Application of Hyperspectral Scanning in Mineral Composition Analysis of Carbonate Rocks
-
摘要:
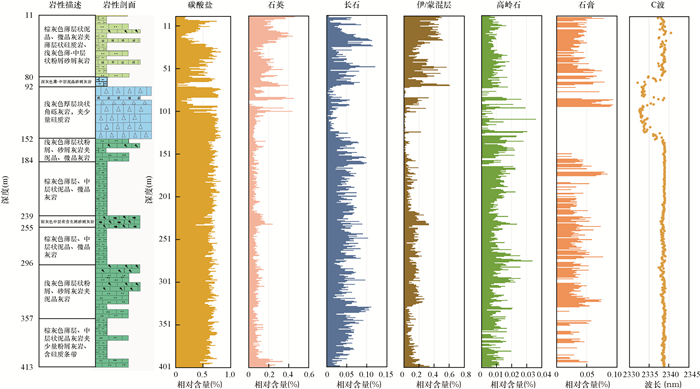
矿物组成及其微观特征对研究油气藏的沉积环境、岩石骨架及储集空间等方面具有重要意义。本文利用高光谱扫描和扫描电镜矿物组成定量分析技术(QEMSCAN),对羌塘盆地二叠系龙格组碳酸盐岩岩心样品的矿物组成、含量及其空间分布规律等进行研究,为羌塘盆地古生代碳酸盐储层油气藏评价提供矿物组成和微观特征方面的依据。结果表明:龙格组岩性以微晶灰岩和粒屑灰岩为主,矿物组成主要为方解石和白云石,两者含量之和普遍大于90%,其次为石英及少量的黏土矿物和长石。矿物组成具有明显纵向分段特征:上段方解石和白云石含量均较高;中段白云石含量较高,且白云化程度较为强烈,孔隙度和渗透率均有所下降;下段以方解石为主。黏土矿物特征分析显示,龙格组地层经历了复杂的沉积-成岩作用和后期热扰动作用及流体作用,这对该地区油气运移及保存有较强的影响。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Mineral composition and its microscopic characteristics are of great significance to the study of sedimentary environment, rock framework and reservoir space of oil and gas reservoirs.
OBJECTIVES To investigate the mineral composition, content and spatial distribution of carbonate core samples of the Permian Longge Formation and provide the basis for oil and gas evaluation of the Paleozoic carbonate reservoirs in Qiangtang Basin.
METHODS The sample was analyzed by hyperspectral scanning and QEMSCAN.
RESULTS The Longge Formation is dominated by microcrystalline limestone and granulated limestone, and the minerals are mainly calcite and dolomite, the contents of which are generally greater than 90%, followed by quartz and a minor clay mineral and feldspar. The mineral composition has obvious characteristics of longitudinal segmentation. The contents of calcite and dolomite are higher in the upper section. The content of dolomite in the middle section is higher, and the degree of dolomization is relatively strong. The porosity and permeability of this section have decreased. The lower section is mainly composed of calcite. In addition, the analysis of clay mineral characteristics shows that the Longge Formation has experienced complex sedimentary-diagenesis and late thermal disturbance and fluid replacement, which has a strong impact on oil and gas migration and preservation in this area.
CONCLUSIONS Hyperspectral scanning technology can be used to quickly and efficiently interpret large-scale mineral features. QEMSCAN enables more precise and quantitative analysis of mineral microscopic features. The Longge Formation is dominated by carbonate and obviously affected by diagenesis and the local dolomization is strong. The oil and gas conditions in this formation are poor.
-
Key words:
- mineral composition /
- hyperspectral scanning /
- QEMSCAN /
- carbonate rock /
- Permian Longe Formation
-

-
表 1 矿物组成定量分析系统(QEMSCAN)设备技术参数
Table 1. Technical parameters of hardware equipment of QEMSCAN
参数 QEMSCAN分析系统工作条件 加速电压 0.2~30kV 探针电流 ≤200nA, 可连续调节 放大倍数 6~1.0×106倍 EDS采集角 35° 水平视场宽度 工作距离为10mm时,水平视场宽度为5mm,工作距离为65mm时,水平视场宽度为18.8mm 样品要求 直径≤150mm直径;高度≤60mm;质量≤2000g;360°旋转 分辨率 高真空模式:0.8nm(30kV,STEM);1.0nm(30kV,SE);2.5nm(30kV,BSE);3.0nm(1kV,SE);
低真空模式:1.4nm(30kV,SE);2.5nm(30kV,BSE);3.0nm(3kV,SE)表 2 羌资5井龙格组碳酸盐岩样品信息
Table 2. Information of carbonate rock samples from the Longge Formation in Qiangzi-5 Well
样品编号 深度(m) 岩性 LG-1 58.25 灰色微晶灰岩 LG-2 81.43 深灰色泥晶砂屑灰岩 LG-3 111.92 灰色灰质白云岩 LG-4 157.93 浅灰色泥晶灰岩 LG-5 160.43 灰色泥晶灰岩 LG-6 248.35 灰色泥晶砂屑灰岩 LG-7 282.83 灰色泥晶灰岩 LG-8 339.69 深灰色泥晶灰岩 LG-9 358.60 深灰色泥晶灰岩 LG-10 391.44 深灰色泥晶灰岩 表 3 羌资5井龙格组碳酸盐岩样品主要矿物分析结果
Table 3. Main mineral composition analysis of carbonate rock sample from the Longe Formation in Qiangzi-5 Well
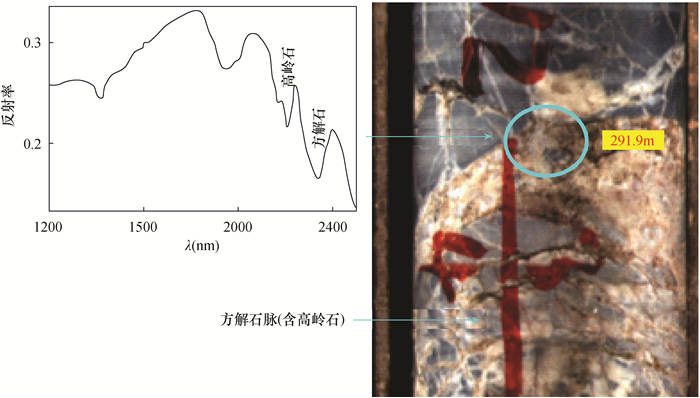
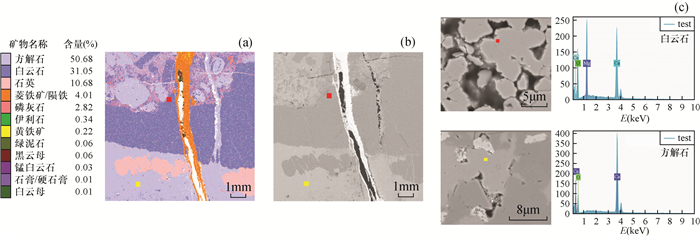
样品编号 岩性 矿物组成及含量 LG-1 微晶灰岩 方解石(96.71%),石英(3.09%),黄铁矿(0.09%) LG-2 泥晶砂屑灰岩 方解石(50.68%),白云石(31.05%),石英(10.68%),菱铁矿(4.01%),磷灰石(2.82%) LG-3 灰质白云岩 白云石(55.36%),方解石(44.31%),石英(0.15%) LG-4 泥晶灰岩 方解石(99.04%),石英(0.89%),伊利石(0.04%) LG-5 泥晶灰岩 方解石(99.33%),石英(0.55%),石膏(0.05%) LG-6 泥晶砂屑灰岩 方解石(87.76%),石英(8.28%),高岭石(1.96%) LG-7 泥晶灰岩 方解石(96.57%),石英(2.43%),高岭石(0.55%) LG-8 泥晶灰岩 方解石(92.82%),石英(5.52%),黄铁矿(0.82%) LG-9 泥晶灰岩 方解石(96.50%),石英(3.35%),高岭石(0.08%) LG-10 泥晶灰岩 方解石(98.62%),石英(1.31%),高岭石(0.02%) -
[1] 费宝生, 刘建礼, 陆艳芬. 羌塘盆地油气勘探前景展望[J]. 海相油气地质, 2006, 11(4): 13-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ200604001.htm
Fei B S, Liu J L, Lu Y F. Oil and gas prospect for exploration in Qiangtang Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2006, 11(4): 13-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ200604001.htm
[2] 赵政璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 等. 青藏高原海相烃源层的油气生成[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000.
Zhao Z Z, Li Y T, Ye H F, et al. Hydrocarbon generation in marine source beds of Qinghai—Xizang Plateau[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000.
[3] 赵光通, 李俊武, 邓翔, 等. 羌塘盆地隆鄂尼地区油砂矿地质特征及成藏模式[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(2): 40-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201902007.htm
Zhao G T, Li J W, Deng X, et al. Geology characterization and hydrocarbon accumulation pattern of oil sand in Longeni of Qiangtang Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(2): 40-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201902007.htm
[4] 李启来, 伊海生, 梁定勇, 等. 羌塘盆地隆鄂尼—昂达尔错地区中侏罗统布曲组碳酸盐岩储层特征研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(31): 183-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201431035.htm
Li Q L, Yin H S, Liang D Y, et al. Study on reservoir characteristics of the carbonate rocks in the middle Jurassic Buqu Formation in Longeni—Angdaercuo area, Qiangtang Basin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(31): 183-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201431035.htm
[5] 刘建清, 陈文斌, 杨平, 等. 羌塘盆地中央隆起带南侧隆额尼—昂达尔错古油藏白云岩地球化学特征及成因意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(6): 1379-1389. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200806022.htm
Liu J Q, Chen W B, Yang P, et al. The Longeni—Angdanrcopaelo-oil dolomite geochemical characteri-stics in southern part of the central uplift zone of Qiangtang Basin and its significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(6): 1379-1389. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200806022.htm
[6] 王剑, 付修根, 沈利军, 等. 论羌塘盆地油气勘探前景[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(5): 1091-1113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005005.htm
Wang J, Fu X G, Shen L J, et al. Prospect of the potential of oil and gas resources in Qiangtang Basin, Xizang[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(5): 1091-1113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202005005.htm
[7] 宋春彦, 曹竣峰, 王剑, 等. 羌塘盆地角木茶卡地区二叠系古油藏的发现及基本特征[J]. 新疆地质, 2014, 32(1): 87-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201401016.htm
Song C Y, Cao J F, Wang J, et al. The discovery and basic characteristics of ancient reservoir in Permian of Jiaomuchaka area, Qiangtang Basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2014, 32(1): 87-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201401016.htm
[8] 王成善, 尹海生, 李亚林, 等. 西藏羌塘盆地古油藏发现及其意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2004, 25(2): 139-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200402003.htm
Wang C S, Yi H S, Li Y L, et al. Discovery of paleo-oil reservoir in Qiangtang Basin in Xizang and its geological significance[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2004, 25(2): 139-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT200402003.htm
[9] Bowker K A. Barnett shale gas production, Fort Worth Basin: Issues and discussion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4): 523-533. doi: 10.1306/06190606018
[10] Ross D, Bustin R M. The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(6): 916-927.
[11] 孙强强. 岩石矿物组成的测定与分析研究[J]. 山东工业技术, 2016(4): 112.
Sun Q Q. Determination and analysis of rock mineral composition[J]. Shandong Industrial Technology, 2016(4): 112.
[12] 宋土顺, 李轩, 张颖, 等. QEMSCAN矿物定量分析技术在成岩作用研究中的运用: 以扶余油层致密砂岩为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(3): 193-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201603025.htm
Song T S, Li X, Zhang Y, et al. QEMSCAN mineral quantitative analysis of tight sandstone diagenesis in Fuyu Oil Layer, Daqing Placanticline[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(3): 193-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201603025.htm
[13] Woodruff L, Cannon W F, Smith D B, et al. The distribution of selected elements and minerals in soil of the conterminous United States[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 154: 49-60.
[14] 冉敬, 杜谷, 王凤玉. X射线衍射全谱拟合法快速分析长石矿物含量[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(5): 489-494. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610110154
Ran J, Du G, Wang F Y. Rapid analysis of feldspar by X-ray diffractometry Rietveld refinement method[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(5): 489-494. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201610110154
[15] 冉敬, 郭创锋, 杜谷, 等. X射线衍射全谱拟合法分析蓝晶石的矿物含量[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6): 660-667. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201902220025
Ran J, Guo C F, Du G, et al. Quantitative analysis of kineral composition of kyanite by X-ray diffraction with Rietveld refinement method[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6): 660-667. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201902220025
[16] 王琦, 马龙, 黄康俊, 等. 蒙脱石, 高岭石和伊利石X射线衍射定量分析[J]. 贵州地质, 2021, 38(1): 71-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ202101011.htm
Wang Q, Ma L, Huang K J, et al. Quantitative analysis of kaolinite, illite and montmorillonite by X-ray diffraction[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2021, 38(1): 71-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ202101011.htm
[17] 孙灵芝, 凌宗成, 张江, 等. 基于辐射传输模型的月表铁镁质矿物定量反演: 以嫦娥三号着陆区为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(1): 43-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201601007.htm
Sun L Z, Ling Z C, Zhang J, et al. Radiative transfer modeling of Lunar mafic minerals: A case study in Chang'E-3 landing region[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(1): 43-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201601007.htm
[18] 曹会, 邢立新, 潘军, 等. 金厂沟梁地区土壤含水黏土矿物含量短波红外光谱反演[J]. 江西农业学报, 2013, 25(1): 55-59.
Cao H, Xing L X, Pan J, et al. Inversion of hydrated clay mineral content in soil of Jinchanggouliang area based on SWIR[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2013, 25(1): 55-59.
[19] 张弘, 高鹏鑫, 高卿楠. 热红外反射光谱技术在石英含量评价中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(5): 710-719. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202104190053
Zhang H, Gao P X, Gao Q N. Application of thermal infrared reflectance spectroscopy in the evaluation of quartz content[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(5): 710-719. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202104190053
[20] 丛丽娟, 贾志业, 梁秀娟, 等. 岩矿石NIR光谱特征与地球化学异常成分之间的关系: 以内蒙古朱拉扎嘎金矿为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(5): 299-305. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201705031.htm
Cong L J, Jia Z Y, Liang X J, et al. The relationship between the NIR spectral characteristics and geochemical anomaly components: Taking Zhulazhaga gold deposit of Inner Mongolia as an example[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(5): 299-305. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201705031.htm
[21] 王祝文, 刘菁华, 黄茜. 确定黏土矿物含量的自然伽马能谱测井方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2007, 19(2): 108-111.
Wang Z W, Liu J H, Huang Q. Using natural Gamma-ray spectroscopy log method to determine clay mineral content[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2007, 19(2): 108-111.
[22] 赵政璋, 李永铁. 青藏高原中生界沉积相及油气储盖层特征[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000.
Zhao Z Z, Li Y T. The features of Mesozoic sedimentary facies, reservoir and seal rock in Xizang[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2000.
[23] 曹竣锋, 宋春彦, 付修根, 等. 藏北羌塘盆地羌资5井二叠系碳酸盐岩储层特征及影响因素[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2014, 34(2): 86-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201402013.htm
Cao J F, Song C Y, Fu X G, et al. Permian carbonate reservoirs from the Qiangzi-5 well in Qiangtang Basin, northern Xizang: Characteristics and influencing factors[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2014, 34(2): 86-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201402013.htm
[24] 史维鑫, 易锦俊, 王浩, 等. 马坑铁矿钻孔岩心红外光谱特征及蚀变分带特征研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(6): 143-152. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060004
Shi W X, Yi J J, Wang H, et al. Study on the characteristics of the infrared spectrum and the alteration zoning of drill core in the Makengiron deposit[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(6): 143-152. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060004
[25] 陈康, 纪广轩, 朱有峰, 等. 基于高光谱岩心扫描系统研究城门山铁路坎铜矿床的蚀变特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(6): 944-953. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060005
Chen K, Ji G X, Zhu Y F, et al. Study on alteration characteristics of the Chengmenshan Tielukan copper deposit by a hyperspectral core scanning system[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(6): 944-953. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060005
[26] Laukamp C, Caccetta M, Chia J, et al. The uses, abuses and opportunities for hyperspestral technologies and derived geoscience information[C]//Proceedings of Geo-computing Conference Brisbane: AIG Bulletin, 2010: 73-76.
[27] 何将启, 丁汝鑫, 梁世友, 等. 基于磷灰石裂变径迹约束的北黄海盆地热演化研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(1): 3347-3353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201410021.htm
He J Q, Ding R X, Liang S Y, et al. Study of thermal evolution of the North Yellow Sea Basin based on apatite fission track data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(1): 3347-3353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201410021.htm
[28] 李才, 王天武, 杨德明, 等. 西藏羌塘中央隆起区物质组成与构造演化[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版): , 2001, 31(1): 25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200101004.htm
Li C, Wang T W, Yang D M, et al. The lithological composition and tectonic evolution of Qiangtang central uplift region, Xizang[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2001, 31(1): 25-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200101004.htm
[29] 周张健. 蒙脱石伊利石化的控制因素、转化机制及其转化模型的研究综述[J]. 地质科技情报, 1994, 13(4): 41-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ404.008.htm
Zhou Z J. Summary of the studying for illitization of the smectite on its controlling factors, transformation mechanism and models[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1994, 13(4): 41-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ404.008.htm
[30] 罗瑞兰, 卢书锷, 周国清, 等. 蒙脱石的成岩转化与油气的形成和初次运移[J]. 石油实验地质, 1985, 7(4): 257-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD198504001.htm
Luo R L, Lu S E, Zhou G Q, et al. Diagenetic transformation of montmorillonite and primary migration of hydrocarbon, and oil-gas generation[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 1985, 7(4): 257-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD198504001.htm
[31] 黄擎宇, 刘伟, 张艳秋, 等. 白云石化作用及白云岩储层研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(5): 539-551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201505004.htm
Huang Q Y, Liu W, Zhang Y Q, et al. Progress of research on dolomitization and dolomite reservoir[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(5): 539-551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201505004.htm
-



 下载:
下载: