Cadmium Bioavailability Based on Diffusive Gradients in Thin Films Technique and Conventional Chemical Extraction in High Geological Background Soil Area of Northwestern Zhejiang Province, China
-
摘要:
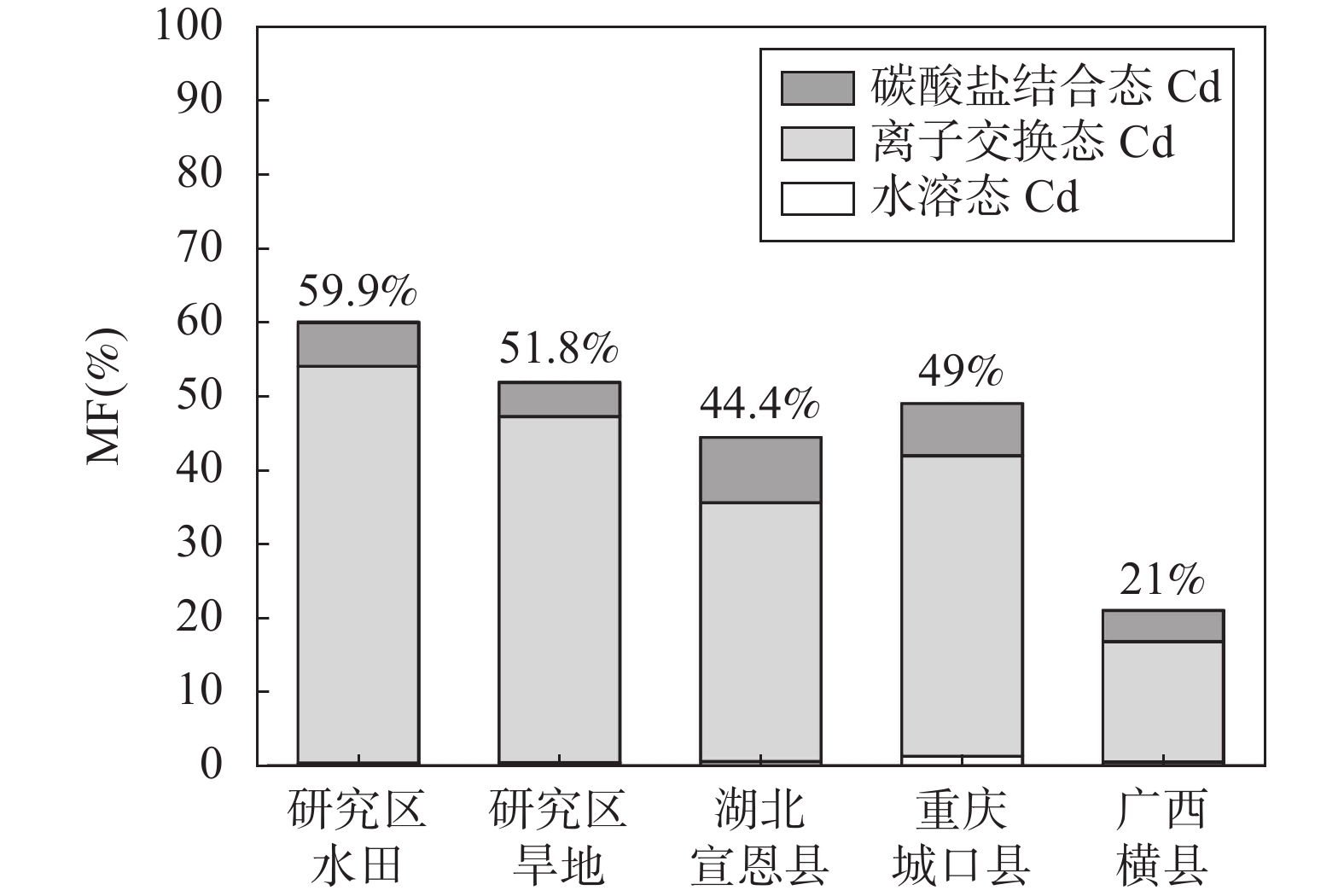
地质高背景区相较于人类活动引起的土壤镉污染影响范围更广,在区域尺度上对生态系统和人类健康构成危害。土壤镉生物有效性是决定其生物可利用性、生物毒性的关键因素,因此探寻可行的土壤镉生物有效性评价方法对污染农用地安全利用和风险管控具有重要的理论和实际意义。DGT技术、单一提取法、连续提取法和土壤溶液法常用于测定土壤有效镉,但已有研究成果主要基于同种土地利用类型土壤的室内盆栽实验,难以代表自然污染土壤中的复杂情况。为探明各土壤重金属有效态提取技术对地质高背景区不同土地利用类型土壤Cd生物有效性评估效果,本文以浙江西北部土壤Cd高地质背景区水田土壤-水稻籽实和旱地土壤-小白菜样品为研究对象,实验应用DGT技术、单一提取法(0.01mol/L氯化钙提取)、连续提取法(七步连续提取)和土壤溶液法评价土壤中镉生物有效性。结果显示:①研究区水田和旱地土壤Cd平均含量分别为1.07mg/kg和0.73mg/kg,显著高于浙江和全国土壤平均水平,Cd的异常富集主要与浙西北地区广泛分布的黑色岩系有关。②相较于碳酸盐岩区,黑色岩系区土壤中Cd的生物有效组分占比较高,水田和旱地土壤Cd的活动系数(MF)高达59.9%和51.8%,Cd易在土壤-作物系统中发生迁移富集;③植物体内镉含量Cd-P与不同方法测定的有效镉含量均呈显著正相关,但Cd-P与DGT技术测定的有效镉含量相关性优于其他三种方法,水田土壤测得的有效Cd与水稻籽实相关关系:
$ {{C}}_{\text{soln}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ $ {{C}}_{\text{soln}} $ Abstract:BACKGROUND High geochemical background has a greater impact on soil Cd pollution than human activities and is more detrimental to the environment and human health on a regional level. Research shows that the bioavailability of Cd in soil is the key factor to determine its bioavailability and biotoxicity, so it is of great theoretical and practical significance to find an effective method to evaluate the bioavailability of Cd in soil for the safe use and risk control of contaminated agricultural land. Single extraction methods with relatively simple operation and relatively low cost and sequential extraction methods providing morphological distribution feature information, are the most common methods for evaluation of heavy metals bioavailability in soil. In general, the available amount of soil heavy metals obtained by chemical extraction methods can better reflect the level of plant absorption than the total amount. However, chemical extraction methods have some drawbacks, including differences between the extraction principle and crop absorption process, a lack of universality in the extracts, redistribution and re-adsorption during the extraction process, and most notably, the failure to take into account dynamic changes in heavy metal concentrations in the root environment. Diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) technique is a new biomimetic in-situ sampling technique, which has been widely used to assess the bioavailability of various elements in soil, water, sediment and other environmental media in recent years. The process of DGT absorbing target elements is similar to plants absorption, which can better reflect bioavailability. However, existing research results using DGT to evaluate soil Cd pollution is mainly based on indoor pot experiments. Exogenous addition of heavy metals to contaminated soil not only has high bioavailability, but also reduces the sensitivity of soil pH and other factors to the bioavailability of heavy metals in soil, which does not accurately represent the complex situation in naturally contaminated soil. It is not clear whether the results of DGT can accurately reflect the bioavailability of soil Cd in high geological background areas. In order to confirm whether DGT technology can effectively evaluate the bioavailability of soil Cd in high geochemical background areas when compared to existing chemical extraction methods, 80 sets of paddy soil-rice and 20 sets of dry soil-bok choy samples were collected in the black shale area of Northwest Zhejiang Province. The DGT technology, 0.01mol/L CaCl2 extraction method, seven-step extraction method and soil solution method were used to evaluate the bioavailability of Cd in soil. Inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) was used to determine Cd content and available Cd in soil and crop. Soil pH was determined by potentiometry (POT), and soil organic matter (OM) was determined by oxidation combustion potentiometry (POT). The migration and accumulation characteristics of Cd in a soil-crop system were analyzed. The evaluation effects of different bioavailability evaluation methods were compared by the correlation between available Cd and crop Cd content.
RESULTS (1) The total content and fraction distribution characteristics of Cd in soil. The results show that the Cd average contents in paddy soil and dry soil in the study area are 1.07mg/kg and 0.73mg/kg, respectively, remarkably higher than the background values of soil in Zhejiang Province and China. The abnormal enrichment of Cd is mainly related to the widespread black shale in Northwest Zhejiang. For the sequential extraction procedures, the average content in paddy soil of water-soluble and exchangeable Cd, carbonate-bound Cd, humic acid-bound Cd, Fe-Mn oxide-bound Cd, strong organic-bound Cd and residual Cd are 54%, 5.9%, 9.3%, 13.5%, 4.2% and 13.2%, respectively. The average content in dry soil of water-soluble and exchangeable Cd, carbonate-bound Cd, humic acid-bound Cd, Fe-Mn oxide-bound Cd, strong organic-bound Cd and residual Cd are 47.2%, 4.6%, 11.5%, 14.3%, 5.5% and 16.9%, respectively. On the whole, the bioavailable component of Cd in the study area accounts for a relatively high proportion. (2) Characteristics of Cd content in crop. The content of Cd in rice seed in the study area ranges from 0.01mg/kg to 3.29mg/kg, with an average of 0.26mg/kg. The Cd content in bok choy ranges from 0.01mg/kg to 0.31mg/kg, with an average of 0.08mg/kg. In comparison to China’s contaminant limit of national food safety standards (GB2762—2017), the over-standard rates of Cd in rice and bok choy are 34% and 10%, respectively. The soil samples are further assessed according to Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB15618—2018), the Cd over-standard rates of paddy soil and dry soil are 70% and 75%, respectively. The Cd over-standard rate of soil samples is significantly higher than crop samples. Therefore, the bioavailability of Cd in soil should be considered to scientifically evaluate the pollution level of Cd in soil. (3) Assessment of Cd bioavailability in soil by four extraction methods. The DGT technology, 0.01mol/L CaCl2 extraction method, seven-step extraction method and soil solution method are used to evaluate the bioavailability of Cd in soil. The results are as follows: CDGT,
$ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ $ {{C}}_{\text{soln}} $ $ {{C}}_{\text{soln}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ $ {{C}}_{\text{soln}} $ DISSCUSION (1) Results of DGT technique. The available Cd (CDGT) content measured by DGT for paddy and dry soil in the study area ranges from 0.02μg/L to 1.69μg/L and from 0.14μg/L to 1.88μg/L, with average values of 0.78μg/L and 0.62μg/L, respectively (Fig.3). The correlation coefficients between CDGT and Cd-P in paddy soil and dry soil are 0.622 and 0.887, respectively (Table 3), which are larger than
$ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ -

-
表 1 研究区土壤、作物Cd含量及土壤理化性质统计
Table 1. Statistical date of Cd concentrations in soil and crop and soil properties in the study area.
土壤-作物系统 参数 Cd-S Cd-P BCF pH 有机质 水田土壤-水稻籽实
(n=80)最小值 0.18 0.01 0.015 4.9 0.74 最大值 6.61 3.29 1.18 8.0 7.48 平均值 1.07 0.26 0.28 6.1 3.40 标准差 1.27 0.43 0.26 0.8 1.16 变异系数(%) 119 167 94 14 34 旱地土壤-小白菜
(n=20)最小值 0.16 0.01 0.03 4.7 1.68 最大值 2.39 0.31 0.24 6.0 4.80 平均值 0.73 0.08 0.11 5.3 3.37 标准差 0.55 0.08 0.06 0.4 0.71 变异系数(%) 75 99 56 7 21 浙江表层土壤背景值[17] 0.07 - - 5.7[18] 2.26[18] 全国土壤背景基准值[19] 0.14 - - 8.0 1.00 注:Cd-S和Cd-P分别为土壤和作物总Cd含量,单位为mg/kg;BCF、pH值无量纲;有机质含量单位为%。 表 2 不同成因Cd污染区水稻籽实生物富集系数(BCF)
Table 2. Bioconcentration factor (BCF) of Cd in rice from different sources.
表 3 土壤有效Cd与作物Cd含量线性相关系数
Table 3. Relationships between available Cd in soil and Cd concentration in crops.
项目 n CDGT ${{C} }_{ {\text{CaCl} }_{\text{2} } }$ ${{C} }_{ {\text{F} }_{\text{1} }\text{+}{\text{F} }_{\text{2} }\text{+}{\text{F} }_{\text{3} } }$ Csoln Cd-P(水稻籽实) 80 0.622** 0.583** 0.577** 0.634** Cd-P(小白菜) 20 0.887** 0.795** 0.717** 0.635** 注:Cd-P为作物Cd含量;“**”表示P<0.01水平(双侧)极显著相关。 表 4 土壤有效Cd与土壤pH值和有机质(OM)线性相关系数
Table 4. Relationships between available Cd, pH value and organic matter (OM) in soil.
土壤类型 项目 CDGT $ {{C}}_{{\text{CaCl}}_{\text{2}}} $ $ {{C}}_{{\text{F}}_{\text{1}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}\text{+}{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}} $ Csoln 水田土壤
(n=80)pH −0.678** 0.154 −0.053 −0.249** 有机质 0.032 0.314** 0.284 −0.126 旱地土壤
(n=20)pH −0.400 0.096 −0.186 −0.515* 有机质 0.241 0.362 0.242 0.160 注:“**”表示P<0.01水平(双侧)极显著相关;“*”表示P<0.05水平(双侧)极显著相关。
-
[1] 杨杰,董静,宋洲,等. 鄂西铜铅锌尾矿库周边农田土壤-水稻重金属污染状况及风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(5): 867−879.
Yang J,Dong J,Song Z,et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and risk assessment of soil and rice in farmland around the copper-lead-zinc tailing,western Hubei Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(5): 867−879.
[2] 马生明,朱立新,汤丽玲,等. 城镇周边和江河沿岸土壤中Hg和Cd存在形式解析与生态风险评估[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(2): 225−234.
Ma S M,Zhu L X,Tang L L,et al. The occurrences of Hg and Cd in soils around cities and rivers and their ecological risk assessment[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(2): 225−234.
[3] 唐豆豆,袁旭音,汪宜敏,等. 地质高背景农田土壤中水稻对重金属的富集特征及风险预测[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(1): 18−26.
Tang D D,Yuan X Y,Wang Y M. Enrichment characteristics and risk prediction of heavy metals for rice grains growing in paddy soils with a high geological background[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(1): 18−26.
[4] 马宏宏,彭敏,刘飞,等. 广西典型碳酸盐岩区农田土壤-作物系统重金属生物有效性及迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1): 449−459.
Ma H H,Peng M,Liu F,et al. Bioavailability,translocation,and accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in a soil-crop system from a typical carbonate rock area in Guangxi,China[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1): 449−459.
[5] 赵万伏,宋垠先,管冬兴,等. 典型黑色岩系分布区土壤重金属污染与生物有效性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(7): 1332−1341.
Zhao W F,Song Y X,Guan D X,et al. Pollution status and bioavailability of heavy metals in soils of a typical black shale area[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(7): 1332−1341.
[6] 成晓梦,吴超,孙彬彬,等. 浙江中部典型黑色岩系分布区土壤-作物富硒特征与重金属风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(2): 1−9.
Cheng X M,Wu C,Sun B B,et al. Selenium-rich characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and crop in a typical black shale area of the central part of Zhejiang Province,China[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(2): 1−9.
[7] 程志中, 谢学锦, 冯济舟, 等. 中国南方地区地球化学图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015: 47.
Cheng Z Z, Xie X J, Feng J Z, et al. Geochemical atlas of Southern China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015: 47.
[8] 宋明义. 浙西地区下寒武统黑色岩系中硒与重金属的表生地球化学及环境效应[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2009: 23-24.
Song M Y. Epigenetic geochemistry and environmental effects of selenium and heavy metals in the lower Cambrian black rock series in Western Zhejiang[D]. Hefei: Hefei Polytechnic University, 2009: 23-24.
[9] 李财,任明漪,石丹,等. 薄膜扩散梯度(DGT)——技术进展及展望[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(3): 2613−2628.
Li C,Ren M Y,Shi D,et al. Diffusive gradient in thin films (DGT):Technological progress and prospects[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(3): 2613−2628.
[10] 魏天娇,管冬兴,方文,等. 梯度扩散薄膜技术(DGT)的理论及其在环境中的应用 Ⅲ:植物有效性评价的理论基础与应用潜力[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(5): 841−849.
Wei T J,Guan D X,Fang W,et al. Theory and application of diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) in the environment Ⅲ:Theoretical basis and application potential in phytoavailability assessment[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(5): 841−849.
[11] Williams P N,Zhang H,Davison W,et al. Organic matter-solid phase interactions are critical for predicting arsenic release and plant uptake in Bangladesh paddy soils[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2011, 45: 6080−6087.
[12] 陈莹,刘汉燚,刘娜,等. 农地土壤重金属Pb和Cd有效性测定方法的筛选与评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(7): 3494−3506.
Chen Y,Liu H Y,Liu N,et al. Screening and evaluation of methods for determining available lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) in farmland soil[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(7): 3494−3506.
[13] 高慧,宋静,吕明超,等. DGT和化学提取法评价贵州赫章土法炼锌区污染土壤中镉的植物吸收有效性[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(10): 1992−1999.
Gao H,Song J,Lyu M C,et al. Evaluation of cadmium phytoavailability in soils from a zinc smelting area in Hezhang County,Guizhou Province,using diffusive gradients in thin films and conventional chemical extractions[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(10): 1992−1999.
[14] 宋宁宁,王芳丽,沈跃,等. 梯度薄膜扩散技术(DGT)与传统化学方法评估黑麦草吸收Cd的对比[J]. 环境化学, 2012, 31(12): 1960−1967.
Song N N,Wang F L,Shen Y,et al. Comparison of the method of diffusive gradients in thin films with traditional chemical extraction techniques for evaluating cadmium bioavailability in ryegrass[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2012, 31(12): 1960−1967.
[15] 吴超,孙彬彬,陈海杰,等. 应用梯度扩散薄膜技术评价天然富硒土壤中硒的生物有效性[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(1): 66−79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2022.1.ykcs202201007
Wu C,Sun B B,Chen H J,et al. Assessment of selenium bioavailability in natural selenium-rich soil based on diffusive gradients in thin films[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(1): 66−79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2022.1.ykcs202201007
[16] Houba V J G,Temminghoff E J M,Gaikhorst G A,et al. Soil analysis procedures using 0.01M calcium chloride as extraction reagent[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 2000, 31(9/10): 1299−1396.
[17] 董岩翔, 郑文, 周建华, 等. 浙江省土壤地球化学背景值[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 130−131.
Dong Y X, Deng W, Zhou J H, et al. Soil geochemical background values in Zhejiang Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007: 130−131.
[18] 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 等. 中国土壤地球化学参数(下册)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020: 2620−2621.
Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, Yu T, et al. Soil geochemical parameters in China (Part Ⅱ)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020: 2620−2621.
[19] 王学求,周建,徐善法,等. 全国地球化学基准网建立与土壤地球化学基准值特征[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(5): 1469−1480.
Wang X Q,Zhou J,Xu S F,et al. China soil geochemical baselines networks:Data characteristics[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(5): 1469−1480.
[20] Lund L J,Betty E E,Page A L,et al. Occurrence of naturally high cadmium levels in soils and its accumulation by vegetation[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1981, 10(4): 551−556.
[21] Park M,Chon H T,Marton L. Mobility and accumulation of selenium and its relationship with other heavy metals in the system rocks/soils-crops in areas covered by black shale in Korea[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 107(2): 161−168. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2010.09.003
[22] 刘意章,肖唐付,熊燕,等. 西南高镉地质背景区农田土壤与农作物的重金属富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6): 2877−2884.
Liu Y Z,Xiao T F,Xiong Y,et al. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops from an area with high geochemical background of cadmium,Southwestern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(6): 2877−2884.
[23] Han T,Fan S F,Zhu X Q,et al. Submarine hydrothermal contribution for extreme element accumulation during the early Cambrian,South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 86: 297−308. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.030
[24] Alamgir M. The effects of soil properties to the extent of soil contamination with metals[A]//Hasegawa H, Rahman I M M, Rahman M A. Environmental remediation technologies for metal-contaminated soils[M]. Tokyo: Springer, 2016: 1−19.
[25] 宋波,肖乃川,马丽钧,等. 基于DGT技术的广西碳酸盐岩区稻米镉含量主控因素[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(1): 463−471.
Song B,Xiao N C,Ma L J,et al. Main control factors of cadmium content in rice in carbonate rock region of Guangxi based on DGT technique[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(1): 463−471.
[26] Chen H Y,Yuan X Y,Li T Y,et al. Characteristics of heavy metal transfer and their influencing factors in different soil-crop systems of the industrialization region,China[J]. Ecotoxicology & Environmental Safety, 2016, 126(2): 193−201.
[27] 倪卫东,朱凰㮠,冯先翠,等. 东莞Cd轻度污染土壤种植水稻安全风险评估[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2022, 50(10): 41−45.
Ni W D,Zhu F R,Feng X C,et al. Safety risk assessment of rice planting on Cd slightly polluted soil in Dongguan[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(10): 41−45.
[28] 白宇明,李永利,周文辉,等. 典型工业城市土壤重金属元素形态特征及生态风险评估[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(4): 632−641.
Bai Y M,Li Y L,Zhou W H,et al. Speciation characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal elements in soils of typical industrial city[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(4): 632−641.
[29] 陈静,孙琴,姚羽,等. DGT和传统化学法比较研究复合污染土壤中Cd的生物有效性[J]. 环境科学研究, 2014, 27(10): 1172−1179.
Chen J,Sun Q,Yao Y,et al. Comparison of DGT technique with traditional method for evaluating cadmium bioavailability in soils with combined pollution[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 27(10): 1172−1179.
[30] 姚羽,孙琴,丁士明,等. 基于薄膜扩散梯度技术的复合污染土壤镉的生物有效性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2014, 33(7): 1279−1298.
Yao Y,Sun Q,Ding S M,et al. Diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) technique for evaluation of cadmium bioavailability in heavy metal Co-polluted soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2014, 33(7): 1279−1298.
[31] 刘小莲,杜平,陈娟,等. 基于梯度扩散薄膜技术评估稻田土壤中镉的生物有效性[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(12): 2429−2437.
Liu X L,Du P,Chen J,et al. Evaluation of cadmium bioavailability via diffusive gradients in thin film technology for agricultural soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017, 36(12): 2429−2437.
[32] Davison W,Zhang H. Progress in understanding the use of diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT)-back to basics[J]. Environment Chemistry, 2012, 9(1): 1−13. doi: 10.1071/EN11084
[33] Tian Y,Wang X,Luo J,et al. Evaluation of holistic approaches to predicting the concentrations of metals in field cultivated rice[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(20): 7649−7654.
[34] Menzies N W,Donn M J,Kopittke P M,et al. Evaluation of extractants for estimation of the phytoavailable trace metals in soils[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2007, 14(5): 121−130.
[35] 周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 31(3): 319−336.
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 31(3): 319−336.
[36] 熊英,王亚平,韩张雄,等. 全国土壤污染状况详查重金属元素可提取态提取试剂的选择[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(3): 384−393.
Xiong Y,Wang Y P,Han Z X,et al. Screening of extractable reagents for heavy metal elements in the detailed survey of soil pollution in China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(3): 384−393.
[37] 周国华. 土壤重金属生物有效性研究进展[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(6): 1097−1106.
Zhou G H. Recent progress in the study of heavy metal bioavailability in soil[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6): 1097−1106.
[38] 戴高乐,侯青叶,杨忠芳,等. 洞庭湖平原土壤铅活动性影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(4): 783−793.
Dai G L,Hou Q Y,Yang Z F,et al. Factors affecting mobility of lead in the soils of the Dongting Lake Plain,China[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(4): 783−793.
[39] 夏伟,吴冬妹,袁知洋. 土壤-农作物系统中重金属元素迁移转化规律研究——以湖北宣恩县为例[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(4): 563−568.
Xia W,Wu D M,Yuan Z Y. Study on the migration and transformation law of heavy metals in soil-crop system[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018, 32(4): 563−568.
[40] 邓帅, 段佳辉, 宁墨奂, 等. 典型黑色岩系地质高背景区土壤和农产品重金属富集特征与污染风险[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(4): 2234-2242.
Deng S, Duan J H, Ning M H, et al. Accumulation and pollution risks of heavy metals in soils and agricultural products from a typical black shale region with high geological background[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(4): 2234-2242.
[41] 马宏宏,彭敏,郭飞,等. 广西典型岩溶区农田土壤-作物系统Cd迁移富集影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3): 1514−1522.
Ma H H,Peng M,Guo F,et al. Factors affecting the translocation and accumulation of cadmium in a soil-crop system in a typical karst area of Guangxi Province,China[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3): 1514−1522.
[42] Luo J,Zhang H,Santner J,et al. Performance characteristics of diffusive gradients in thin films equipped with a binding gel layer containing precipitated ferrihydrite for measuring arsenic(Ⅴ),selenium(Ⅵ),vanadium(Ⅴ),and antimony(Ⅴ)[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 82(21): 8903−8909. doi: 10.1021/ac101676w
[43] Frohne T,Rinklebe J. Biogeochemical fractions of mercury in soil profiles of two different floodplain ecosystems in Germany[J]. Water Air & Soil Pollution, 2013, 224(6): 1591.
[44] 余贵芬,蒋新,孙磊,等. 有机物质对土壤镉有效性的影响研究综述[J]. 生态学报, 2002, 22(5): 770−776.
Yu G F,Jiang X,Sun L,et al. A review for effect of organic substances on the availability of cadmium in soils[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2002, 22(5): 770−776.
-




 下载:
下载: