Pollution Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the River Sediments in Anning, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
云南安宁是长江经济带上游重要的工业、矿业城市,是滇中新区经济发展和生态文明建设的支点。对安宁地区地球化学水系沉积物、水文地质等方面的调查尚停留在二十世纪七八十年代,而近年来人类生产生活对生态环境造成的影响也不明确。为揭示安宁地区水系沉积物污染状况、空间分布特征与潜在生态风险,本文以2019年采集的云南安宁地区水系表层沉积物为研究对象,利用X射线荧光光谱、电感耦合等离子体质谱、气相色谱-质谱等方法系统分析其中常量元素、微量元素和16种优先控制的多环芳烃(PAHs)含量和空间分布特征,采用地累积指数法、Hankanson潜在生态风险指数法对8种典型重金属(As、Cd、Cr、Cu、Ni、Zn、Pb、Hg)以及采用质量基准法对PAHs进行了生态风险评价。结果表明:①水系沉积物中的重金属含量不同程度地高于中国全国和南方水系沉积物背景值,且变异程度较高、空间分布不均,Cd、Hg和As的潜在生态风险处于中等到严重等级;②∑PAHs平均含量为20856.0ng/g,较长江流域均值显著偏高,16种单体检出率接近100%,但PAHs总体生态风险较低,石化工业和石油燃料的燃烧是PAHs主要来源;③污染物重点潜在生态风险主要集中于普渡河流域螳螂川沿岸钢铁、化工等厂矿周边。本研究结果为加强流域工业点源污染监管、减少和控制工业污水排放提供了科学依据。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Anning is an important industrial and mining city in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. It is a fulcrum for economic development and ecological civilization construction in the Central Yunnan New Area. The investigation of geochemical water system sediments and hydrogeology in the Anning area was last performed in the 1970s and the 1980s. In recent years, the impact of human production and life on the ecological environment remains unclear.
OBJECTIVES Surface sediment samples from the Anning area were investigated to reveal their pollution status, spatial distribution characteristics, and potential ecological risks of river sediments.
METHODS X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy, inductively coupled plasma optical mass spectrometry, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, and other methods were used to systematically analyze the contents and distribution characteristics of major elements, trace elements, and 16 priority-controlled PAHs. Geoaccumulation index, Hankanson ecological risk index, and sediment quality criteria were used to assess the ecological risk of eight typical heavy metals (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Zn, Pb, and Hg) and PAHs.
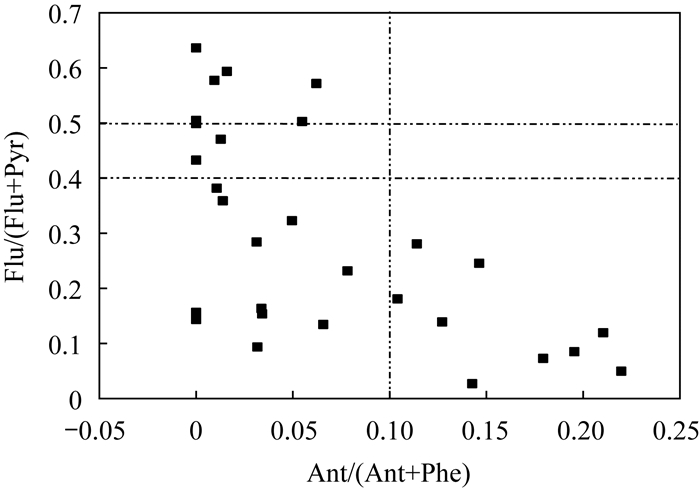
RESULTS Results showed that the heavy metal content in the river sediments from the Anning area was higher than the background values of the national and southern rivers. The spatial distributions of the heavy metals were highly variable and uneven. Additionally, Cd, Hg, and Ad showed medium to severe potential ecological risks. The average content of ∑PAHs was 20856ng/g, and the detection rate of the 16 monomers was ~100%. The overall ecological risk of PAHs was low, and their main sources were petrochemical industry and combustion of petroleum fuels. The major risks of pollutants in the river sediments of the Anning area were mainly concentrated in the vicinity of steel plants and chemical factories in the Tanglangchuan River.
CONCLUSIONS This research provides a scientific basis for local governments to strengthen key industrial point source pollution control, and reduce and control industrial sewage discharge.
-

-
表 1 安宁地区水系沉积物主量元素、碳、硫等含量统计
Table 1. Statistics of major elements, carbon, sulfur and other elements contents in the surface sediments from Anning area
检测项目 SiO2
(%)Al2O3
(%)CaO (%) TFe2O3
(%)K2O
(%)MgO
(%)MnO
(%)Na2O
(%)P2O5
(%)TiO2
(%)S
(%)Cl
(μg/g)C
(%)水溶性氟
(μg/g)Th
(μg/g)U
(μg/g)Se
(μg/g)平均值 57.08 11.14 5.56 8.94 1.70 1.47 0.23 0.12 1.38 0.98 0.24 91.13 3.51 10.38 11.75 4.78 1.10 中位数 60.28 10.87 3.58 7.25 1.61 1.23 0.15 0.07 0.71 0.80 0.09 60.00 2.83 6.55 10.85 4.26 0.46 最大值 79.81 28.67 28.28 53.69 3.34 4.00 0.86 0.43 11.02 3.97 1.73 326.00 11.20 62.60 29.50 11.80 6.02 最小值 21.66 3.50 0.14 3.94 0.63 0.22 0.02 0.01 0.13 0.30 0.02 33.00 0.27 3.10 5.70 1.36 0.12 变异系数 0.23 0.46 1.15 0.99 0.45 0.51 0.91 0.92 1.49 0.71 1.79 0.82 0.83 1.13 0.48 0.53 1.28 页岩[25] 50.93 19.75 2.21 4.76 2.75 2.22 0.086 0.89 0.176 0.751 0.3 160 - 500 11 3.2 0.6 中国全国水系沉积物元素丰度值[27] 65.40 12.60 2.00 4.30 2.40 1.30 0.08 1.40 0.13 0.64 - - - 475.00 (总氟) 11.40 2.40 - 中国南方水系沉积物元素丰度值[28] 64.90 13.80 1.10 4.80 2.30 1.10 0.10 0.60 0.14 0.77 0.03 71.00 1.69 527 (总氟) 13.30 3.50 0.33 注:"-"表示相关文献没有提供数据。 表 2 安宁地区水系沉积物重金属含量统计
Table 2. Statistics of heavy metal contents in the surface sediments from Anning area
检测项目 Ni
(μg/g)Cu
(μg/g)Zn
(μg/g)As
(μg/g)Cd
(μg/g)Hg
(μg/g)Pb
(μg/g)Cr
(μg/g)平均值 48.81 69.97 495.83 27.46 1.14 0.47 126.36 94.72 中位数 46.60 47.30 225.50 20.70 0.54 0.17 107.00 87.85 最大值 97.00 298.00 5068.00 113.00 7.31 3.61 566.00 186.00 最小值 17.80 22.00 69.70 6.28 0.07 0.02 24.30 55.70 变异系数 0.37 0.92 1.88 0.78 1.51 1.60 0.83 0.32 页岩[25] 95.00 57.00 80.00 6.60 0.30 0.04 20.00 100.00 中国全国水系沉积物元素丰度[27] 23.00 20.00 67.00 9.00 0.13 0.03 23.00 54.00 中国南方水系沉积物元素丰度[28] 29.00 25.00 81.00 13.10 0.23 0.075 32.30 67.00 滇池外海丰水期0~5m[36] 39.90 72.76 176.88 31.30 1.00 0.18 66.79 77.78 滇池外海枯水期0~5m[36] 48.76 127.87 553.57 44.79 12.32 0.83 115.50 89.51 滇池宝象河流域丰水期[37] 56.75 129.90 164.80 - - - 51.88 108.28 滇池宝象河流域枯水期[37] 52.68 147.93 272.08 - - - 65.25 94.05 南盘江流域云南段[38] - 80.00 239.00 146.20 4.52 - 101.00 150.00 长江上游宜宾至泸州段[39] 34.52 42.92 98.93 6.71 0.76 - 35.41 78.77 三峡库区[41] 42.80 58.80 148.50 12.30 0.90 0.12 53.10 103.20 沱江流域石亭江[2] 27.00 27.34 121.00 6.72 0.99 0.19 32.03 76.53 沱江流域绵远河[2] 23.00 24.98 97.00 10.14 0.79 0.09 29.37 55.36 沱江流域沱江[2] 43.00 48.95 261.00 11.84 1.48 0.19 47.16 100.07 岷江流域金马河[40] - 35.23 108.78 8.87 0.33 0.04 37.64 84.69 岷江流域文锦江/西江[40] - 18.69 127.64 5.79 0.71 0.04 98.69 67.89 岷江流域斜江河[40] - 27.58 137.15 6.74 0.51 0.07 37.03 76.06 岷江流域南河[40] - 47.43 141.00 6.78 0.59 0.14 34.93 250.30 岷江流域青衣江[40] - 29.05 199.00 7.05 0.83 0.09 64.88 86.73 岷江流域大渡河[40] - 34.68 710.71 18.12 4.58 0.24 - 136.66 注:"-"表示相关文献没有提供数据。 表 3 安宁地区水系沉积物多环芳烃含量统计
Table 3. Statistics of ∑PAHs concentrations in the surface sediments from Anning area
多环芳烃化合物 简称 多环芳烃含量(ng/g) 变异系数 检出限
(ng/g)控制加标样回收率
(%)平均值 中位数 最大值 最小值 萘 Nap 164.4 37.5 2555.2 0.0 2.9 5.00 71.3 苊烯 Acy 278.0 4.5 7595.2 0.0 5.0 2.00 75.1 苊 Ace 106.4 9.2 2406.7 0.0 4.1 2.00 80.0 芴 Flu 213.4 31.3 4508.4 3.7 3.8 2.00 79.3 菲 Phe 1693.3 166.3 40645.8 40.3 4.4 5.00 70.8 蒽 Ant 420.5 7.6 11444.1 0.0 5.0 2.00 75.5 荧蒽 Fla 4081.3 134.2 112033.4 16.6 5.0 5.00 89.8 芘 Pyr 3124.8 77.3 86287.4 6.1 5.0 2.00 94.8 苯并[a]蒽 BaA 1961.2 34.5 54526.6 1.9 5.1 2.00 95.5 屈 Chr 1330.5 24.7 36478.7 2.7 5.0 2.00 89.7 苯并[b]荧蒽 BbF 2731.5 76.0 73829.7 3.2 4.9 2.00 108 苯并[k]荧蒽 BkF 1068.5 38.3 28572.2 0.0 4.9 2.00 114 苯并[a]芘 BaP 1273.8 30.3 34963.0 0.0 5.0 2.00 96.4 茚并[1, 2, 3-cd]芘 InP 1125.1 43.2 30325.9 0.0 4.9 2.00 99.7 二苯并[a, h]蒽 DahA 265.7 11.8 6921.3 0.0 4.7 2.00 104 苯并[g, h, i]苝 BghiP 1017.7 39.8 27088.1 0.0 4.8 2.00 98.7 2~3环 / 2875.9 256.5 69155.4 43.9 4.4 - - 4环 / 10497.8 270.7 289326.1 27.4 5.0 - - 5~6环 / 7482.3 239.3 201700.2 3.2 4.9 - - 16种多环芳烃合计 ∑PAHs 20856.0 850.2 560181.7 84.9 4.9 - - 注:"-"表示方法未涉及相关数据。 表 4 安宁地区水系沉积物地累积指数生态风险评价结果
Table 4. Heavy metal ecological risk assessment results based on geoaccumulation index in the surface sediments from Anning area
重金属元素 参数 无污染 轻度污染 偏中度污染 中度污染 偏重度污染 重度污染 严重污染 Cr 样品个数 21 0 4 1 0 0 3 总样品数占比(%) 72.41 0 13.79 3.45 0 0 10.34 Ni 样品个数 14 1 5 2 2 1 4 总样品数占比(%) 48.28 3.45 17.24 6.90 6.90 3.45 13.79 Cu 样品个数 7 7 4 4 3 1 3 总样品数占比(%) 24.14 24.14 13.79 13.79 10.34 3.45 10.34 Zn 样品个数 5 14 6 3 0 0 1 总样品数占比(%) 17.24 48.28 20.69 10.34 0 0 3.45 As 样品个数 12 7 0 0 3 1 6 总样品数占比(%) 41.38 24.14 0 0 10.34 3.45 20.69 Cd 样品个数 10 12 5 0 0 0 2 总样品数占比(%) 34.48 41.38 17.24 0 0 0 6.90 Hg 样品个数 13 12 2 0 1 0 1 总样品数占比(%) 44.83 41.38 6.90 0 3.45 0 3.45 Pb 样品个数 5 17 4 1 0 0 2 总样品数占比(%) 17.24 58.62 13.79 3.45 0 0 6.90 表 5 安宁地区水系沉积物多环芳烃生态风险评价结果
Table 5. Evaluation results of the ecological risk of ∑PAHs based on SQGs in the surface sediments from Anning area
多环芳烃化合物 简称 质量基准法阈值 点位数 ERL ERM <ERL ERL≤PAHs ≤ERM >ERM 萘 Nap 160 2100 23 5 1 苊烯 Acy 44 640 24 4 1 苊 Ace 16 500 16 12 1 芴 Flu 19 540 8 20 1 菲 Phe 240 1500 17 10 2 蒽 Ant 85.3 1100 24 4 1 荧蒽 Fla 600 5100 25 3 1 芘 Pyr 665 2600 25 3 1 苯并[a]蒽 BaA 261 1600 25 2 2 屈 Chr 384 2800 26 2 1 苯并[b]荧蒽 BbF 320 1880 22 6 1 苯并[k]荧蒽 BkF 280 1620 25 3 1 苯并[a]芘 BaP 430 1600 26 2 1 茚并[1, 2, 3-cd]芘 InP - - - - - 二苯并[a, h]蒽 DahA 430 1600 28 0 1 苯并[g, h, i]苝 BghiP 63.4 260 18 7 4 2~3环 / 564.3 6380 21 7 1 4环 / 1910 12100 29 0 0 5~6环 / 1523.4 6960 24 3 2 16种多环芳烃合计 ∑PAHs 3997.7 25440 24 4 1 注:"-"表示相关方法中未提供数据。 -
[1] Forstner U. Metal pollution in the aquatic environment[M]. Berlin: Spring Verleg, 1978.
[2] 李佳宣, 施泽明, 郑林, 等. 沱江流域水系沉积物重金属的潜在生态风险评价[J]. 地球与环境, 2010, 38(4): 481-487. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201004017.htm
Li J X, Shi Z M, Zheng L, et al. Evaluation on potential ecological risk of heavy metals pollution in sediments from Tuojiang Drainage[J]. Earth and Environment, 2010, 38(4): 481-487. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201004017.htm
[3] 肖冬冬, 史正涛, 苏斌, 等. 滇池宝象河表层沉积物重金属含量空间分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(12): 2719-2728. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017041102
Xiao D D, Shi Z T, Su B, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediment of Baoxiang River, Dianchi Lake[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(12): 2719-2728. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017041102
[4] Zoumis T, Schmidt A, Grigorova L, et al. Contaminants in sediments: Remobilization and demobilization[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2001, 266: 195-202. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00740-3
[5] Liu Y, Huang H, Sun T, et al. Comprehensive risk assessment and source apportionment of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediment of the Yangtze River Anqing Section, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77: 493. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7621-1
[6] Enuneku A, Omoruyi O, Tongo I, et al. Evaluating the potential health risks of heavy metal pollution in sediment and selected benthic fauna of Benin River, southern Nigeria[J]. Applied Water Science, 2018, 8(8): 1-13. doi: 10.1007/s13201-018-0873-9
[7] 张杰, 郭西亚, 曾野, 等. 太湖流域河流沉积物重金属分布及污染评估[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(5): 2202-2210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.05.049
Zhang J, Guo X Y, Zeng Y, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in river sediments from Lake Taihu Basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(5): 2202-2210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.05.049
[8] Abuduwaili J, Zhang Z Y, Jiang F Q. Assessment of the distribution, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the dry surface sediment of Aibi Lake in northwest China[J]. PLOS One, 2015, 10(3): 1-16. http://europepmc.org/articles/pmc4363597
[9] 田建民, 徐争启, 张富贵, 等. 四川雷波磷矿区沉积物重金属污染特征研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(11): 59-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS202011008.htm
Tian J M, Xu Z Q, Zhang F G, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in sediments of Leibo phosphate mine area, Sichuan Province[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(11): 59-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS202011008.htm
[10] Hong W J, Jia H L, Li Y F, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and alkylated PAHs in the coastal seawater, surface sediment and oyster from Dalian, northeast China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2016, 128: 11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.02.003
[11] Ke X, Gui S F, Huang H, et al. Ecological risk assess-ment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 175: 473-481. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.029
[12] 马晗宇, 申月芳, 应耀明, 等. 独流减河湿地沉积物中多环芳烃生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(8): 2253-2262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202008024.htm
Ma H Y, Shen Y F, Ying Y M, et al. Ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments of Duliujian River Wetland[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(8): 2253-2262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202008024.htm
[13] 尚文郁, 谢曼曼, 王淑贤, 等. 应用近红外光谱法研究泻湖湿地沉积物重金属活动态特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(4): 597-608. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202001010001
Shang W Y, Xie M M, Wang S X, et al. Detection of heavy metals mobile fraction in Lagoonal wetland sediment using near-infrared spectroscopy and ecological risk assessment[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(4): 597-608. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202001010001
[14] Ayari J, Barbieri M, Agan Y, et al. Trace element contam-ination in the mine-affected stream sediments of Oued Rarai in north-western Tunisia: A river basin scale assessment[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2021, doi: 10.1007/S10653-021-00887-1.
[15] Yuan Z, He N, Wu X, et al. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban stream sediments of Suzhou Industrial Park, an emerging eco-industrial park in China: Occurrence, sources and potential risk[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 214: 112095. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112095
[16] 张塞, 于扬, 王登红, 等. 赣南离子吸附型稀土矿区土壤重金属形态分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(5): 726-738. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911050152
Zhang S, Yu Y, Wang D H, et al. Forms distribution of heavy metals and their ecological risk evalution in soils of ion adsorption type in the rare earth mining area of southern Jiangxi, China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(5): 726-738. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201911050152
[17] 沈小明, 吕爱娟, 沈加林, 等. 长江口启东-崇明岛航道沉积物中多环芳烃分布来源及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2014, 33(3): 379-385. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/9865b25e-a1b9-47c1-9abd-9aec581dfaa4
Shen X M, Lv A J, Shen J L, et al. Distribution characteristics, sources and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in waterway sediments from Qidong and Chongming Island of Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2014, 33(3): 379-385. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/9865b25e-a1b9-47c1-9abd-9aec581dfaa4
[18] Müller G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River[J]. GeoJournal, 1969, 2: 108-118. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/303060644_Index_of_geoaccumulation_in_sediments_of_the_Rhine_River
[19] Zhao H, Zhao J, Yin C, et al. Index models to evaluate the potential metal pollution contribution from washoff of road-deposited sediment[J]. Water Research, 2014, 50: 71-79. doi: 10.1002/2013WR013939
[20] Hankanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control-A sediment ecological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[21] Ingersoll C G, Macdonald D, Wang N, et al. Predictions of sediment toxicity using consensus-based freshwater sediment quality guidelines[J]. Achieves of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2001, 41: 8-21. doi: 10.1007/s002440010216
[22] Field L J, MacDonald D D, Norton S B, et al. Evaluating sediment chemistry and toxicity data using logistic regression modeling[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 1999, 18(6): 1311-1322. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620180634
[23] Field L J, MacDonald D D, Norton S B, et al. Predicting amphipod toxicity from sediment chemistry using logistic regression models[J]. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 2002, 21(9): 1993-2005. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620210929
[24] Forstner U, Wittmann G T W著. 王忠玉, 姚重华译. 水环境的重金属污染[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1987.
Forstner U, Wittmann G T W(Editors). Wang Z Y, Yao Z H(Translators). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1987.
[25] 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987.
Chi Q H, Yan M C. Handbook of applied geochemical element abundance data[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987.
[26] 黎彤. 中国陆壳及其沉积层和上陆壳的化学元素丰度[J]. 地球化学, 1994, 23(2): 140-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX402.004.htm
Li T. Element abundances of China's continental crust and its sedimentary layer and upper continental crust[J]. Geochimica, 1994, 23(2): 140-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX402.004.htm
[27] 史长义, 梁萌, 冯斌. 中国水系沉积物39种元素系列背景值[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(2): 235-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201602005.htm
Shi C Y, Liang M, Feng B. Average background values of 39 chemical elements in stream sediments of China[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(2): 235-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201602005.htm
[28] 程志中, 谢学锦, 潘含江, 等. 中国南方地区水系沉积物中元素丰度[J]. 地学前缘, 2011, 18(5): 289-295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201105026.htm
Cheng Z Z, Xie X J, Pan H J, et al. Abundance of elements in stream sediment in South China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2011, 18(5): 289-295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201105026.htm
[29] 宁增平, 蓝小龙, 黄正玉, 等. 贺江水系沉积物重金属空间分布特征、来源及潜在生态风险[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(8): 3036-3047. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.08.028
Ning Z P, Lan X L, Huang Z Y, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics, sources and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of Hejiang River[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(8): 3036-3047. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.08.028
[30] Long E R, Macdonald D D, Smith S L, et al. Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments[J]. Environmental Management, 1995, 19(1): 81-97. doi: 10.1007/BF02472006
[31] 杜耘. 保护长江生态环境, 统筹流域绿色发展[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2016, 25(2): 171-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201602002.htm
Du Y. Protecting the eco-environment, and striving for the green development in the Yangtze River Basin[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2016, 25(2): 171-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201602002.htm
[32] 李亚东. 昆明幅G-48-25 1/20万地球化学图说明书: 水系沉积物测量[D]. 昆明: 云南省地质矿产勘查开发局, 1989.
Li Y D. Kunming sheet G-48-25 1: 200000 geochemical map manual: Water system sediment survey[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development, 1989.
[33] 曹其林. 昆明幅G-48-25 1/20万区域水文地质普查报告[D]. 昆明: 云南省地质局水文工程地质公司, 1977.
Cao Q L. Kunming sheet G-48-25 1: 200000 regional hydrogeological survey report[D]. Kunming: Hydrological Engineering Geology Company of Yunnan Geology Bureau, 1977.
[34] 张丽, 段云龙, 字润祥, 等. 螳螂川河流磷、氟污染与防治对策分析研究[J]. 环境科学导刊, 2015, 34(6): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNHK201506010.htm
Zhang L, Duan Y L, Zi R X, et al. Study on phosphorus and fluorine pollution and control in Tanglangchuan River[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 2015, 34(6): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNHK201506010.htm
[35] Wilding L P. Spatial variability: Its documentation, accommodation and implication to soil surveys[M]//Wageningen. Soil spatial variability. 1985.
[36] 邵晓华. 云南滇池底泥重金属元素分布规律研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2003.
Shao X H. Study on the distribution of heavy metal elements in sediment of Dianchi Lake, Yunnan[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2003.
[37] 肖冬冬. 滇池宝象河表层沉积物重金属特征及潜在生态风险评价[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2018.
Xiao D D. Characteristics and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Baoxiang River, Dianchi[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University, 2018.
[38] 熊燕, 宁增平, 刘意章, 等. 南盘江流域(云南段)水系沉积物中重金属含量分布特征及其污染状况评价[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(2): 171-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201702008.htm
Xiong Y, Ning Z P, Liu Y Z, et al. Distribution and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in sediments in the Nanpan River Basin (Yunnan Section)[J]. Earth and Environment, 2017, 45(2): 171-178. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201702008.htm
[39] 王丹. 长江上游(宜宾至泸州段)毒害污染物分布特征及风险评价——以重金属和多环芳烃为例[D]. 邯郸: 河北工程大学, 2016.
Wang D. Pollution characteristics and risk of persistent toxic substances from Yangtze River (Yibin to Luzhou)-A case study for heavy metal and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[D]. Handan: Hebei University of Engineering, 2016.
[40] 孙洁. 岷江中游水系沉积物中重金属的环境地球化学评价[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2010.
Sun J. Environmental geochemistry evolution of heavy metal elements in sediments from middle reaches of Minjiang River[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2010.
[41] 郭威. 三峡库区低水运行期表层沉积物重金属污染特征研究[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2016.
Guo W. Study on heavy metals pollution of sediments in the Three Gorges Reservoir during its operating period with low water level[D]. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2016.
[42] 李利荣, 王艳丽, 高璟赟, 等. 中国表层水体沉积物中多环芳烃源解析及评价[J]. 中国环境监测, 2013, 29(6): 92-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB201306018.htm
Li L R, Wang Y L, Gao J Y, et al. Source and risk assessment of PAHs in surface sediments from rivers and lakes of China[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2013, 29(6): 92-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB201306018.htm
[43] 詹咏, 韦婷婷, 叶汇彬, 等. 三亚河沉积物PAHS和PCBs的分布、来源及风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202008267.
Zhan Y, Wei T T, Ye H B, et al. Distribution, sources, and ecological risk evolution of the PAHs and PCBs in the sediments from Sanya River[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202008267.
[44] 王喆, 卢丽, 裴建国. 城郊型地下河表层沉积物多环芳烃来源分析与生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(10): 2733-2741. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202010011.htm
Wang Z, Lu L, Pei J G. Source analysis and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from suburban type underground river[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(10): 2733-2741. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX202010011.htm
[45] 高秋生, 焦立新, 杨柳, 等. 白洋淀典型持久性有机污染物污染特征与风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(4): 1616-1627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201804021.htm
Gao Q S, Jiao L X, Yang L, et al. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of typical persistent organic pollutants in Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(4): 1616-1627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201804021.htm
-




 下载:
下载: