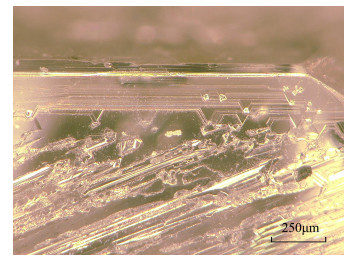
摘要: 我国作为世界上最大的合成钻石生产国,其产量占据世界总产量的90%以上,其中以高温高压法(HPHT)合成钻石为主。国内外学者对于HPHT合成钻石物性的测试方法和性质分析较为完备,但是对HPHT合成钻石生长完成后的酸洗过程以及酸洗后留下的内外部微形貌亟待研究。本文采用激光共聚焦显微镜和超景深三维显微镜对118粒产自我国的HPHT合成钻石进行内外部特征观察,并配合激光拉曼光谱仪对这些微细结构内的包裹残余进行定性分析。发现了三类特征的结构类型:成一定夹角的阶梯型生长结构,揭示了HPHT合成钻石聚型晶的结晶学特质;近平行线状划痕,反映了生长腔体内钻石晶粒间的接触关系;通过独特的"绳捆纹"结构进行观察和分析,认为这一结构反映了HPHT合成钻石的生长速率。这些钻石表面的微形貌反映了HPHT合成钻石梯度高温和持续高压的生长条件和环境,对于HPHT合成钻石的鉴别具有指导意义。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDAs the world's largest producer of synthetic diamonds, China accounts for more than 90% of the world's total production, of which high pressure-high temperature (HPHT) synthetic diamonds are dominant. Previous scholars have conducted many studies on analytical methods and property analysis of HPHT synthetic diamonds. However, the research on the pickling process after the growth of HPHT synthetic diamonds and the internal and external micro-structures after pickling is still insufficient. OBJECTIVESTo characterize 118 synthetic diamonds produced in China by high temperature and high pressure method. METHODSThe HPHT synthetic diamonds were observed by laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM) and ultra-depth-of-field 3D microscopy, and the dark inclusions in these micro-structures were qualitatively analyzed by laser Raman spectroscopy. RESULTSThree structure types were found. Step-like growth structures with certain angles revealed the crystallographic characteristics of HPHT synthetic diamond poly-crystals. Near-parallel linear scratches reflected the contact relationship between diamond grains in the growth chamber. The 'rope-tied' structures reflected the growth rate of HPHT synthetic diamonds. CONCLUSIONSThe micromorphology of these diamond surfaces reflects the growth conditions and environment of HPHT synthetic diamond gradient high temperature and continuous high pressure, which is of significance for the identification of HPHT synthetic diamonds. -

-
[1] D'Haenens-Johansson U F S, Katrusha A, Moe K S, et al.Large colorless HPHT-grown synthetic gem diamonds from new diamond technology, Russia[J].Gems & Gemology, 2015, 51(3):260-279. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dfdd1d8b548d6307425f24e61a07141d
[2] D'Haenens-Johansson U F S, Kyaw S M, Johnson P, et al.Near-colorless HPHT synthetic diamonds from AOTC group[J].Gems & Gemology, 2014, 50(1):2-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0232797763/
[3] 尹龙卫, 李木森, 孙东升, 等.人造金刚石晶体生长的微观机制[J].人工晶体学报, 2000, 29(4):386-389. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2000.04.018
Yin L W, Li M S, Sun D S, et al.Microscopic observation of synthetic diamond growth produced in Fe-Ni-C system[J].Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2000, 29(4):386-389. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2000.04.018
[4] 陆太进.钻石鉴定和研究的进展[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2010, 12(4):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2010.04.001
Lu T J.Development on identification and research of diamond[J].Journal of Gems and Gemmology, 2010, 12(4):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2010.04.001
[5] 宋中华, 陆太进, 柯捷, 等.国产大颗粒宝石级无色高压高温合成钻石的鉴定特征[J].宝石和宝石学杂志, 2016, 18(3):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2016.03.001
Song Z H, Lu T J, Ke J, et al.Identification characteristic of large near-colorless HPHT synthetic diamond from China[J].Journal of Gems and Gemmology, 2016, 18(3):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2016.03.001
[6] Liu W C.A self-designed laser scanning differential confocal microscopy with a novel vertical scan algorithm for fast image scanning[J].IFAC PapersOnLine, 2017, 50(1):3221-3226. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2017.08.446
[7] 杨志军, 彭明生, 谢先德, 等.金刚石的微区显微红外光谱分析及其意义[J].岩矿测试, 2002, 21(3):161-165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2002.03.001 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20020340
Yang Z J, Peng M S, Xie X D, et al.Micro-area analysis of diamond by micro-infrared spectrometry and its significance[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2002, 21(3):161-165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2002.03.001 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20020340
[8] 宋中华, 陆太进, 苏隽, 等.无色-近无色高温高压合成钻石的谱图特征及其鉴别方法[J].岩矿测试, 2016, 35(5):496-504. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.05.008
Song Z H, Lu T J, Su J, et al.The spectral characteristics and identification techniques for colorless and near-colorless HPHT synthetic diamonds[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(5):496-504. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.05.008
[9] 杨志军, 彭明生, 蒙宇飞, 等.金刚石中氮、氢含量的变化及在金刚石生长中的意义[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2007, 27(6):1066-1070. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2007.06.008
Yang Z J, Peng M S, Meng Y F, et al.Distribution of nitrogen and hydrogen in diamond and its significance to nucleation and growth of diamond[J].Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2007, 27(6):1066-1070. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0593.2007.06.008
[10] Lu T J, Ke J, Qiu Z L.Surface dissolution features and contact twinning in natural diamonds[J].Journal of Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2018, 195(2):145-153. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=355083e73210f2ea947187e2a5e098a6
[11] 苑执中, 杨志军, 彭明生.金刚石的晶格畸变[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2002, 21(2):114-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2002.02.008
Yuan Z Z, Yang Z J, Peng M S.Lattice distortion in diamonds[J].Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2002, 21(2):114-116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2002.02.008
[12] Ferrari A C, Robertson J.Raman spectroscopy of amor-phous, nanostructured, diamond-like carbon, and nanodiamond[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society London, Series A (Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences), 2004, 362(1824):2477-2512. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2004.1452
[13] Bulanova G P.The formation of diamond[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1995, 53:1-23. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(94)00016-5
-




 下载:
下载: