The Experimental Conditions for Quantitative Determination of Trace Elements Si, Ta and W in Rare Polymetallic Ore by Electron Probe Microanalyzer
-
摘要:
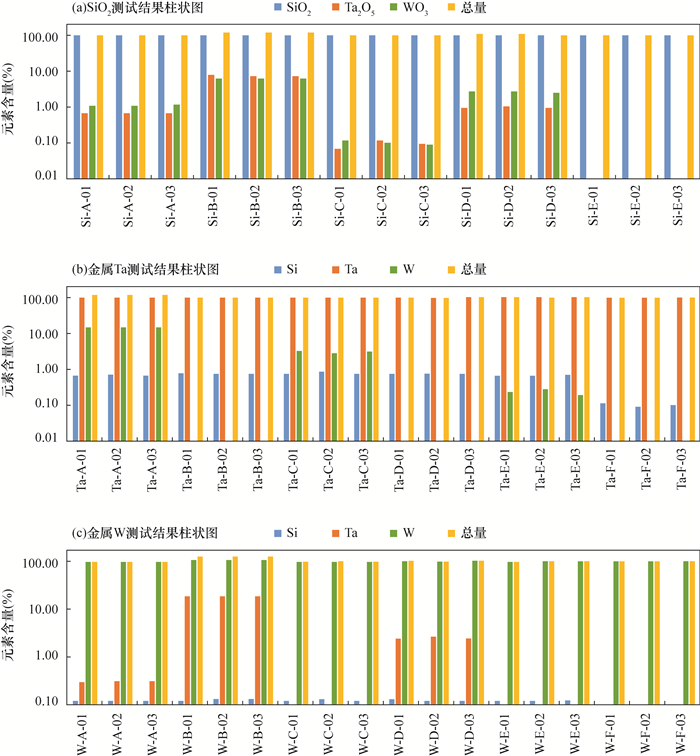
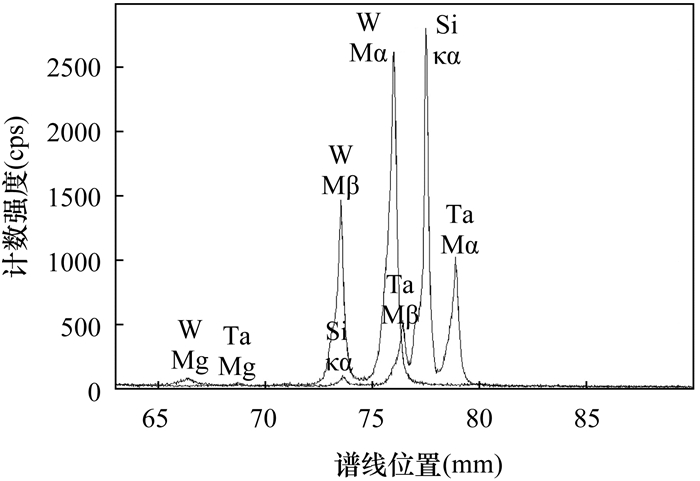
近年来对稀有多金属矿的研究越来越趋向于微区化、微量化,作为其重要研究手段之一,电子探针定量分析在微量元素测试方面取得很大的进展。在微量测试过程中,除了增大测试束流,提高测试时间来降低检出限以外,更要注意去除来自其他元素,特别是主量元素的干扰。在日常测试稀有多金属样品的过程中,Si、Ta、W三个元素存在相互干扰,这种干扰对影响微量元素的测试结果,且因含量低不易被察觉,从而影响最终结论的准确性。本文以SPI标样公司的SiO2、金属Ta和W为研究对象,查明Si、Ta、W三者之间在不同测试条件下的干扰关系并给出建议:硅酸盐测试中,Si建议使用TAP-Kα,Ta和W建议使用LIF-Lα;铌钽矿测试中,Si、Ta、W建议分别使用PET-Kα、PET-Mα和TAP-Mβ,并配合Ta对Si的干扰校正测试结果更为准确。
Abstract:BACKGROUND In recent years, the study of rare polymetallic ore tends to be increasingly detailed. As one of the important research methods, electron probe quantitative analysis has made great progress in trace element measurement. During analysis, in addition to increasing the beam size and time to reduce the detection limit, more attention should be paid to removing the interference from other elements, especially the main elements. During the routine testing of rare polymetallic samples, Si, Ta, W interfere with each other. Such interference affects the analytical results of trace elements, and is not easily detected due to its low content, thus affecting the accuracy of the final conclusion.
OBJECTIVES To determine the interference relationship among Si, Ta and W under different analytical conditions.
METHODS Taking SiO2, metal Ta and W of SPI as the research object, each element was analyzed under different conditions by electron probe microanalyzer.
RESULTS In the analysis of silicate, TAP-Kα is used for Si, and LIF-Lα is recommended for Ta and W. In the analysis of niobium tantalum ore, it is suggested to use PET-Kα, PET-Mα and TAP-Mβ for Si, Ta and W, respectively; since 100% Ta will produce about 0.1% Si, therefore, the results are more accurate with the interference correction of Ta on Si.
CONCLUSIONS It is important to understand the spectral peak stripping method and the principle of element interference and spectral peak overlap, adjusting the parameters according to the actual situation to ensure the accuracy of data.
-
Key words:
- rare polymetallic deposits /
- silicon /
- tantalum /
- wolfram /
- electron probe microanalyzer /
- spectral interference
-

-
表 1 JXA-8230型电子探针谱仪配置基本信息
Table 1. Basic configuration of JXA-8230 EPMA spectrometer
波谱道数 晶体类型 计数器类型 分光晶体 罗兰圆半径(mm) CH1 XCE型 GPC TAP/LDE1 140 CH2 XCE型 GPC TAP/LDE2 140 CH3 XCE型 XPC LIF/PETJ 140 CH4 H型 H-XPC LIFH/PETH 100 CH5 L型 XPC LIFL/PETL 140 表 2 样品编号及背景位置
Table 2. Sample number and background position
样品编号 Si Ta W 晶体-线系 上背景(Bg-) 下背景(Bg+) 晶体-线系 上背景(Bg-) 下背景(Bg+) 晶体-线系 上背景(Bg-) 下背景(Bg+) Si-A TAP-Kα 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mα 8.18 5.00 TAP-Mα 5.19 5.42 Si-B TAP-Kα 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mβ 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mβ 5.00 7.30 Si-C TAP-Kα 5.00 5.00 PETL-Mα 8.48 5.00 PETL-Mα 9.31 10.13 Si-D TAP-Kα 5.00 5.00 PETL-Mβ 5.00 6.14 PETL-Mβ 5.00 5.74 Si-E TAP-Kα 5.00 5.00 LIFL-Lα 5.96 7.09 LIFL-Lα 5.00 5.00 Ta-A TAP-Kα 5.00 6.44 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.30 Ta-B TAP-Kα 5.00 6.44 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mβ 7.52 8.03 Ta-C TAP-Kα 5.00 6.44 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 PETL-Mα 5.00 4.45 Ta-D TAP-Kα 5.00 6.44 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 PETL-Mβ 5.00 3.91 Ta-E TAP-Kα 5.00 6.44 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 LIFL-Lα 5.00 5.00 Ta-F PETL-Kα 9.94 9.43 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mβ 7.50 9.76 W-A TAP-Kα 6.44 5.00 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 W-B TAP-Kα 6.44 5.00 TAP-Mβ 5.65 5.00 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 W-C TAP-Kα 6.44 5.00 PETL-Mα 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 W-D TAP-Kα 6.44 5.00 PETL-Mβ 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 W-E TAP-Kα 6.44 5.00 LIFL-Lα 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 W-F PETL-Kα 8.87 5.00 PETL-Mα 5.00 5.00 TAP-Mα 5.00 5.00 表 3 SPI样品测试结果、误差和检出限
Table 3. Analytical results, errors and detection limits of SPI samples
样品编号 Si Ta W 总量(%) 含量(%) 1σ误差(%) 检出限(μg/g) 含量(%) 1σ误差(%) 检出限(μg/g) 含量(%) 1σ误差(%) 检出限(μg/g) Si-A-01 100.71 0.23 158.00 0.67 4.01 147.00 1.11 2.66 140.00 102.49 Si-A-02 99.69 0.23 164.00 0.67 1.00 147.00 1.07 2.78 146.00 101.43 Si-A-03 100.31 0.23 152.00 0.70 3.86 146.00 1.17 2.56 141.00 102.19 Si-B-01 103.77 0.23 161.00 7.52 1.14 393.00 6.34 1.17 324.00 117.62 Si-B-02 103.22 0.23 166.00 7.41 1.16 405.00 6.46 1.16 317.00 117.09 Si-B-03 102.76 0.23 157.00 7.46 1.15 399.00 6.22 1.19 328.00 116.44 Si-C-01 99.74 0.23 171.00 0.07 34.19 169.00 0.12 17.69 137.00 99.94 Si-C-02 98.94 0.23 169.00 0.12 20.90 158.00 0.10 23.08 155.00 99.16 Si-C-03 99.63 0.23 169.00 0.10 25.40 160.00 0.09 24.20 146.00 99.81 Si-D-01 100.87 0.23 165.00 0.95 9.93 813.00 2.67 3.76 486.00 104.49 Si-D-02 100.74 0.23 165.00 1.05 9.17 804.00 2.70 3.78 514.00 104.49 Si-D-03 100.73 0.23 156.00 0.94 10.50 879.00 2.53 3.91 500.00 104.21 Si-E-01 100.50 0.23 159.00 / 100.00 227.00 / 524.99 254.00 100.51 Si-E-02 100.38 0.23 156.00 / 100.00 227.00 / 100.00 180.00 100.38 Si-E-03 100.45 0.23 157.00 / 366.45 223.00 / 109.87 178.00 100.48 Ta-A-01 0.66 1.63 68.00 101.09 0.28 323.00 14.70 0.56 201.00 116.44 Ta-A-02 0.70 1.56 69.00 100.75 0.28 324.00 14.80 0.55 197.00 116.25 Ta-A-03 0.66 1.62 68.00 100.58 0.29 310.00 14.72 0.56 198.00 115.96 Ta-B-01 0.76 1.45 61.00 100.97 0.28 326.00 / 100.00 471.00 101.73 Ta-B-02 0.74 1.47 61.00 100.59 0.28 320.00 / 100.00 467.00 101.33 Ta-B-03 0.75 1.47 61.00 100.60 0.28 317.00 / 100.00 462.00 101.35 Ta-C-01 0.78 1.41 60.00 100.66 0.28 319.00 3.12 1.55 179.00 104.55 Ta-C-02 0.85 1.33 61.00 100.80 0.29 329.00 2.78 1.77 206.00 104.43 Ta-C-03 0.78 1.41 60.00 100.24 0.29 323.00 3.03 1.63 193.00 104.05 Ta-D-01 0.76 1.45 60.00 100.99 0.28 319.00 / 100.00 276.00 101.75 Ta-D-02 0.75 1.46 60.00 100.74 0.28 328.00 / 100.00 280.00 101.50 Ta-D-03 0.75 1.47 60.00 101.24 0.28 331.00 / 100.00 282.00 101.99 Ta-E-01 0.66 1.67 67.00 100.69 0.29 331.00 0.23 17.70 392.00 101.58 Ta-E-02 0.67 1.65 66.00 100.68 0.29 327.00 0.27 15.13 390.00 101.62 Ta-E-03 0.69 1.61 67.00 101.64 0.28 325.00 0.19 21.00 392.00 102.53 Ta-F-01 0.11 7.76 52.00 100.91 0.28 329.00 / 100.00 556.00 101.02 Ta-F-02 0.09 9.44 56.00 100.79 0.28 321.00 / 100.00 555.00 100.88 Ta-F-03 0.10 8.44 56.00 100.39 0.28 323.00 / 100.00 547.00 100.49 W-A-01 0.12 4.44 64.00 0.30 6.67 176.00 99.03 0.28 345.00 99.45 W-A-02 0.12 4.59 64.00 0.31 6.40 172.00 98.52 0.29 337.00 98.94 W-A-03 0.12 4.35 63.00 0.31 6.40 175.00 99.04 0.28 333.00 99.48 W-B-01 0.12 5.13 65.00 18.77 0.56 518.00 106.99 0.29 345.00 125.87 W-B-02 0.13 4.58 64.00 18.63 0.57 544.00 107.56 0.28 352.00 126.31 W-B-03 0.13 4.61 64.00 18.71 0.56 535.00 108.14 0.28 337.00 126.97 W-C-01 0.12 4.50 64.00 / 100.00 390.00 98.37 0.29 334.00 98.49 W-C-02 0.13 4.26 63.00 / 100.00 355.00 99.51 0.28 332.00 99.63 W-C-03 0.12 4.46 63.00 / 100.00 359.00 99.38 0.28 334.00 99.50 W-D-01 0.13 4.21 63.00 2.44 4.30 1093.00 100.43 0.28 343.00 103.00 W-D-02 0.12 4.62 65.00 2.67 4.05 1101.00 101.13 0.28 333.00 103.92 W-D-03 0.12 4.49 64.00 2.56 4.18 1110.00 99.97 0.29 347.00 102.65 W-E-01 0.12 4.52 65.00 / 109.37 515.00 99.32 0.28 336.00 99.48 W-E-02 0.12 4.50 65.00 / 100.00 519.00 99.97 0.28 337.00 100.09 W-E-03 0.12 4.40 64.00 / 100.00 516.00 99.77 0.28 343.00 99.90 W-F-01 / 84.16 67.00 / 100.00 394.00 99.71 0.28 335.00 99.72 W-F-02 / 1978.06 67.00 / 100.00 380.00 99.64 0.28 341.00 99.64 W-F-03 / 100.00 68.00 / 100.00 369.00 99.85 0.28 337.00 99.85 注:“/”表示低于检出限。 -
[1] 周剑雄. 矿物微区分析概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1980.
Zhou J X. Introduction to mineral microregion analysis[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1980.
[2] 周剑雄, 毛水和, 陈克樵, 等. 电子探针分析[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1988.
Zhou J X, Mao S H, Chen K Q, et al. Electron probe microanalysis[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1988.
[3] 徐萃章. 电子探针分析原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990.
Xu C Z. Principle of electron probe analysis[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1990.
[4] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 等. 华南地区中生代主要金属矿床时空分布规律和成矿环境[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14(4): 510-526. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.04.005
Mao J W, Xie G Q, Guo C L, et al. Spatial-temporal distribution of Mesozoic ore deposits in South China and their metallogenic settings[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2008, 14(4): 510-526. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.04.005
[5] 毛景文, 陈懋弘, 袁顺达, 等. 华南地区钦杭成矿带地质特征和矿床时空分布规律[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(5): 636-658. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201105006.htm
Mao J W, Chen M H, Yuan S D, et al. Geological characteristics of the Qinhang (or Shihang) metallogenic belt in South China and spatial-temporal distribution regularity of mineral deposits[J]. Acta Geologica Sinca, 2011, 85(5): 636-658. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201105006.htm
[6] 李洁. 华南中生代稀有金属花岗岩岩浆演化与热液作用过程的矿物学约束[D]. 广州: 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所, 2015.
Li J. Mineralogical constraints on magmatic and hydro-thermal evolutions of the Mesozoic rare-metal granites in South China[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015.
[7] Melcher F, Graupner T, Gäbler H E, et al. Tantalum-(niobium-tin) mineralisation in African pegmatites and rare metal granites: Constraints from Ta-Nb oxide mineralogy, geochemistry and U-Pb geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 64: 667-719. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.09.003
[8] 代鸿章, 王登红, 刘丽君, 等. 电子探针和微区X射线衍射研究陕西镇安钨-铍多金属矿床中祖母绿级绿柱石[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3): 336-345. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712140193
Dai H Z, Wang D H, Liu L J, et al. Study on emerald-level beryl from the Zhen'an W-Be polymetallic deposit in Shannxi Province by electron probe microanalyzer and micro X-ray diffractometer[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3): 336-345. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201712140193
[9] 万建军, 潘春蓉, 严杰, 等. 应用电子探针-扫描电镜研究陕西华阳川铀稀有多金属矿床稀土矿物特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1): 145-155. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060009
Wan J J, Pan C R, Yan J, et al. EPMA-SEM study on the rare earth minerals from the Huayangchuan uranium rare polymetallic deposit Shannxi Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(1): 145-155. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060009
[10] Nash W P, Crecraft H R. Partition coefficients for trace elements in silicic magmas[J]. Pergamon, 1985, 49(11): 2309-2322.
[11] Stephen J B R. Quantitative trace analysis by wavelength-dispersive EPMA[J]. Mikrochimica Acta: An International Journal for Physical and Chemical Methods of Analysis, 2000, 132(2-4): 145-151.
[12] Batanova V G, Sobolev A V, Kuzmin D V. Trace element analysis of olivine: High precision analytical method for JEOL JXA-8230 electron probe microanalyser[J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 419: 149-157. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.10.042
[13] 王娟, 陈意, 毛骞, 等. 金红石微量元素电子探针分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(6): 1934-1946. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201706019.htm
Wang J, Chen Y, Mao Q, et al. Electron microprobe trace element analysis of rutile[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(6): 1934-1946. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201706019.htm
[14] Batanova V G, Sobolev A V, Magnin V. Trace element ana-lysis by EPMA in geosciences: Detection limit, precision and accuracy[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 304(1): 012001.
[15] Cui J Q, Yang S Y, Jiang S Y, et al. Improved accuracy for trace element analysis of Al and Ti in quartz by electron probe microanalysis[J]. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 2019, 25(1): 47-57. doi: 10.1017/S1431927618015672
[16] 崔继强, 郭晟彬, 张若曦, 等. 电子探针多道波谱仪同时测试同一个元素的方法: 以石英中Al和Ti含量的测试为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 2021, 27(3): 340-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202103010.htm
Cui J Q, Guo S B, Zhang R X, et al. EPMA simultaneous determination of an element by multi-spectrometer: A case study of the determination of Al and Ti contents in quartz[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2021, 27(3): 340-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202103010.htm
[17] Pyle J M, Spear F S, Wark D A. Electron microprobe analysis of REE in apatite, monazite and xenotime: Protocols and pitfalls[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2002, 48(1): 337-362. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2002.48.8
[18] 周剑雄, 陈振宇, 芮宗瑶. 独居石的电子探针钍-铀-铅化学测年[J]. 岩矿测试, 2002, 21(4): 241-246. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20020467
Zhou J X, Chen Z Y, Rui Z Y. Th-U-Pb chemical dating of monazite by electron probe[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2002, 21(4): 241-246. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20020467
[19] Stefan P, Stephan K. Effect of melt composition on the partitioning of trace elements between titanite and silicate melt[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2004, 69(3): 695-709.
[20] 聂潇, 王宗起, 陈雷, 等. 蚀变粗面岩中再平衡结构黑云母的电子探针分析[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(5): 565-574. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201807100081
Nie X, Wang Z Q, Chen L, et al. Electron microprobe analysis of biotite with reequilibration texture in altered trachyte[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(5): 565-574. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201807100081
[21] 张迪, 陈意, 毛骞, 等. 电子探针分析技术进展及面临的挑战[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(1): 261-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201901022.htm
Zhang D, Chen Y, Mao Q, et al. Progress and challenge of electron probe microanalysis technique[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(1): 261-274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201901022.htm
[22] 陈意, 胡兆初, 贾丽辉, 等. 微束分析测试技术十年(2011~2020)进展与展望[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(1): 1-35, 253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202101004.htm
Chen Y, Hu Z C, Jia L H, et al. Progress of microbeam analytical technologies in the past decade (2011—2020) and prospect[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(1): 1-35, 253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202101004.htm
[23] 王微, 姚立, 于洪林. 电子探针微量元素精确测试方法初探[J]. 电子显微学报, 2004(4): 423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2004.04.125
Wang W, Yao L, Yu H L. A preliminary study on the precise determination of microelements by electron probe[J]. Journal of Electron Microscopy, 2004(4): 423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6281.2004.04.125
[24] 姚立. 低含量、微量元素的电子探针分析方法研究与应用[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2008.
Yao L. Research and application of electron probe microanalytical method for minor and trace elements[D]. Changchun: Jinlin University, 2008.
[25] Michael J J, Michael L W. Analytical perils (and progress) in electron microprobe trace element analysis applied to geochronology: Background acquisition, interferences, and beam irradiation effects[J]. American Mineralogist, 2015, 90(4): 526-546.
[26] 刘源骏. 铌钽地质及普查勘探[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1979.
Liu Y J. Niobium tantalum geology and exploration[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1979.
[27] 郭春丽, 郑佳浩, 楼法生, 等. 华南印支期花岗岩类的岩石特征、成因类型及其构造动力学背景探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(3): 457-472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.03.020
Guo C L, Zheng J H, Lou F S, et al. Petrography, genetic types and geological dynamical settings of the Indosinian granitoids in South China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2012, 36(3): 457-472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.03.020
[28] Stepanov A S, Hermann J. Fractionation of Nb and Ta by biotite and phengite: Implications for the "missing Nb paradox"[J]. Geology, 2013, 41: 303-306.
[29] 王盘喜, 包民伟. 我国钽铌等稀有金属矿概况及找矿启示[J]. 金属矿山, 2015(6): 92-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2015.06.020
Wang P X, Bao M W. General situation and prospecting revelation of tantalum-niobium rare metal deposits in China[J]. Metal Mine, 2015(6): 92-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2015.06.020
[30] 李丽婵, 黄思莹, 李金勇, 等. 五台地区铁瓦殿岩体中铌钽矿物的成因矿物学研究[J]. 河北地质大学学报, 2020, 43(5): 51-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDX202005008.htm
Li L C, Huang S Y, Li J Y, et al. Genetic mineralogy study on niobium and tantalum minerals in iron tile hall rock mass in Wutai Mountain[J]. Journal of Hebei Geo-University, 2020, 43(5): 51-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDX202005008.htm
[31] 李小犁. 电子探针微量元素分析的一些思考[J]. 高校地质学报, 2021, 27(3): 306-316. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202103007.htm
Li X L. Several perspectives on microprobe trace elements analysis[J]. Journal Geological of Colleges and Universities, 2021, 27(3): 306-316. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202103007.htm
[32] 姚立, 田地, 梁细荣. 电子探针背景扣除和谱线干扰修正方法的进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2008, 27(1): 49-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.01.013 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080118
Yao L, Tian D, Liang X R. Progress in background subtraction and spectral interference correction in electron probe microanalysis[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008, 27(1): 49-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2008.01.013 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_20080118
[33] 胡欢, 王汝成, 谢磊, 等. 基于大罗兰圆(R=140mm)大分光晶体的SPI独居石标样化学成分精准测定[J]. 高校地质学报, 2021, 27(3): 317-326. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202103008.htm
Hu H, Wang R C, Xie L, et al. High precision analysis of chemical composition of SPI monazite standard on large spectrometer of 140mm rowland circle[J]. Journal Geological of Colleges and Universities, 2021, 27(3): 317-326. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX202103008.htm
[34] 王汝成, 朱金初, 张文兰, 等. 南岭地区钨锡花岗岩的成矿矿物学: 概念与实例[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14(4): 485-495. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.04.003
Wang R H, Zhu J C, Zhang W L, et al. Ore-forming mineralogy of W-Sn granites in the Nanling Range: Concept and case study[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2008, 14(4): 485-495. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.04.003
[35] 刘莹, 谢磊, 王汝成, 等. 赣北大湖塘矿床的含铌钽与含钨花岗岩成岩成矿特征对比研究[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(10): 2120-2137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.10.012
Liu Y, Xie L, Wang R H, et al. Comparative study of petrogenesis and mineralization characteristics of Nb-Ta-bearing and W-bearing granite in the Dahutang deposit, northern Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinca, 2018, 92(10): 2120-2137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.10.012
-



 下载:
下载: