A Review of Research Progress on the Analytical Method of Large-n Detrital Zircon U-Pb Geochronology
-
摘要:
碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学是识别沉积物来源和确定地层最大沉积年龄的重要工具。利用激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱(LA-ICP-MS)进行物源分析的碎屑锆石测试数量为60~120颗,在这个范围内,年龄组分通常不能从样本中识别出来。近年来,为提高物源分析的可靠性,LA-ICP-MS测试要求有更多数量的锆石颗粒(n≥300),甚至大于1000颗的大样本量(large-n)试验。大样本量碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学的出现对数据测试方法、处理和评估都提出了挑战。本文通过对国内外大样本量文献进行梳理,总结了大样本量碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学在测试方法、数据处理以及数据评估方面的进展。首先,单颗粒测试需要对U、Pb同位素信号进行快速获取,这可以通过改进气溶胶传输效率实现,“峰值”信号模式代替“平顶”信号接收也可实现快速测试。其次,大样本量产生的数据,需要高效的数据处理协议和强大的软件(如Iolite)进行处理,以减少实验室间比较的误差;针对U-Pb数据处理流程,介绍了同位素分馏校正以及不确定度传播等方面的方法优化;此外,还引入了累积计数法和线性回归校正法两种处理方法专门处理“峰形”信号。在数据评估方面,新的U-Pb和Pb-Pb年龄不谐和度计算方法的提出,如采用Aitchison谐和距离,使数据过滤更加合理。基于上述新进展,对仪器和处理软件的选取进行了讨论,并对未来大样本量碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学分析的自动化、规范化提出了展望。基于已有研究,未来大样本量碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学的发展具有广阔前景,在物源示踪及确定地层年代等研究中将发挥更大的作用。
-
关键词:
- 碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学 /
- 大样本量 /
- 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱法 /
- 快速U-Pb定年 /
- 不谐和度
Abstract:BACKGROUND Detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology is an important tool for identifying sedimentary provenance and determining the maximum depositional age. The numbers of grains for detrital zircon provenance investigations using laser-ablation inductively coupled-plasma mass spectrometer (LA-ICP-MS) typically range from 60 to 120. In this range, age components are commonly not identified from the sample aliquot. In order to improve the reliability of provenance investigation, analysis of more grains (n≥300) or even the large-n aliquot with more than 1000 grains (n > 1000) are required. The emergence of large-n detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology is challenging the methods of data measurement, reduction and evaluation.
OBJECTIVES To summarize the progress of measurement, data reduction and data evaluation of large-n detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology.
METHODS By summarizing the method innovation of domestic and foreign literature.
RESULTS Firstly, each measurement requires rapid acquisition of U and Pb isotope signals, which can be conducted by improving the transmission efficiency of aerosol. The "flat" signal acquisition time can be shortened or transformed to a "peak" signal mode for rapid measurement. Secondly, large-n data require efficient data reduction protocol or powerful software (e.g. iolite) to improve visualization and reduce the variability between inter-laboratory comparisons. For U-Pb data processing flow, several optimized methods are introduced for fractionation correction and propagating uncertainty. In addition, total integrated counts and linear regression correction are introduced to specially process "peak" signals. Thirdly, the new calculation method of U-Pb and Pb-Pb age discordance, such as using Aitchison concordia distance, makes data filtering more reasonable. Based on recent research progress, the future of automation and standardization of large-n detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology is discussed and advice on the selection of instruments and reduction software is provided.
CONCLUSIONS In the future, the development of large-n detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology has great prospects, and will play a greater role in the study of provenance tracing and stratigraphic dating.
-

-
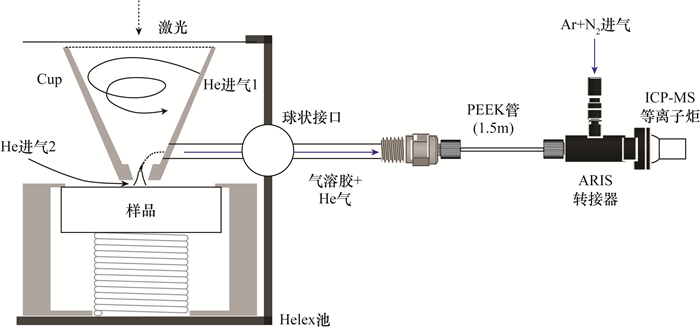
图 1 气溶胶快速引入系统(Aerosol Rapid Introduction System,ARIS)与激光和ICP-MS连接示意图:激光端与PEEK管相接,并通过ARIS转接器将气溶胶传输至ICP-MS(据文献[25])
Figure 1.
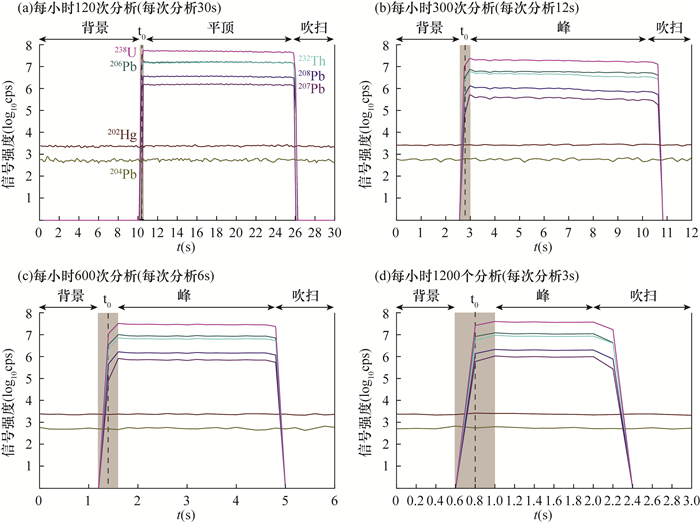
图 2 单颗粒分析时间分别为30s(a)、12s(b)、6s(c)和3s(d)条件下的信号特征。信号强度以对数坐标呈现,不同颜色的线条分别表示不同同位素的信号强度(据文献[26])
Figure 2.
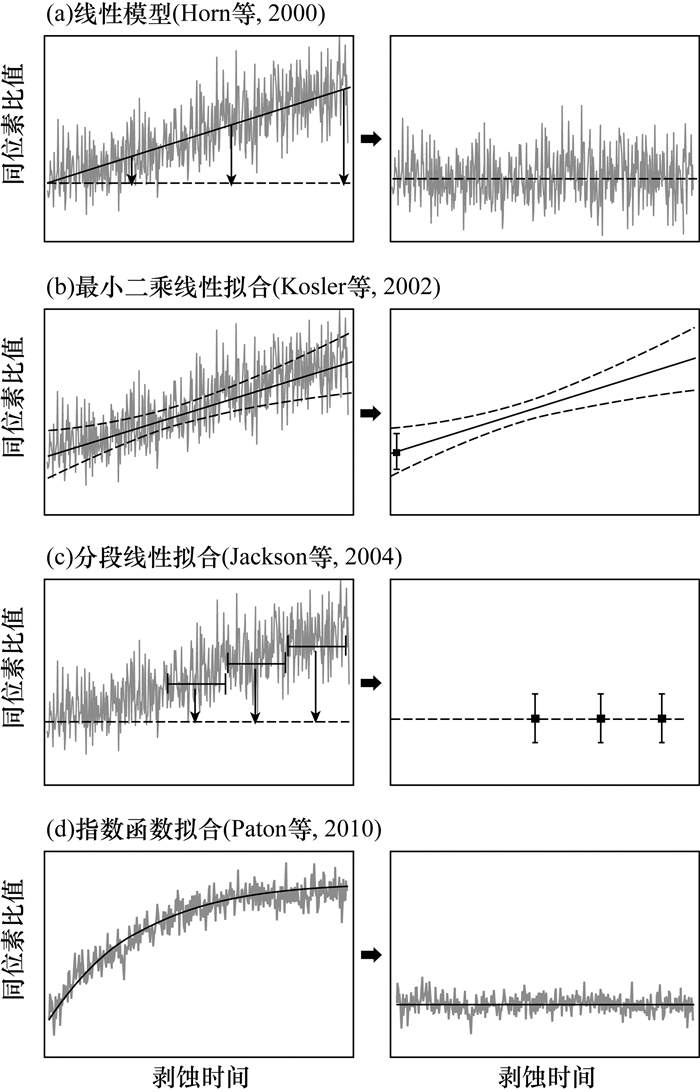
图 3 线性拟合(a、b、c)和指数函数拟合(d)的激光诱导元素分馏校正方法(据文献[37])
Figure 3.
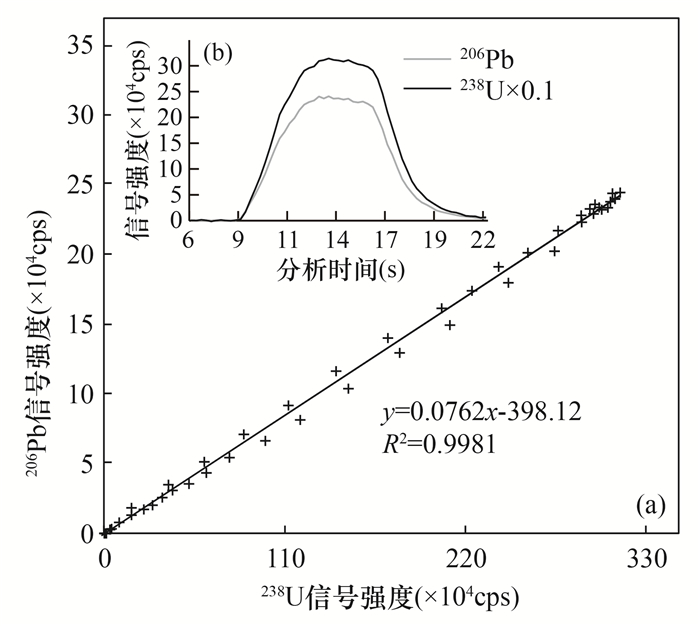
图 4 (a) 采用LRC法计算206Pb/238U的比值;(b)206Pb和238U的“峰形”信号图(据文献[31])
Figure 4.
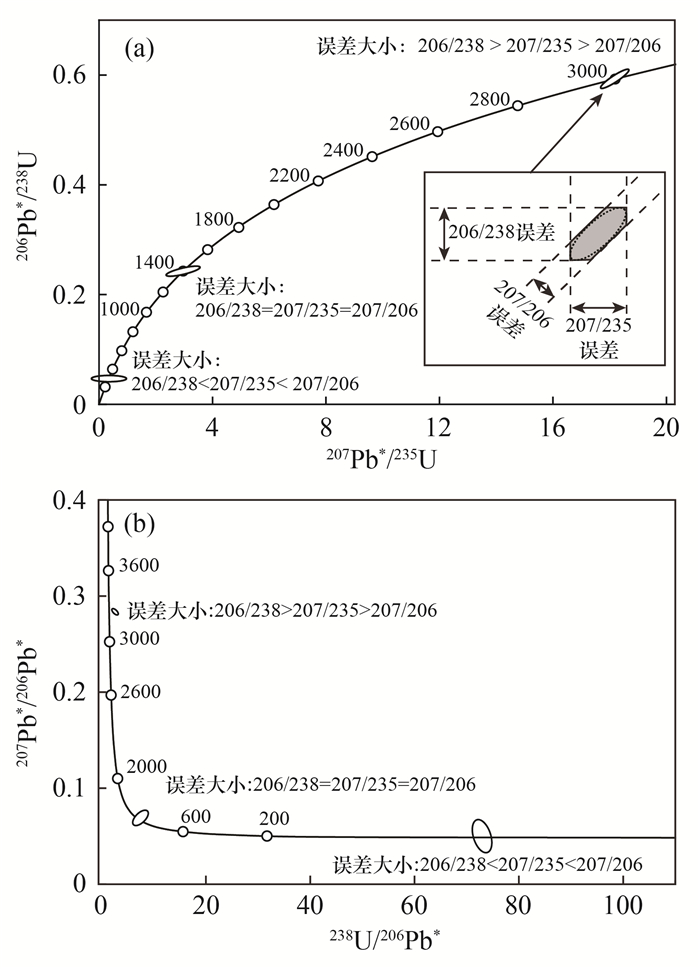
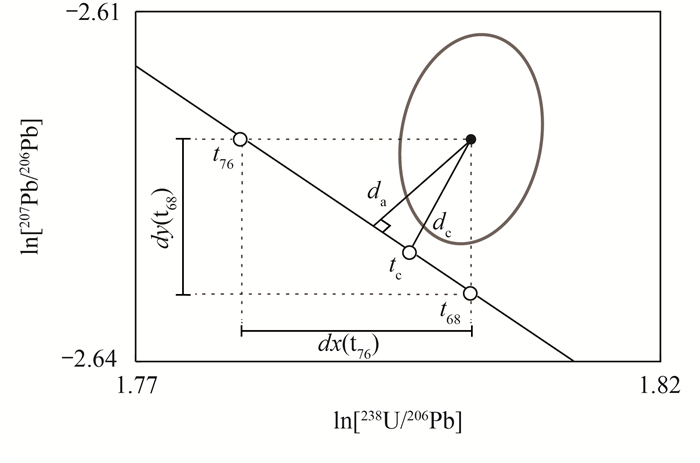
图 6 两个不谐和度对数比值距离的定义:da表示数据点到谐和线的垂直Aitchison距离;dc表示数据点与计算的谐和年龄(tc)之间的Aitchison距离(据文献[60])
Figure 6.
表 1 不谐和度计算方法及特点
Table 1. Different definitions of discordance and their characteristics
参数 计算方法 表示公式 特点 dr[61] 相对年龄差异 dr=1- t68/ t76 滤除年轻的年龄组分 dt[57] 绝对年龄差异 dt =t76- t68 滤除年老的年龄组分 dp[55] U-Pb比值 dp=Prob(s>S~χ22) 影响准确度和精度 dsk[62] 地幔演化模型 $d_{\mathrm{sk}}=1-\left[\frac{{ }^{238} \mathrm{U}}{{ }^{206} \mathrm{~Pb}}\right] /\left[\frac{{ }^{238} \mathrm{U}}{{ }^{206} \mathrm{~Pb}}\right]^*$ 滤除年老组分 da[60] Aitchison距离 $d_{\mathrm{a}}=\mathrm{d} x\left(t_{68}\right) \sin \left[\arctan \frac{\mathrm{d} y\left(t_{76}\right)}{\mathrm{d} x\left(t_{68}\right)}\right]$ 滤除1000~2000Ma的锆石颗粒 dc[60] Aitchison谐和距离 $d_{\mathrm{c}}=\operatorname{sgn}\left(t_{76}-t_{68}\right) \sqrt{\mathrm{d} x\left(t_{\mathrm{c}}\right)^2+\mathrm{d} y\left(t_{\mathrm{e}}\right)^2}$ 最合理 DMS[63] 年龄差异绝对值的较小值 $D_{\mathrm{MS}}=\left\{\left|t_{68}-t_{75}\right|, \left|t_{76}-t_{75}\right|\right\}$ 滤除较老的年龄组分 -
[1] Fedo C M, Sircombe K N, Rainbird R H. Detrital zircon analysis of the sedimentary record[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, Geoscience World, 2003, 53(1): 277-303. doi: 10.2113/0530277
[2] Shaulis B, Lapen T J, Toms A. Signal linearity of an exten-ded range pulse counting detector: Applications to accurate and precise U-Pb dating of zircon by laser ablation quadrupole ICP-MS[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2010, 11(11): Q0AA11.
[3] 徐杰, 姜在兴. 碎屑岩物源研究进展与展望[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(3): 379-396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201903001.htm
Xu J, Jiang Z X. Provenance analysis of clastic rocks: Current research status and prospect[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2019, 21(3): 379-396. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201903001.htm
[4] 杨仁超, 李进步, 樊爱萍, 等. 陆源沉积岩物源分析研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(1): 99-107. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2013.01.018
Yang R C, Li J B, Fan A P, et al. Research progress and development tendency of provenance analysis on terrigenous sedimentary rocks[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(1): 99-107. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2013.01.018
[5] Moecher D P, Samson S D. Differential zircon fertility of source terranes and natural bias in the detrital zircon record: Implications for sedimentary provenance analysis[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2006, 247(3): 252-266.
[6] Thomas W A. Detrital-zircon geochronology and sedimentary provenance[J]. Lithosphere, 2011, 3(4): 304-308. doi: 10.1130/RF.L001.1
[7] Andersen T, Kristoffersen M, Elburg M A. How far can we trust provenance and crustal evolution information from detrital zircons? A South African case study[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 34: 129-148. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.03.003
[8] Hadlari T, Swindles G T, Galloway J M, et al. 1.8 billion years of detrital zircon recycling calibrates a refractory part of Earth's sedimentary cycle[J]. PLOS ONE, 2015, 10(12): e0144727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144727
[9] Copeland P. On the use of geochronology of detrital grains in determining the time of deposition of clastic sedimentary strata[J]. Basin Research, European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, 2020, 32(6): 1532-1546.
[10] Sharman G R, Malkowski M A. Needles in a haystack: Detrital zircon U-Pb ages and the maximum depositional age of modern global sediment[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 203: 103109. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103109
[11] Wang P, Zheng H, Wang Y, et al. Sedimentology, geochronology, and provenance of the late Cenozoic "Yangtze Gravel": Implications for lower Yangtze River reorganization and tectonic evolution in southeast China[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2022, 134(1-2): 463-486. doi: 10.1130/B35851.1
[12] Zhang J, Zhang B, Zhao H. Timing of amalgamation of the Alxa Block and the North China Block: Constraints based on detrital zircon U-Pb ages and sedimentologic and structural evidence[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, 668-669: 65-81. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.12.006
[13] Huang X, Song J, Yue W, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb ages in the East China seas: Implications for provenance analysis and sediment budgeting[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(5): 398. doi: 10.3390/min10050398
[14] Iizuka T, Campbell I H, Allen C M, et al. Evolution of the African continental crust as recorded by U-Pb, Lu-Hf and O isotopes in detrital zircons from modern rivers[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2013, 107: 96-120. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.12.028
[15] White C, Gehrels G E, Pecha M, et al. U-Pb and Hf isotope analysis of detrital zircons from Paleozoic strata of the southern Alexander terrane (southeast Alaska)[J]. Lithosphere, 2016, 8(1): 83-96. doi: 10.1130/L475.1
[16] Vermeesch P. How many grains are needed for a provenance study?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 224(3-4): 441-451. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2004.05.037
[17] Dodson M H, Compston W, Williams I S, et al. A search for ancient detrital zircons in Zimbabwean sediments[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 1988, 145(6): 977-983. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.145.6.0977
[18] Andersen T. Detrital zircons as tracers of sedimentary provenance: Limiting conditions from statistics and numerical simulation[J]. Chemical Geology, 2005, 216(3): 249-270.
[19] Pullen A, Ibáñez-Mejía M, Gehrels G E, et al. What happens when n=1000? Creating large-n geochronological datasets with LA-ICP-MS for geologic investigations[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29(6): 971-980. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00024B
[20] Saylor J E, Sundell K E. Quantifying comparison of large detrital geochronology data sets[J]. Geosphere, 2016, 12(1): 203-220. doi: 10.1130/GES01237.1
[21] Pettit B S, Blum M, Pecha M, et al. Detrital-zircon U-Pb paleodrainage reconstruction and geochronology of the Campanian Blackhawk-Castlegate Succession, Wasatch Plateau and Book Cliffs, Utah, U.S.A. [J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2019, 89(4): 273-292. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2019.18
[22] Coutts D S, Matthews W A, Hubbard S M. Assessment of widely used methods to derive depositional ages from detrital zircon populations[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2019, 10(4): 1421-1435. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2018.11.002
[23] Gray A L. Solid sample introduction by laser ablation for inductively coupled plasma source mass spectrometry[J]. The Analyst, 1985, 110(5): 551-556. doi: 10.1039/an9851000551
[24] Matthews W A, Guest B. A practical approach for collecting large-n detrital zircon U-Pb data sets by quadrupole LA-ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2017, 41(2): 161-180. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12146
[25] Chew D, Drost K, Petrus J A. Ultrafast, >50Hz LA-ICP-MS spot analysis applied to U-Pb dating of zircon and other U-bearing minerals[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2019, 43(1): 39-60. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12257
[26] Sundell K E, Gehrels G E, Pecha M E. Rapid U-Pb geochronology by laser ablation multi-collector ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2021, 45(1): 37-57. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12355
[27] van Acker T, van Malderen S J M, van Heerden M, et al. High-resolution laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry imaging of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxic side effects[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, 945: 23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2016.10.014
[28] van Malderen S J M, Managh A J, Sharp B L, et al. Recent developments in the design of rapid response cells for laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry and their impact on bioimaging applications[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2016, 31(2): 423-439. doi: 10.1039/C5JA00430F
[29] Cottle J M, Horstwood M S A, Parrish R R. A new approach to single shot laser ablation analysis and its application to in situ Pb/U geochronology[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2009, 24(10): 1355-1363. doi: 10.1039/b821899d
[30] Cottle J M, Kylander-Clark A R, Vrijmoed J C. U-Th/Pb geochronology of detrital zircon and monazite by single shot laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (SS-LA-ICPMS)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 332-333: 136-147. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.09.035
[31] 冯彦同, 张文, 胡兆初, 等. 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱仪新分析模式及其在地球科学中的应用[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2022, 52(1): 98-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202201005.htm
Feng Y T, Zhang W, Hu Z C, et al. A new analytical mode and application of the laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer in the Earth sciences[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2022, 65(1): 182-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202201005.htm
[32] Griffin W L. GLITTER: Data reduction software for laser ablation ICP-MS[M]//Laser Ablation ICP-MS in the Earth Sciences: Current practices and outstanding issues. Mineralogical Association of Canada, 2008: 308-311.
[33] Paton C, Hellstrom J, Paul B, et al. Iolite: Freeware for the visualisation and processing of mass spectrometric data[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2011, 26(12): 2508-2518. doi: 10.1039/c1ja10172b
[34] Andersen T, Elburg M A, Magwaza B N. Sources of bias in detrital zircon geochronology: Discordance, concealed lead loss and common lead correction[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 197: 102899. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102899
[35] Garcia C, Lindner H, Niemax K. Laser ablation induc-tively coupled plasma mass spectrometry—Current shortcomings, practical suggestions for improving perfor-mance, and experiments to guide future development[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2009, 24(1): 14-26. doi: 10.1039/B813124B
[36] 李献华, 柳小明, 刘勇胜, 等. LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb定年的准确度: 多实验室对比分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2015, 45(9): 1294-1303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201509004.htm
Li X H, Liu X M, Liu Y S, et al. Accuracy of LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb age determination: An inter-laboratory comparison[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2015, 58: 1722-1730. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201509004.htm
[37] Paton C, Woodhead J D, Hellstrom J C, et al. Improved laser ablation U-Pb zircon geochronology through robust downhole fractionation correction: Improved laser ablation U-Pb geochronology[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2010, 11(3): 1-36.
[38] Heinrich C A, Pettke T, Halter W E, et al. Quantitative multi-element analysis of minerals, fluid and melt inclusions by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(18): 3473-3497. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00084-X
[39] 罗涛. LA-ICP-MS分析过程中元素分馏效应机理及其在副矿物U-Pb年代学中的应用研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.
Luo T. Further investigation of elemental fractionation in LA-ICP-MS: Implications for non-matrix-matched analysis of the in situ U-Pb dating of accessory minerals[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018.
[40] LaHaye N L, Harilal S S, Diwakar P K, et al. The effect of ultrafast laser wavelength on ablation properties and implications on sample introduction in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 114(2): 023103. doi: 10.1063/1.4812491
[41] 王辉, 汪方跃, 关炳庭, 等. 激光能量密度对LA-ICP-MS分析数据质量的影响研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6): 609-619. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201903010029
Wang H, Wang F Y, Guan B T, et al. Effect of laser energy density on data quality during LA-ICP-MS measurement[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6): 609-619. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201903010029
[42] 侯振辉. 激光剥蚀束斑大小及深度对锆石U-Pb定年准确度的影响[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(6): 1067-1076. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202006002.htm
Hou Z H. Assessing the effects of aperture and depth of hole ablated by laser beam on the accuracy of zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020, 39(6): 1067-1076. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202006002.htm
[43] 周亮亮, 魏均启, 王芳, 等. LA-ICP-MS工作参数优化及在锆石U-Pb定年分析中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(4): 350-359. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201701160007
Zhou L L, Wei J Q, Wang F, et al. Optimization of the working parameters of LA-ICP-MS and its application to zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(4): 350-359. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201701160007
[44] Horn I, Rudnick R L, McDonough W F. Precise elemental and isotope ratio determination by simultaneous solution nebulization and laser ablation-ICP-MS: Application to U-Pb geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 164(3-4): 281-301. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00168-0
[45] Košler J, Longerich H P, Tubrett M N. Effect of oxygen on laser-induced elemental fractionation in LA-ICP-MS analysis[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2002, 374(2): 251-254. doi: 10.1007/s00216-002-1481-x
[46] Jackson S E, Pearson N J, Griffin W L, et al. The application of laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry to in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211(1): 47-69.
[47] Horstwood M S A, Košler J, Gehrels G, et al. Community- derived standards for LA-ICP-MS U-(Th-)Pb geochronology—Uncertainty propagation, age interpretation and data reporting[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2016, 40(3): 311-332. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2016.00379.x
[48] Jaffey A H, Flynn K F, Glendenin L E, et al. Precision measurement of half-lives and specific activities of 235U and 238U[J]. Physical Review C, 1971, 4(5): 1889-1906. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevC.4.1889
[49] Johnston S, Gehrels G, Valencia V, et al. Small-volume U-Pb zircon geochronology by laser ablation-multicollector-ICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 259(3): 218-229.
[50] Fietzke J, Liebetrau V, Günther D, et al. An alternative data acquisition and evaluation strategy for improved isotope ratio precision using LA-MC-ICP-MS applied to stable and radiogenic strontium isotopes in carbonates[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2008, 23(7): 955-961. doi: 10.1039/b717706b
[51] Bouchet S, Bérail S, Amouroux D. Hg compound-specific isotope analysis at ultratrace levels using an on line gas chromatographic preconcentration and separation strategy coupled to multicollector-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 90(13): 7809-7816. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04555
[52] Wetherill G W. Discordant uranium-lead ages, I[J]. Eos, 1956, 37(3): 320-326.
[53] Tera F, Wasserburg G J. U-Th-Pb systematics in three Apollo 14 basalts and the problem of initial Pb in lunar rocks[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1972, 14(3): 281-304. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(72)90128-8
[54] 张凌, 王平, 陈玺赟, 等. 碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学数据获取、分析与比较[J]. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(4): 414-430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ202004008.htm
Zhang L, Wang P, Chen X Y, et al. Review in detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology: Data acquisition, analysis and comparison[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2020, 35(4): 414-430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ202004008.htm
[55] Spencer C J, Kirkland C L, Taylor R J M. Strategies towards statistically robust interpretations of in situ U-Pb zircon geochronology[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2016, 7(4): 581-589. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2015.11.006
[56] Gehrels G E, Valencia V A, Ruiz J. Enhanced precision, accuracy, efficiency, and spatial resolution of U-Pb ages by laser ablation-multicollector-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2008, 9(3): Q03017.
[57] Puetz S J, Ganade C E, Zimmermann U, et al. Statistical analyses of global U-Pb database 2017[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2018, 9(1): 121-145. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2017.06.001
[58] Vermeesch P. Isoplot R: A free and open toolbox for geochronology[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2018, 9(5): 1479-1493. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2018.04.001
[59] Ludwig K R. On the treatment of concordant uranium-lead ages[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(4): 665-676. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00059-3
[60] Vermeesch P. On the treatment of discordant detrital zircon U-Pb data[J]. Geochronology, 2021, 3(1): 247-257. doi: 10.5194/gchron-3-247-2021
[61] Gehrels G. Detrital zircon U-Pb geochronology: Current methods and new opportunities[M]//Tectonics of Sedimentary Basins: Recent Advances, 2011: 45-62.
[62] Stacey J S, Kramers J D. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two-stage model[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1975, 26(2): 207-221. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(75)90088-6
[63] Puetz S J, Spencer C J, Ganade C E. Analyses from a validated global U-Pb detrital zircon database: Enhanced methods for filtering discordant U-Pb zircon analyses and optimizing crystallization age estimates[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2021, 220: 103745. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103745
[64] Bleiner D, Bogaerts A. Computer simulations of sample chambers for laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma spectrometry[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2007, 62(2): 155-168. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2007.02.010
[65] Gundlach-Graham A, Günther D. Toward faster and higher resolution LA-ICPMS imaging: On the co-evolution of LA cell design and ICPMS instrumentation[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2016, 408(11): 2687-2695. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-9251-8
[66] Lindner H, Autrique D, Garcia C C, et al. Optimized transport setup for high repetition rate pulse-separated analysis in laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry, American Chemical Society, 2009, 81(11): 4241-4248.
[67] Halicz L, Günther D. Quantitative analysis of silicates using LA-ICP-MS with liquid calibration[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2004, 19(12): 1539-1545. doi: 10.1039/B410132D
[68] Gurevich E L, Hergenröder R. A simple laser ICP-MS ablation cell with wash-out time less than 100ms[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2007, 22(9): 1043-1050. doi: 10.1039/b704700b
[69] Chew D, Drost K, Marsh J H, et al. LA-ICP-MS imaging in the geosciences and its applications to geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2021, 559: 119917. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119917
[70] 李凤春, 侯明兰, 栾日坚, 等. 电感耦合等离子体质谱仪与激光器联用测量条件优化及其在锆石U-Pb定年中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2016, 35(1): 17-23. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.01.004
Li F C, Hou M L, Luan R J, et al. Optimization of analytical conditions for LA-ICP-MS and its application to zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2016, 35(1): 17-23. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2016.01.004
[71] Jakubowski N, Prohaska T, Vanhaecke F, et al. Inductively coupled plasma- and glow discharge plasma-sector field mass spectrometry Part Ⅱ. Applications[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2011, 26(4): 727-757. doi: 10.1039/c0ja00007h
[72] Hendriks L, Gundlach-Graham A, Hattendorf B, et al. Characterization of a new ICP-TOFMS instrument with continuous and discrete introduction of solutions[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2017, 32(3): 548-561. doi: 10.1039/C6JA00400H
[73] Borovinskaya O, Gschwind S, Hattendorf B, et al. Simul-taneous mass quantification of nanoparticles of different composition in a mixture by microdroplet generator-ICPTOFMS[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, 86(16): 8142-8148. doi: 10.1021/ac501150c
[74] Tanner M, Günther D. In torch laser ablation sampling for inductively coupled plasma time of flight mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2006, 21(9): 941-947. doi: 10.1039/B602915A
[75] Guilhaus M. Essential elements of time-of-flight mass spectrometry in combination with the inductively coupled plasma ion source[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy, 2000, 55(10): 1511-1525. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(00)00261-5
[76] Thompson J M, Danyushevsky L V, Borovinskaya O, et al. Time-of-flight ICP-MS laser ablation zircon geochronology: Assessment and comparison against quadrupole ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2020, 35(10): 2282-2297. doi: 10.1039/D0JA00252F
[77] Košler J, Fonneland H, Sylvester P, et al. U-Pb dating of detrital zircons for sediment provenance studies—A comparison of laser ablation ICPMS and SIMS techniques[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 182(2): 605-618.
[78] Liu Y, Hu Z, Zong K, et al. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15): 1535-1546. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
[79] McLean N M, Bowring J F, Gehrels G. Algorithms and software for U-Pb geochronology by LA-ICPMS: U-Pb LA-ICPMS algorithms and software[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2016, 17(7): 2480-2496. doi: 10.1002/2015GC006097
[80] Bowring J F, McLean N M, Bowring S A. Engineering cyber infrastructure for U-Pb geochronology: Tripoli and U-Pb redux[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2011, 12(6): Q0AA19.
-



 下载:
下载: