Spatial Analysis and Risk Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution in the Xishimen Iron Mining Area of Hebei Province
-
摘要:
矿区土壤重金属污染严重威胁着生态环境和周边居民的健康,对其进行有效监管意义重大。河北西石门铁矿是邯邢地区的大型磁铁矿床,针对该矿区土壤重金属污染亟待开展综合研究。本文以西石门铁矿一号矿区为研究对象,利用地球化学、统计学、地理信息学等多学科技术,对9种典型土壤重金属的空间分布和污染风险进行分析。采用ICP-MS测定重金属含量,通过描述性统计分析、多元统计分析和空间插值分析得到重金属超标率、污染来源及空间分布特征,并结合单因子污染指数、内梅罗综合污染指数、潜在生态危害指数评价其污染风险。描述性统计分析结果显示,矿区土壤Co的超标率为75.83%,属重度污染,Cu、Cd、As的超标率分别为14.70%、21.40%和13.29%,属中轻度污染,Cr、Ni、Zn、Pb和Hg的超标率均低于5%,属轻度污染;多元统计分析结果显示,Cr、Ni、Zn、Cd、As和Pb来源于成矿区自然风化环境污染,Co和Cu来源于采矿生产、化肥使用造成的人为环境污染,Hg来源于人为因素造成的局部污染;空间插值分析结果显示,重金属含量在马会河两岸露天采矿区较高,在河流和居民区较低;污染风险评估结果显示,研究区内梅罗综合污染指数为13.49,综合生态风险指数为55.50。该矿区存在人为因素导致的Hg、Co、Cu污染,需要重点关注并开展治理工作;该矿区的重金属污染属重度,但生态风险仍处于可控范围。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Heavy metal pollution in the soil of mining areas is a serious threat to the ecological environment and the health of surrounding residents, and it is of great significance to effectively supervise it. The Xishimen iron deposit in Hebei Province is a large magnetite deposit in the Hanxing area. Comprehensive research on soil heavy metal pollution in this mining area is urgently needed.
OBJECTIVES To evaluate soil heavy metal pollution in the Xishimen iron mining area in Hebei Province.
METHODS The No.1 mining area of the Xishimen iron deposit was selected as the research object. ICP-MS was used to determine the heavy metal content. The exceedance rate, pollution sources and spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals were obtained by descriptive statistical analysis, multivariate statistical analysis and spatial interpolation analysis, and the pollution risk was evaluated by combining the single factor pollution index, Nemero comprehensive pollution index and potential ecological hazard index.
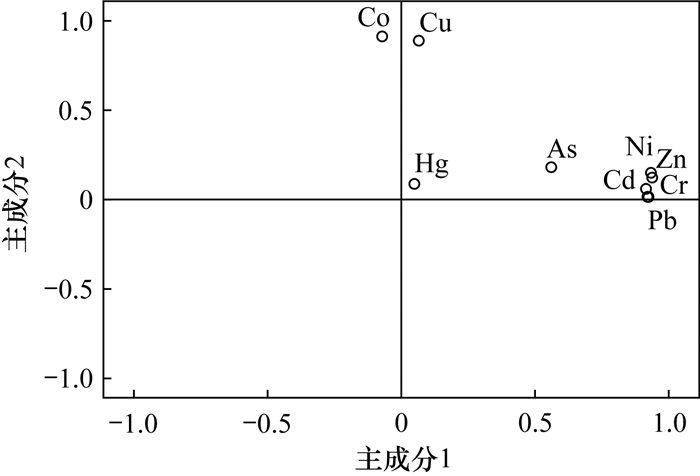
RESULTS Descriptive statistical analysis showed that the exceedance rate of Co in the mining area was 75.83%, indicating heavy pollution, while the exceedance rates of Cu, Cd and As were 14.70%, 21.40% and 13.29%, indicating moderate to light pollution. The exceedance rates of Cr, Ni, Zn, Pb and Hg were less than 5%, which were light pollution. The multivariate statistical analysis showed that Cr, Ni, Zn, Cd, As and Pb were from the natural weathering environmental pollution in the mineralized area, and Co and Cu were from the anthropogenic environmental pollution caused by mining production and fertilizer use. Hg came from the local pollution caused by human factors. Spatial interpolation analysis showed that the nine heavy metals had a high distribution in the open pit mining area on both sides of the Mahui River and a low distribution in the rivers and residential areas. The Nemero comprehensive pollution index of heavy metals in the study area was 13.49, and the comprehensive ecological risk index was 55.50.
CONCLUSIONS The results indicate that there is Hg, Co, and Cu pollution caused by human factors in the mining area, which needs to be addressed. The heavy metal pollution in this area is serious but the ecological risk is still in a controllable range.
-

-
表 1 土壤重金属元素含量统计结果
Table 1. Statistical results of heavy metal element contents in soil
统计参数 Cr Co Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb As Hg 平均值(mg/kg) 38.15 17.18 19.01 27.65 53.53 0.12 15.81 10.44 0.055 最小值(mg/kg) 5.94 2.67 2.76 2.44 10.5 0.018 1.24 0.17 0.004 最大值(mg/kg) 102 121 44.7 172 176 0.50 105 35.20 5.30 标准差(mg/kg) 23.22 11.54 11.19 21.00 27.81 0.08 13.29 5.14 0.293 变异系数(%) 60.86 67.19 58.89 75.94 51.95 67.24 84.08 49.26 532.73 自然背景值(mg/kg) 90 12.7[23] 40 35 100 0.20 35 15 0.15 土壤质量筛选值(mg/kg) 250 15 190 100 300 0.6 170 25 3.4 超标率(%) 0.30 75.83 0.90 14.70 3.60 21.40 3.00 13.29 1.81 表 2 土壤重金属元素间的相关系数
Table 2. Correlation coefficients of heavy metal elements in soil
重金属元素 Cr Co Ni Cu Zn Cd Pb As Hg Cr 1 -0.049 0.947** 0.082 0.820** 0.783** 0.797** 0.463** 0.034 Co 1 0.110 0.645** 0.048 -0.016 -0.062 0.129 0.036 Ni 1 0.157 0.847** 0.810** 0.797** 0.536** 0.041 Cu 1 0.184 0.133 0.116 0.093 0.034 Zn 1 0.867** 0.909** 0.461** 0.047 Cd 1 0.854** 0.437** 0.055 Pb 1 0.387** 0.039 As 1 0.025 Hg 1 注:“**”表示在0.01水平(双侧)上极显著相关。 表 3 土壤重金属含量主成分分析成分矩阵
Table 3. Component matrix of principal component analysis of heavy metal contents in soil
重金属 初始因子载荷 旋转后因子载荷 F1 F2 F1 F2 Cr 0.921 -0.121 0.929 0.016 Co 0.064 0.914 -0.071 0.914 Ni 0.946 0.014 0.934 0.153 Cu 0.196 0.873 0.065 0.892 Zn 0.945 -0.015 0.937 0.124 Cd 0.913 -0.077 0.914 0.058 Pb 0.914 -0.120 0.922 0.015 As 0.582 0.100 0.561 0.185 Hg 0.061 0.079 0.049 0.088 方差贡献率(%) 52.127 18.334 51.395 19.066 累积方差贡献率(%) 52.127 70.461 51.395 70.461 表 4 重金属潜在生态危害指数
Table 4. Potential ecological hazard index of heavy metals
重金属元素 Eri 重金属元素 Eri Cr 0.85 Cd 18.06 Co 5.73 Pb 2.26 Ni 2.38 As 6.96 Cu 3.95 Hg 14.79 Zn 0.54 RI 55.50 表 5 Hakanson潜在生态风险分级标准
Table 5. Grading standards of Hakanson potential ecological risk
单项生态风险因子(Eri) 综合生态危害指数(RI) 等级 得分 等级 得分 低生态风险 < 40 低生态风险 < 150 中等生态风险 40~80 中等生态风险 150~300 较高生态风险 80~160 高生态风险 300~600 高生态风险 160~320 极高生态风险 >600 极高生态风险 >320 -
[1] 苏辉跃, 刘江川, 王璐, 等. 城乡过渡区土壤-蔬菜中重金属耦合分异特征及形成机理解析[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2022, 38(2): 184-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCST202202007.htm
Su H Y, Liu J C, Wang L, et al. Analysis of heavy metal coupling differentiation characteristics and formation mechanism in soil-vegetable in urban-rural transition area[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2022, 38(2): 184-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NCST202202007.htm
[2] Pekey H, Doǧan G. Application of positive matrix factori-sation for the source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments: A comparison with a previous factor analysis study[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2013(106): 233-237.
[3] 姚春卉, 宁曙光, 武波, 等. 青岛市新兴工业园区土壤重金属污染特征[J]. 中国科技论文, 2020, 15(9): 1050-1057. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2020.09.013
Yao C H, Ning S G, Wu B, et al. Characteristics of heavy metal pollution in soil of Qingdao Xinxing Industrial Park[J]. China Science and Technology Paper, 2020, 15(9): 1050-1057. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2020.09.013
[4] Hadzi G Y, Ayoko G A, Essumang D K, et al. Contami-nation impact and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in surface soils from selected major mining areas in Ghana[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2019, 41(2): 2821-2843.
[5] Ren Z Q, Xiao R, Zhang Z H, et al. Risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in agricultural soil: A case study in the coastal city of Zhejiang Province, China[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2019, 33(11-12): 2109-2118. doi: 10.1007/s00477-019-01741-8
[6] Kolo M T, Khandaker M U, Amin Y M, et al. Assessment of health risk due to the exposure of heavy metals in soil around Mega coal-fired cement factory in Nigeria[J]. Results in Physics, 2018, 11: 755-762. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2018.10.003
[7] Abrahams P W. Soils: Their implications to human health[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2002, 291(1-3): 1-32. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01102-0
[8] Seifeddine S, Ouahida Z, Ferid D, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in urban and peri-urban soil of Setif City (High Plains, eastern Algeria)[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2022, 194(2): 1-17.
[9] 郭晗, 孙英君, 王绪璐, 等. 县域城市土壤重金属空间分布特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2022, 42(1): 287-297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202201032.htm
Guo H, Sun Y J, Wang X L, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of soil heavy metals in county cities[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 2022, 42(1): 287-297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202201032.htm
[10] 冯乾伟, 王兵, 马先杰, 等. 黔西北典型铅锌矿区土壤重金属污染特征及其来源分析[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(4): 863-870. doi: 10.19658/j.issn.1007-2802.2020.39.051
Feng Q W, Wang B, Ma X J, et al. Characteristics of soil heavy metal contamination in typical Pb-Zn mining areas in northwest Qianxi and its source analysis[J]. Mineral and Rock Geochemistry Bulletin, 2020, 39(4): 863-870. doi: 10.19658/j.issn.1007-2802.2020.39.051
[11] 王锐, 邓海, 贾中民, 等. 汞矿区周边土壤重金属空间分布特征、污染与生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(6): 3018-3027. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202010140
Wang R, Deng H, Jia Z M, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in soils around mercury mining areas, pollution and ecological risk assessment[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(6): 3018-3027. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202010140
[12] 迟晓杰, 谷海红, 李富平, 等. 重金属污染土壤植物修复效果评价方法——高光谱遥感[J]. 金属矿山, 2019(1): 16-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201901004.htm
Chi X J, Gu H H, Li F P, et al. Evaluation method of phytoremediation effect of heavy metal contaminated soil by hyperspectral remote sensing[J]. Metal Mining, 2019(1): 16-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS201901004.htm
[13] 赵恒谦, 张文博, 朱孝鑫, 等. 煤炭矿区植被冠层光谱土地复垦敏感性分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2019, 39(6): 1858-1863. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201906038.htm
Zhao H Q, Zhang W B, Zhu X X, et al. Sensitivity analysis of vegetation canopy spectra for land reclamation in coal mining areas[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2019, 39(6): 1858-1863. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201906038.htm
[14] 刘恒凤, 张吉雄, 周楠, 等. 矸石基胶结充填材料重金属浸出及其固化机制[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2021, 50(3): 523-531. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202103014.htm
Liu H F, Zhang J X, Zhou N, et al. Heavy metal leaching from gangue-based cemented filling materials and its curing mechanism[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2021, 50(3): 523-531. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD202103014.htm
[15] 孙厚云, 吴丁丁, 毛启贵, 等. 新疆东天山某铜矿区土壤重金属污染与生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(12): 2690-2699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201912007.htm
Sun H Y, Wu D D, Mao Q G, et al. Evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in a copper mining area in East Tianshan, Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(12): 2690-2699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201912007.htm
[16] 段友春, 梁兴光, 臧浩, 等. 日照市典型农用地土壤重金属来源分析及环境质量评价[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(11): 1410-1414, 1429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR202011019.htm
Duan Y C, Liang X G, Zang H, et al. Analysis of heavy metal sources and environmental quality evaluation of typical agricultural land in Rizhao[J]. Environmental Pollution and Prevention, 2020, 42(11): 1410-1414, 1429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR202011019.htm
[17] 董霁红, 卞正富, 于敏, 等. 矿区充填复垦土壤重金属分布特征研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2010, 39(3): 335-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201003008.htm
Dong J H, Bian Z F, Yu M, et al. Study on the distribution characteristics of heavy metals in mine reclamation soils[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2010, 39(3): 335-341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201003008.htm
[18] 陈佳林, 李仁英, 谢晓金, 等. 南京市绿地土壤重金属分布特征及其污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(2): 909-916. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202102046.htm
Chen J L, Li R Y, Xie X J, et al. Distribution characteristics of heavy metals in greenland soils of Nanjing and its pollution evaluation[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(2): 909-916. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202102046.htm
[19] 周艳, 陈樯, 邓绍坡, 等. 西南某铅锌矿区农田土壤重金属空间主成分分析及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201806045.htm
Zhou Y, Chen Q, Deng S P, et al. Spatial principal component analysis and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of a Pb-Zn mining area in southwest China[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(6): 2884-2892. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201806045.htm
[20] Lin Q, Liu E, Zhang E, et al. Spatial distribution, contami-nation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China[J]. Catena, 2016, 145: 193-203.
[21] Qin F, Ji H B, Li Q, et al. Evaluation of trace elements and identification of pollution sources in particle size fractions of soil from iron ore areas along the Chao River[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 138: 33-49.
[22] Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975-1001.
[23] 张锂, 韩国才, 陈慧, 等. 黄土高原煤矿区煤矸石中重金属对土壤污染的研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2008(10): 1141-1146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB200810013.htm
Zhang L, Han G C, Chen H, et al. Study on soil contamination by heavy metals in coal gangue in the Loess Plateau coal mining area[J]. Journal of Coal, 2008(10): 1141-1146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB200810013.htm
[24] Hao J L, Han Z Z, Wang C Z, et al. Distribution of heavy metals in the topsoil of the Jining mining area[J]. Mining Science and Technology, 2010, 20(3): 395-399.
[25] Guo G H, Wu F C, Xie F Z, et al. Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in urban soils from southwest China[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 24(3): 410-418.
[26] 黄石德. 铁矿废弃地不同修复模式土壤重金属污染特征及评价[J]. 防护林科技, 2019(3): 5-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FHLK201903002.htm
Huang S D. Characteristics and evaluation of heavy metal pollution in soils of iron ore waste sites with different remediation modes[J]. Protective Forest Technology, 2019(3): 5-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FHLK201903002.htm
[27] 葛晓颖, 欧阳竹, 杨林生, 等. 环渤海地区土壤重金属富集状况及来源分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(6): 1979-1988. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201906030.htm
Ge X Y, Ouyang Z, Yang L S, et al. Analysis of the enrichment status and sources of heavy metals in soils in the Bohai Sea Rim[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 2019, 39(6): 1979-1988. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201906030.htm
[28] 赵俊兴, 李光明, 秦克章, 等. 富含钴矿床研究进展与问题分析[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(24): 2484-2500. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201924005.htm
Zhao J X, Li G M, Qin K Z, et al. Research progress and problem analysis of cobalt-rich deposits[J]. Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(24): 2484-2500. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201924005.htm
[29] 张晓薇, 王恩德, 安婧. 辽阳弓长岭铁矿区重金属污染评价[J]. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(6): 1789-1796. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201806025.htm
Zhang X W, Wang E D, An J. Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in the Gongchangling iron ore mining area of Liaoyang[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2018, 37(6): 1789-1796. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201806025.htm
-




 下载:
下载: