Determination of Iodide in Groundwater by Suppressed Conductance-Ion Chromatography
-
摘要:
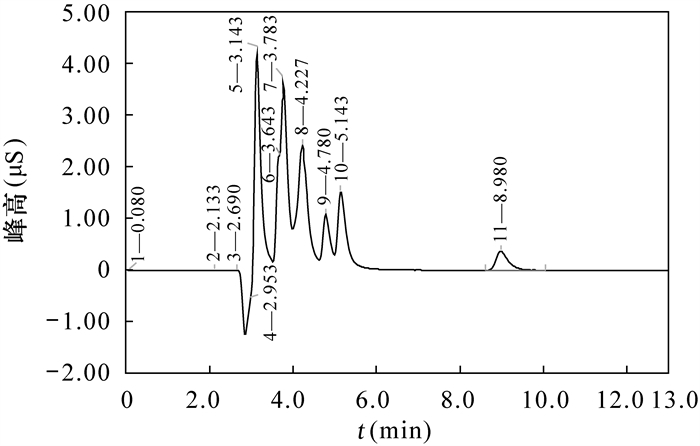
在无外来碘食物的环境下,水中碘含量是衡量人体碘摄入量的重要指标,因此准确测定饮用水中碘化物的含量对人类健康有着至关重要的作用。具有烷醇基季铵功能团的IonPac AS23色谱柱,具有较强亲水性,可在很宽的pH范围内(0~14)保持高容量,适于氢氧根淋洗液体系和碳酸根淋洗液体系,基于此,本文建立了一种抑制型电导-离子色谱法检测地下水中碘化物的方法。采用IonPac AS23型阴离子分析柱和IonPac AS23阴离子保护柱,50mmol/L的KOH淋洗液,其流速为1.2mL/min,抑制型电导检测器电流为125mA,对地下水中碘化物进行检测。该方法在8.980min出峰,方法检测限为0.5μg/L,方法标准曲线的相关性r=0.9998,线性范围较广(0.01~2mg/L)。该方法检测限更低、出峰时间更短,且不受水中7种无机阴离子的测定干扰,提高了氢氧根淋洗液体系下,烷醇基季铵功能团色谱柱AS23测定地下水中碘化物的准确度。
-
关键词:
- 离子色谱法 /
- AS23型阴离子分析柱 /
- 烷醇基季铵功能团 /
- 氢氧化钾淋洗液
Abstract:BACKGROUND In an environment without foreign iodine food, the iodine content of water is an important index to measure the iodine intake of the human body, so the accurate determination of iodide content in drinking water has a crucial role in human health. The detection limit of ion chromatography-amperometric detection method is generally lower than that of conductance detection method, and the sensitivity is higher. This method is suitable for the determination of trace iodide in water, but the apparent peak time is later than that of the conductance detection method. Under the same test conditions, for the ion chromatography-hydroxide eluent detection method for the determination of iodide in water, the peak time is obviously better than that of the carbonate body eluent detection method. Using carbonate eluent to analyze iodide requires adding toxic organic improvers, which is complicated, difficult to elute, has a long analysis time, high detection limit and low sensitivity.
OBJECTIVES IonPac AS23 column with alkanol-based quaternary ammonium functional group has strong hydrophilicity and can maintain high capacity in a wide pH range (0-14), which is suitable for hydroxide and carbonate leaching systems. Based on this, a method for the determination of iodide in groundwater by suppressed conduction-ion chromatography was developed.
METHODS IonPac AS23 (4mm×250mm) anion analysis column and IonPac AS23 anion protection column, Dionex AERS 500(4mm) anion inhibited conductivity detector, HPIC separation method, were used to detect iodide in groundwater with 50mmol/L KOH eluent (hydroxide eluent, the product after conductivity inhibition is zero conductivity water, providing an ideal conductivity baseline) at a flow rate of 1.2mL/min (the concentration and flow rate of the eluent increased, and the retention time was shortened) and a suppressive conductance detector current of 125mA (the current increased, the instrument detection sensitivity increased). The sample volume was 250μL, and the samples were filtered through a 0.45μm water microporous filter membrane. 10mL of initial filtrate was discarded, and about 10mL of subsequent filtrate was collected. After that the iodide in the groundwater samples was detected.
RESULTS The chromatographic peak separation was good, peak shape was symmetrical, and no trailing extension. The iodide peak emerged in 8.980min, the detection limit of the method was 0.5μg/L, the correlation coefficient of the calibration curve was 0.9998, and the linear range was wide (0. 01-2mg/L).
CONCLUSIONS This method has a lower detection limit than that of the existing standard method for the determination of iodide in water, shorter peak time, and the detection range is better than that of the existing ion chromatography method. The experimental results show that the peak time is faster than that reported by its predecessors. This method is used to determine iodide in groundwater and is not disturbed by seven inorganic anions (F-, Cl-, NO3-, NO2-, SO42-, PO43-, Br-) in water. This method improves the accuracy of the determination of iodide in groundwater by alkanol-based quaternary ammonium functional group column AS23 under the hydroxide eluent system.
-

-
表 1 离子色谱分离和检测方式的选择(无机阴离子)
Table 1. Selection of separation and detection methods of ion chromatography (inorganic anions)
检测方式 分离方式 测定离子 电导,UV 高效离子交换色谱(HPIC) 无机阴离子F-、Cl-、NO3-、NO2-、SO42-、PO43-、Br-等,低分子量有机酸 安培 高效离子排斥色谱(HPICE) SO32-、亚砷酸 电导 高效离子交换色谱(HPIC) 砷酸盐、硒酸盐、亚硒酸盐 电导 高效离子排斥色谱(HPICE) BO3-、CO32- 电导/安培 高效离子交换色谱(HPIC),离子对色谱(MPIC) I-、BF4-、SCN-、ClO4-、S2O32- 电导/安培 高效离子排斥色谱(HPICE) CN-、HS-、高离子强度基体 电导 高效离子交换色谱(HPIC),离子对色谱(MPIC) 金属络合物 电导,柱后衍生VIS 高效离子交换色谱(HPIC) 缩合磷酸盐多价螯合剂 表 2 现有水中碘化物标准检测方法检出限、测定范围及适用范围汇总
Table 2. Summary of detection limits, determination ranges and applicable ranges of existing standard methods for iodide detection in water
标准名称 检测方法 检测限 测定范围 样品适用范围 《生活饮用水标准检验方法无机非金属指标》(GB/T 5750.5—2006),《食品安全国家标准饮用天然矿泉水检验方法》(GB 8538—2022) 硫酸铈催化比色法 1μg/L 低浓度:1~10μg/L
高浓度:10~100μg/L生活饮用水及其水源水,饮用天然矿泉水 高浓度碘化物比色法 0.05mg/L 0.05~0.1mg/L 气相色谱法 1μg/L 1~10μg/L,10~100μg/L 《生活饮用水标准检验方法无机非金属指标》(GB/T 5750.5—2006) 高浓度碘化物容量法 0.025mg/L / 生活饮用水及其水源水 《地下水质分析方法第56部分碘化物的测定淀粉分光光度法》(DZ/T 0064.56—2021) 淀粉比色法 25μg/L 25~500μg/L 地下水 《地下水质分析方法第55部分碘化物的测定催化还原分光光度法》(DZ/T 0064.55—2021) 催化还原法 1μg/L 1~16μg/L 地下水 《食品安全国家标准饮用天然矿泉水检验方法》(GB 8538—2022) 离子色谱法 10.25μg/L 0.25~100μg/L 饮用天然矿泉水 《水质碘化物的测定离子色谱法》(HJ 778—2017) 离子色谱法 0.002mg/L 0.01~1mg/L 地表水和地下水 表 3 方法精密度和回收率
Table 3. Precision and recovery results of the method
DXS01-16
样品I-测定值
(μg/L)加标低测定结果
(0.050mg/L)加标中测定结果
(0.100mg/L)加标高测定结果
(1.00mg/L)DXS01-20
样品I-测定值
(μg/L)加标低测定结果
(0.050mg/L)加标中测定结果
(0.100mg/L)加标高测定结果
(1.00mg/L)平行测定值(mg/L) ND 0.0435 0.1090 1.046 平行测定值(mg/L) ND 0.0455 0.1040 1.042 ND 0.0444 0.1030 1.049 ND 0.0464 0.1040 1.043 ND 0.0442 0.1019 1.044 ND 0.0432 0.1039 1.046 ND 0.0466 0.1043 1.042 ND 0.0476 0.1043 1.046 ND 0.0454 0.1015 1.043 ND 0.0434 0.1055 1.044 ND 0.0477 0.0995 1.049 ND 0.0467 0.1059 1.044 平均值(mg/L) ND 0.045 0.103 1.04 平均值(mg/L) ND 0.045 0.105 1.04 标准偏差(mg/L) - 0.0016 0.0033 0.0030 标准偏差(mg/L) - 0.0018 0.0008 0.0016 RSD(%) - 3.50 3.15 0.29 RSD(%) - 3.97 0.83 0.15 加标量(μg) - 1.0 2.0 20.0 加标量(μg) - 1.0 2.0 20.0 平均加标回收率(%) - 90.0 103.0 104.0 平均加标回收率(%) - 90.0 105.0 104.0 注:ND表示检测结果低于方法检测限(0.5μg/L),未检出。 -
[1] 张媛静, 张玉玺, 向小平, 等. 沧州地区地下水碘分布特征及其成因浅析[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4): 59-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404008.htm
Zhang Y J, Zhang Y X, Xiang X P, et al. Analysis on the distribution characteristics and genesis of iodine of Cangzhou groundwater[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4): 59-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404008.htm
[2] Shinoda T, Miyamoto N, Kuromoto T, et al. Pyrohydrolysis coupled to ion chromatography for sensitive determination of iodine in food-related materials[J]. Analytical Letters, 2012, 45(8): 862-871. doi: 10.1080/00032719.2012.655659
[3] 宫霞, 蓝倩云, 黄玲. 上海市饮用水中微量元素碘含量的检测与分析[J]. 环境工程, 2015, 33(S1): 989-991. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC2015S1246.htm
Gong X, Lan Q Y, Huang L. Detection and analysis of iodine content in drinking water of Shanghai[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2015, 33(S1): 989-991. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC2015S1246.htm
[4] 杨瑞丰. 地表水中碘化物含量测定方法研究[J]. 水资源开发与管理, 2019(7): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJYF201907008.htm
Yang R F. Determination of iodide content in surface water[J]. Water Resources Development and Management, 2019(7): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJYF201907008.htm
[5] 寇志华, 刘克克, 任增辉. 生活饮用水中碘化物检测方法的探讨[J]. 河南预防医学杂志, 2020, 31(12): 910-911, 933. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYF202012010.htm
Kou Z H, Liu K K, Ren Z H. Discussion on the determination method of iodide in drinking water[J]. Henan Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2020, 31(12): 910-911, 933. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYF202012010.htm
[6] 贾亮亮, 尹云. 催化分光光度法测定水中微量碘的方法优化[J]. 化学试剂, 2020, 42(11): 1341-1344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXSJ202011016.htm
Jia L L, Yin Y. Optimization of catalytic spectrophoto-metric method for determination of trace iodine in water[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2020, 42(11): 1341-1344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXSJ202011016.htm
[7] 杨瑞丰. 离子色谱法和气相色谱法测定水质中碘化物对比研究[J]. 水资源开发与管理, 2019(9): 16-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJYF201909006.htm
Yang R F. Comparative study on determination of iodide in water quality by ion chromatography and gas chromatography[J]. Water Resources Development and Management, 2019(9): 16-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJYF201909006.htm
[8] 朱红霞, 杨艳娥, 许秀艳. 气相色谱法测定水中碘化物前处理方法的比较[J]. 环境化学, 2015, 34(11): 2142-2145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201511026.htm
Zhu H X, Yang Y E, Xu X Y. Comparison of pretreatment methods for determination of iodide in water by gas chromatography[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2015, 34(11): 2142-2145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201511026.htm
[9] 张钦龙, 高舸. 带八极杆碰撞/反应池的电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定尿中碘[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2012, 22(9): 2023-2024, 2027. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ201209007.htm
Zhang Q L, Gao G. Determination of iodine in urine by ORS-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2012, 22(9): 2023-2024, 2027. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ201209007.htm
[10] Wang M H, Huang Z P, Liu J W, et al. Iodide analysis by ion chromatography on a new stationary phase of polystyrene-divi-nylbenzene agglomerated with polymerized-epichlorohydrin-dimethylamine[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2015, 26(8): 1026-1030. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2015.05.002
[11] 杜韶娴, 李用倩, 刘胜玉. 电导检测离子色谱法同时测定饮用水中溴化物和碘化物[J]. 化学试剂, 2016, 38(3): 242-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXSJ201603014.htm
Du S X, Li Y Q, Liu S Y. Simultaneous determination of bromide and iodide in drinking water by ion chromatography with conductivity detection[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2016, 38(3): 242-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXSJ201603014.htm
[12] 寇志华, 刘克克, 任增辉. 离子色谱法测定生活饮用水中碘化物[J]. 河南预防医学杂志, 2020, 31(4): 264-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYF202004010.htm
Kou Z H, Liu K K, Ren Z H. Determination of iodide in drinking water by ion chromatography[J]. Henan Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2020, 31(4): 264-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYF202004010.htm
[13] 张艳, 田耕, 毕军平, 等. 分光光度法测定水体中痕量碘化物[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2014, 50(9): 1171-1172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH201409040.htm
Zhang Y, Tian G, Bi J P, et al. Determination of trace iodide in water by spectrophotometry[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2014, 50(9): 1171-1172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH201409040.htm
[14] 张克梅, 袁明珠. 改良砷铈催化分光光度法测定水中碘[J]. 安徽预防医学杂志, 2019, 25(1): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYF201901008.htm
Zhang K M, Yuan M Z. Determination of iodine in water by improved arsenic-cerium catalytic spectrophotometry[J]. Anhui Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2019, 25(1): 29-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHYF201901008.htm
[15] 胥彦琪. 基于HRP催化诱导金纳米棒形貌改变的碘离子检测研究[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2018, 30(1): 133-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYJ201801024.htm
Xu Y Q. Detection of iodide ion based on HRP catalyzed morphology change of gold nanorods[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2018, 30(1): 133-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYJ201801024.htm
[16] 姜翠凤, 李卓健, 莫贵和, 等. 基于聚乙烯亚胺-金纳米粒子聚集的碘离子检测[J]. 分析试验室, 2020, 39(6): 654-657. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY202006008.htm
Jiang C F, Li Z J, Mo G H, et al. Detection of iodide ion based on polyethylene imine gold nanoparticles aggregation[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2020, 39(6): 654-657. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY202006008.htm
[17] 张建伟. 离子色谱-安培检测法检测饮用水中碘化物[J]. 城镇供水, 2021(2): 66-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CZGS202102014.htm
Zhang J W. Determination of iodide in drinking water by ion chromatography-amperometric detection[J]. City and Town Water Supply, 2021(2): 66-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CZGS202102014.htm
[18] 郭晶晶, 林冬, 李旭冉. 积分安培检测-离子色谱法测定水中痕量碘离子[J]. 广州化工, 2016, 44(16): 128-130, 169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZHA201616046.htm
Guo J J, Lin D, Li X R. Determination of trace iodide ion in water by integral Ampere detection-ion chromatography[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2016, 44(16): 128-130, 169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZHA201616046.htm
[19] 杨晟, 张巧, 谢帮蜜, 等. 华南某市地表水碘分布特征及其成因浅析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2019, 19(4): 1468-1472. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201904050.htm
Yang S, Zhang Q, Xie B M, et al. Distribution characteristics and genesis of iodine in surface water of a city in South China[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2019, 19(4): 1468-1472. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201904050.htm
[20] 蒋园园, 程海, 徐蕾. 电导和直流安培双检测器离子色谱法测定清洁水样中的碘化物[J]. 环境监测与预警, 2020, 12(2): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HTJK202002006.htm
Jiang Y Y, Cheng H, Xu L. Determination of iodide in clean water by conductivity and DC amperometric double detector ion chromatography[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 2020, 12(2): 31-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HTJK202002006.htm
[21] 王新旺. 离子色谱-安培检测器法测定尿中碘含量[J]. 河南预防医学杂志, 2016, 27(7): 518-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYF201607011.htm
Wang X W. Determination of iodine in urine by ion chromatography-amperometric detector[J]. Henan Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2016, 27(7): 518-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYF201607011.htm
[22] 宋冰冰, 田耘, 李仁勇, 等. 碳酸盐体系离子色谱法快速测定水体中碘化物[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2017, 29(4): 50-52, 56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJS201704012.htm
Song B B, Tian Y, Li R Y, et al. Rapid determination of iodide in water by ion chromatography with carbonate system[J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2017, 29(4): 50-52, 56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJS201704012.htm
[23] 袁湘, 范旭, 冯丽娟, 等. 离子色谱法检测芦荟胶化妆品中无机阴离子[J]. 应用化工, 2022, 51(5): 1520-1522, 1526. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHG202205043.htm
Yuan X, Fan X, Feng L J, et al. Determination of inorganic anions in aloe gel cosmetics by ion chromatography[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2022, 51(5): 1520-1522, 1526. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHG202205043.htm
[24] 吴家钰, 王勇, 李泳宜, 等. 基于离子转换色谱的紫外检测系统测定饮料中的无机阳离子含量[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2021, 37(1): 88-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJYX202101009.htm
Wu J Y, Wang Y, Li Y Y, et al. Determination of inorganic cation content in beverage by UV detection system based on ion conversion chromatography[J]. Ion Exchange and Adsorption, 2021, 37(1): 88-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LJYX202101009.htm
[25] 佘小林. 离子色谱法快速测定土壤中碘量[J]. 岩矿测试, 2005, 24(2): 145-147. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_20050240
She X L. Rapid determination of iodine content in soil by ion chromatography[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2005, 24(2): 145-147. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_20050240
[26] 宋冰冰, 田耘, 罗岳平, 等. 离子色谱法测定多种水体中碘化物应用研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2015, 40(10): 124-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFHJ201510029.htm
Song B B, Tian Y, Luo Y P, et al. Determination of iodide in various water bodies by ion chromatography[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2015, 40(10): 124-126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BFHJ201510029.htm
[27] Xia N, Ji H Z. Simultaneous determination of iodide, sulphate, fluoride and nitrite in salt samples by ion chromatography[J]. Asian Journal of Chemistry, 2014, 26(22): 7869-7870.
[28] 薛智凤, 胡智杰, 王亚娇, 等. 离子色谱法测定水中无机阴离子检测条件的优化与探索[J]. 分析仪器, 2020(6): 133-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXYQ202006025.htm
Xue Z F, Hu Z J, Wang Y J, et al. Optimization and exploration of determination conditions of inorganic anions in water by ion chromatography[J]. Analytical Instrumentation, 2020(6): 133-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXYQ202006025.htm
[29] 贾丽, 刘肖. 全新离子色谱柱-抑制型电导法检测饮用水中痕量溴酸盐[J]. 环境化学, 2006, 25(6): 793-795. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX200606031.htm
Jia L, Liu X. Determination of trace bromate in drinking water by a novel ion chromatography column-suppressed conductivity method[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2006, 25(6): 793-795. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX200606031.htm
[30] Rong L, Lim L W, Takeuchi T. Rapid determination of iodide in seawater samples by ion chromatography with chemically-bonded vitamin-U stationary phase[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2013, 108: 113-116.
[31] 佘小林, 胡兰, 刘军, 等. 离子色谱法测定牛皮纸样袋中海底沉积物的氯量[J]. 岩矿测试, 2009, 28(4): 373-375. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_20090415
She X L, Hu L, Liu J, et al. Determination of chlorine content in seabed sediments in kraft paper sample bags by ion chromatography[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2009, 28(4): 373-375. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/id/ykcs_20090415
-



 下载:
下载: