Elemental Geochemical Characteristics of Topsoil in Tangchang Town, Chengdu, Sichuan Province and Quality Evaluation
-
摘要:
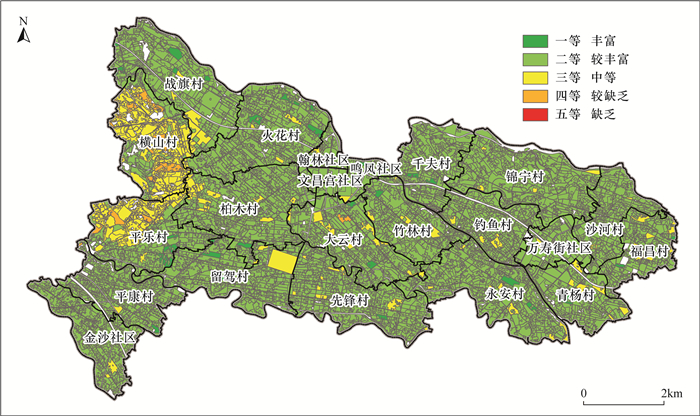
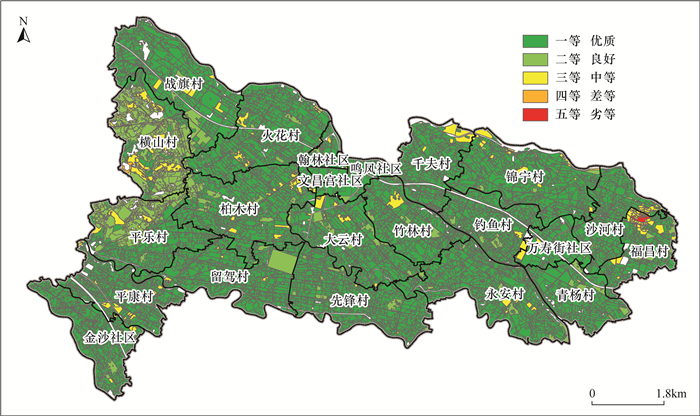
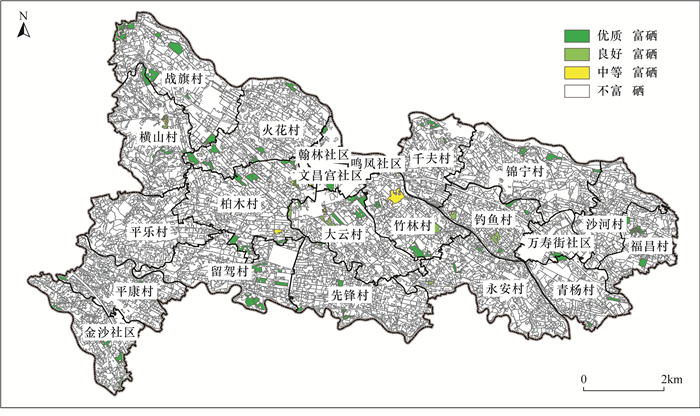
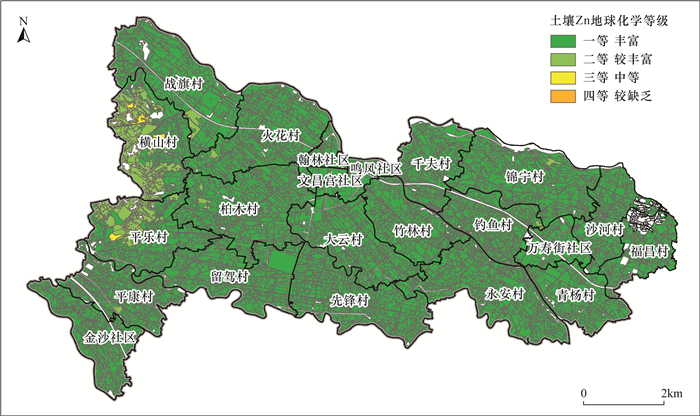
土壤质量状况直接关系到农产品安全和人类健康,是农业种植和土地规划重要的参考依据。四川成都唐昌镇作为成都市重要的菜篮子基地,农业种植发达,目前该地区土壤质量状况尚不清楚。为了准确掌握当前唐昌镇农业种植区表层土壤元素含量特征和质量等级,本文通过开展1∶5万土壤质量地球化学调查,采集表层土壤810件,采用X射线荧光光谱法、电感耦合等离子体质谱法、原子荧光光谱法等方法测定了N、P、K、As、Cd、Hg、Pb、Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、Se等元素含量和pH值, 进行土壤养分等级、土壤环境质量等级、土壤地球化学综合等级评价。结果表明:①与全国表层土壤相比,研究区表层土壤略富集Zn、Pb,较富集Se,强烈富集N、P、Cd、Hg,土壤总体呈弱酸性。②土壤养分综合等级以二等较丰富为主,面积占比88.0%,土壤肥力较丰富;土壤8项重金属元素环境质量等级中的一等土壤面积占比均大于96.0%,综合环境质量等级以一等清洁型为主,占比达98.06%。土壤综合质量以一等优质级为主,占比85.85%。③区内富硒土壤面积2.49km2,占比3.7%,零星分布于研究区中部;富铜土壤面积63.13km2,占94.0%;富锌土壤面积63.31km2,占比94.17%。综上所述,唐昌镇地区表层土壤养分较丰富,土壤环境整体清洁,土壤综合质量属优质级。
Abstract:BACKGROUND The quality of soil is directly related to human health and the safety of agricultural products, which has important references for agricultural planting and land planning. As an important vegetable basket base in Chengdu, Tangchang Town has developed agricultural planting, but the recent soil quality in the region is still unclear.
OBJECTIVES In order to accurately understand the current content of nutrient and heavy metal elemental characteristics and soil quality grade of topsoil in the Tangchang agricultural planting area.
METHODS According to 1∶50000 soil quality geochemical survey, 810 topsoil samples were collected. The contents of N, P, K, As, Cd, Hg, Pb, Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, Se and pH in these soil samples were determined by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, atomic fluorescence spectrometry, element analyzer and ion selective electrode method. The element geochemical characteristics and soil nutrient grade, soil environmental quality grade and comprehensive soil geochemical grade were then evaluated.
RESULTS (1) Compared with the general topsoil in China, Zn and Pb in the topsoil of the study area are slightly enriched, Se is relatively enriched, N, P, Cd and Hg are strongly enriched. The topsoil is generally weakly acidic. (2) The comprehensive grade of soil nutrients is rich in second grade, accounting for 88.0% of the area, and the soil fertility is rich. The proportion of the first grade soil area in the environmental quality grade of the eight heavy metal elements in the soil is more than 96.0%, and the comprehensive environmental quality grade is dominated by first grade clean type, accounting for 98.06%. The comprehensive quality of soil is mainly grade one, accounting for 85.85%. (3) The area of selenium-rich soil in the region is 2.49km2, accounting for 3.7%, sporadically distributed in the central study area. Copper-rich soil area is 63.13km2, accounting for 94.0%, and zinc-rich soil area is 63.31km2, accounting for 94.17%.
CONCLUSIONS In summary, the nutrients of topsoil in Tangchang Town are rich, the soil environment is clean and the comprehensive quality of the soil is high.
-

-
表 1 土壤元素分析方法及检出限
Table 1. Analytical methods of soil samples and their detection limits
元素 分析方法 检出限 单位 元素(指标) 分析方法 检出限 单位 本文测试 规范要求 本文测试 规范要求 Cu XRF 1 1 10-6 Cr XRF 5 5 10-6 Pb XRF 2 2 10-6 As AFS 0.5 1 10-6 Zn XRF 4 4 10-6 Hg AFS 0.0003 0.0005 10-6 Ni XRF 2 2 10-6 Se AFS 0.01 0.01 10-6 Cd ICP-MS 0.01 0.03 10-6 N COB 20 20 10-6 K XRF 0.01 0.05 % pH ISE 0.1 0.1 1 P XRF 10 10 10-6 表 2 土壤中N、P、K养分指标等级划分标准
Table 2. Classification standard of N, P, K nutrient index in soil
指标 土壤养分指标等级 一等
(丰富)二等
(较丰富)三等
(中等)四等
(较缺乏)五等
(缺乏)N(mg/g) >2.0 1.5~2.0 1.0~1.5 0.75~1.0 ≤0.75 P(mg/g) >1.0 0.8~1.0 0.6~0.8 0.4~0.6 ≤0.4 K(mg/g) >25 20~25 15~20 10~15 ≤10 表 3 土壤元素地球化学参数
Table 3. Geochemical parameters of elements in soil
指标 N P K Se pH Cu Zn Pb Cr Ni Cd As Hg N 783 776 733 780 788 758 761 771 775 783 777 774 752 X 1.33 1.12 24.11 0.34 6.17 34.3 105.5 31.9 91.7 37.1 0.22 9.63 0.14 Std 0.25 0.34 1.45 0.06 1.02 4.05 11.84 3.81 7.19 3.58 0.06 1.87 0.06 CV 0.19 0.31 0.06 0.19 0.16 0.12 0.11 0.12 0.08 0.10 0.28 0.19 0.42 Min 0.70 0.22 19.76 0.14 4.16 22.2 70.7 20.8 71.6 26.6 0.08 4.17 0.022 Max 2.00 2.14 27.98 0.53 9.04 46.2 140.0 43.3 112.0 47.6 0.40 15.20 0.32 Q 0.64 0.52 25 0.20 - 24 68 23 65 26 0.09 10 0.04 C 1.70 0.84 24 - - 32.7 89.4 40.4 86.2 35.5 0.34 10.3 0.11 K1 2.07 2.15 0.965 1.69 - 1.43 1.552 1.39 1.411 1.43 2.42 0.96 3.51 K2 0.8 1.3 1.0 - - 1.0 1.2 0.8 1.1 1.0 0.6 0.9 1.3 注:N、K含量单位为mg/g,其他元素为mg/kg,pH值为无量纲。Q代表全国表层土壤平均值[24],C代表成都经济区表层土壤背景值[23]。 表 4 研究区土壤养分等级评价
Table 4. Evaluation of soil nutrient grade in the study area
元素 土壤养分等级 一等
(丰富)二等
(较丰富)三等
(中等)四等
(缺乏)五等
(较缺乏)N 面积(km2) 0.10 5.76 58.71 2.71 0.06 比例(%) 0.15 8.55 87.19 4.02 0.09 P 面积(km2) 52.35 8.84 3.84 2.15 0.16 比例(%) 78.0 13.0 5.70 3.20 0.20 K 面积(km2) 9.79 52.64 4.72 0.19 0 比例(%) 14.54 78.17 7.01 0.28 0 养分综合 面积(km2) 0.91 59.25 6.66 0.51 0 比例(%) 1.35 88.00 9.90 0.76 0 表 5 研究区土壤环境等级评价
Table 5. Evaluation of soil environment grade in the study area
元素 土壤环境等级 一等
(清洁)二等
(轻微污染)三等
(轻度污染)四等
(中度污染)五等
(重度污染)As 面积(km2) 67.05 0.29 0 0 0 比例(%) 99.60 0.40 0 0 0 Cd 面积(km2) 66.70 0.72 0 0 0 比例(%) 98.89 0.11 0 0 0 Cr 面积(km2) 67.31 0.03 0 0 0 比例(%) 99.95 0.05 0 0 0 Cu 面积(km2) 67.01 2.11 0.03 0 0.01 比例(%) 96.90 3.05 0.04 0 0.01 Hg 面积(km2) 67.32 0.02 0 0 0 比例(%) 99.97 0.03 0 0 0 Ni 面积(km2) 67.34 0 0 0 0 比例(%) 100.0 0 0 0 0 Pb 面积(km2) 67.33 0.01 0 0 0 比例(%) 99.985 0.015 0 0 0 Zn 面积(km2) 67.07 0.228 0.001 0 0.039 比例(%) 99.600 0.339 0.002 0 0.058 环境综合 面积(km2) 66.03 1.23 0.03 - 0.05 比例(%) 98.06 1.83 0.04 - 0.07 -
[1] 郭志娟, 周亚龙, 王乔林, 等. 雄安新区土壤重金属污染特征及健康风险[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(1): 431-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.01.049
Guo Z J, Zhou Y L, Wang Q L, et al. Characteristics of soil heavy metal pollution and health risk in Xiong'an New District[J]. China Environment Science, 2021, 41(1): 431-441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.01.049
[2] 贺灵, 吴超, 曾道明, 等. 中国西南典型地质背景区土壤重金属分布及生态风险特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(3): 395-407. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101260016
He L, Wu C, Zeng D M, et al. Distribution of heavy metals and ecological risk of soils in the typical geological background region of southwest China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(3): 395-407. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101260016
[3] 韩伟, 王乔林, 宋云涛, 等. 四川省沐川县北部土壤硒地球化学特征与成因探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(1): 215-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202101026.htm
Han W, Wang Q L, Song Y T, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of selenium in soil in northern Muchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 215-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202101026.htm
[4] 陶春军, 周天健, 张笑春, 等. 安徽岳西翠兰产地土壤环境质量及种植适宜性评价研究[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(1): 261-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202001026.htm
Tao C J, Zhou T J, Zhang X C, et al. Research on soil environment quality and planting suitability evaluation of Cuilan producing area in Yuexi, Anhui Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(1): 261-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDI202001026.htm
[5] 陶春军, 史春鸿, 张笑蓉, 等. 淮北平原覆盖区土壤采样密度及其环境质量研究——以1∶5万高炉集幅为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(1): 200-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202101024.htm
Tao C J, Shi C H, Zhang X R, et al. Research on soil sampling density and environmental quality of Huaibei Plain covered area: A case study of 1∶50000 Gaoluji Sheet[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 200-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202101024.htm
[6] 杨帆, 张舜尧, 宋云涛, 等. 云南省盐津县1∶5万土地质量地球化学评价方法研究[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(6): 1318-1332. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202006020.htm
Yang F, Zhang S Y, Song Y T, et al. Research of 1∶50, 000 Land Quality Geochemical Assessment at Yanjin County in Yunnan Province[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(6): 1318-1332. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ202006020.htm
[7] 范薇, 曾妍妍, 周金龙, 等. 新疆若羌县土壤质量地球化学评价[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(5): 1190-1196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201905027.htm
Fan W, Zeng Y Y, Zhou J L, et al. Geochemical evaluation of soil quality in Ruoqiang County, Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(5): 1190-1196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201905027.htm
[8] 周国华, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 等. 安溪土壤-茶叶铅含量关系与土壤铅临界值研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(1): 148-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201601026.htm
Zhou G H, Sun B B, He L, et al. The relationship of lead concentration between soils and tea leaves and the critical value of lead for soil in Anxi, Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(1): 148-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201601026.htm
[9] 王立胜, 汪媛媛, 余涛, 等. 土地质量地球化学评估与绿色产能评价研究: 以吉林大安市为例[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 879-885. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.006
Wang L S, Wang Y Y, Yu T, et al. Study on geochemical assessment of land quality and green productivity evaluation in Da'an City, Jilin Province[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5): 879-885. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.05.006
[10] 刘亮, 张杰, 张杰琼, 等. 四川旺苍县华龙乡土地质量及生态农业建设[J]. 矿产勘查, 2020, 12(12): 2601-2609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS202012004.htm
Liu L, Zhang J, Zhang J Q, et al. Land quality and ecological agriculture construction in Hualong Township of Wangcang County, Sichuan Province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2020, 12(12): 2601-2609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSJS202012004.htm
[11] 杨泽, 刘国栋, 戴慧敏, 等. 黑龙江兴凯湖平原土壤硒地球化学特征及富硒土地开发潜力[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(10): 1773-1782. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202110020.htm
Yang Z, Liu G D, Dai H M, et al. Selenium geochemistry of soil and development potential of Se-rich soil in Xingkai Lake Plain, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(10): 1773-1782. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202110020.htm
[12] 黄园英, 魏吉鑫, 刘久臣, 等. 江西赣州瑞金—石城地区土壤与白莲果实中Se及其他有益元素地球化学特征[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(12): 1944-1951. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202012010.htm
Huang Y Y, Wei J X, Liu J C, et al. The geochemical characteristics of selenium and other beneficial element in soil and white lotus in Ruijin—Shicheng, Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(12): 1944-1951. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202012010.htm
[13] 刘久臣, 魏吉鑫, 张明, 等. 江西赣州市石城县天然富锌土地资源特征与开发利用[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(2-3): 442-450. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2021Z1026.htm
Liu J C, Wei J X, Zhang M, et al. Characteristics and effective utilization of natural zinc-enriched land resources in Shicheng County of Ganzhou City, Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(2-3): 442-450. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2021Z1026.htm
[14] 王懿铮, 杨忠芳, 刘旭, 等. 广西贵港市覃塘区土壤Cu地球化学特征与生态健康研究[J/OL]. 中国地质, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20200529.1230.002.html.
Wang Y Z, Yang Z F, Liu X, et al. Geochemical characteristics of copper in soil and ecological health research in Qintang District of Guigang City in Guangxi[J/OL]. Geology in China, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20200529.1230.002.html.
[15] 成晓梦, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 等. 四川省沐川县西部地区土壤硒含量特征及影响因素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(6): 808-819. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202106080072
Cheng X M, Sun B B, He L, et al. Content characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium in western Muchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(6): 808-819. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202106080072
[16] 蔡大为, 李龙波, 任明强, 等. 贵州省土壤硒含量背景值研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2021, 49(5): 504-509. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202105005.htm
Cai D W, Li L B, Ren M Q, et al. Study on the background value of soil Se content in Guizhou Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 2021, 49(5): 504-509. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202105005.htm
[17] 曹宁, 孙彬彬, 曾道明, 等. 珠江三角洲西部典型乡镇稻米与根系土重金属元素含量关系研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(5): 739-752. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201912240177
Cao N, Sun B B, Zeng D M, et al. Study on the relationship between the contents of heavy metals in rice and root soils in typical townships in the western Pearl River Delta[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(5): 739-752. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201912240177
[18] 刘冬, 贺灵, 文雪琴, 等. 金衢盆地典型地区土壤-稻米重金属含量及土壤酸碱度的影响研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(6): 883-893. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011100139
Liu D, He L, Wen X Q, et al. Concentration of heavy metals in soils and rice and its influence by soil pH in Jinqu Basin[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(6): 883-893. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011100139
[19] 吴峰, 王永, 向武, 等. 基于土壤地球化学特征的茶叶适生模式及种植区划研究——以浙江余杭为例[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2021, 38(5): 909-918.
Wu F, Wang Y, Xiang W, et al. Establishment of a suitable model and planting division of tea: A case study based on soil geochemical characteristics in Yuhang, Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2021, 38(5): 909-918.
[20] 成杭新, 李括, 李敏, 等. 中国城市土壤化学元素的背景值与基准值[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(3): 265-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201403035.htm
Cheng H X, Li K, Li M, et al. Geochemical background and baseline value of chemical in urban soil in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(3): 265-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201403035.htm
[21] 成杭新, 李括, 李敏, 等. 中国城市土壤微量金属元素的管理目标值和整治行动值[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(5): 215-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201505021.htm
Cheng H X, Li K, Li M, et al. Management target value (MTV) and rectification action value (RAV) of trace metals in urban soil in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(5): 215-225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201505021.htm
[22] 刘应平, 阚泽忠, 张海. 成都经济区土地质量地球化学评估报告[R]. 成都: 四川省地质调查院, 2008: 1-36.
Liu Y P, Kan Z Z, Zhang H. Geochemical assessment report of land quality in Chengdu Economic Zone[R]: Chengdu: Sichuan Geological Survey Institute, 2008: 1-36.
[23] 四川省成都市郫都区唐昌镇, 农业产业强镇建设实施方案[R]. 2021: 1-40.
Tangchang Town, Pidu District, Chengdu, Sichuan Province, Implementation Plan of Agricultural Industrial Town Construction[R]. 2021: : 1-40.
[24] 迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 82-83.
Chi Q H, Yan M C. Data manual of applied geochemical element abundance[M]: Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 82-83.
[25] 卢阳, 宋科官, 黄志鹏. 铜结合蛋白在癌症中作用的研究进展[J]. 肿瘤药学, 2019, 3(9): 358-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LIYX201903003.htm
Lu Y, Song K G, Huang Z P. Research progress on the roles of copper-binding proteins in cancer[J]. Anti-Tumor Pharmacy, 2019, 9(3): 358-364. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LIYX201903003.htm
[26] Gall J E, Boyd R S, Rajakaruna N. Transfer of heavy metals through terrestrial food webs: A review[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2015, 187(4): 201-222.
[27] 中国营养学会. 中国居民膳食指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016: 3-4.
Chinese Nutrition Society. Dietary guidelines for Chinese people[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2016: 3-4.
[28] Dalcorso G, Manara A, Furini A. An overview of heavy metal challenge in plants: From roots to shoots[J]. Metallomics, 2013, 5(9): 11-17.
[29] Silvia B, Federica P, Carla M C, et al. Effects of a copper-deficient diet on the biochemistry, neural morphology and behavior of aged mice[J]. PLOS ONE, 2012, 7(10): 1-9.
[30] 肖飞, 王朝旭, 杨丽. 铜缺乏对大鼠铁代谢的影响[J]. 卫生研究, 2013, 42(4): 652-655. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSYJ201304028.htm
Xiao F, Wang C X, Yang L. Effects of copper deficiency on iron metabolism in rats[J]. Journal of Hygiene Research, 2013, 42(4): 652-655. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSYJ201304028.htm
[31] 牛丽凤, 刘剑辉. 微量元素锌与儿童健康关系的研究现状[J]. 中国中西医结合儿科学, 2011, 3(3): 235-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYEK201103022.htm
Niu L F, Liu J H. Research status of the relationship between trace element zinc and children's health[J]. Chinese Pediatrics of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2011, 3(3): 235-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYEK201103022.htm
[32] 宁运旺, 张永春, 汪吉东, 等. 土壤-植物-人类系统中锌与富锌农产品的开发[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2009, 37(3): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNY200903002.htm
Ning Y W, Zhang Y C, Wang J D, et al. Development of zinc and zinc-rich agricultural products in soil-plant-human system[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 37(3): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSNY200903002.htm
-




 下载:
下载: