Chemical Characteristics and Evolutionary Patterns of Groundwater in the Daqing River Plain Area of Haihe Basin
-
摘要:
地下水超采引发大清河流域范围内一系列生态环境负效应,地下水与地表水关系密切,厘清大清河流域平原区地下水化学特征及演化规律,对大清河流域水资源合理开发利用具有重要意义,然而目前尚缺乏对大清河流域地下水化学特征特别是其历史以来的演变规律作系统的分析。本文以海河流域大清河平原区地下含水系统为例,采集浅层含水层组47个水样和深层含水层组32个水样,测试了主要阴离子(Cl-、SO42-、NO3-)和阳离子(K+、Na+、Ca2+、Mg2+)等指标,利用水化学类型、吉布斯模型、离子比值关系等方法,研究其水化学特征及演化规律。测试结果显示:浅层含水层组受到气象和人为因素影响较大,浅层和深层含水层组pH值(7.35~8.92)差异不大,偏碱性;浅层含水层组由于农业活动等影响,造成局部地区的硝酸盐和硫酸盐污染。水岩相互作用分析显示:硅酸盐矿物风化是研究区主要的矿物来源,硅酸盐矿物溶解、阳离子交换为主要的水化学作用。研究区浅层地下水水化学特征总体上受地形和水文地质条件的影响,由山前平原-中部平原呈规律性分布。现状地下水化学类型为沿地下水径流方向由山前的HCO3-Ca·Mg(Ca)型,经HCO3-Mg·Ca、HCO3-Mg·Ca·Na、HCO3-Na·Mg·Ca向HCO3·Cl-Na·Ca、HCO3·Cl·SO4-Na至平原中部冲湖积平原的Cl(SO4)-Na转变。水化学演变分析显示中部平原地下水由以Cl·HCO3-Ca·Na、HCO3·Cl-Ca·Na型为主,转变为当前条件下以Cl·HCO3-Ca·Na、SO4·Cl-Na·Mg型为主。总体上,研究区现状水化学类型复杂多样,且分布上虽然仍受地形与地质条件的控制,但越来越多地受到以开采为主的人类活动的影响,应重视人类活动对该区域地下水的影响,合理布置开采方案。本文利用水化学方法研究了大清河流域平原区地下水化学特征及演化规律,厘清了大清河流域平原的水化学特征以及水化学类型演变规律,初步分析了演变趋势造成的原因,特别是指明地下水化学演变越来越受到人类活动的影响,后续将在水化学未来的演变预测上进行相关的研究。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Groundwater is closely related to surface water. Groundwater over-extraction has triggered a series of negative ecological effects in the Daqing River basin. The evolution of groundwater chemical characteristics is influenced by both natural and anthropogenic factors. The analysis of groundwater chemical characteristics can indicate the meteorological-hydrological and water-rock interaction during groundwater runoff, thus reflecting the groundwater circulation path, groundwater system characteristics and evolution laws, etc. It also helps to monitor groundwater dynamics and prevent the occurrence of groundwater pollution.
OBJECTIVES To clarify the chemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the plain area of the Daqing River basin, which will be important for the rational development and utilization of water resources in the basin.
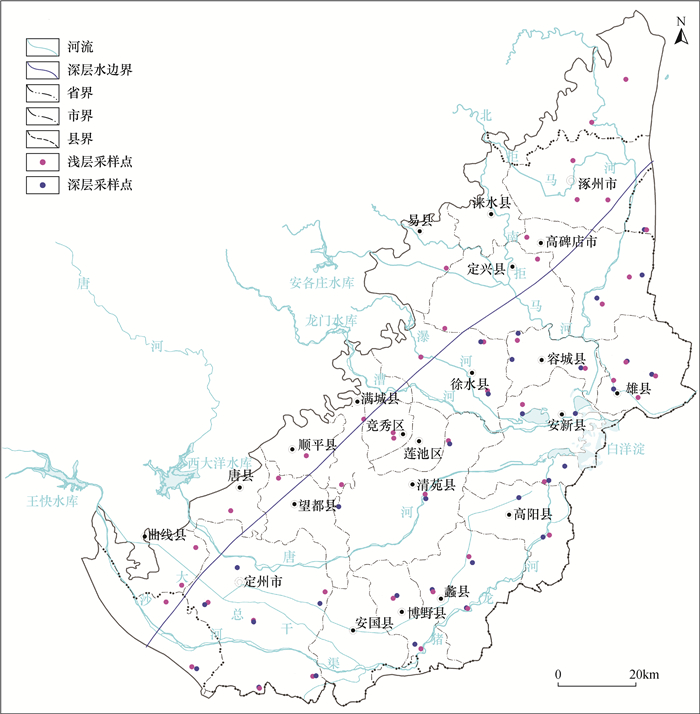
METHODS 47 water samples from the shallow aquifer groups and 32 water samples from the deep aquifer groups were collected to analyze the main anions (Cl-, SO42-, NO3-) and cations (K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+). The water chemistry characteristics and evolution laws were studied by using the water chemistry type, Gibbs model and ion ratio relationship. On-site portable water quality analyzer (HACH-HQ40d) was used to test pH (accuracy 0.01), total dissolved solids (TDS, accuracy 0.01) and other parameters, and groundwater samples were collected after the indicators were stabilized. All samples were sent to the laboratory at low temperature and stored in a refrigerator at 4℃, and groundwater alkalinity was determined by titration on the same day. Seven days later, the samples were sent to the Institute of Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences for testing of major anions (Cl-, SO42-, NO3-) and major cations (K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+) using inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry (iCAP6300). The anion and cation charge balance error was less than 5%, and the anion and cation test accuracy was 0.01mg/L.
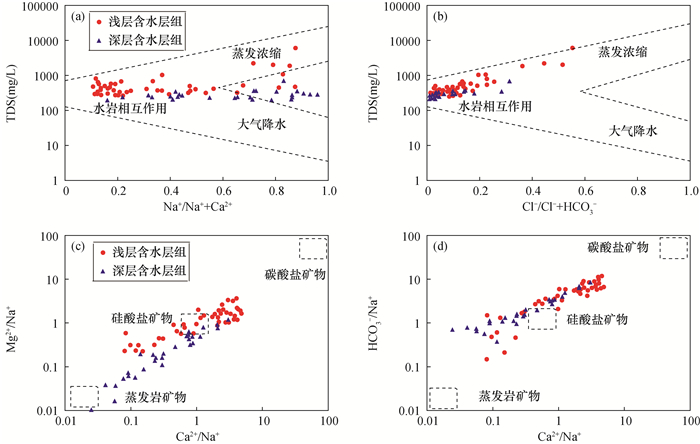
RESULTS The test results showed that the largest deviation was in the water sample from Hanbao Village, Liu Lizhuang Town, Anxin County, Baoding City, Hebei Province, which was from the shallow aquifer groups, and the maximum TDS reached 6015.00mg/L. The TDS of the shallow aquifer groups ranged from 254.10 to 6015.00mg/L, with an average of 664.14mg/L, a large coefficient of variation and a large variation in TDS, indicating that the shallow aquifer groups were affected by meteorological and human factors. The TDS of the deep aquifer groups ranged from 197.10 to 691.40mg/L, with an average of 278.58mg/L, and the coefficient of variation was small, indicating that the groundwater of the deep aquifer groups was less affected by meteorological and human activities than that of the shallow aquifer groups. A small portion of the sampling points of the shallow aquifer groups in the area were brackish water and salt water. The TDS of the deep aquifer groups was generally less than 1000mg/L, which was suitable for use as a mining layer. The pH values of the shallow and deep aquifer groupss in the study area were not very different (7.35-8.92) and were alkaline. The NO3- maximum value of 298.40mg/L and SO42-maximum value of 3091.00mg/L in the shallow aquifer groups, but the average value was not significant, indicating that the shallow aquifer groups have caused nitrate and sulfate pollution in local areas due to agricultural activities and other effects.
In the shallow layer of the study area, except for the difference in hydraulic conditions in the northern piedmont plain where flaky or spotty HCO3-Cl-SO4 and HCO3-Cl type water occurred, the anions in most of the piedmont plain were mainly HCO3 type, and the cations were mainly Ca and Ca-Mg and Mg-Ca. During the discharge of groundwater along the piedmont plain to the mouth of the alluvial fan, the cations changed from Ca-Mg type to Na type in order through Ca-Mg-Na, Na-Ca-Mg, Na-Mg-Ca, Na-Ca to Na type, and anions from HCO3 type to SO4 and Cl type via HCO3-SO4, HCO3-SO4-Cl, HCO3-Cl-SO4, SO4-Cl. The deep groundwater cations were relatively more complex, and the zonation was more obvious: from the piedmont plain to the bottom of the alluvial fan, the cations transition from Ca, Ca-Mg, Mg-Ca, Na-Mg-Ca (Mg-Ca-Na) type to Na-Ca and Na type water.
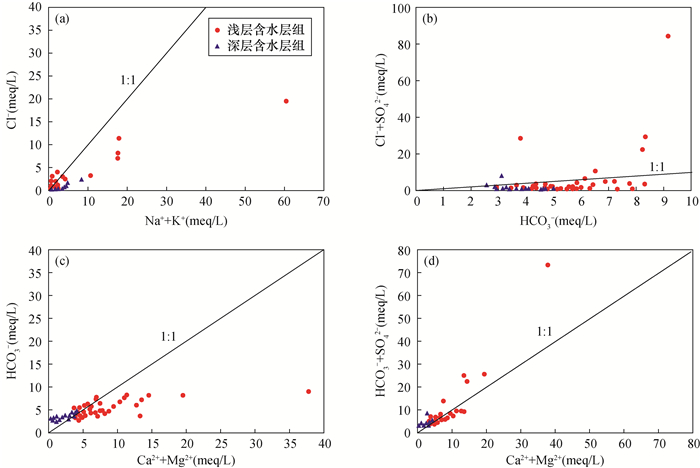
The shallow aquifer groups were basically located in the area of water-rock interaction, and individual points showed some influence of evaporation concentration. The deep aquifer groups were subjected to water-rock interaction and less affected by evaporation and atmospheric precipitation. The analysis results showed that the milligram equivalent concentration ratio of (Ca2++Mg2+)+(HCO3-+SO42-) to Na++K+-Cl- was close to -1, indicating a more significant cation exchange effect. The groundwater samples in this study area were mostly distributed near the end elements of silicate minerals, indicating that weathering of silicate minerals (such as feldspar) was the main hydrogeochemical control factor in the study area, which was consistent with the lithological characteristics of aquifers in the groundwater of the Daqing River basin plain, and the test results also showed that HCO3- was the dominant ion in both shallow and deep aquifer groups.
The SI values of calcite in the shallow aquifer groups in this study area ranged from -0.46 to 1.35, dolomite SI values from -0.88 to 3.02, gypsum SI values from -3.1 to -0.68, and rock salt SI values from -8.53 to -4.75, indicating that calcite and dolomite were partially saturated and partially unsaturated, and both gypsum and rock salt were unsaturated. Cl-/(Na++K+) could determine whether the groundwater was influenced by the dissolution of silicate rock. Most of the groundwater samples in this study area exhibited Cl-/(Na++K+) < 1, indicating that, in addition to rock salt in dissolved state, silicate mineral dissolution (e.g., potassium feldspar and sodium feldspar) was the main source of excess Na+ and K+. The Na+ content may also originate from cation exchange, and the high Cl-, the higher concentration may be the input of foreign contamination. The HCO3-/(Ca2++Mg2+) of the samples from the shallow aquifer groups was basically less than 1, showing excess Ca2+ and Mg2+, suggesting other sources of Ca2+ or Mg2+, while the (HCO3-+SO42-)/(Ca2++Mg2+) of the shallow aquifer groups was distributed above and below the 1∶1 line on both sides, suggesting that evaporite minerals (e.g. gypsum) may also be an important source of Ca2+ for the shallow aquifer groups, as evidenced by the unsaturated state of gypsum in groundwater, in addition to the increase in SO42- due to human activities. Both HCO3-/(Ca2++Mg2+) and (HCO3-+SO42-)/(Ca2++Mg2+) of the deep aquifer groups lay above the 1∶1 line, and the excess HCO3- implied silicate dissolution dominance, or the presence of cation exchange, leading to a lower Ca2+ content. (Cl-+SO42-)/(HCO3-) could indicate the dissolution status of evaporites and carbonates, and water samples from shallow and deep aquifer groups were mainly distributed in the (Cl-+SO42-)/(HCO3-)=1∶1 line below, which indicated that its chemical components were more dissolved by carbonate rocks.
In the influence zone of the Caohe River in the northern part of Mancheng District, the water chemistry changed from HCO3-Ca-Mg water to Cl-HCO3-Ca-Na water; at the alluvial fan margin of Jiehe River in Shunping County and at the alluvial fan margin of Rejected Horse River in Zhuozhou City, the proportion of Na content in groundwater gradually exceeded that of Mg as the cation content second only to Ca, and the water chemistry changed from HCO3-Ca-Mg water to HCO3-Ca-Na-Mg type water. The groundwater in the central plain changed from Cl-HCO3-Ca-Na and HCO3-Cl-Ca-Na type water with island and strip distribution of SO4-HCO3-Na-Mg, SO4-HCO3-Na, SO4-Na-Mg and HCO3-Na-Mg type water to Cl-HCO3-Ca-Na, SO4-Cl-Na-Mg type water dominated and mingled with HCO3-Cl-Ca-Mg, Cl-SO4-Na-Mg, HCO3-Cl-SO4-Na, HCO3-SO4-Na, HCO3-SO4-Na, HCO3-SO4-Na-Mg, and Cl-SO4-Na-Mg type water.
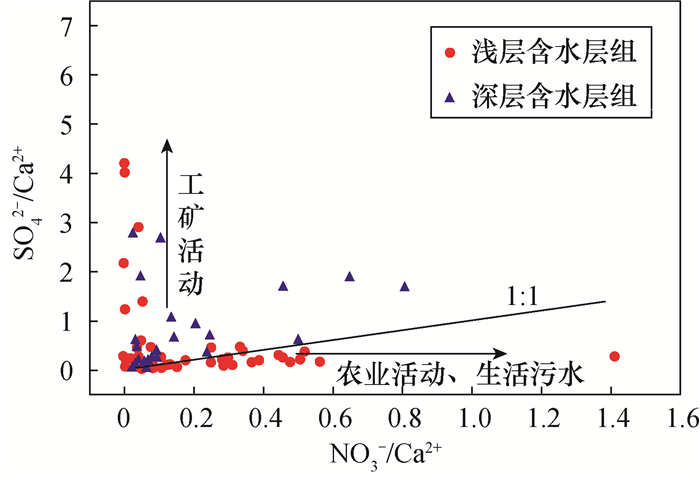
The average NO3- content of the shallow aquifer was 28.78mg/L, and the average NO3- content of the deep aquifer was 4.55mg/L, indicating that nitrate pollution was serious in the shallow groundwater local area of the study area. Referring to the groundwater quality standard (GB/T 14848—2017) for ClassⅢ water, there were 17 sampling points in the shallow aquifer groups with NO3- content over 20mg/L and 5 sampling points in the shallow aquifer groups with SO42- greater than 250g/L, indicating that these sampling sites were affected by anthropogenic activities, resulting in nitrate and sulfate pollution. A ratio of SO42-/Ca2+ to NO3-/Ca2+ greater than 1 indicated that industrial and mining activities had a greater impact on groundwater, and a ratio less than 1 was more disturbed by agricultural activities and residential sewage. The results showed that the ratio of the deep aquifer groups was greater than 1, and only the 240m well in the north of Erlangmiao Village, Dingzhou City, Baoding City, Hebei Province, was less than 1. This indicated that the deep aquifer groups were basically affected by industrial and mining activities, but not by agricultural activities and residential sewage. In the shallow aquifer groups, there were 27 water samples with SO42--Ca2+ to NO3-Ca2+ ratio greater than 1, and 20 water samples with SO42--Ca2+ to NO3--Ca2+ ratio less than 1, indicating that the shallow aquifer groups were partly influenced by industrial and mining activities, and partly influenced by agricultural activities and domestic sewage of residents.
CONCLUSIONS The characteristics and evolution of groundwater chemistry in the plain area of the Daqing River basin was investigated by using the water chemistry method, clarifying the characteristics of the water chemistry and the evolution of water chemistry types in the plain area of the Daqing River Basin. Reasons for the evolution trend were also investigated, indicating that the evolution of groundwater chemistry is increasingly influenced by human activities. Relevant research will be conducted on the prediction of the future evolution of water chemistry.
-

-
表 1 研究区地下水水化学参数统计
Table 1. Statistical results of groundwater hydrochemical parameters in the study area
地下水类型 特征值 pH TDS
(mg/L)K+
(mg/L)Na+
(mg/L)Ca2+
(mg/L)Mg2+
(mg/L)Cl-
(mg/L)SO42-
(mg/L)HCO3-
(mg/L)NO3-
(mg/L)浅层含水层组 最小值 7.35 254.10 0.26 7.61 12.88 14.44 5.26 6.48 177.30 0.20 最大值 8.92 6015.00 2.69 1393.00 194.00 341.40 693.30 3091.00 558.30 298.40 平均值 7.90 664.14 1.14 87.49 76.15 47.60 70.66 162.27 333.28 28.78 标准偏差 0.35 907.40 0.66 218.22 39.03 51.66 120.67 483.46 90.21 48.99 变异系数 0.04 1.37 0.58 2.49 0.51 1.09 1.71 2.98 0.27 1.70 深层含水层组 最小值 7.40 197.10 0.30 8.26 4.43 1.12 1.75 4.99 155.60 0.71 最大值 8.80 691.40 2.61 189.80 58.29 20.82 86.22 255.70 305.10 17.46 平均值 8.03 278.58 1.46 56.52 28.98 10.60 15.37 27.41 221.23 4.55 标准偏差 0.38 88.95 0.65 37.97 14.91 5.54 19.14 43.89 39.67 4.05 变异系数 0.05 0.32 0.45 0.67 0.51 0.52 1.25 1.60 0.18 0.89 Note: The test results showed that the largest deviation was in the water sample from Hanbao Village, Liu Lizhuang Town, Anxin County, Baoding City, Hebei Province, which was from the shallow aquifer groups, and the maximum TDS reached 6015.00mg/L. The TDS of the shallow aquifer groups ranged from 254.10 to 6015.00mg/L, with an average of 664.14mg/L, with a large coefficient of variation and a large variation in TDS, indicating that the shallow aquifer groups were affected by meteorological and human factors. The TDS of the deep aquifer group ranged from 197.10 to 691.40mg/L, with an average of 278.58mg/L, and the coefficient of variation was small, indicating that the groundwater of the deep aquifer groups was less affected by meteorological and human activities than that of the shallow aquifer groups. The pH values of the shallow and deep aquifer groups in the study area were not significantly different (7.35-8.92) and were alkaline. The NO3-maximum value of 298.40mg/L and the SO42-maximum value of 3091.00mg/L in the shallow aquifer groups, but the average value is not significant, indicating that the shallow aquifer groups have caused local nitrate and sulfate pollution due to agricultural activities and other influences. -
[1] 何宝南, 何江涛, 孙继朝, 等. 区域地下水污染综合评价研究现状与建议[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(3): 51-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202203005.htm
He B N, He J T, Sun J C, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of regional groundwater pollution: Research status and suggestions[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(3): 51-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202203005.htm
[2] 陈典, 张照荷, 赵微, 等. 北京市再生水灌区地下水中典型全氟化合物的分布现状及生态风险[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(3): 499-510. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202111300190
Chen D, Zhang Z H, Zhao W, et al. The occurrence, distribution and risk assessment of typical perfluorinated compounds in groundwater from a reclaimed wastewater irrigation area in Bejing[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(3): 499-510. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202111300190
[3] 胡宗义, 何冰洋, 李毅. 中国流域水污染协同治理研究[J]. 中国软科学, 2022(5): 66-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRK202205007.htm
Hu Z Y, He B Y, Li Y, et al. Research on collaborative governance of water pollution in river basin[J]. China Soft Science, 2022(5): 66-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRK202205007.htm
[4] Said I, Merz C, Salman E R, et al. Identification of hydrochemical processes using multivariate statistics in a complex aquifer system of Sohag region, Egypt[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2020, 79(8): 1-14.
[5] Ahmed A, Clark I. Groundwater flow and geochemical evolution in the central Flinders Ranges, South Australia[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 572(1): 837-851.
[6] Han D M, Liang X, Jin M G, et al. Hydrogeochemical indicators of groundwater flow systems in the Yangwu River Alluvial Fan, Xinzhou Basin, Shanxi, China[J]. Environmental Management, 2009, 44(2): 243-255. doi: 10.1007/s00267-009-9301-0
[7] Chen J, Qian H, Gao Y Y, et al. Insights into hydrological and hydrochemical processes in response to water replenishment for lakes in arid regions[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 581, 124386. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124386
[8] Xiao Y, Shao J L, Cui Y L, et al. Groundwater circulation and hydrogeochemical evolution in Nomhon of Qaidam Basin, northwest China[J]. Journal of Earth System Science, 2017, 126(2): 1-16.
[9] Jla B, Ywa B, Cza B, et al. Hydrogeochemical processes controlling the mobilization and enrichment of fluoride in groundwater of the North China Plain[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 730: 1-11.
[10] 刘君, 陈宗宇, 王莹, 等. 大规模开采条件下我国北方区域地下水水化学变化特征[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(4): 408-414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201704004.htm
Liu J, Chen Z Y, Wang Y, et al. Evaluation of hydrochemical characteristics of regional groundwater systems in northern China under the conditions of large-scale exploitation[J]. Earth and Environment, 2017, 45(4): 408-414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201704004.htm
[11] 赵奕博, 尹钊, 史常青, 等. 大清河流域河岸植被带污染物净化能力研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2022, 36(5): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS202205018.htm
Zhao Y B, Yin Z, Shi C Q, et al. Study on pollutant purification capacity of riparian vegetation zonein daqing river basin[J]. Journal of Soiland Water Conservation, 2022, 36(5): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQS202205018.htm
[12] 杨忠俭, 董思远. BIM技术在京杭运河大清河航道工程中的应用[J]. 山东交通科技, 2022(2): 151-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JTKE202202047.htm
Yang Z J, Dong S Y. Application of BIM technology in the Daqing River waterway project of the Beijing—Hangzhou Canal[J]. Shandong Communications Technology, 2022(2): 151-153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JTKE202202047.htm
[13] 姜鲁光, 杨成, 封志明, 等. 面向多目标情景的大清河流域水资源利用权衡[J]. 资源科学, 2021, 43(8): 1649-1661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZY202108012.htm
Jiang L G, Yang C, Feng Z M, et al. Multi-scenario trade-off on water resources utilization in Daqing River Basin[J]. Resources Science, 2021, 43(8): 1649-1661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZY202108012.htm
[14] 王钰升. 大清河流域平原区地下水人工补给方式研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021.
Wang Y S. Study of groundwater artificial recharge modes in plain area of Daqing River Basin[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021.
[15] 赵婧彤. 地下水人工补给过程中的促渗技术研究——以大清河流域典型区为例[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021.
Zhao J T. Study on infiltration promotion techniques during artificial recharge of groundwater——A case study of Daqing River Basin[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021.
[16] 庄玉峰. 大清河中下游地下水水源评价区水量安全性评价[J]. 水利规划与设计, 2017(5): 24-25, 83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLGH201705008.htm
Zhuang Y F. Water safety assessment of groundwater source assessment area in the middle and lower reaches of Daqing River[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design, 2017(5): 24-25, 83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLGH201705008.htm
[17] 董冬, 边静. 趋势面分析法在地下水动态预测中的应用[J]. 吉林地质, 2020, 39(2): 96-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLDZ202002018.htm
Dong D, Bian J. Application of trend surface analysis method in groundwater dynamic prediction[J]. Jilin Geology, 2020, 39(2): 96-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLDZ202002018.htm
[18] 刘旭东, 张瑞, 万宝. 基于Piper-PCA-MLP神经网络的矿井涌水水源识别方法研究[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2022, 34(7): 50-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT202207010.htm
Liu X D, Zhang R, Wan B. Study on mine water inrush source discrimination method based on Piper-PCA-MLP neural network[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2022, 34(7): 50-55. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT202207010.htm
[19] Ma B, Jin M G, Liang X, et al. Groundwater mixing and mineralization processes in a mountain-oasis-desert basin, northwest China: Hydrogeochemistry and environmental tracer indicators[J]. Hydrogelogy Journal, 2018, 26: 233-250.
[20] 陈毅. 白洋淀流域平原区地下水-孔隙水的水化学特征和水文地球化学过程[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.
Chen Y. Pore-water and groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and hydrogeochemical processes in Baiyangdian Lake Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018.
[21] 秦怡, 唐小惠, 李艳龙, 等. 枣庄市南部地下水水化学特征及其主要控制因素[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(6): 132-138, 155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ202206016.htm
Qin Y, Tang X H, Li Y L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and main controlling factor of the ground water in southern Zaozhuang[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(6): 132-138, 155. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ202206016.htm
[22] 李锴雯. 河北省自然地理环境对植物的影响[J]. 现代农村科技, 2016(6): 73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBNK201606073.htm
Li K W. Influence of natural geographical environment on plants in Hebei Province[J]. Modern Rural Science and Technology, 2016(6): 73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBNK201606073.htm
[23] 侯思琰, 徐鹤, 刘德文, 等. 大清河流域主要河流与湿地生态水量计算与保障分析[J]. 吉林水利, 2021(8): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLSL202108002.htm
Hou S Y, Xu H, Liu D W, et al. Calculation and guarantee analysis of ecological water volume of main rivers and wetlands in Daqing River Basin[J]. Jilin Water Conservancy, 2021(8): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLSL202108002.htm
[24] 任宇, 曹文庚, 潘登, 等. 2010—2020年黄河下游河南典型灌区浅层地下水中砷和氟的演化特征及变化机制[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(6): 846-859. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202110090143
Ren Y, Cao W G, Pan D, et al. Evolution characteristics and change mechanism of arsenic and fluorine in shallow groundwater from a typical irrigation area in the lower reaches of the Yellow River (Henan) in 2010—2020[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(6): 846-859. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202110090143
[25] 李谨丞, 曹文庚, 潘登, 等. 黄河冲积扇平原浅层地下水中氮循环对砷迁移富集的影响[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(1): 120-132. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202110080140
Li J C, Cao W G, Pan D, et al. Influences of nitrogen cycle on arsenic enrichment in shallow groundwater from the Yellow River Alluvial Fan Plain[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(1): 120-132. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202110080140
[26] 曹文庚, 杨会峰, 高媛媛, 等. 南水北调中线受水区保定平原地下水质量演变预测研究[J]. 水利学报, 2020, 51(8): 12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB202008005.htm
Cao W G, Yang H G, Gao Y Y, et al. Prediction of groundwater quality evolution in the Baoding Plain of the SNWDP benefited regions[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2020, 51(8): 12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLXB202008005.htm
-



 下载:
下载: