Accumulation and Source Apportionment of Soil Heavy Metals in Molybdenum-Lead-Zinc Polymetallic Ore Concentration Area of Luanchuan
-
摘要:
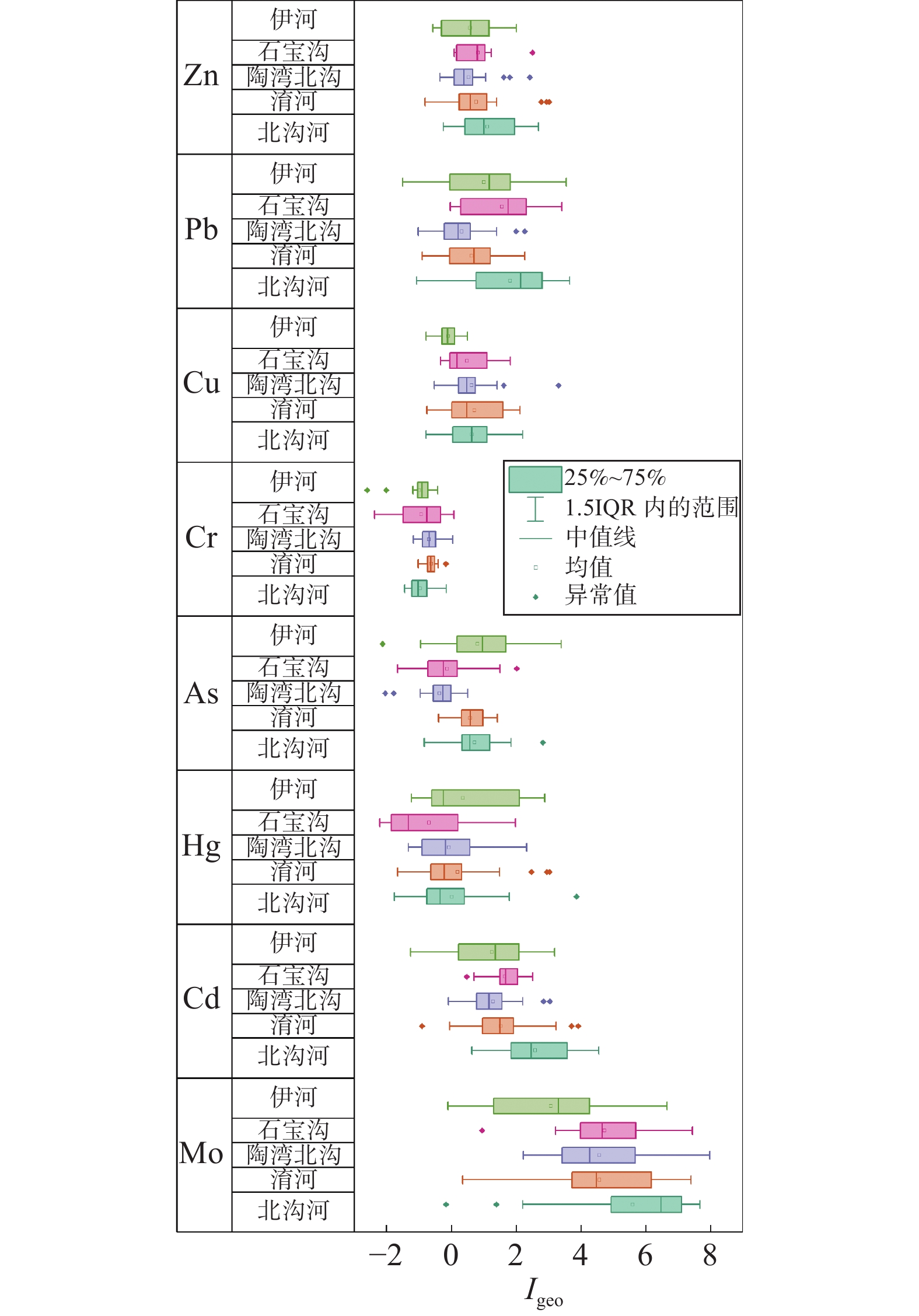
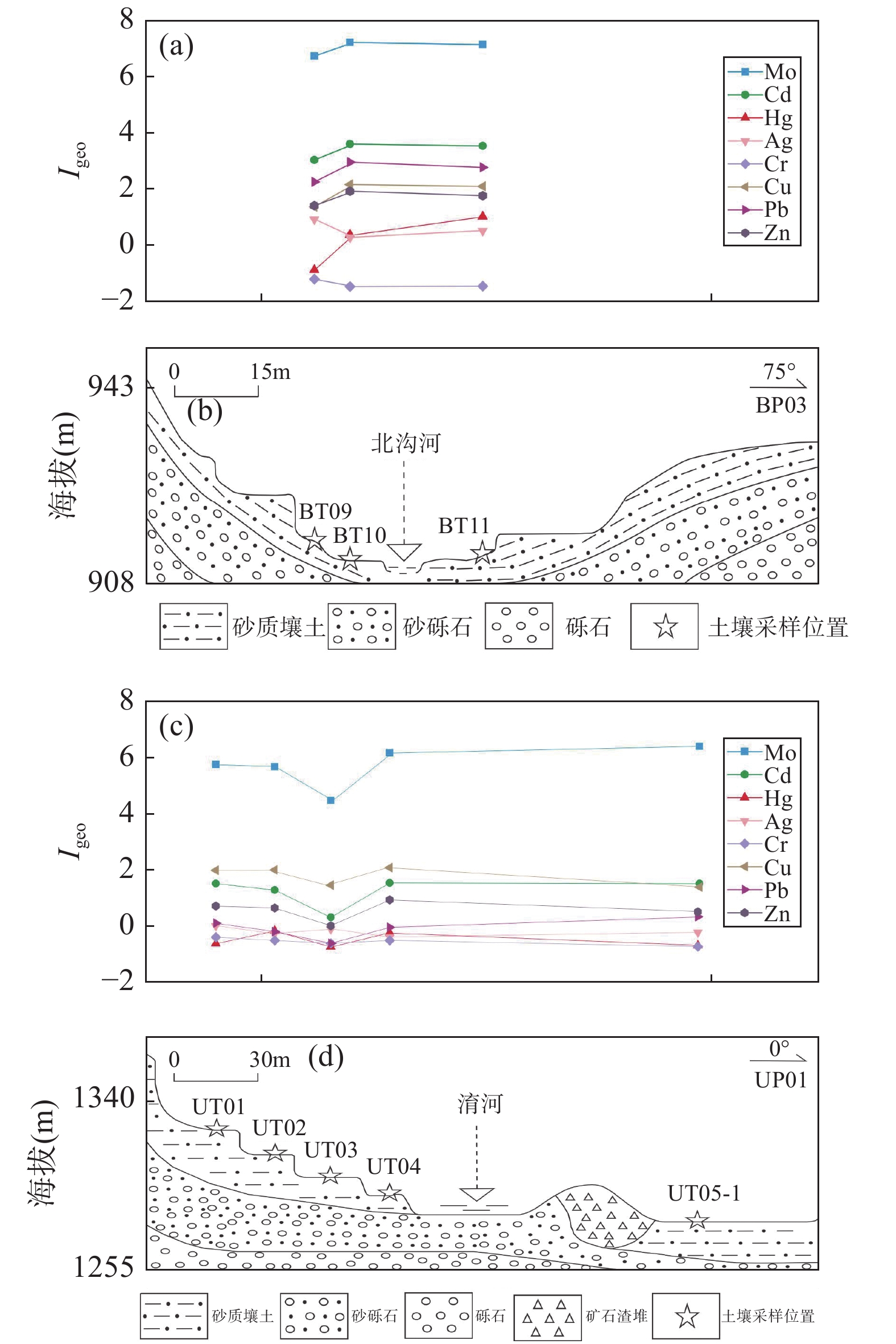
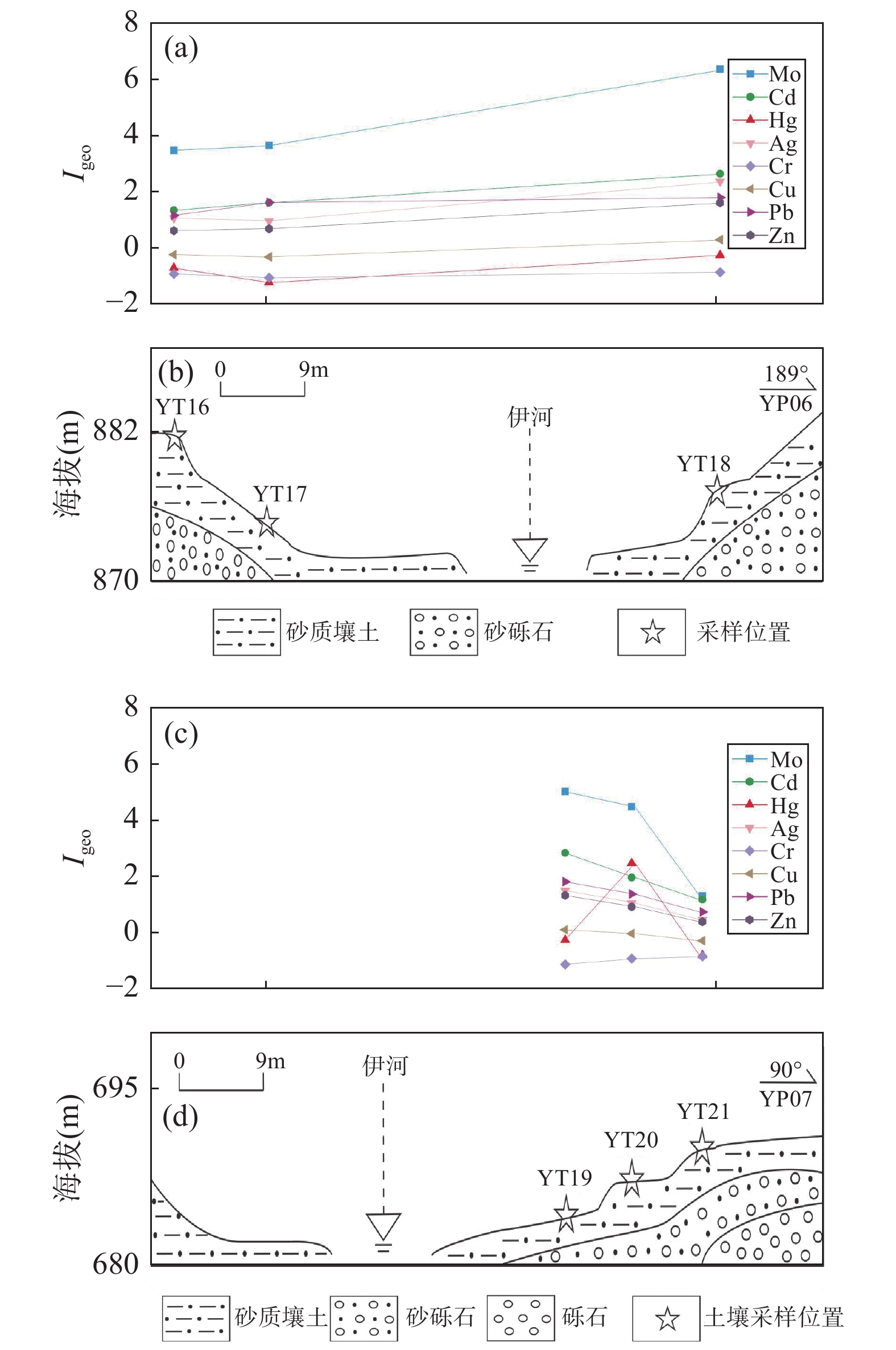
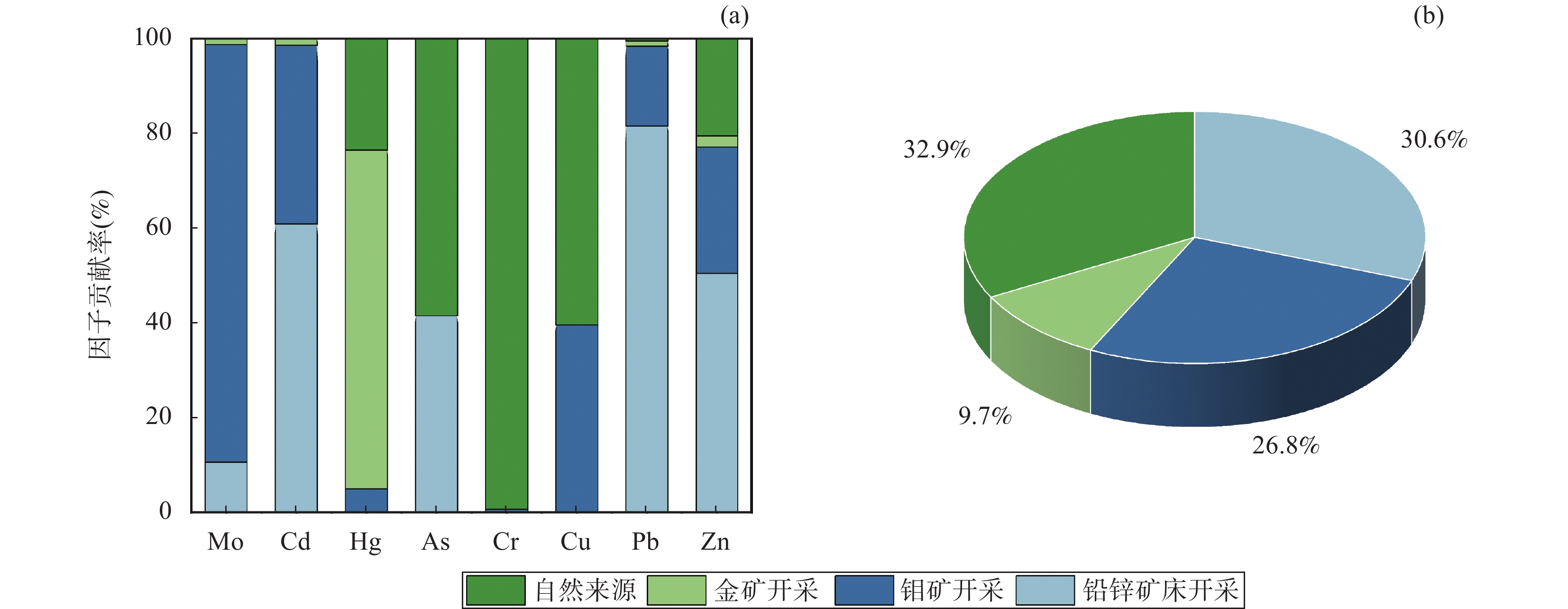
河南栾川钼铅锌多金属矿集区内长期矿产资源开发产生了大量的重金属,目前研究区农田表层土壤重金属累积及不同种类矿业活动对其影响尚不明晰。本文选取研究区内5个典型小流域,采集河流沿岸29条水平土壤剖面上95件农田表层土壤样品,采用极谱法测定Mo,电感耦合等离子体质谱法测定Cd,X射线荧光光谱法测定Cr、Cu、Pb和Zn,原子荧光分光光度法测定Hg和As含量,通过地累积指数法、内梅罗综合污染指数法和潜在生态风险指数法分别评价重金属的累积特征、污染程度和生态风险;采用多元统计分析和PMF模型对表层土壤重金属的来源进行解析。结果表明:研究区农田表层土壤中主要污染物为Mo,局部为Hg;除Cr外,其他重金属均不同程度地受到周边矿业活动的影响;5个流域土壤重金属富集程度依次是:北沟河>淯河>石宝沟>陶湾北沟>伊河。北沟河土壤总体为重污染,中等生态风险,其他流域土壤总体污染程度为轻度,生态风险等级为轻微;但不同流域均存在重金属污染较重和生态风险较强的点位。典型横向土壤剖面分析表明,近岸部分土壤重金属富集程度明显高于远岸土壤。研究区农田表层土壤重金属来源于自然源(32.9%)、铅锌矿矿业活动(30.6%)、钼矿矿业活动(26.8%)和金矿矿业活动(9.7%)。
Abstract:BACKGROUND The Luanchuan Mo-Pb-Zn polymetallic ore concentration area, located in Henan Province, China, has a long-term history of mining activities. Heavy metals have been liberated during mining, which induces heavy metal pollution of water and soil near the mines. There have been many studies about the pollution of heavy metals by mining activities, but it is still unclear as to the impact of various mine types in a polymetallic ore concentration area on accumulation of heavy metals in soil.
OBJECTIVES To study the impact of various mine types on accumulation of soil heavy metals, pollution level and ecological risk, and to identify the sources of soil heavy metals.
METHODS A total of 95 surface soil samples were collected from 29 soil profiles along the rivers in five typical basins in the Luanchuan Mo-Pb-Zn polymetallic ore concentration area, Henan Province, China. Mo, Hg, As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil were measured by polarography, atomic fluorescence spectrophotometry (AFS) and inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The Igeo, Nemerow index and potential ecological risk index were used to study the accumulation, pollution level and source apportionment of heavy metals.
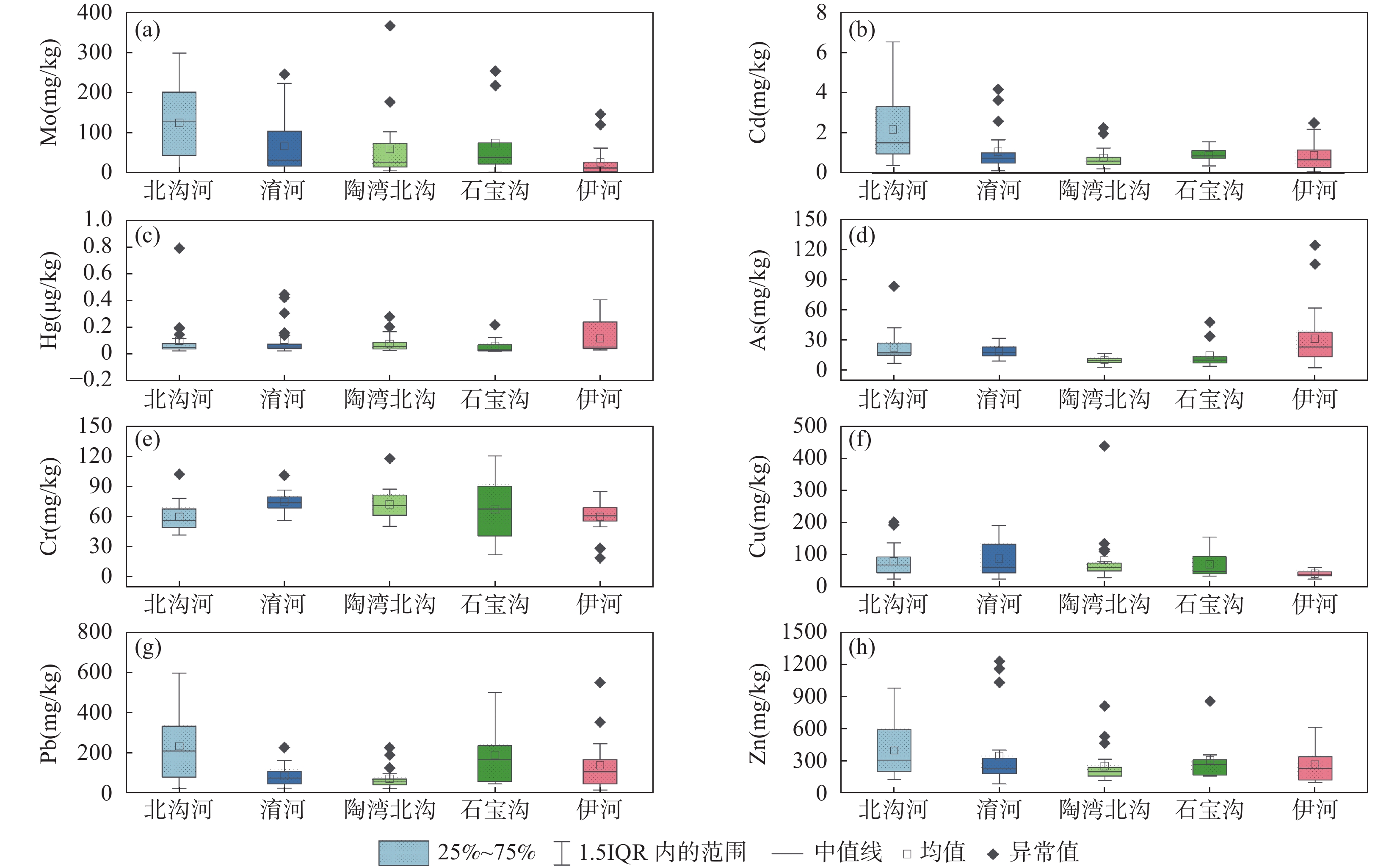
RESULTS The results showed that Mo was the main pollutant, and part of the soil was obviously polluted by Hg. Cd, Pb, Zn, Cu and As in soil were also affected by the mining activities in the study area to some extent. Accumulation extent of heavy metals in soil from various river basins followed Beigou River > Yu River > Shibao River > Taowanbei River > Yi River. Soil samples from the Beigouhe River Basin were heavily polluted and posed a moderate risk level. In addition, soil samples from other river basins contained a low level of pollution and ecological risk. However, some sites which possessed a higher pollution level and ecological risk were found in all of the river basins. It was worth noting that soil samples near a river in a soil profile can accumulate more heavy metals than other soil samples, indicating that accumulation of heavy metals in the soil is affected by the river. The main sources of heavy metals in the surface soil were parent rock weathering (32.9%), lead zinc mining activities of Pb/Zn mines (30.6%), mining activities of Mo mines (26.8%), and mining activities of Au (9.7%), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS Mining activities cause heavy metal accumulation in the soil to some extent, and Mo and Hg pollution more heavily. Pb/Zn mines account for 30.59% of the source of soil heavy metals, which are higher than Mo mines and Au mines, indicating mining activities of Pb/Zn should be paid more attention. More heavy metals from parent rock (32.9%) indicate that it is necessary to measure the speciation of soil heavy metals and concentrations of heavy metals in crops.
-
Key words:
- Mo-Pb-Zn molybdenum ore concentration area /
- heavy metals /
- soil /
- accumulation /
- PMF model /
- source apportionment
-

-
表 1 栾川钼铅锌多金属矿集区农田表层土壤重金属含量特征(N=95)
Table 1. Characteristics of heavy metal contents in agricultural surface soils in Luanchuan Mo-Pb-Zn polymetallic ore concentration area (N=95).
重金属
元素最大值
(mg/kg)最小值
(mg/kg)中位数
(mg/kg)算术平均值
(mg/kg)标准差 变异系数
(%)土壤背景值
(mg/kg)Mo 366.85 1.31 32.35 71.77 81.60 113.69 0.98 Cd 6.56 0.12 0.85 1.23 1.17 95.14 0.19 Hg 0.78 0.01 0.05 0.09 0.12 131.35 0.04 As 124.20 2.71 15.00 20.27 18.96 93.56 7.92 Cr 120.00 18.70 67.10 66.31 17.75 26.77 75.80 Cu 438.80 25.70 52.70 74.19 57.88 78.02 29.60 Pb 595.60 16.60 82.70 139.33 130.87 93.93 31.60 Zn 1226.00 86.30 229.70 315.54 240.46 76.21 101.40 表 2 栾川钼铅锌多金属矿集区土壤重金属Spearman相关关系矩阵(N=95)
Table 2. Spearman’s correlation matrix for heavy metals in soils of Luanchuan Mo-Pb-Zn polymetallic ore concentration area (N=95).
元素 Mo Cd Hg As Cr Cu Pb Zn Mo 1 Cd 0.552** 1 Hg −0.104 −0.057 1 As 0.142 0.402** −0.063 1 Cr −0.301** −0.073 0.011 0.02 1 Cu 0.359** 0.299** 0.006 −0.105 0.263* 1 Pb 0.381** 0.612** −0.122 0.446** −0.139 0.157 1 Zn 0.537** 0.830** 0.002 0.376** 0.008 0.436** 0.607** 1 注:**表示在0.01的水平上显著相关;*表示在0.05水平上显著相关。 表 3 主成分分析因子载荷系数
Table 3. Factor loading factor of PCA.
重金属元素 因子1 因子2 因子3 因子4 Mo 0.364 0.587 −0.526 −0.103 Cd 0.780 0.423 −0.151 0.004 Hg −0.049 −0.005 0.010 0.995 As 0.819 −0.320 0.137 −0.032 Cr −0.020 0.165 0.940 −0.011 Cu 0.046 0.885 0.228 0.008 Pb 0.788 0.142 −0.160 −0.107 Zn 0.750 0.532 −0.052 0.068 -
[1] 孙厚云,卫晓锋,贾凤超,等. 承德伊逊河钒钛磁铁矿小流域土壤重金属地球化学基线及生态风险累积效应[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(2): 588−604.
Sun H Y,Wei X F,Jia F C,et al. Geochemical baseline and ecological risk accumulation effect of soil heavy metals in the small-scale drainage catchment of V-Ti-magnetite in the Yixun River Basin,Chengde[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(2): 588−604.
[2] 宋绵,龚磊,王艳,等. 河北阜平县表层土壤重金属对人体健康的风险评估[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(1): 133−144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2022.1.ykcs202201013
Song M,Gong L,Wang Y,et al. Risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil on human health in Fuping County,Hebei Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(1): 133−144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2022.1.ykcs202201013
[3] 丛俏,袁星,曲蛟,等. 钼矿区周边农田土壤中重金属污染状况的分析与评价[J]. 中国环境监测, 2009, 25(1): 47−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2009.01.014
Cong Q,Yuan X,Qu J,et al. The analysis and assessment on the pollution condition of heavy metals in the soil in the farmland around the molybdenum ore areas[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2009, 25(1): 47−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2009.01.014
[4] 贾婷,贾洋洋,余淑娟,等. 闽东某钼矿周边农田土壤钼和重金属的污染状况[J]. 中国环境监测, 2015, 31(1): 45−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.01.009
Jia T,Jia Y Y,Yu S J,et al. Pollution of molybdenum and heavy metals of the soils and rice near a molybdenum mining site in Eastern Fujian[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2015, 31(1): 45−49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2015.01.009
[5] 曲蛟,袁星,丛俏,等. 钼矿区选矿场周边农田土壤重金属污染状况分析与评价[J]. 生态环境, 2008, 17(2): 677−681.
Qu J,Yuan X,Cong Q,et al. Analysis and assessment on the pollution condition of heavy metals in the soil in the farmland around the collection areas of molybdenum ore[J]. Ecology and Environment, 2008, 17(2): 677−681.
[6] 王涛,司万童,欧阳琰,等. 陕西某钼矿区土壤重金属污染特征及评价[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2019, 9(4): 440−446. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.01.080
Wang T,Si W T,Ouyang Y,et al. Characteristics and evaluation of soil heavy metals pollution in the molybdenum mine area in Shaanxi[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2019, 9(4): 440−446. doi: 10.12153/j.issn.1674-991X.2019.01.080
[7] 毛香菊,马亚梦,邹安华,等. 内蒙古草原某铜钼矿区土壤重金属污染特征研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2016, 39(6): 156−161.
Mao X G,Ma Y M,Zou A H,et al. Characteristics of heavy metals in soils from a copper-molybdenum mining area of grassland in Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 39(6): 156−161.
[8] Ghazaryan K A,Movsesyan H S,Khachatryan H E,et al. Geochemistry of potentially toxic trace elements in soils of mining area:A case study from Zangezur copper and molybdenum combine,Armenia[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2018, 101(6): 732−737. doi: 10.1007/s00128-018-2443-0
[9] 郑红星,赵荣军,吴澎,等. 河南省三川—赤土店地区地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2004, 28(4): 294−297.
Zheng H X,Zhao R J,Wu P,et al. Geochemical characteristics of Sanchuan—Chitudian area,Henan Province[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2004, 28(4): 294−297.
[10] 张浩,王辉,汤红妍,等. 铅锌尾矿库土壤和蔬菜重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(3): 1085−1094.
Zhang H,Wang H,Tang H Y,et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and health risk evaluation of soil and vegetables in various functional areas of lead-zinc tailings pond[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(3): 1085−1094.
[11] 何玉良,韩江伟,云辉,等. 河南省栾川钼矿集区深部发现世界级钨钼矿[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1934−1936. doi: 10.12029/gc20200630
He Y L,Han J W,Yun H,et al. The discovery of a world-class tungsten and molybdenum ore deposit from deep exploration in the Luanchuan molybdenum ore concentration area,Henan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1934−1936. doi: 10.12029/gc20200630
[12] 于沨,王伟,于扬,等. 川西九龙地区锂铍矿区土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(3): 408−424. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011300154
Yu F,Wang W,Yu Y,et al. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from Jiulong Li-Be mining area,Western Sichuan Province,China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(3): 408−424. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202011300154
[13] 孙建伟,贾煦,刘向东,等. 豫西金矿集区矿业活动对周边农田土壤重金属影响研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2023, 42(1): 192−202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2023.1.ykcs202301015
Sun J W,Jia X,Liu X D,et al. Influence of mining activities in the gold ore concentration area in Western Henan on the heavy metals in surrounding farmland soil[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2023, 42(1): 192−202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2023.1.ykcs202301015
[14] Chen Z Y,Zhao Y Y,Chen D L,et al. Ecological risk assessment and early warning of heavy metal accumulation in the soils near the Luanchuan molybdenum polymetallic mine concentration area,Henan Province,central China[J]. China Geology, 2023, 6(1): 15−26.
[15] Wang L F,Bai Y X,Gai S N. Single-factor and Nemerow multi-factor index to assess heavy metals contamination in soils on railway side of Harbin—Suifenhe railway in Northeastern China[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2011, 71-78: 3033−3036. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.71-78.3033
[16] Hakanson L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control:A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14(8): 975−1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[17] 张塞,于扬,王登红,等. 赣南离子吸附型稀土矿区土壤重金属形态分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(5): 726−738.
Zhang S,Yu Y,Wang D H,et al. Forms distribution of heavy metals and their ecological risk evaluation in soils of ion adsorption type in the rare earth mining area of Southern Jiangxi,China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(5): 726−738.
[18] 马建华,韩昌序,姜玉玲. 潜在生态风险指数法应用中的一些问题[J]. 地理研究, 2020, 39(6): 1233−1241. doi: 10.11821/dlyj020190632
Ma J H,Han C X,Jiang Y L. Some problems in the application of potential ecological risk index[J]. Geographical Research, 2020, 39(6): 1233−1241. doi: 10.11821/dlyj020190632
[19] 张连科,李海鹏,黄学敏,等. 包头某铝厂周边土壤重金属的空间分布及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2016, 37(3): 1139−1146.
Zhang L K,Li H P,Huang X M,et al. Soil heavy metal spatial distribution and source an analysis around an aluminum plant in Baotou[J]. Environmental Science, 2016, 37(3): 1139−1146.
[20] 魏迎辉,李国琛,王颜红,等. PMF模型的影响因素考察——以某铅锌矿周边农田土壤重金属源解析为例[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(11): 2549−2559. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0492
Wei Y H,Li G C,Wang Y H,et al. Investigating factors influencing the PMF model:A case study of source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soils near a lead-zinc ore[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(11): 2549−2559. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-0492
[21] 韩琳,徐夕博. 基于PMF模型及地统计的土壤重金属健康风险定量评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(11): 5114−5124.
Han L,Xu X B. Quantitative evaluation of human health risk of heavy metals in soils based on positive matrix factorization model and geo-statistics[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(11): 5114−5124.
[22] Liu Y B,Ma Z H,Liu G N,et al. Accumulation risk and source apportionment of heavy metals in different types of farmland in a typical farming area of Northern China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2021, 40(7): 1195−1202.
[23] 夏子书,白一茹,王幼奇,等. 基于PMF模型的宁南山区小流域土壤重金属空间分布及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1): 432−441. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202105128
Xia Z S,Bai Y R,Wang Y Q,et al. Spatial distribution and source analysis of soil heavy metals in a small watershed in the mountainous area of Southern Ningxia based on PMF model[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(1): 432−441. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202105128
[24] 赵元艺,王晓亮,赵希涛,等. 赣东北乐安江德兴铜矿段河流阶地的发育及环境意义[J]. 地球学报, 2014, 35(4): 454−462. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.04.07
Zhao Y Y,Wang X L,Zhao X T,et al. Terraces development of the Le’an river in the Dexing copper mine of Northeast Jiangxi and its environmental significance[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2014, 35(4): 454−462. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2014.04.07
[25] 高健翁,龚晶晶,杨剑洲,等. 海南岛琼中黎母山—湾岭地区土壤重金属元素分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(5): 807−816.
Gao J W,Gong J J,Yang J Z,et al. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in the soil of Limu Mountain—Wanling Town,Qiongzhong,Hainan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(5): 807−816.
[26] 陈佳林,李仁英,谢晓金,等. 南京市绿地土壤重金属分布特征及其污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(2): 909−916.
Chen J L,Li R Y,Xie X J,et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in greenbelt soils of Nanjing City[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(2): 909−916.
[27] 史国良. 大气颗粒物来源解析复合受体模型的研究和应用[D]. 天津: 南开大学, 2010.
Shi G L. Study and application of complex receptor model for atmospheric particulate matter source analysis[D]. Tianjin: Nankai University, 2010.
[28] 焦振恒. 辽宁某铅锌矿周边农田土壤重金属污染特征与风险评价[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳大学, 2021.
Jiao Z H. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil around a lead-zinc mine in Liaoning Province[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang University, 2021.
[29] 郭俊刚,赵恒勤,卞孝东,等. 江西于都某钨矿区土壤重金属特征及生态风险评价[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(7): 1195−1202.
Guo J G,Zhao H Q,Bian X D,et al. Characteristics and ecological risk of soil heavy metals of a Tungsten mine in Yudu,Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(7): 1195−1202.
[30] 姚红胜,杨涛明,和丽萍,等. 滇东喀斯特镉砷高背景值区耕地土壤重金属污染现状及潜在生态风险评估[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(4): 29−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2022.04.04
Yao H S,Yang T M,He L P,et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of the soils in karst farmland with high background levels of cadmium and arsenic in Eastern Yunnan[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2022, 37(4): 29−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7461.2022.04.04
-




 下载:
下载: