Chemical Speciation and Environmental Risk of Cd in Soil Stabilized with Alkali-modified Attapulgite
-
摘要:
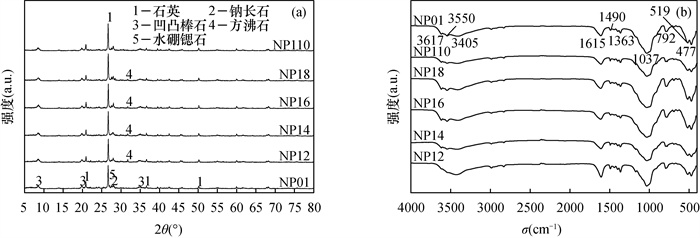
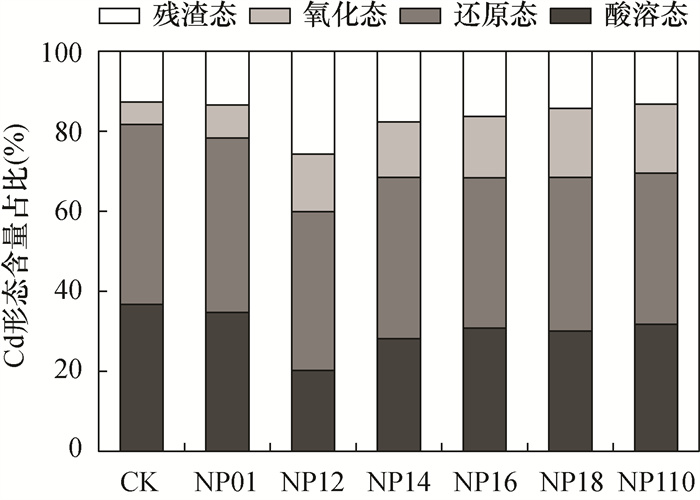
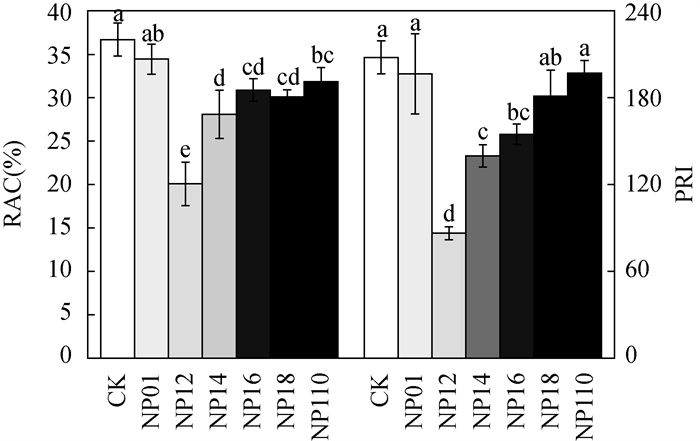
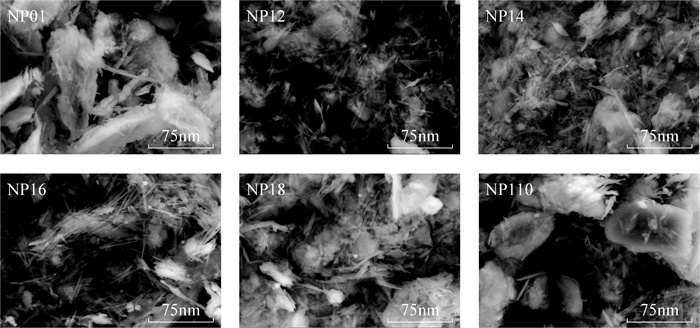
凹凸棒石进行碱改性后性能的提高,为其钝化修复重金属污染土壤提供重要基础。本文采用不同比例的氢氧化钠对凹凸棒石进行改性,利用扫描电镜(SEM)、X射线衍射(XRD)和傅里叶变换红外光谱法(FTIR)分析改性前后凹凸棒石理化特性的变化,并在人工配制的重金属Cd污染土壤上进行钝化实验,研究氢氧化钠改性凹凸棒石对污染土壤中Cd的化学形态变化以及环境风险的影响。结果表明:与对照相比,添加氢氧化钠与凹凸棒石质量比为1:2的改性材料,土壤pH值显著升高0.85个单位。酸溶态Cd含量显著降低46.25%,残渣态Cd含量显著增加1.99倍;土壤中Cd的风险评价指数和潜在风险指数分别由36.70%和207.90降至20.08%和86.40,有效降低了土壤中Cd的迁移能力和环境风险。SEM、XRD和FTIR分析表明,凹凸棒石经过改性后表面粗糙程度增加,Si-O-Si键等化学键打开,用于吸附重金属的活性位点增加。碱改性凹凸棒石主要通过吸附作用,硅羟基和氢氧根与Cd2+反应生成沉淀来固定土壤Cd,从而达到钝化修复Cd污染土壤的效果。因此碱改性凹凸棒石可对土壤中Cd进行有效钝化,在重金属污染土壤修复中具有较显著的应用前景。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Heavy metal pollution in soil has been a serious threat to human health and ecological environmental safety. Stabilization remediation has become an important means of remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil due to the high efficiency and low cost. Attapulgite modified by alkali with an improved performance, provides an important basis for its stabilization and remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil.
OBJECTIVES To analyze the changes in physical and chemical properties of attapulgite before and after modification, and to study the effects of attapulgite modified by NaOH on the chemical speciation changes and environmental risks of Cd in contaminated soil, and to explore the stabilization effects of attapulgite modified by NaOH on Cd in the soil.
METHODS Different proportions of NaOH were used to modify attapulgite. The surface characteristics, crystal structure and functional groups of the materials were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Stabilization experiments were carried out on artificially prepared heavy metal Cd contaminated soil to study the effects of NaOH-modified attapulgite on the changes of chemical speciation of Cd and environmental risks in contaminated soil.
RESULTS By adding the modified material with the mass ratio of NaOH to attapulgite of 1:2, the pH value of the soil was significantly increased by 0.85 units. The exchangeable Cd content decreased by 46.28% and the residual Cd content increased by 1.98 times. The risk assessment code (RAC) and potential risk index (PRI) of Cd in soil decreased the most from 36.70% and 207.90 to 20.08% and 86.40, respectively, which effectively reduced the transfer capacity and environmental risk of Cd in soil. According to SEM, XRD and FTIR analyses, after modification, the surface roughness of attapulgite increased, chemical bonds such as Si-O-Si bonds were opened, so active sites for adsorption of heavy metals increased. Attapulgite modified by alkali immobilized Cd mainly through adsorption, and the reaction of silanol and hydroxide with Cd2+ generated precipitate, so as to achieve the effect of stabilizing and repairing Cd contaminated soil.
CONCLUSIONS Alkali-modified attapulgite can effectively stabilize Cd in soil, which has a significant application prospect in remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil.
-

-
表 1 氢氧化钠改性凹凸棒石钝化Cd污染土壤的pH值、阳离子交换容量(CEC)和电导率(EC)
Table 1. The pH, cation exchange capacity (CEC), electrical conductivity (EC) of Cd polluted soil stabilized with attapulgite modified by NaOH
钝化剂 pH 阳离子交换量(cmol/kg) 电导率(μS/cm) CK 7.29±0.03e 22.79±0.34f 328.67±5.51f NP01 7.29±0.03e 24.32±0.30e 317.33±9.29f NP12 8.14±0.01a 34.19±0.28a 805.67±3.51a NP14 8.10±0.00b 29.22±0.22b 763.33±6.81b NP16 8.03±0.00c 26.76±0.84bc 622.00±15.10c NP18 7.99±0.01d 25.24±0.56c 559.00±5.29d NP110 7.98±0.01d 25.06±0.07d 456.67±9.50e F值 2665.64*** 108.09*** 1529.53*** 注:同列不同小写字母(a、b、c、d)本身没有具体的含义,是通过相互之间的比较来体现差异是否显著(P < 0.05),字母不同表示两者差异显著,差异性显著表明数据变化较为明显(本文其他表格和图内的a、b、c、d含义同此)。F值后的“***”表示在0.001水平上差异显著。 表 2 氢氧化钠改性凹凸棒石钝化土壤中Cd的BCR连续萃取态含量和回收率
Table 2. BCR sequential extractions and percentage recovery of Cd in soil stabilized with attapulgite modified by NaOH
钝化剂 酸溶态Cd (mg/kg) 还原态Cd (mg/kg) 氧化态Cd (mg/kg) 残渣态Cd (mg/kg) Cd回收率(%) CK 5.73±0.31a 7.03±0.20a 0.88±0.14e 1.97±0.14d 100.82 NP01 5.27±0.14ab 6.63±0.00b 1.24±0.20d 2.04±0.36d 98.04 NP12 3.08±0.57d 6.06±0.11cd 2.19±0.00c 3.93±0.11a 98.55 NP14 4.30±0.52c 6.16±0.11c 2.11±0.27c 2.69±0.08b 98.57 NP16 4.59±0.21bc 5.63±0.07e 2.29±0.09bc 2.43±0.07bc 96.52 NP18 4.53±0.32c 5.79±0.26de 2.59±0.30ab 2.14±0.13cd 97.27 NP110 4.96±0.29bc 5.89±0.26cde 2.70±0.17a 2.06±0.05d 100.84 F值 15.29*** 24.07*** 36.91*** 50.74*** 注:同列不同小写字母(a、b、c、d)表示处理之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。F值后的“***”表示在0.001水平上差异显著。 表 3 钝化土壤的理化性质与Cd化学形态和环境风险指数之间的相关系数
Table 3. Correlation coefficients among physiochemical traits of the stabilized soil, chemical speciation and environmental risk factors of Cd in soil
指标 酸溶态Cd 还原态Cd 氧化态Cd 残渣态Cd RAC PRI pH -0.767** -0.844** 0.827** 0.579** -0.795** -0.659** EC -0.847** -0.602** 0.499* 0.819** -0.879** -0.876** CEC -0.839** -0.496* 0.397 0.867** -0.878** -0.897** 注:“*”表示相关系数达到显著水平(0.01 < P < 0.05);“**”表示相关系数达到极显著水平(0.001 < P < 0.01)。 -
[1] Chai L, Wang Y H, Wang X, et al. Pollution characteristics, spatial distributions, and source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil in Lanzhou, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 125: 107507. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107507
[2] 余涛, 蒋天宇, 刘旭, 等. 土壤重金属污染现状及检测分析技术研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(2): 460-476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202102009.htm
Yu T, Jiang T X, Liu X, et al. Research progress in current status of soil heavy metal pollution and analysis technology[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(2): 460-476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202102009.htm
[3] Basan H, Sirin M, Gokbayrak E, et al. A case study on pollution and a human health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils around Sinop Province, Turkey[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 241: 125015. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125015
[4] Huang B, Li Z W, Huang J Q, et al. Aging effect on the leaching behavior of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, and Cd) in red paddy soil[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2015, 22(15): 11467-11477. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4386-x
[5] 张静静, 朱爽阁, 朱利楠, 等. 不同钝化剂对微碱性土壤镉、镍形态及小麦吸收的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 460-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202001055.htm
Zhang J J, Zhu S G, Zhu L N, et al. Effects of different amendments on fractions and uptake by winter wheat in slightly alkaline soil contaminated by cadmium and nickel[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 460-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202001055.htm
[6] 杨国航, 李合莲, 李菊梅, 等. 污泥农用对碱性土壤重金属元素形态分布的影响[J]. 济南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 32(2): 124-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDJC201802008.htm
Yang G H, Li H L, Li J M, et al. Effect of agricultural application of sludge on forms of heavy metal elements in alkaline soil[J]. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology), 2018, 32(2): 124-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDJC201802008.htm
[7] 邢金峰, 仓龙, 任静华. 重金属污染农田土壤化学钝化修复的稳定性研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2019, 51(2): 224-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201902003.htm
Xing J F, Cang L, Ren J H. Remediation stability of in situ chemical immobilization of heavy metals contamin-ated soil: A review[J]. Soils, 2019, 51(2): 224-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201902003.htm
[8] 冉洪珍, 郭朝晖, 肖细元, 等. 改良剂连续施用对农田水稻Cd吸收的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(3): 1117-1123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.03.027
Ran H Z, Guo Z H, Xiao X Y, et al. Effects of continuous application of soil amendments on cadmium availability in paddy soil and uptake by rice[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(3): 1117-1123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2019.03.027
[9] 安茂国, 赵庆玲, 谭现锋, 等. 化学还原-稳定化联合修复铬污染场地土壤的效果研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(2): 204-211. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201806040068
An M G, Zhao Q L, Tan X F, et al. Research on the effect of chemical reduction-stabilization combined reme-diation of Cr contaminated soil[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(2): 204-211. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201806040068
[10] Li M Y, Zhang J C, Yang X, et al. Responses of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms to biochar and compost amendments of heavy metals-polluted soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 102: 263-272. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2020.09.029
[11] Ren J, Dai L, Tao L. Stabilization of heavy metals in sewage sludge by attapulgite[J]. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 2021, 71(3): 392-399. doi: 10.1080/10962247.2020.1843563
[12] 陶雪, 杨琥, 季荣, 等. 固定剂及其在重金属污染土壤修复中的应用[J]. 土壤, 2016, 48(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201601001.htm
Tao X, Yang H, Ji R, et al. Stabilizers and their applications in remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil[J]. Soils, 2016, 48(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA201601001.htm
[13] 赵廷伟, 李洪达, 周薇, 等. 施用凹凸棒石对Cd污染农田土壤养分的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(10): 2313-2318. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0783
Zhao T W, Li H D, Zhou W, et al. Effects of attapulgite application on soil nutrients in Cd-contaminated farmland[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(10): 2313-2318. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2019-0783
[14] 谭科艳, 刘晓端, 刘久臣, 等. 凹凸棒石用于修复铜锌镉重金属污染土壤的研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2011, 30(4): 451-456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.04.012 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110411
Tan K Y, Liu X R, Liu J C, et al. Remediation experiments of attapulgite clay to heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(4): 451-456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.04.012 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20110411
[15] 陈展祥, 陈传胜, 陈卫平, 等. 凹凸棒石及其改性材料对土壤镉生物有效性的影响与机制[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(10): 4744-4751. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201810042.htm
Chen Z X, Chen C S, Chen W P, et al. Effect and mechanism of attapulgite and its modified materials on bioavailability of cadmium in soil[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(10): 4744-4751. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201810042.htm
[16] 陶玲, 杨欣, 颜子皓, 等. 酸活化坡缕石制备重金属钝化材料的研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2018, 41(1): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2018.01.004
Tao L, Yang X, Yan Z H, et al. Study on the function of passivant for heavy metals with palygorskite modified by acid[J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 2018, 41(1): 11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2018.01.004
[17] 王金明, 易发成. 改性凹凸棒石表征及其对模拟核素Cs+的吸附研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2006, 29(2): 53-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJSK200602018.htm
Wang J M, Yi F C. Study on characterization of modified attapulgite and its adsorption capacity on simulated nuclide Cs+[J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 2006, 29(2): 53-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJSK200602018.htm
[18] 余树荣, 张婷, 戴虎虎, 等. 凹凸棒石复合氧化钙脱硫剂脱除SO2的试验研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2009, 32(6): 1-2, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2009.06.001
Yu S R, Zhang T, Dai H H, et al. Study on desulfurization of SO2 by attapulgite/calcium oxide compound desulfuri-zation agent[J]. Non-Metallic Mines, 2009, 32(6): 1-2, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2009.06.001
[19] 任珺, 刘丽莉, 陶玲, 等. 甘肃地区凹凸棒石的矿物组成分析[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2013, 32(11): 2362-2365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201311043.htm
Ren J, Liu L L, Tao L, et al. Mineral composition analysis of attapulgite from Gansu area[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2013, 32(11): 2362-2365. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201311043.htm
[20] Dai L, Ren J, Tao L, et al. Chemical speciation and phytoavailability of Cr, Ni, Zn and Cu in loess amended with attapulgite-stabilized sewage sludge[J]. Environmental Pollutants and Bioavailability, 2019, 31(1): 112-119. doi: 10.1080/26395940.2019.1588076
[21] Nemati K, Bakar N K A, Abas M R, et al. Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192(1): 402-410.
[22] Xu X B, Hu X, Ding Z H, et al. Effects of copyrolysis of sludge with calcium carbonate and calcium hydrogen phosphate on chemical stability of carbon and release of toxic elements in the resultant biochars[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 189: 76-85. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.09.021
[23] Ke X, Gui S F, Huang H, et al. Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 175: 473-481. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.029
[24] Wang W B, Tian G Y, Zhang Z F, et al. A simple hydro-thermal approach to modify palygorskite for high-efficient adsorption of methylene blue and Cu(Ⅱ) ions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 265: 228-238. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.135
[25] 张平萍, 陈雪刚, 程继鹏, 等. 水热条件下坡缕石在NaOH溶液中的行为及结构变化[J]. 无机化学学报, 2009, 25(9): 1545-1550. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4861.2009.09.006
Zhang P P, Chen X G, Cheng J P, et al. Behavior and structural transformation of palygorskite in NaOH solution under hydrothermal conditions[J]. Chinese Jouranl of Inorganic Chemistry, 2009, 25(9): 1545-1550. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4861.2009.09.006
[26] Suarez M, Garcia R E. FTIR spectroscopic study of palygorskite: Influence of the composition of the octahedral sheet[J]. Applied Clay Science, 2006, 31(1-2): 154-163. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2005.10.005
[27] Yan W C, Liu D, Tan D Y, et al. FTIR spectroscopy study of the structure changes of palygorskite under heating[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2012, 97: 1052-1057. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2012.07.085
[28] Suarez M, Garcia R E. Macroscopic palygorskite from lisbom volcanic complex[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2006, 18(1): 119-126. doi: 10.1127/0935-1221/2006/0018-0119
[29] 辜娇峰, 周航, 吴玉俊, 等. 复合改良剂对稻田Cd、As活性与累积的协同调控[J]. 中国环境科学, 2016, 36(1): 206-214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.01.035
Gu J F, Zhou H, Wu Y J, et al. Synergistic control of combined amendment on bioavailability and accumulation of Cd and As in rice paddy soil[J]. China Environmental Science, 2016, 36(1): 206-214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2016.01.035
[30] 陶玲, 管天成, 刘瑞珍, 等. 热改性坡缕石对土壤Cd污染的钝化修复研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2021, 40(4): 782-790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH202104012.htm
Tao L, Guan T C, Liu R Z, et al. Stabilization remediation of cadmium contaminated soil by using heat-modified palygorskite[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2021, 40(4): 782-790. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NHBH202104012.htm
[31] Yin X L, Xu Y M, Huang R, et al. Remediation mechanisms for Cd-contaminated soil using natural sepiolite at the field scale[J]. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, 2017, 19(12): 1563-1570.
[32] 廖启林, 刘聪, 朱伯万, 等. 凹凸棒石调控Cd污染土壤的作用及其效果[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(5): 1693-1704. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.05.023
Liao Q L, Liu C, Zhu B W, et al. The role and effect of applying attapulgite to controlling Cd-contaminated soil[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(5): 1693-1704. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.05.023
[33] Qin F, Shan X Q, Wei B. Effects of low-molecular-weight organic acids and residence time on desorption of Cu, Cd, and Pb from soils[J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 57(4): 253-263. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.06.010
[34] 武成辉, 李亮, 晏波, 等. 新型硅酸盐钝化剂对镉污染土壤的钝化修复效应研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(10): 2007-2013. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-0471
Wu C H, Li L, Yan B, et al. Remediation effects of a new type of silicate passivator on cadmium-contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(10): 2007-2013. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2017-0471
[35] 王永昕, 孙约兵, 徐应明, 等. 施用鸡粪对海泡石钝化修复镉污染菜地土壤的强化效应及土壤酶活性影响[J]. 环境化学, 2016, 35(1): 159-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201601020.htm
Wang Y X, Sun Y B, Xu Y M, et al. Enhancement of chicken manure on the immobilization remediation of cadmium contaminated vegetable soil and enzyme activity using sepiolite[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2016, 35(1): 159-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201601020.htm
[36] Zotiadis V, Argyraki A, Theologou E. Pilot scale application of attapulgitic clay for stabilization of toxic elements in contaminated soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2012, 138(5): 633-637. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000620
[37] 罗宁临, 李忠武, 黄梅, 等. 壳聚糖(改性)-沸石对农田土壤重金属镉钝化技术研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 47(4): 132-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDX202004017.htm
Luo N L, Li Z W, Huang M, et al. Immobilizing cadmium in paddy soil by using modified chitosan-zeolite[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences), 2020, 47(4): 132-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDX202004017.htm
[38] Shi L, Guo Z H, Peng C, et al. Immobilization of cadmium and improvement of bacterial community in contaminated soil following a continuous amendment with lime mixed with fertilizers: A four-season field experiment[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019, 171: 425-434. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.006
[39] Zhao B W, Xu R Z, Ma F F, et al. Effects of biochars derived from chicken manure and rape straw on speciation and phytoavailability of Cd to maize in artificially contaminated loess soil[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 184(3): 569-574.
[40] 陈哲, 冯秀娟, 朱易春, 等. 天然及改性凹凸棒对稀土尾矿土壤中重金属铅的钝化效果研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(6): 847-855. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202006250096
Chen Z, Feng X J, Zhu Y C, et al. Study on the passivation effect of natural and modified attapulgite on heavy metal lead in soils of the rare earth tailings[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(6): 847-855. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202006250096
[41] 窦韦强, 安毅, 秦莉, 等. 土壤pH对镉形态影响的研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(3): 439-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA202003002.htm
Dou W Q, An Y, Qin L, et al. Advances in effects of soil pH on cadmium form[J]. Soils, 2020, 52(3): 439-444. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TURA202003002.htm
[42] 郭炜辰, 杜立宇, 梁成华, 等. 天然与改性沸石对土壤Cd污染赋存形态的影响研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2019, 50(3): 719-724. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201903030.htm
Guo W C, Du L Y, Liang C H, et al. Effects of natural and ammonium chloride/calcium chloride-modified zeolites on cadmium speciation in cintaminated soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2019, 50(3): 719-724. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRTB201903030.htm
[43] 迟荪琳, 徐卫红, 熊仕娟, 等. 不同镉水平下纳米沸石对土壤pH、CEC及Cd形态的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2017, 38(4): 1654-1666. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201704049.htm
Chi S L, Xu W H, Xiong S J, et al. Effects of nano zelites on pH, CEC in soil and Cd fractions in plant and soil at different cadmium levels[J]. Environmental Science, 2017, 38(4): 1654-1666. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201704049.htm
-



 下载:
下载: