Spectral Characteristics and Electrical-Magnetic Properties of Gem-quality Synthetic Diamonds under High Temperature and Pressure
-
摘要:
为快速鉴定高温高压(HPHT)合成钻石,前人已开展了系统的发光特征和谱学特征研究,但对比性分析较少,且对电学性质和磁学性质关注不多。本文结合常规宝石学观察、高精度谱学测试以及导电性和磁性测试,对49粒无色、黄色样品进行了深入研究和对比分析。结果表明:①铁、钴、镍等金属元素的触媒残余是HPHT合成钻石的磁性来源,测试样品均能被磁强达到12000Gs的磁棒吸引。②无色HPHT合成钻石为Ⅱa+Ⅱb型钻石,硼元素的存在导致其具有良好的导电能力,且随着硼含量的增多,导电能力逐渐增强;黄色样品为Ⅰb+ⅠaA型钻石,约三分之一的孤氮转化为A集合体,揭示合成钻石在生长完成后经过了高温退火处理。③硼元素的普遍存在,以及氮元素主要以孤氮原子和A集合体的方式存在,导致了HPHT合成钻石的特征红外光谱;HPHT合成钻石中常含有氮、镍、硅等杂质元素引起的晶格缺陷,导致了特征的光致发光光谱。④无色HPHT合成钻石具有强蓝绿色荧光和磷光,黄色HPHT合成钻石具有绿色荧光,可见明显的立方体-八面体分区现象。本研究表明:谱学特征和发光特征仍然是筛查鉴定HPHT合成钻石的重要依据。现生长技术下合成的HPHT合成钻石在导电性和磁性两方面也与天然钻石存在明显差异,可以作为快速鉴定合成钻石的辅助性依据。
Abstract:BACKGROUND In order to quickly identify and screen high pressure and high temperature (HPHT) grown synthetic diamonds, a lot of research about their luminescent and spectral characteristics has been done. However, the comparative analysis is lacking, and less attention is paid to electrical and magnetic properties.
OBJECTIVES To summarize the spectral characteristics and investigate the electrical and magnetic properties of HPHT synthetic diamonds systematically.
METHODS Conventional gemological observation, high precision spectroscopy and electrical conductivity and magnetism testing were used for comparative analysis of 49 colorless and yellow samples.
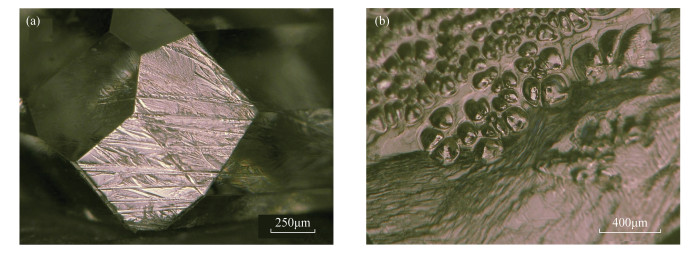
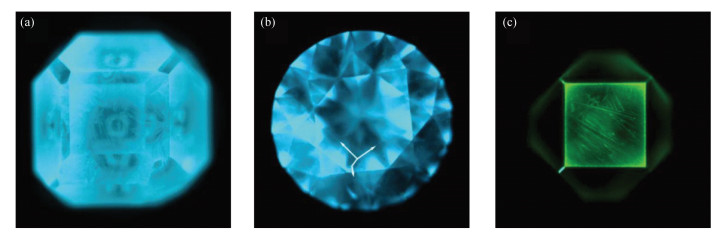
RESULTS The residual metal catalysts, including iron, cobalt, and nickel, caused the ferromagnetism of diamonds. All of the HPHT synthetic diamond samples could be attracted by the magnetic bar with magnetic intensity up to 12000Gs. The colorless samples were type Ⅱa+Ⅱb diamonds. The presence of boron led to its good conductivity, and the conductivity increased with increased boron content. The yellow samples were Ib+IaA type diamonds, and about one-third of the single nitrogen was converted into A aggregate. The synthetic diamond had undergone high temperature annealing treatment after growth. The ubiquitous presence of boron, and the presence of nitrogen mainly as single atoms and A aggregates led to the characteristic infrared spectra of HPHT synthetic diamonds. HPHT synthetic diamonds often contained crystal lattice defects caused by impurity elements such as nitrogen, nickel and silicon, which led to characteristic photoluminescence spectra. Colorless samples showed strong blue-green fluorescence and phosphorescence, whereas yellow samples had green fluorescence, with obvious cube-octahedron patterns.
CONCLUSIONS Spectral and luminescent characteristics are still an important basis for screening and identification of HPHT synthetic diamonds. HPHT synthetic diamonds under the current growth technology also have obvious differences from natural diamonds in both conductivity and magnetism, which can be used as an auxiliary basis for rapid identification.
-

-
表 1 HPHT合成钻石的氮含量
Table 1. Nitrogen content of HPHT synthetic diamond
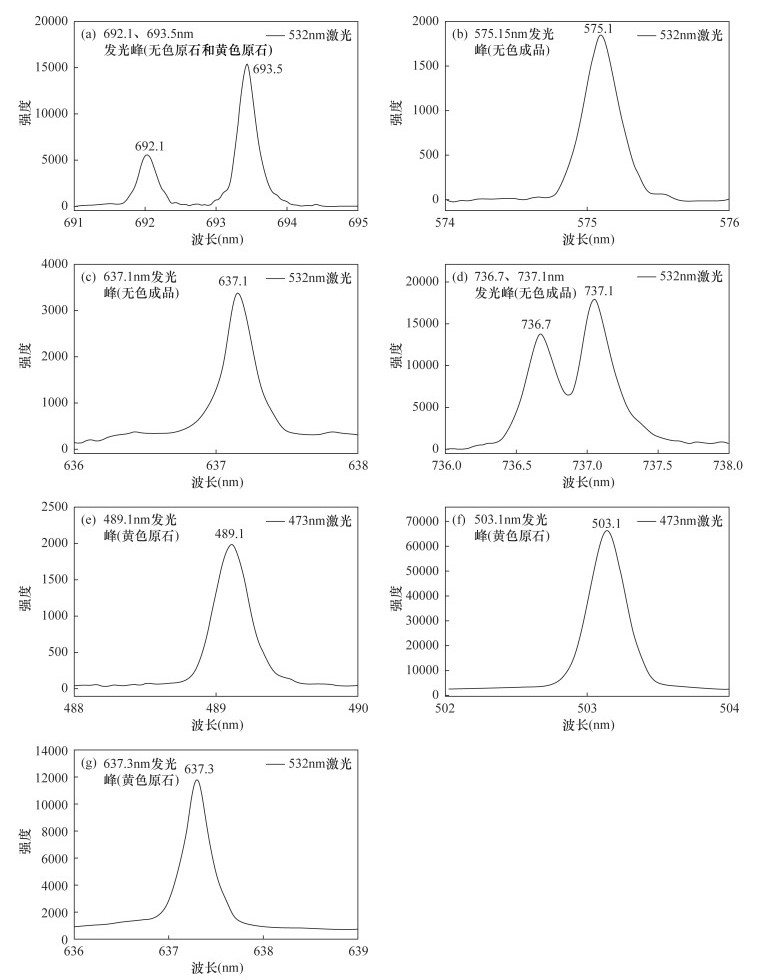
样品编号 孤氮含量(μg/g) 双原子氮含量(μg/g) Liliang-Y-1 208.36 46.91 Liliang-Y-2 198.65 45.41 Liliang-Y-3 251.83 57.81 Liliang-Y-4 153.70 35.15 Liliang-Y-5 201.21 46.50 Liliang-Y-6 186.78 44.03 Liliang-Y-7 240.14 54.28 Liliang-Y-8 143.89 33.74 Liliang-Y-9 195.60 44.47 Liliang-Y-10 166.50 38.92 表 2 HPHT合成钻石的B0含量和电阻值的关系
Table 2. Uncompensated boron content B0 and resistance of HPHT synthetic diamond
HPHT合成钻石编号 B0含量(μg/g) 电阻值(MΩ) Hold-7 0.088 3 Hold-1 0.085 5.4 Hold-3 0.073 5.6 Hold-9 0.054 7 Hold-5 0.043 35 Hold-2 红外光谱未检测到 25000 Hold-4 红外光谱未检测到 5400 Hold-6 红外光谱未检测到 4000 Hold-8 红外光谱未检测到 22500 Hold-10 红外光谱未检测到 11300 LLC-10 0.056 6.8 LLC-2 0.054 7.7 LLCC-3 0.043 13.8 LLC-1 0.036 19.9 LLC-12 0.033 22.2 LLC-4 红外光谱未检测到 4200 LLC-5 红外光谱未检测到 1600 LLC-6 红外光谱未检测到 22500 LLC-7 红外光谱未检测到 1500 LLC-8 红外光谱未检测到 7000 LLC-9 红外光谱未检测到 2900 LLC-11 红外光谱未检测到 5000 -
[1] Lu T J, Ke J, Lan Y, et al. Current status of Chinese synthetic diamonds[J]. The Journal of Gemmology, 2019, 36(8): 642-651.
[2] Ulrika F S, Johannsson D H, Moe K S, et al. Near-colorless HPHT synthetic diamonds from AOTC group[J]. Gems & Gemology, 2014, 50(1): 30-45.
[3] Ulrika F S, Johannsson D H, Katrusha A, et al. Large colorless HPHT synthetic diamonds from new diamond technology[J]. Gems & Gemology, 2015, 51(3): 260-279.
[4] 宋中华, 陆太进, 苏隽, 等. 无色-近无色高温高压合成钻石的谱图特征及其鉴别方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(5): 496-504. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.05.008
Song Z H, Lu T J, Su J, et al. The spectral characteristics and identification techniques for colorless and near-colorless HPHT synthetic diamonds[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(5): 496-504. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.05.008
[5] 张健, 陆太进, 柯捷, 等. 黄河旋风宝石级黄色与无色HPHT合成钻石的宝石学特征[J]. 中国宝石, 2018(5): 186-189.
Zhang J, Lu T J, Ke J, et al. Gemmological characteristics of yellow and colorless HPHT synthetic diamonds from Henan Huanghe Whirlwind Co, LTD[J]. China Gems, 2018(5): 186-189.
[6] 梁榕, 兰延, 张天阳, 等. 山东产大颗粒高温高压合成钻石的多种谱学方法研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2019, 39(6): 1840-1845. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201906035.htm
Liang R, Lan Y, Zhang T Y, et al. Multi-spectroscopy studies on large grained HPHT synthetic diamonds from Shandong, China[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(6): 1840-1845. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201906035.htm
[7] 宋中华, 陆太进, 柯捷, 等. 国产大颗粒宝石级无色高压高温合成钻石的鉴定特征[J]. 宝石和宝石学杂志, 2016, 18(3): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2016.03.001
Song Z H, Lu T J, Ke J, et al. Identification characteristics of large near-colorless HPHT synthetic diamonds from China[J]. Journal of Gems and Gemmology, 2016, 18(3): 1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-214X.2016.03.001
[8] 兰延, 陆太进, 张丛森, 等. 新型GV5000宽频诱导发光测试仪的研制及其应用于筛分无色小颗粒合成钻石和天然钻石[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(5): 505-512. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.05.009
Lan Y, Lu T J, Zhang C S, et al. Development of a new muti-spectral induced luminscence imaging system (GV5000) and its application in screening melee-sized near colorless synthetic diamonds and natural diamonds[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(5): 505-512. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.05.009
[9] Kirk F. Detecting HPHT synthetic diamond using handheld magnet[J]. Gem & Gemmology, 2012, 48(4): 262-272.
[10] Yelisseyev A P, Afanasiev V P, Ikorsky V N. Magnetic susceptibility of natural diamonds[J]. Doklady Earth Sciences, 2009, 425(2): 330-333.
[11] 吴旭旭, 陆太进, 杨池玉, 等. 高温高压合成钻石晶体表面微形貌观察及其成因探讨[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(4): 411-417. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201811150122
Wu X X, Lu T J, Yang C Y, et al. Observation of surface microstructure of HPHT synthetic diamond crystals and genesis discussion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(4): 411-417. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201811150122
[12] Ščajev P, Trinkler L, Berzina B, et al. Influence of boron on donor-acceptor pair recombination in type Ⅱa HPHT diamonds[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2013, 36: 35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2013.03.011
[13] Sally E M, James E, Christopher M B. Observations on HPHT-grown synthetic diamonds: A review[J]. Gems & Gemology, 2017, 53(3): 262-285.
[14] Shigley J E, Breeding C M. Optical defects in diamond: A quick reference chart[J]. Gems & Gemology, 2013, 49(2): 107-111.
[15] Kennedy L, Johnson P. Yellow synthetic diamond with nickel-related green fluorescence[J]. Gems & Gemology, 2016, 52(2): 196-197.
[16] Klepikov I V, Koliadin A V, Vasilev E A. Analysis of type Ⅱb synthetic diamond using FTIR spectrometry[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 286: 1757-8981.
[17] Babamoradi M, Asgari S, Ranjbar A, et al. Many-electron states of the N2 and N3 color centers in diamond: A first- principles and many-body study[J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2017, 505(16): 17-21.
[18] Salustro S, Ferrari A M, Gentile F S, et al. Characterization of the B-center defect in diamond through the vibrational spectrum: A quantum-mechanical approach (Article)[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2018, 122(2): 594-600. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.7b11551
[19] Zaitsev A M. Optical properties of diamond: A data handbook[M]. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer-Verlag, 2001: 48-49, 52, 57-63, 203, 218-225, 260-275.
[20] Kazuchits N M, Rusetsky M S, Kazuchits V N, et al. Aggregation of nitrogen in synthetic diamonds annealed at high temperature without stabilizing pressure[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2016, 64: 202-207. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2016.03.002
[21] 陈宁. 硫(氢)掺杂金刚石单晶的高压合成及金刚石色心研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018.
Chen N.High pressure synthesis of sulfur (hydrogen)-doped diamond single crystal and study on diamond color center[D].Changchun: Jilin University, 2018.
[22] 梁中翥, 梁静秋, 郑娜, 等. 掺氮金刚石的光学吸收与氮杂质含量的分析研究[J]. 物理学报, 2009, 58(11): 8039-8043. doi: 10.7498/aps.58.8039
Liang Z Z, Liang J Q, Zheng N, et al. Optical absorbance of diamond doped with nitrogen and the nitrogen concentration analysis[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2009, 58(11): 8039-8043. doi: 10.7498/aps.58.8039
[23] Hisao K, Minoru A, Shinobu Y. Synthesis of diamond with the highest nitrogen concentration[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 1999(8): 1441-1443.
[24] Zaitsev A M, Moe K S, Wang W. Optical centers and their depth distribution in electron irradiated CVD diamond[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2017, 71: 38-52. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2016.11.015
[25] Peng J, Balili R, Beaumariage J, et al. Multiple-photon excitation of nitrogen vacancy centers in diamond[J]. Physical Review B, 2018, 97(13): 2469.
[26] Ashfold M N R, Goss J P, Green B L, et al. Nitrogen in diamond[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2020, doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00518.
[27] Tang S, Song Z H, Lu T J, et al. Two natural type Ⅱa diamonds with strong phosphorescence and Ni-related defects[J]. Gems & Gemology, 2017, 53(4): 476-478.
[28] Lawson S C, Kanda H. An annealing study of nickel point defects in high-pressure synthetic diamond[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1993, 73: 3967-3973. doi: 10.1063/1.352861
[29] Eaton M S, Shigley J E. Observations on CVD-grown synthetic diamonds: A review[J]. Gems & Gemology, 2016, 52(3): 222-245.
[30] Fisher D, Sibley S J, Kelly C J. Brown colour in natural diamond and interaction between the brown related and other colour-inducing defects[J]. Journal of Physics. Condensed Matter: An Institute of Physics Journal, 2009, 21(36): 364213-364223. doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/21/36/364213
[31] Stuart A G, Ramon E, Rupert H, et al. Anatomy of a pressure-induced, ferromagnetic-to-paramagnetic transition in pyrrhotite: Implications for the formation pressure of diamonds[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2011, 116(B10): 148-227.
[32] Nestola F, Cerantola V, Milani S, et. al. Synchrotron mossbauer source technique for in situ measurement of iron-bearing inclusions in natural diamonds[J]. Lithos, 2016, 265: 328-333. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2016.06.016
-



 下载:
下载: