Application of LA-ICP-MS in the Analysis of Archaeological Glass and Source Discrimination
-
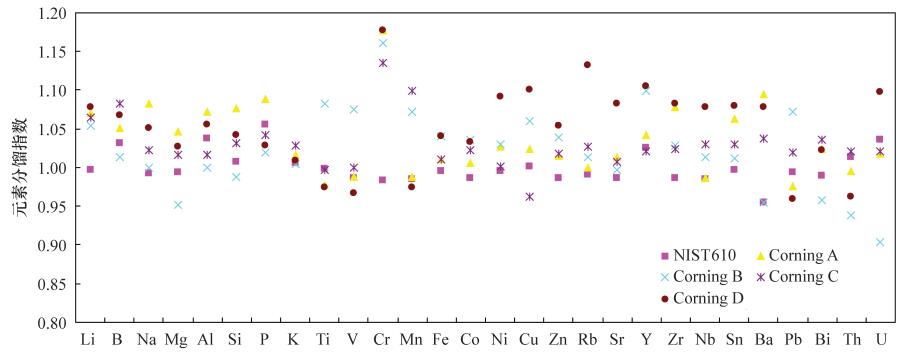
摘要: 古代玻璃及玻璃质材料的定量分析对于研究其制作年代及产地、原料的来源以及制作工艺有着重要的参考意义。与电子探针(EMPA)、能谱扫描-电子显微镜(EDX-SEM)等分析方法相比,LA-ICP-MS能够快速且准确地提供样品主次量及微量元素信息。本文对LA-ICP-MS古代玻璃元素定量分析中的影响因素进行研究认为:在193nm激光下玻璃标准NIST610和康宁玻璃标准之间基体差异造成的影响较小,而采用玻璃标准NIST610为外标结合基体归一化法的校正策略测定康宁标准结果表明,该策略能够准确反映不同类型古代玻璃材料中成分组成;实验中不同剥蚀模式的研究,有助于不同实验条件的建立,从而满足不同研究的需要。本次研究对出土样品进行了分析,为该制品的产源研究提供了数据支持。Abstract:
BACKGROUNDQuantitative analysis of ancient glass and vitreous materials has important significance for studying its production time, origin, source of raw materials and production process. Compared with traditional analysis methods (eg. EMPA, EDX-SEM), LA-ICP-MS can be used to analyze the primary, minor and trace elements in samples quickly and accurately. OBJECTIVESTo investigate the composition of archaeological glass and discriminate its sources. METHODSThe element concentration in ancient glass and vitreous materials were determined by LA-ICP-MS. The surface morphologies of pits in glasses were displayed by AFM. RESULTSThe matrix effect among NIST610 and Corning A-D was insignificant under 193nm laser system and this experimental condition. A quantification strategy based on NIST610 and normalization to 100% (w/w) was suitable for analyzing Corning A-D and ancient glass samples. Study on different ablation modes in the experiment is helpful for the establishment of different experimental conditions to meet the requirement of different studies. CONCLUSIONSUnearthed samples were analyzed, which provided data support for the source of the product. -

-
表 1 LA-ICP-MS仪器工作参数
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS operation conditions
电感耦合等离子体质谱
(ICP-MS)激光剥蚀系统 ICP-MS Element 2 激光类型 ArF准分子 分辨率 低分辨(300) 波长 193nm 射频功率 1300W 能量 70mJ 扫描模式 E-scan 频率 5Hz, 10Hz 冷却气(Ar)流速 16.05L/min 样品气(He)流速 0.65L/min 辅助气(Ar)流速 0.75L/min 束斑直径 线扫描:16μm 载气(Ar)流速 0.93L/min 点剥蚀:60μm 表 2 康宁标准A、B、C、D中主次量元素分析结果
Table 2. Analytical results of major and minor element compositions in Corning reference glass A, B, C and D
元素 A B C D 推荐值
(%)5次测定
平均值(%)RSD
(%)推荐值
(%)5次测定
平均值(%)RSD
(%)推荐值
(%)5次测定
平均值(%)RSD
(%)推荐值
(%)5次测定
平均值(%)RSD
(%)SiO2 66.56 68.28 0.6 61.55 62.48 0.1 34.87 34.39 1.0 55.24 55.90 0.7 Na2O 14.30 14.27 1.7 17.00 16.99 0.6 1.07 1.08 1.3 1.20 1.32 2.4 MgO 2.66 2.56 0.9 1.03 0.99 0.6 2.76 2.62 1.1 3.94 3.92 2.1 Al2O3 1.00 0.99 1.3 4.36 4.41 0.7 0.87 0.86 1.4 5.30 5.07 1.0 P2O5 0.130 0.113 2.0 0.82 0.79 1.1 0.14 0.10 1.5 3.93 3.83 1.7 K2O 2.87 3.09 1.0 1.00 1.07 0.4 2.84 2.97 1.9 11.30 12.0 1.4 CaO 5.03 5.13 1.5 8.56 8.75 1.1 5.07 5.26 1.2 14.80 15.12 1.5 MnO 1.00 1.11 2.5 0.25 0.26 1.4 0.0011 0.0016 2.1 0.55 0.58 0.6 Fe2O3 1.09 1.08 1.9 0.34 0.33 2.2 0.34 0.30 1.4 0.52 0.49 0.6 BaO 0.460 0.489 3.3 0.077 0.078 2.0 11.40 11.19 1.2 0.29 0.30 2.7 PbO 0.073 0.075 2.5 0.61 0.476 2.5 36.70 35.66 1.1 0.24 0.23 1.0 TiO2 0.79 0.79 1.1 0.089 0.102 1.5 0.79 0.76 1.4 0.38 0.36 1.6 CuO 1.17 1.23 2.0 2.66 2.74 2.2 1.13 1.19 2.7 0.38 0.37 2.4 CoO 0.170 0.173 1.6 0.046 0.044 0.1 0.180 0.173 3.0 0.023 0.018 2.6 B2O3 0.20 0.21 2.4 0.035 0.032 1.7 0.20 0.19 3.8 0.10 0.11 2.6 Li2O 0.01 0.011 5.7 0.003 0.0025 4.2 0.01 0.009 4.6 0.005 0.006 4.2 V2O5 0.006 0.007 1.5 0.034 0.034 1.4 0.006 0.007 1.2 0.015 0.017 1.5 Cr2O3 0.003 0.004 3.8 0.0096 0.01 3.0 0.0023 0.0035 3.5 0.003 0.004 4.9 NiO 0.02 0.025 2.4 0.100 0.097 1.6 0.020 0.020 0.6 0.050 0.050 2.3 ZnO 0.044 0.050 2.9 0.190 0.204 2.7 0.052 0.069 0.9 0.10 0.10 2.1 Rb2O 0.010 0.010 3.9 0.001 0.0011 1.5 0.010 0.009 0.4 0.005 0.0046 1.8 SrO 0.10 0.110 3.9 0.019 0.018 1.0 0.29 0.30 0.7 0.057 0.059 2.1 ZrO2 0.005 0.005 4.6 0.025 0.022 1.5 0.005 0.005 1.6 0.013 0.010 2.4 SnO2 0.19 0.180 3.7 0.024 0.024 1.8 0.190 0.181 0.4 0.10 0.09 3.1 Bi2O3 0.001 0.001 1.6 0.004 0.004 2.8 0.004 0.005 1.2 0.001 0.001 2.1 注:推荐值来自文献[11]。 表 3 康宁标准A、B、C、D中微量元素分析结果
Table 3. Analytical results of trace element compositions in Corning reference glass A, B, C and D
元素 A B C D 参考值
(μg/g)5次测定
平均值(μg/g)相对
偏差参考值
(μg/g)5次测定
平均值(μg/g)相对
偏差参考值
(μg/g)5次测定
平均值(μg/g)相对
偏差参考值
(μg/g)5次测定
平均值(μg/g)相对
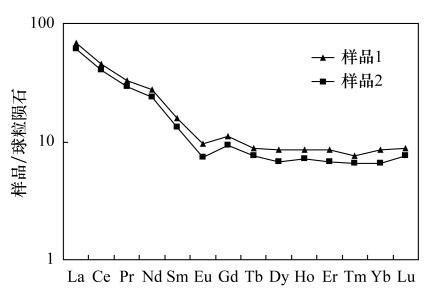
偏差Y 0.365 0.705 0.037 0.474 0.443 0.020 4.284 8.766 0.095 0.370 0.504 0.012 Cs 0.255 0.240 0.011 0.061 0.057 0.008 0.368 0.256 0.002 0.14 0.13 0.017 Ce 0.236 0.246 0.015 0.164 0.169 0.005 0.046 0.273 0.005 0.256 0.261 0.011 Hf 0.949 0.986 0.061 4.152 3.989 0.185 1.677 0.916 0.026 2.115 1.854 0.101 Ta 0.124 0.116 0.010 0.089 0.084 0.011 0.120 0.095 0.002 0.231 0.192 0.014 Th 0.288 0.273 0.009 0.805 0.776 0.020 0.204 0.183 0.001 0.648 0.555 0.017 U 0.182 0.159 0.010 0.226 0.223 0.010 0.079 0.070 0.004 0.160 0.155 0.014 注:参考值来自文献[23]。 表 4 古代玻璃材质样品LA-ICP-MS分析结果
Table 4. Analytical results of elements in archaeological glass by LA-ICP-MS
元素 含量
单位样品1
测定值样品2
测定值Na2O % 0.91 1.84 MgO % 0.94 0.87 Al2O3 % 3.01 3.08 SiO2 % 73 71 P2O5 % 0.45 0.50 K2O % 12.15 12.95 CaO % 4.90 5.54 TiO2 % 0.22 0.23 MnO % 0.11 0.15 Fe2O3 % 1.43 1.27 Pb μg/g 163 71 Li μg/g 39 61 B μg/g 17 28 V μg/g 508 284 Cr μg/g 49 32 Co μg/g 6.56 6.27 Ni μg/g 49 47 Cu μg/g 14981 18650 Zn μg/g 482 321 Rb μg/g 128 147 Y μg/g 17.6 13.1 Zr μg/g 80 69 Sr μg/g 310 251 Mo μg/g 8.51 4.91 Sn μg/g 265 97 Ba μg/g 1920 1073 La μg/g 15.9 14.4 Ce μg/g 28 25 Pr μg/g 3.09 2.79 Nd μg/g 12.7 11.2 Sm μg/g 2.40 2.00 Eu μg/g 0.55 0.43 Gd μg/g 2.25 1.93 Tb μg/g 0.33 0.29 Dy μg/g 2.15 1.71 Ho μg/g 0.49 0.40 Er μg/g 1.42 1.12 Tm μg/g 0.20 0.17 Yb μg/g 1.43 1.10 Lu μg/g 0.22 0.19 Hf μg/g 1.96 1.82 Th μg/g 3.61 3.25 U μg/g 8.43 3.95 -
[1] (英)科林·伦福儒, 保罗·巴恩著.陈淳, 译.考古学理论、方法与实践[M].上海: 上海古籍出版社, 2015.
Renfrew C, Bahn P G(Editor).Chen C (Translator).Archaeology: Theories, methods and practice[M].Shanghai: Shanghai Classics Publishing House, 2015.
[2] Rehren T, Freestone I C.Ancient glass:From kaleidoscope to crystal ball[J].Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015, 56:233-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2015.02.021
[3] Dussubieux L, Golitko M, Gratuze B.Recent advances in laser ablation ICP-MS for archaeology[M].Heidelberg:Springer, 2016:137-211.
[4] Humphry D.Some experiments and observations on the colours used in painting by the ancients[J].Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, 1815, 105(1):97-124. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/249347298_Some_Experiments_and_Observations_on_the_Colours_Used_in_Painting_by_the_Ancients
[5] Seligman C G, Beck H C.Far eastern glass:Some western origins[J].The Bulletin of the Museum of Far Eastern Antiquities, 1938(10):1-64. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/291191583_Far_Eastern_glass_some_Western_origins
[6] Gratuze B, Giovagnoli A, Barrandon J N, et al.Apport de la méthode ICP-MS couplée à l'ablation laser pour la caractérisation des archéomatériaux[J].Revue d'Archéométrie, 1993(17):89-104. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285847091_Apport_de_la_methode_ICP-MS_couplee_a_l'ablation_laser_pour_la_caracterisation_des_archeomateriaux
[7] Lin J, Liu Y, Yang Y, et al.Calibration and correction of LA-ICP-MS and LA-MC-ICP-MS analyses for element contents and isotopic ratios[J].Solid Earth Sciences, 2016, 1(1):5-27. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2451912X16300022
[8] 刘勇胜, 胡兆初, 李明, 等.LA-ICP-MS在地质样品元素分析中的应用[J].科学通报, 2013, 58(36):3753-3769. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB201336003.htm
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Li M, et al.Applications of LA-ICP-MS in the elemental analyses of geological samples[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(32):3863-3878. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KXTB201336003.htm
[9] Li Z, Hu Z C, Liu Y S, et al.Accurate determination of elements in silicate glass by nanosecond and femtosecond laser ablation ICP-MS at high spatial resolution[J].Chemical Geology, 2015, 400:11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.02.004
[10] Guillong M, Horn I, Günther D.A comparison of 266nm, 213nm and 193nm produced from a single solid state Nd:YAG laser for laser ablation ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2003, 18:1224-1230. doi: 10.1039/B305434A
[11] Wagner B, Nowak A, Bulska E, et al.Critical assessment of the elemental composition of Corning archeological reference glasses by LA-ICP-MS[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2012, 402:1667-1677. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5597-8
[12] 王辉, 汪方跃, 关炳庭, 等.激光能量密度对LA-ICP-MS分析数据质量的影响研究[J].岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6):609-619. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201903010029
Wang H, Wang F Y, Guan B T, et al.Effect of laser energy density on data quality during LA-ICP-MS measurement[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6):609-619. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201903010029
[13] 吴石头, 许春雪, Klaus S, 等.193nm ArF准分子激光系统对LA-ICP-MS分析中不同基体的剥蚀行为和剥蚀速率探究[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5):451-459. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201703290044
Wu S T, Xu C X, Klaus S, et al.Study on ablation behaviors and ablation rates of a 193nm ArF excimer laser system for selected substrates in LA-ICP-MS analysis[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5):451-459. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201703290044
[14] 吴石头, 王亚平, 许春雪.激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体质谱:双外标结合基体归一定量校准策略[J].岩矿测试, 2017, 45(7):965-972. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201707005.htm
Wu S T, Wang Y P, Xu C X.Laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer:A quantification strategy based on two reference materials and bulk normalization as 100%(wt)[J].Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 45(7):965-972. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXHX201707005.htm
[15] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al.In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICPMS without applying an internal standard[J].Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1-2):34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
[16] Luo Y, Gao S, Longerich H P, et al.The uncertainty budget of the multi-element analysis of glasses using LA-ICP-MS[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2007, 22:122-130. doi: 10.1039/B608010C
[17] Rehren T, Connolly P, Schibille N, et al. Changes in glass consumption in Pergamon (Turkey) from Hellenistic to Late Byzantine and Islamic times[J].Journal of Archaeological Science, 2015, 55:266-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2014.12.025
[18] Bertini M, Izmer A, Vanhaecke F, et al.Critical evaluation of quantitative methods for the multi-elemental analysis of ancient glasses using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2013, 28:77-91. doi: 10.1039/C2JA30036B
[19] Miliszkiewicz N, Walas S, Tobiasz A.Current approaches to calibration of LA-ICP-MS analysis[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2015, 30(2):327-338. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00325J
[20] 袁继海, 詹秀春, 孙冬阳, 等.激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱分析硅酸盐矿物基体效应的研究[J].分析化学, 2011, 39(10):1582-1588. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fxhx201110024
Yuan J H, Zhan X C, Sun D Y, et al.Investigation on matrix effects in silicate minerals by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 39(10):1582-1588. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fxhx201110024
[21] Jochum K P, Nohl U, Herwig K, et al.GeoReM:A new geochemical database for reference materials and isotopic standards[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2005, 29(3):333-338. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2005.tb00904.x
[22] 斯琴毕力格, 李青会, 干福熹.激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱/质谱法分析中国古代钾玻璃组分[J].分析化学, 2013, 41(9):1328-1333. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fxhx201309006
Siqin B L G, Li Q H, Gan F X.Analysis of ancient Chinese potash glass by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry/mass spectrometry[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 41(9):1328-1333. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fxhx201309006
[23] Vicenzi E P, Eggins S, Logan A, et al. Microbeam characterization of Corning archeological reference glasses:New additions to the Smithsonian microbeam standard collection[J]. Journal of Research of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2002, 107:719-727. doi: 10.6028/jres.107.058
[24] Shortland A, Rogers N, Eremin K.Trace element discri-minants between Egyptian and Mesopotamian Late Bronze Age glasses[J].Journal of Archaeological Science, 2007, 34:781-789. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2006.08.004
[25] Longerich H P, Jackson S E, Günther D.Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric transient signal data acquisition and analyte concentration calculation[J].Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 1996, 11:899-904. doi: 10.1039/JA9961100899
[26] Horn I, Guillong M, Günther D.Wavelength dependant ablation rates for metals and silicate glasses using homogenized laser beam profiles-Implications for LA-ICP-MS[J].Applied Surface Science, 2001, 182(1-2):91-102. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4332(01)00465-2
[27] Fryer B J, Jackson S E, Longerich H P.The design, operation and role of the laser-ablation microprobe coupled with an inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer (LAM-ICP-MS) in the Earth sciences[J].Canadian Mineralogist, 1995, 33:303-312. https://researchers.mq.edu.au/en/publications/the-design-operation-and-role-of-the-laser-ablation-microprobe-co/fingerprints/
[28] 赵令浩, 孙冬阳, 胡明月, 等.激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱小激光斑束线扫描定量分析技术[J].分析化学, 2018, 46(6):931-937. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fxhx201806018
Zhao L H, Sun D Y, Hu M Y, et al.Line scanning quantitative analysis by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with small laser beam[J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 46(6):931-937. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fxhx201806018
[29] Pollard A M, Heron C.Archaeological chemistry[M].Cambridge:The Royal Society of Chemistry, 1996:172.
[30] Evans D, Müller W.Automated extraction of a five-year LA-ICP-MS trace element data set of ten common glass and carbonate reference materials:Long-term data quality, optimisation and laser cell homogeneity[J].Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2018, 42(2):159-188. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12204
[31] 林怡娴, Rehren T.凉山州博物馆藏盐源征集费昂斯串珠的考察[J].四川文物, 2017(6):60-71. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=674203686
Lin Y X, Rehren T.A string of faience beads in the museum of Liangshan Yi autonomous prefecture[J].Sichuan Cultural Relics, 2017(6):60-71. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=674203686
[32] Tite M, Shortland A J.Production technology of faience and related early vitreous materials[M].Oxford School of Archaeology, 2008:38-42.
[33] Turner W S.Studies in ancient glass and glassmaking processes.Part Ⅴ.Raw materials and melting processes[J].Journal of Society of Glass Technology, 1956(40):277-300. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285808566_Studies_in_ancient_glasses_and_glass_making_processes_Part_III_The_chronology_of_glass_making_constituents
[34] 宁夏考古所, 彭阳县文物管理所.王大户与九龙山——北方青铜文化墓地[M].北京:文物出版社, 2016:703-736.
Ningxia Institute of Archaeology, Pengyang County Heritage Management Institute.Excavation report on Wangdahu and Jiulongshan[M].Beijing:Cultural Relics Press, 2016:703-736.
[35] Mullins P R.The archaeology of consumption[J]. Annual Review of Anthropology, 2011(40):133-144.
-



 下载:
下载: