In situ LA-ICP-MS Determination of Trace Elements in Magnetite from a Gypsum-Salt Bearing Iron Deposit and Geochemical Characteristics
-
摘要:
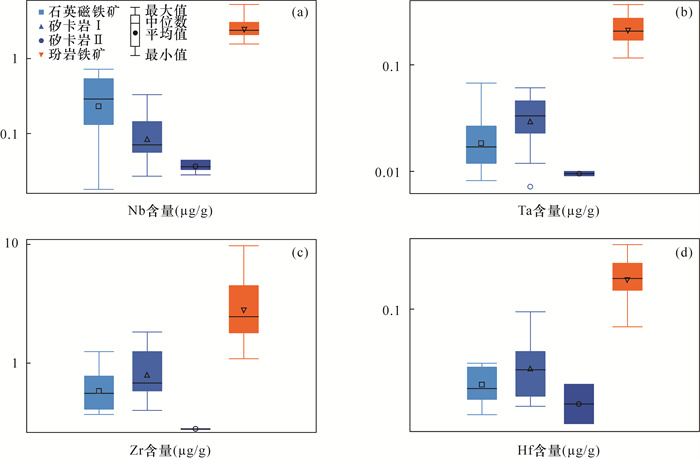
膏盐建造会影响成矿流体的氧逸度和成矿流体成分,表现在磁铁矿元素组成会发生变化,从而对铁矿床的形成具有重要的指示作用,因此可以应用磁铁矿元素组成变化进行矿床类型划分和成因的厘定。膏盐建造广泛发育在新疆“帕米尔式”铁矿床和长江中下游宁芜铁矿床中,但膏盐建造的控矿机制尚不清楚。本文以新疆“帕米尔式”铁矿床和长江中下游宁芜玢岩铁矿床中的磁铁矿为研究对象,应用激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱法(LA-ICP-MS)测定其元素组成,分析磁铁矿中微量元素种类、含量及其地球化学特征,进而反演两种类型磁铁矿的成矿过程与形成环境,探讨膏盐建造在磁铁矿床形成过程中的控制作用。结果表明:①宁芜地区磁铁矿主要具有高Ti(平均含量16401μg/g)、V(平均含量2256μg/g)特征,说明其与岩浆作用密切相关。②新疆塔什库尔干地区磁铁矿床中的磁铁矿中Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf等高场强元素(HFSE)含量明显偏低,结合磁铁矿类型判别图将该地区磁铁矿床主要划分为两种成因类型,即与海相火山活动相关的岩浆热液型磁铁矿特征和热液交代矽卡岩型。分析表明两地区膏盐建造控矿作用明显不同:在塔什库尔干地区磁铁矿床形成过程中改变了氧逸度,而在宁芜地区玢岩铁矿形成过程中,为成矿提供了重要成矿物质来源。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Gypsum-salt formation affects the oxygen fugacity of ore-forming fluid and changes the fluid composition, and then affects the trace element composition, which plays an important indicator role in the formation of iron ore deposits. Therefore, changes in the elemental composition of magnetite can be used to classify the types of deposits and determine their genesis. Gypsum-salt formation is widely developed in "Pamir-type" iron deposits in Xinjiang and Ningwu iron deposits in the middle and lower part of the Yangtze River. However, the controlling mechanism of gypsum-salt formation is still unclear.
OBJECTIVES In order to investigate the metallogenic process and formation environment of the two types of magnetite, and to discuss the role of gypsum-salt formation in the formation of magnetite deposits.
METHODS In situ LA-ICP-MS were employed to determine trace elements in magnetite. RESULTS: LA-ICP-MS results showed that magnetite in the Ningwu area were mainly rich in Ti and V, indicating that it was closely related to magmatism, while the contents of Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf and other high field strength elements (HFSE) in magnetite in the Tashkurgan magnetite deposit in Xinjiang were depleted. Combined with the discrimination diagram of magnetite types, it was mainly divided into two genetic types: magmatic hydrothermal magnetite and hydrothermal metasomatic skarn magnetite related to marine volcanic activity.
CONCLUSIONS The results show that the gypsum-salt formation changes the oxygen fugacity during the formation of magnetite deposits in the Tashkurgan area, and provides an important source of ore-forming material for mineralization during the formation of porphyrite-type iron ore in the Ningwu area.
-
Key words:
- LA-ICP-MS /
- gypsum-salt formation /
- magnetite /
- trace elements /
- "Pamir-type" iron deposit /
- Ningwu iron deposit
-

-
图 1 新疆塔什库尔干地区铁矿床分布地质简图(修改自张德贤等[21])
Figure 1.
图 6 磁铁矿(Ca+Al+Mn)-(Ti+V)成因分类图解(底图据Dupuis等[27])
Figure 6.
图 7 岩浆型和热液型磁铁矿化学成分区划图(底图据Dare等[4])
Figure 7.
表 1 磁铁矿中微量元素测定时LA-ICP-MS仪器设定参数
Table 1. Machine conditions for LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of magnetite
激光参数 实验条件 ICP-MS参数 实验条件 激光源 Telydyne Cetac HE Photon Machines Excimer ICP-MS系统 Analytik Jena Plasma Quant MS Elite 波长 193nm 功率 1400W 脉冲宽度 20ns 等离子冷却气(Ar)流速 13.5L/min 激光束 均值化平顶光束 辅助气(He)流速 0.850L/min 脉冲能量 0.01~0.1mJ/pulse 样品传输气(He)流速 0.250L/min 能量密度 2.5J/cm2 样品传输气(Ar)流速 0.90L/min 焦点 表面 扫描模式 峰跳跃模式,1点/峰 光栅扫描速度 5Hz 获取模式 时间分辨率分析 激光束直径 35μm (仪器配置1~180μm) 分析持续时间 70s(20s背景,30s信号,20s冲洗) -
[1] 李延河, 段超, 韩丹, 等. 膏盐层氧化障在长江中下游玢岩铁矿成矿中的作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(5): 1355-1368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201405012.htm
Li Y H, Duan C, Han D, et al. Effect of sulfate evaporate salt layer for formation of porphyrite iron ores in the middle-lower Yangtze River area[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(5): 1355-1368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201405012.htm
[2] 蔡本俊. 长江中下游地区内生铁铜矿床与膏盐的关系[J]. 地球化学, 1980, 9(2): 193-199. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1980.02.008
Cai B J. The relationship of gypsum salt beds with endogenic copper and iron ores in the middle-lower Yangtze Valley[J]. Geochemistry, 1980, 9(2): 193-199. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1980.02.008
[3] 侯增谦, 杨竹森, 李荫清, 等. 碰撞造山过程中流体向前陆盆地大规模迁移汇聚: 来自长江中下游三叠纪膏盐建造和区域蚀变的证据[J]. 矿床地质, 2004, 23(3): 310-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2004.03.005
Hou Z Q, Yang Z S, Li Y Q, et al. Large-scale migration of fluids towards foreland basins during collisional orogeny: Evidence from Triassic Anhydrock sequences and regional alteration in middle-lower Yangtze area[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2004, 23(3): 310-326. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2004.03.005
[4] Nadoll P, Mauk J L, Hayes T S, et al. Geochemistry of magnetite from hydrothermal ore deposits and host rocks of the Mesoproterozoic Belt Supergroup, United States[J]. Economic Geology and the Bulletin of the Society of Economic Geologists, 2012, 107(6): 1275-1292. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.107.6.1275
[5] 叶庆同. 粤东一些铁矿床中磁铁矿的标型特征及其成因意义[J]. 岩矿测试, 1982, 1(1): 44-51. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_19820108
Ye Q T. Typomorphic characteristics and genesis significance of magnetite from some iron ore deposita in eastern Guangdong[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 1982, 1(1): 44-51. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_19820108
[6] Nadoll P, Angerer T, Mauk J L, et al. The chemistry of hydrothermal magnetite: A review[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 61: 1-32. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.12.013
[7] Reguir E P, Chakhmouradian A R, Halden N M, et al. Early magmatic and reaction-induced trends in magnetite from the carbonatites of Kerimasi, Tanzania[J]. Canadian Mineralogist, 2008, 46(4): 879-900. doi: 10.3749/canmin.46.4.879
[8] 陈意, 胡兆初, 贾丽辉, 等. 微束分析测试技术十年(2011~2020)进展与展望[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(1): 1-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202101004.htm
Chen Y, Hu Z C, Jia L H, et al. Progress of microbeam analytical technologies in the past decade (2011—2020) and prospect[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(1): 1-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202101004.htm
[9] 李丽君, 薛静. 微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定高岭土中10种微量元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(1): 22-31. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202103240042
Li L J, Xue J. Determination of 10 trace elements in kaolin by ICP-MS with microwave digestion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(1): 22-31. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202103240042
[10] 万秋, 李延河, 王利民, 等. 北淮阳晓天火山岩盆地片麻状花岗岩成岩年代学及地球化学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(4): 620-630. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201908120125
Wan Q, Li Y H, Wang L M, et al. The age and geochemical characteristics of neoproterozoic gneissic moyite in the Xiaotian Basin[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(4): 620-630. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201908120125
[11] 郭东旭, 刘琰, 李自静, 等. 应用电感耦合等离子体质谱技术研究牦牛坪矿床霓长岩化蚀变矿物微量元素特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(6): 896-907. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060003
Guo D X, Liu Y, Li Z J, et al. Determination of trace element compositions of altered minerals in fenitization veins by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(6): 896-907. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060003
[12] 贾玉衡, 钱建平. 电子探针-电感耦合等离子体质谱法研究不同种类石榴石的稀土元素配分矿物学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(6): 886-895. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060007
Jia Y H, Qian J P. Study on REE distribution and mineralogical characteristics of different garnets by electron probe and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(6): 886-895. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005060007
[13] 胡健卫, 庄道泽, 杨万志. 新疆西南部塔什库尔干地区赞坎铁矿综合信息预测模型及其在区域预测中的应用[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(10): 1495-1503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.10.012
Hu J W, Zhuang D Z, Yang W Z. The integrated information predicting model of the Zankan iron deposit, Tashikuergan area, southwestern Xinjiang, China and its application in regional metallogenic prognosis[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(10): 1495-1503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.10.012
[14] 燕长海, 陈曹军, 曹新志, 等. 新疆塔什库尔干地区"帕米尔式"铁矿床的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2012, 31(4): 549-557. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.04.008
Yan C H, Chen C J, Cao X Z, et al. The discovery of the "Pamir-type" iron deposits in Taxkorgan area of Xinjiang and its geological significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2012, 31(4): 549-557. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2012.04.008
[15] 燕长海, 曹新志, 张旺生, 等. 帕米尔式铁矿床[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012.
Yan C H, Cao X Z, Zhang W S, et al. Pamir type iron deposit[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2012.
[16] 陈曹军. 新疆塔什库尔干地区铁矿床成矿规律及找矿方向研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2012.
Chen C J. Study of metallogenic regularity and prospecting direction of iron deposits in Taxkorgan area, Xinjiang Province[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2012.
[17] 胡亮. 新疆塔县老并磁铁矿成矿地质特征及找矿方向[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
Hu L. Geological characteristics and prospecting direction of the magnetite deposit in Laobing mining area, Xinjiang[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014.
[18] 陈登辉, 伍跃中, 李文明, 等. 西昆仑塔什库尔干地区磁铁矿矿床特征及其成因[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2013, 37(4): 671-684. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201304012.htm
Chen D H, Wu Y Z, Li W M, et al. Geological characteristics and genesis of the iron deposits in the Taxkorgan area, West Kunlun[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2013, 37(4): 671-684. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201304012.htm
[19] 陈石义. 新疆塔什库尔干走克本矿区磁铁矿矿床地质特征[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.
Chen S Y. Geological characteristics of the magnetite deposit in Taxkorgan mining area, Xinjiang[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2013.
[20] 陈俊魁, 燕长海, 张旺生, 等. 新疆塔什库尔干地区磁铁矿床地质特征与找矿方向[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2011, 34(3): 179-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2011.03.003
Chen J K, Yan C H, Zhang W S, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting direction of the magnetite iron deposits in the Taxkorgan, Xinjiang[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2011, 34(3): 179-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2011.03.003
[21] 张德贤, 曹汇, 曾敏, 等. 新疆"帕米尔式"铁矿床成因与成矿背景分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(12): 3847-3864. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201612019.htm
Zhang D X, Cao H, Zeng M, et al. Study on metallogenic genesis and metallogenic settings of Xinjiang "Pamir-type" iron deposit[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(12): 3847-3864. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201612019.htm
[22] 范裕, 刘一男, 周涛发, 等. 安徽庐枞盆地泥河铁矿床年代学研究及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(5): 1369-1381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201405013.htm
Fan Y, Liu Y N, Zhou T F, et al. Geochronology of the Nihe deposit and in the Lu—Zong Basin and its metallogenic significances[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(5): 1369-1381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201405013.htm
[23] Zhu Q, Xie G, Mao J, et al. Mineralogical and sulfur isotopic evidence for the incursion of evaporites in the Jinshandian skarn Fe deposit, Edong District, eastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 1253-1267. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.05.022
[24] Griffin W L, Powell W J, Pearson N J, et al. GLITTER: Data reduction software for laser ablation ICP-MS[M]//Sylvester P. Laser ablation-ICP-MS in the Earth sciences: Current practices and outstanding issues. Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course, 2008: 308-311.
[25] 张德贤, 戴塔根, 胡毅. 磁铁矿中微量元素的激光剥蚀-电感耦合等离子体质谱分析方法探讨[J]. 岩矿测试, 2012, 31(1): 120-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.01.015 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_20120116
Zhang D X, Dai T G, Hu Y. Analysis of trace elements in magnetite using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(1): 120-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2012.01.015 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_20120116
[26] Nadoll P. Geochemistry of magnetite from hydrothermal ore deposits and host rocks—Case studies from the Proterozoic belt supergroup, Cu-Mo-porphyry+skarn and Climax-Mo deposits in the western United States[M]. New Zealand: The University of Auckland, 2011.
[27] Dupuis C, Beaudoin G. Discriminant diagrams for iron oxide trace element fingerprinting of mineral deposit types[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2011, 46(4): 319-335. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0334-y
[28] 张乐骏. 安徽庐枞盆地成岩成矿作用研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2011.
Zhang L J. Polymetallic mineralization and associated magmatic and volcanic activity in the Luzong Basin, Anhui Province, eastern China[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2011.
[29] Mallmann G, O'Neill H S C. The crystal/melt partitioning of V during mantle melting as a function of oxygen fugacity compared with some other elements (Al, P, Ca, Sc, Ti, Cr, Fe, Ga, Y, Zr and Nb)[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2009, 50(9): 1765-1794. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp053
[30] Zhi Z, Li L, Li S, et al. Magnetite as an indicator of granite fertility and gold mineralization: A case study from the Xiaoqinling Gold Province, North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 115: 103159. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103159
[31] 陈述荣, 谢家亨, 许超南, 等. 福建龙岩马坑铁矿床成因的探讨[J]. 地球化学, 1985, 14(4): 350-357. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1985.04.008
Chen S R, Xie J H, Xu C N, et al. The origin of Makeng iron deposit, Fujian[J]. Geochimica, 1985, 14(4): 350-357. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1985.04.008
[32] 陈健. 新疆老并磁铁矿床地质地球化学特征及成因分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
Chen J. Geological geochemical characteristics and genetic analysis of Laobing magnetite deposits, Xinjiang Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2014.
[33] 李树勋, 冀树楷, 马志红, 等. 五台山区变质沉积铁矿地质[M]. 吉林: 吉林科学技术出版社, 1986.
Li S X, Ji S K, Ma Z H, et al. Geology of metamorphic sedimentary iron ore in Wutaishan area[M]. Jilin: Jilin Science and Technology Press, 1986.
[34] 沈其韩, 宋会侠, 杨崇辉, 等. 山西五台山和冀东迁安地区条带状铁矿的岩石化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2011, 30(2): 161-171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.02.001
Shen Q H, Song H X, Yang C H, et al. Petrochemical characteristics and geological significations of banded iron formations in the Wutai Mountain of Shanxi and Qian'an of eastern Hebei[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2011, 30(2): 161-171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.02.001
[35] 刘一男. 安徽庐枞盆地罗河—小包庄铁矿床成矿作用研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2015.
Liu Y N. Mineralization of Luohe—Xiaobaozhuang iron deposit in the Lu—Zong Volcanic Basin, Anhui Province[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2015.
[36] 范洪源, 李文达, 王文斌. 长江中下游海相三叠系膏盐层与铜(金)、铁矿床[J]. 火山地质与矿产, 1995, 16(2): 32-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ199502002.htm
Fan H Y, Li W D, Wang W B. On the relationship between the marine Triassic evaporite horizons and Cu(Au), Fe deposits in the middle-lower Yangtze area[J]. Volcanology & Mineral Resources, 1995, 16(2): 32-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ199502002.htm
-




 下载:
下载: