Research on the Determination of 14 Synthetic Musks in Sediment Samples by Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Accelerated Solvent Extraction
-
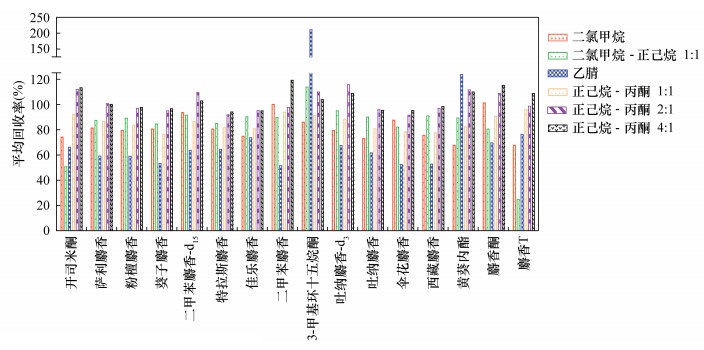
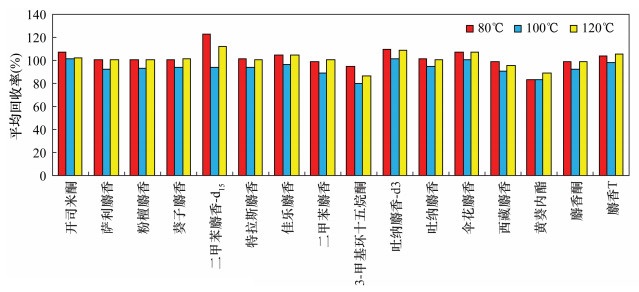
摘要: 近年人工合成麝香在环境中污染状况加剧,该类化合物具有潜在致癌和环境激素作用,对人类健康构成了威胁,因此越来越受到科学工作者的重视。水和土壤等环境样品中的人工合成麝香检测技术发展迅速,并朝着快速绿色的方向发展。人工合成麝香在沉积物中的浓度达到了几个到几千个ng/g的水平,但对于沉积物复杂基质中的多种类人工合成麝香,采取同步提取与净化,并快速分析的方法还有待研究。本文建立了沉积物样品中硝基麝香、多环麝香和大环麝香共三类、14种典型人工合成麝香的快速分析方法。通过实验优化了提取溶剂、提取温度、在线净化吸附剂等条件,大大降低了样品的前处理成本。最终确定样品采用加速溶剂萃取,萃取池中依次装入净化吸附剂(0.4g GCB和1.0g SAX)及5.0g沉积物样品,在80℃条件下采用提取溶剂正己烷-丙酮(4:1,V/V)循环提取2次,提取液浓缩后采用气相色谱-三重四极杆串联质谱(GC-MS/MS)进行测定。结果表明:14种目标化合物的线性范围为5~200ng/mL,平均添加回收率为70.6%~121.5%,相对标准偏差(RSD,n=7)为0.97%~19.5%。替代物回收率为72.2%~116.8%,方法检出限为硝基麝香0.10~0.19ng/g,多环麝香0.09~0.14ng/g,大环麝香0.11~1.93ng/g。该方法能够满足复杂基质沉积物样品的分析要求。
-
关键词:
- 人工合成麝香 /
- 沉积物 /
- 气相色谱-三重四极杆串联质谱法 /
- 加速溶剂萃取 /
- 复杂基质样品
Abstract:BACKGROUNDIn recent years, the pollution of synthetic musk in the environment has increased. This kind of material has potential carcinogenic and environmental hormone effects and poses a threat to human health. Therefore, it has attracted increasing attention from scientists. The analytical technology of synthetic musk in environmental samples such as water and soil has developed rapidly. The concentration of synthetic musk in sediments has reached several thousand ng/g, but the methods for the simultaneous extraction and purification and rapid analysis of various types of synthetic musk in complex matrices of sediments are yet to be studied. OBJECTIVESTo establish a rapid method for the analysis of 14 typical synthetic musks in sediment samples by accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) combined with gas chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS). METHODSAccelerated solvent extraction was used for sample preparation. The ASE cell was filled up with sorbent (0.4g GCB combined with 1.0g SAX) and 5.0g sediment samples. The sample was extracted in two cycles with mixed solvents hexane-acetone (V/V, 4:1) at 80℃. After preconcentration, the extracted solution was determined by GC-MS/MS. RESULTSThe linear range of this method for fourteen target compounds ranged from 5ng/mL to 200ng/mL. The average spike-added recoveries ranged from 70.6% to 121.5%, the relative standard deviations (RSD, n=7) were 0.97%-19.5%. The recoveries of surrogates were 72.2%-116.8%. The detection limits of the method were 0.10-0.19ng/g for nitro musk, 0.09-0.14ng/g for polycyclic musk, and 0.11-1.93ng/g for macrocyclic musk. CONCLUSIONSThis method can satisfy the analysis of musk in sediments with complex matrices. -

-
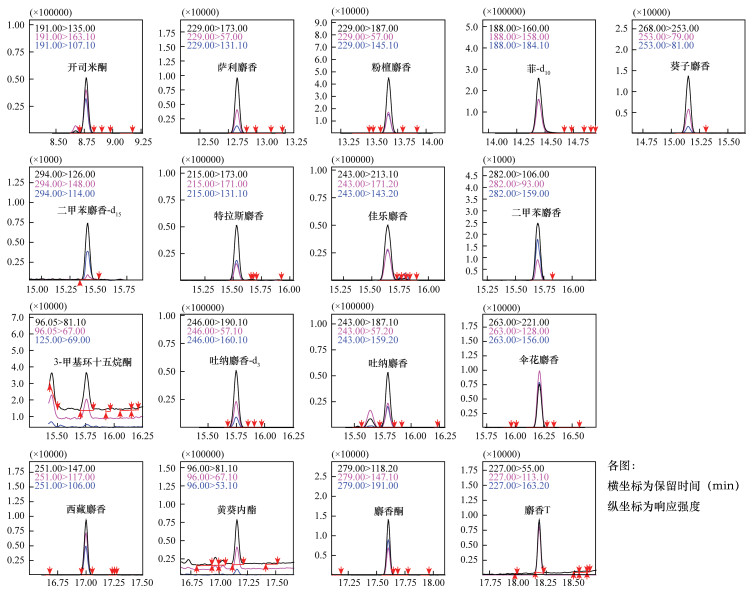
表 1 目标化合物的保留时间、监测离子对和碰撞能量
Table 1. Retention times, monitoring ion pairs and collision energies of target compounds
化合物 保留时间(min) 离子对(m/z) 碰撞能量(eV) 开司米酮 8.767 191>135▲
191>163126 萨利麝香 12.830 229>173▲
229>57918 粉檀麝香 13.670 229>187▲
229>57615 菲-d10 14.450 188>160▲
188>1582130 葵子麝香 15.155 268>253▲
253>79927 二甲苯麝香-d15 15.394 294>126▲
294>114633 特拉斯麝香 15.535 215>173▲
215>17196 佳乐麝香 15.646 243>213▲
243>1711518 二甲苯麝香 15.711 282>106▲
282>159219 3-甲基环十五烷酮 15.755 96>81▲
96>67912 吐纳麝香-d3 15.757 246>190▲
246>57921 吐纳麝香 15.801 243>187▲
243>57621 伞花麝香 16.215 263>221▲
263>128630 西藏麝香 17.001 251>147▲
251>117927 黄葵内酯 17.159 96>81▲
96>67612 麝香酮 17.604 279>118▲
279>191249 麝香T 18.190 227>55▲
227>163246 注:“▲”表示定量离子对。 表 2 净化吸附剂对目标物提取回收率的影响
Table 2. Effect of different purification adsorbents on extraction recovery of target compounds
化合物 目标物回收率(%) 1.0g SCX 1.0g SAX 0.5g GCB 0.5g炭黑 0.2g GCB+1.0g SAX 0.4g GCB+1.0g SAX 0.5g GCB+1.0g SAX 开司米酮 120.3 86.3 85.6 87.5 83.7 103.5 101.9 萨利麝香 128.1 93.5 91.9 106.8 104.4 95.6 96.6 粉檀麝香 126.9 94.9 92.9 114.8 104.9 96.2 97.4 葵子麝香 97.6 99.1 96.4 129.5 112.3 97.5 97.8 二甲苯麝香-d15 106.3 81.7 81.9 84.1 98.1 104.6 103.2 特拉斯麝香 171.0 97.6 99.1 107.0 112.7 96.8 97.2 佳乐麝香 - 98.2 100.3 106.6 114.9 99.7 100.6 二甲苯麝香 120.7 96.4 89.2 63.3 99.8 93.1 94.8 3-甲基环十五烷酮 - 111.3 131.4 93.7 126.8 86.6 83.7 吐纳麝香-d3 203.8 88.1 92.5 138.1 102.1 104.3 105.5 吐纳麝香 3168.1 88.8 92.4 100.3 97.4 97.3 98.1 伞花麝香 109.9 103.4 104.0 67.5 94.6 103.7 103.9 西藏麝香 127.8 101.5 110.9 91.9 103.8 94.1 93.5 黄葵内酯 - 127.9 123.8 1000.2 113.9 81.4 86.2 麝香酮 224.4 116.6 108.6 82.4 125.3 95.8 95.9 麝香T - 109.1 107.8 115.9 123.0 99.4 101.7 注:“-”表示未检出,下表同。 表 3 目标物测定线性范围、相关系数、相对标准偏差、平均回收率及方法检出限
Table 3. Linear range, correlation coefficients, relative standard deviation (RSD), average recovery and detection limit of the method for target compounds
化合物 线性范围(ng/mL) 相关系数(R2) 平均回收率(%)及相对标准偏差(%,n=7) 方法检出限(ng/g) 0.5ng/g 5.0ng/g 10.0ng/g 开司米酮 2~200 0.9977 121.5 4.80 101.1 2.94 70.6 2.34 0.09 萨利麝香 2~200 0.9980 98.5 8.56 92.7 2.16 85.3 0.97 0.13 粉檀麝香 2~200 0.9980 97.1 8.89 93.6 1.81 84.7 1.31 0.14 葵子麝香 2~200 0.9960 86.2 11.8 95.6 5.08 85.7 4.50 0.16 特拉斯麝香 2~200 0.9981 97.8 8.20 93.9 1.78 90.7 3.29 0.13 佳乐麝香 2~200 0.9981 118.3 5.00 97.2 2.86 84.8 2.36 0.09 二甲苯麝香 2~200 0.9983 94.4 12.6 88.9 6.92 84.0 3.02 0.19 3-甲基环十五烷酮▲ 10~200 0.9978 84.4 14.6 109.6 8.55 88.2 10.9 1.93 吐纳麝香 2~200 0.9982 97.9 6.43 94.8 1.43 80.8 3.64 0.10 伞花麝香 2~200 0.9959 101.2 8.01 101.2 5.00 90.0 5.03 0.13 西藏麝香 2~200 0.9975 91.4 9.00 91.0 3.10 87.8 3.29 0.13 黄葵内酯 2~200 0.9986 95.8 11.8 80.3 5.52 109.4 6.33 0.18 麝香酮 2~200 0.9974 84.8 7.23 94.3 3.18 116.5 5.09 0.10 麝香T 2~200 0.9984 94.0 7.50 97.2 1.98 96.1 4.97 0.11 二甲苯麝香-d15 - - 92.9 9.47 94.6 6.05 81.5 19.5 - 吐纳麝香-d3 - - 106.1 2.62 100.9 1.40 82.7 9.65 - 注:“▲”表示添加水平为5.0、10.0、20.0ng/g。 表 4 各类样品目标物分析方法检出限的比较
Table 4. Comparison of detection limit of the method for target compounds in different samples
样品类型 待测物数量(个) 分析方法 方法检出限(ng/g) 参考文献 多环麝香 硝基麝香 大环麝香 土壤 5 2 - SE-GC-MS 0.03~0.33 [18] 土壤、底泥 2 - - MAE-GC-MS 0.66~0.72 [19] 污泥、底泥、土壤 5 2 - ASE-GC-MS 0.25~0.33 [20] 土壤 2 - - ASE-GC-MS 0.19和0.295 [21] 污泥 - - 8 SPME-GC-MS 0.010~0.025 [25] 污泥、沉积物 6 - - SPME-GC-MS 0.04~0.1 [26] 污泥 5 4 - SPME-GC-MS 0.049~0.611 [27] 土壤 6 2 - SBSE-TD-GC-MS 0.01~1.1 [28] 污泥 6 3 4 SBSE-TD-GC-MS 5~30 [29] 沉积物 6 5 3 ASE-GC-MS/MS 0.09~0.19和1.93 本方法 表 5 实际沉积物样品中人工合成麝香检测结果
Table 5. Analytical results of synthetic musks in real sediment samples
样品序号 含量(ng/g) 佳乐麝香(HHCB) 吐纳麝香(AHTN) 1 0.17 0.11 2 0.17 - 3 0.09 - 4 0.40 0.20 5 - - 6 0.36 0.16 7 0.21 - 8 0.09 - 9 0.09 - 10 0.21 - 11 - - 12 0.18 - 13 0.12 - 14 - - 15 - - 16 0.10 - 17 0.09 - 18 0.19 - 19 - - 20 0.12 - -
[1] 曾祥英, 陈多宏, 桂红艳, 等.环境中合成麝香污染物的研究进展[J].环境监测管理与技术, 2006, 18(3):7-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HJJS200603002.htm
Zeng X Y, Chen D H, Gui H Y, et al.Anvance in study on synthetic musk in environment[J].The Admini-stration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2006, 18(3):7-10. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HJJS200603002.htm
[2] Taylor K M, Weisskopf M, Shine J.Human exposure to nitro musks and the evaluation of their potential toxicity:An overview[J].Environmental Health:A Global Acess Science, 2014, 13:14. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2c48306266075e348c41ad9c89ed9ccf&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[3] 周启星, 王美娥, 范飞, 等.人工合成麝香的环境污染、生态行为与毒理效应研究进展[J].环境科学学报, 2008, 28(1):1-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX200801003.htm
Zhou Q X, Wang M E, Fan F, et al.Research progress in environmtntal pollution, ecological behavior and toxicological effects of synthetic musks[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2008, 28(1):1-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX200801003.htm
[4] 李菊, 谢建军, 黄雪琳, 等.人造麝香的危害性及其残留检测方法研究进展[J].理化检验(化学分册), 2015, 51(2):272-276. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LHJH201502046.htm
Li J, Xie J J, Huang X L, et al.Recent advances of researches on the harmfulness of artificial musk and methods of determination of its residual amount[J].Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2015, 51(2):272-276. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LHJH201502046.htm
[5] 佟玲, 田芹, 潘萌, 等.环境中合成麝香类化合物的残留现状及其分析方法研究进展[J].生态学杂志, 2017, 36(5):1426-1435. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201705032.htm
Tong L, Tian Q, Pan M, et al.Recent advances of the research of pollution status and analysis methods for synthetic musks in environment[J].Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2017, 36(5):1426-1435. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201705032.htm
[6] Trabalón L, Cano-Sancho G, Pocurull E, et al.Exposure of the population of Catalonia (Spain) to musk fragrances through seafood consumption:Risk assessment[J].Environmental Research:Part B, 2015, 143:116-122. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=bcf0539f3ce8a602e2ffd9011e2e87a9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[7] 王征.气相色谱-负化学源-三重四极杆质谱法测定化妆品中的硝基麝香类化合物[J].色谱, 2012, 30(11):1178-1182. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SPZZ201211016.htm
Wang Z.Determination of synthetic nitro-musks in cosmtics by gas chromatography coupled with negative chemical ionization-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2012, 30(11):1178-1182. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SPZZ201211016.htm
[8] Ternes T A, Herrmann N, Bonerz M, et al.A rapid method to measure the solid-water distribution coefficient (Kd) for pharmaceuticals and musk fragrances in sewage sludge[J].Water Research, 2004, 38:4075-4084. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2004.07.015
[9] Villa S, Assi L, Ippolito A, et al.First evidences of the occurrence of polycyclic synthetic musk fragrances in surface water systems in Italy:Spatial and temporal trends in the Molgora River (Lombardia Region, Northern Italy)[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 416:137-141. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.11.027
[10] Dsikowitzky L, Schwarzbauer J, Littke R.Distribution of polycyclic musks in water and particulate matter of the Lippe River (Germany)[J].Organic Geochemistry, 2002, 33:1747-1758. doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(02)00115-8
[11] Reiner J L, Kannan K.Polycyclic musks in water, sediment, and fishes from the upper Hudson River, New York, USA[J].Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 2011, 214:335-342. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d664602f49fc2325c27cf0cd9ab1a73a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[12] Hu Z, Shi Y, Cai Y.Concentrations, distribution, and bioaccumulation of synthetic musks in the Haihe River of China[J].Chemosphere, 2011, 84:1630-1635. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.05.013
[13] Shek W M, Murphy M B, Lam J C W, et al.Polycyclic musks in green-lipped mussels (Perna viridis) from Hong Kong[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2008, 57:373-380. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2008.02.037
[14] Zhang X, Liang G, Zeng X, et al.Levels of synthetic musk fragrances in human milk from three cities in the Yangtze River Delta in eastern China[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23:983-990. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60506-2
[15] Zhang X, Jing Y, Ma L, et al.Occurrence and transport of synthetic musks in paired maternal blood, umbilical cord blood, and breast milk[J].International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 2015, 218:99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2014.08.005
[16] Yin J, Wang H, Zhang J, et al.The occurrence of syn-thetic musks in human breast milk in Sichuan, China[J].Chemosphere, 2012, 87:1018-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.11.068
[17] 佟玲, 潘萌, 杨志鹏, 等.搅拌棒萃取-气相色谱-质谱法分析地表水中合成麝香及紫外线吸收剂[J].质谱学报, 2019, 40(3):233-243. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZPXB201903004.htm
Tong L, Pan M, Yang Z P, et al.Determination of synthetic musks and UV filters in surface water by stir bar sorption extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2019, 40(3):233-243. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZPXB201903004.htm
[18] 喻月, 王玲, 赵全升, 等.气相色谱质谱联用测定长江三角洲农田土壤中的合成麝香[J].环境化学, 2015, 34(11):2046-2052. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HJHX201511010.htm
Yu Y, Wang L, Zhao Q S, et al.Determination of synthetic musks in farmland soil from Yangtze River Delta by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(11):2046-2052. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HJHX201511010.htm
[19] 罗庆, 孙丽娜.微波辅助萃取气相色谱质谱法测定土壤、底泥及植物样品中的多环麝香[J].分析试验室, 2011, 30(4):50-53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FXSY201104014.htm
Luo Q, Sun L N.Determination of polycyclic musks in soil, sediment and plants using microwave-assisted solvent extraction with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2011, 30(4):50-53. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FXSY201104014.htm
[20] 胡正君, 史亚利, 蔡亚岐.加速溶剂萃取气相色谱质谱法测定污泥、底泥及土壤样品中的合成麝香[J].分析化学, 2010, 38(6):885-888. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FXHX201006036.htm
Hu Z J, Shi Y L, Cai Y Q.Determination of synthetic musk fragrances in sewage sludge, sediment and soil using accelerated solvent extraction with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 38(6):885-888. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FXHX201006036.htm
[21] Wang M, Peng C, Chen W, et al.Ecological risks of polycyclic musk in soils irrigated with reclaimed municipal wastewater[J].Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2013, 97:242-247. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.07.032
[22] 丁立平, 郭菁, 陈志涛, 等.分散固相萃取气相色谱质谱联用法测定水产品中的痕量酮麝香[J].色谱, 2013, 31(5):485-489. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=45851023
Ding L P, Guo J, Chen Z T, et al.Determination of musk ketone in aquatic products by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry with dispersive solid phase extraction[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2013, 31(5):485-489. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=45851023
[23] 丁立平, 蔡春平, 林永辉, 等.多重吸附同步净化气相色谱质谱联用法测定水产品中痕量的二甲苯麝香和酮麝香[J].色谱, 2014, 32(3):309-313. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SPZZ201403017.htm
Ding L P, Cai C P, Lin Y H, et al.Determination of trace musk xylene and musk ketone in aquatic products by multiple adsorption synchronous purification-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Chromatography, 2014, 32(3):309-313. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SPZZ201403017.htm
[24] Vallecillos L, Pocurull E, Borrull F.Influence of pre-treatment process on matrix effect for the determination of musk fragrances in fish and mussel[J].Talanta, 2015, 134:690-698. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2014.12.010
[25] Vallecillos L, Pocurull E, Borrull F.A simple and automated method to determine macrocyclic musk fragrances in sewage sludge samples by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2013, 1314:38-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.09.033
[26] Wu S F, Ding W H.Fast determination of synthetic polycyclic musks in sewage sludge and sediments by microwave-assisted headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2010, 1217:2776-2781. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2010.02.067
[27] Llompart M, Garcıa-Jares C, Salgado C, et al.Determination of musk compounds in sewage treatment plant sludge samples by solid-phase microextraction[J].Journal of Chromatography A, 2003, 999:185-193. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(03)00449-7
[28] Aguirre J, Bizkarguenaga E, Iparraguirre A, et al.Development of stir-bar sorptive extraction thermal desorption gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the analysis of musks in vegetables and amended soils[J].Analytica Chimica Acta, 2014, 812:74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.12.036
[29] Vallecillos L, Pedrouzo M, Pocurull E, et al.Headspace stir bar sorptive extraction followed by thermal desorption and gas chromatography with mass spectrometry to determine musk fragrances in sludge samples without sample pretreatment[J].Journal of Separation Science, 2014, 37:1322-1329. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201400048
[30] 李贵梅, 陈东辉, 黄满红, 等.固相萃取-气质联用测定水环境中痕量多环麝香[J].分析试验室, 2011, 30(1):55-58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201101017.htm
Li G M, Chen D H, Huang M H, et al.Study on determination of polycyclic musks in water by GC-MS with solid-phase extraction[J].Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2011, 30(1):55-58. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY201101017.htm
[31] Vallecillos L, Borrull F, Eva P.Determination of musk fragrances in sewage sludge by pressurized liquid extration coupled to automated ionic liquid-based headspace single-drop microextraction followed by GC-MS/MS[J].Journal of Separation Science, 2012, 35:2735-2742. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201200326
[32] 吴春英, 白鹭, 陆文龙, 等.气相色谱串联质谱法同时快速检测环境水样中11种合成麝香[J].分析科学学报, 2016, 32(2):188-192. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FXKX201602008.htm
Wu C Y, Bai L, Lu W L, et al.Simutaneous and rapid determination of 11 synthetic musks in environmental water samples using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Analytical Science, 2016, 32(2):188-192. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-FXKX201602008.htm
[33] 佟玲, 杨佳佳, 阎妮, 等.加速溶剂提取/GC-MS对动物组织中有机氯农药和多氯联苯的同时测定[J].岩矿测试, 2014, 33(2):262-269. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/94f70f9e-8a7d-49c0-99ac-50ef9d45cb66
Tong L, Yang J J, Yan N, et al.Simultaneous analysis of organochlorinated pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls from animal tissue using gas chromatography mass spectrometry combined with accelerated solvent extraction[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(2):262-269. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/94f70f9e-8a7d-49c0-99ac-50ef9d45cb66
[34] Zhang X, Yao Y, Zeng X, et al.Synthetic musks in the aquatic environment and personal care products in Shanghai, China[J].Chemosphere, 2008, 72:1553-1558. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.04.039
[35] 车金水, 虞锐鹏, 王利平, 等.太湖流域人工合成麝香的分布调查研究[J].香料香精化妆品, 2010(6):12-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XLXJ201006004.htm
Che J S, Yu R P, Wang L P, et al.Investigation on content of distribution of the synthetic musks in Taihu Lake[J]. Flavour Fragrance Cosmetics, 2010(6):12-16. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XLXJ201006004.htm
-



 下载:
下载: