Application of Automated Quantitative Mineral Analysis System in Process Mineralogy of Low-grade Copper Slag
-
摘要:
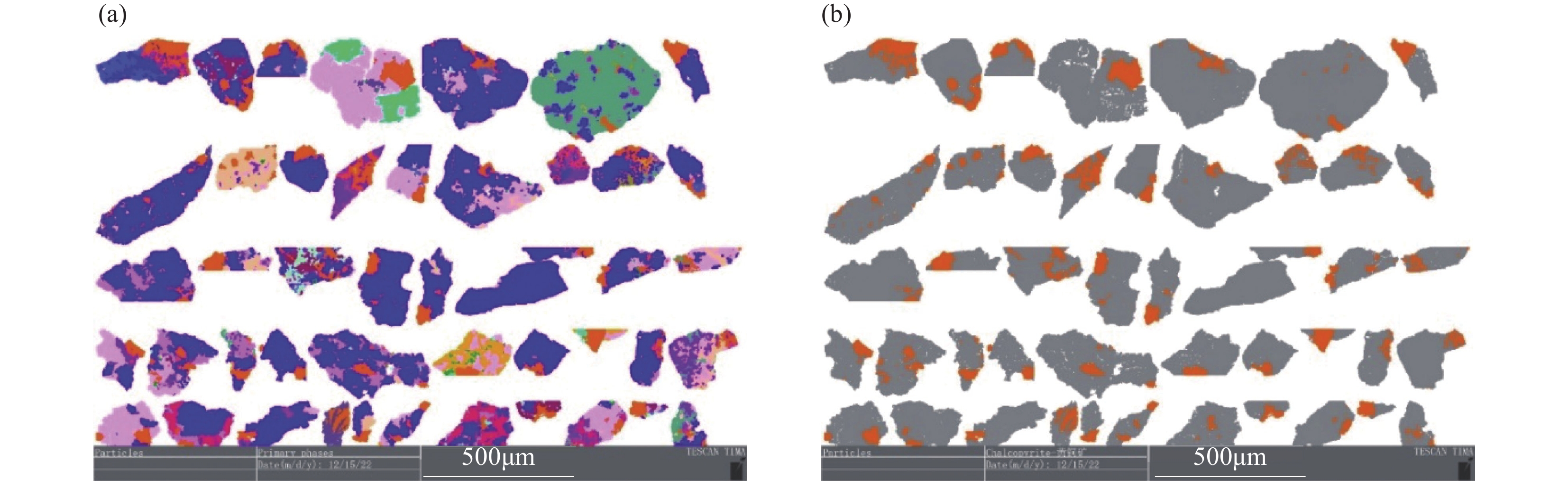
矿产资源高效综合利用是目前全球矿业发展的主要方向。传统的光学显微镜和扫描电镜等技术在查明许多低品位矿石的元素赋存状态等方面具有局限性,且无法提供定量化的矿物学信息,制约了对这些金属矿石选矿工艺的提升。近年来,基于扫描电镜和X射线能谱仪的矿物自动定量分析系统越来越多地应用到复杂矿石和工艺矿物学的研究中。为了进一步丰富和拓展该类系统在工艺矿物学领域的应用研究,本文利用矿物自动定量分析系统TIMA(TESCAN Integrated Mineral Analyzer)对中国某矿山低品位铜矿渣样品进行矿物学测试分析,展示其在提取多种工艺矿物学参数研究中的具体应用。分析结果表明:该铜矿渣中铜元素含量(0.08%)很低,主要赋存在黄铜矿中,该矿物含量为0.21%;脉石矿物含有大量石英(47.46%)、白云母(10.10%)和方解石(9.88%)等;黄铜矿连生关系复杂,主要以连生体形式呈不规则粒状零散分布在石英和方解石等脉石矿物中,粒度小且分布极不均匀,其中11~76μm颗粒占比较大;解离度低于30%的黄铜矿颗粒质量占全部的85%左右,整体解离度较低,因而需要进一步磨矿来提升黄铜矿回收率。以上研究表明,对于有用矿物含量低、粒度细小且嵌布关系复杂的矿石样品,包括TIMA在内的矿物分析系统能够提供快速、定量、全面且准确的工艺矿物学参数信息,有利于优化选冶流程,在提高矿产资源的综合利用方面具有非常广阔的应用前景。
Abstract:BACKGROUND The high-efficient utilization of mineral resources is the leading research aspect of global mining development. Traditional optical and scanning electron microscopy have limitations in identifying the occurrence of elements in many low-grade ores and usually cannot provide quantitative mineralogy information, hindering the improvement of mineral processing of these ores. In recent years, automated mineral quantitative analysis systems based on scanning electron microscope and X-ray energy spectrometer have been increasingly applied to study complex ore formation and process mineralogy.
OBJECTIVES To enrich and expand the application of an automated quantitative mineral analysis system in process mineralogy.
METHODS The low-grade copper slag from a copper mine in China is analyzed using the TESCAN Integrated Mineral Analyzier (TIMA).
RESULTS The results show that the content of the copper element (0.08%) in the copper slag is very low, and it is mainly distributed in chalcopyrite, which accounts for 0.21%. Gangue minerals include quartz (47.6%), muscovite (10.10%), and calcite (9.88%). Chalcopyrite usually occurs in irregular granular form and shows complex associations with the above gangue minerals. The particle size is small and variable, and the particles of 10-76μm occupy a large proportion. The mass of chalcopyrite with a liberation degree below 30% accounts for 85% of the total mass, and the overall liberation degree is low, so further grinding is needed to improve chalcopyrite recovery.
CONCLUSIONS Research shows that for the ore samples with low content of useful minerals, small particle size, and complex mineralogical associations, the automated mineral analysis system, including TIMA, can provide rapid, quantitative, comprehensive, and accurate process mineralogy parameter information, which is conducive to optimizing the ore extraction and smelting process, and has an extensive application prospect in improving the comprehensive utilization of mineral resources.
-
Key words:
- TIMA /
- automated mineral quantitative analysis /
- process mineralogy /
- copper slag /
- liberation degree
-

-
[1] 孟晶, 杨洪英, 张忠辉, 等. 青海—阿斯哈矿区金矿工艺矿物学及金赋存状态研究[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2022(5): 1−7,15.
Meng J, Yang H Y, Zhang Z H, et al. Study on process mineralogy and gold hosting state of gold deposits in Qinghai Asha mining area[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2022(5): 1−7,15.
[2] 杨波, 杨莉, 沈茂森, 等. TIMA测试技术在白云鄂博矿床铌工艺矿物学中的应用[J]. 矿冶工程, 2021, 41(6): 65−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2021.06.016
Yang B, Yang L, Shen M S, et al. Application of TIMA in process mineralogy study of niobium minerals in Bayan Obo deposit[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2021, 41(6): 65−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2021.06.016
[3] 陈福林, 杨晓军, 何婷, 等. 四川冕宁牦牛坪稀土矿尾矿工艺矿物学分析[J]. 现代矿业, 2018, 34(8): 110−112.
Chen F L, Yang X J, He T, et al. Process mineralogy analysis of tailings from Mianning Maoniuping rare earth mine in Sichuan Province[J]. Modern Mining, 2018, 34(8): 110−112.
[4] 周乐光. 工艺矿物学(第三版)[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2002: 1-301.
Zhou L G. Process mineralogy (The 3rd edition)[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002: 1-301.
[5] 肖仪武, 方明山, 付强, 等. 工艺矿物学研究的新技术与新理念[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2018(3): 49−54. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2018.03.009
Xiao Y W, Fang M S, Fu Q, et al. New techniques and concepts in process mineralogy[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(3): 49−54. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2018.03.009
[6] Gu Y. Automated scanning electron microscope based mineral liberation analysis[J]. Journal of Minerals and Materials Characterization and Engineering, 2003, 2(1): 33−41. doi: 10.4236/jmmce.2003.21003
[7] 彭明生, 刘晓文, 刘羽, 等. 工艺矿物学近十年的主要进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2012, 31(3): 210−217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2012.03.003
Peng M S, Liu X W, Liu Y, et al. The main advances in process mineralogy in China in the last decade[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2012, 31(3): 210−217. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2012.03.003
[8] 叶小璐, 肖仪武. 工艺矿物学在选厂流程优化中的作用[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2020(4): 13−16,33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2020.04.003
Ye X L, Xiao Y W. Role of process mineralogy in process optimization of concentrator[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2020(4): 13−16,33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2020.04.003
[9] 温利刚, 贾木欣, 王清, 等. 基于扫描电子显微镜的自动矿物学新技术——BPMA及其应用前景[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2021(2): 12−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2021.02.003
Wen L G, Jia M X, Wang Q, et al. New automatic mineralogy technology based on scanning electron microscope—BPMA and its application prospect[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing), 2021(2): 12−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2021.02.003
[10] 陈倩, 宋文磊, 杨金昆, 等. 矿物自动定量分析系统的基本原理及其在岩矿研究中的应用——以捷克泰思肯公司TIMA为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40(2): 345−368. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2021.02.010
Chen Q, Song W L, Yang J K, et al. Principle of automated mineral quantitative analysis system and its application in petrology and mineralogy:An example from TESCAN TIMA[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2021, 40(2): 345−368. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2021.02.010
[11] 温利刚, 贾木欣, 王清, 等. 自动矿物学新技术——BPMA技术及在煤中的应用[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2019, 31(9): 8−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2019.09.02
Wen L G, Jia M X, Wang Q, et al. A new technology for automated process mineralogy:BPMA technology and its application in coal research[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2019, 31(9): 8−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2019.09.02
[12] 施明哲. 扫描电镜和能谱仪的原理与实用分析技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2015: 1-400.
Shi M Z. Principles and practical analysis techniques of scanning electron microscopy and energy spectrometer[M]. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 2015: 1-400.
[13] 高歌, 王艳. MLA自动检测技术在工艺矿物学研究中的应用[J]. 黄金, 2015, 36(10): 4.
Gao G, Wang Y. Application of MLA automatic detection technology in process mineralogy research[J]. Gold, 2015, 36(10): 4.
[14] 李建华, 孙小俊. MLA技术在某铜钼矿选矿工艺研究中的应用[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2018(5): 1−5.
Li J H, Sun X J. Application of MLA technology in process mineralogy research on copper-molybdenum ore[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2018(5): 1−5.
[15] Al-Ali S, Wall F, Fitzpatrick R, et al. Key process mineralogy parameters for rare earth fluorcarbonate-bearing carbonatite deposits:The example of Songwe Hill, Malawi[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 159: 106617. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2020.106617
[16] 李广, 肖琴, 胡海祥, 等. MLA在斑岩型锡石矿工艺矿物学研究中的应用[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2019(6): 5−11.
Li G, Xiao Q, Hu H X, et al. Application of MLA to study characteristics and occurrences of porphyry tin ore[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2019(6): 5−11.
[17] 张文, 田承涛, 翁孝卿, 等. 矿物解离分析系统在磷石膏工艺矿物学研究中的应用[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(1): 205−210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2022.01.030
Zhang W, Tian C T, Weng X Q, et al. Research on the process mineralogy of phosphogypsum using mineral liberation analysis system[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(1): 205−210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2022.01.030
[18] 温利刚, 付强, 于志超, 等. 矿物自动定量分析系统在低品位微细粒钼矿工艺矿物学研究中的应用[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2022(2): 31−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2022.02.004
Wen L G, Fu Q, Yu Z C, et al. Application of automated quantitative mineralogy system in the process mineralogy study of low-grade fine-grained molybdenum ore[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2022(2): 31−38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2022.02.004
[19] 曾广圣, 欧乐明. X射线衍射-扫描电镜等技术研究秘鲁铜硫矿石选矿工艺矿物学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(2): 160−168. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201804130042
Zeng G S, Ou L M. Study on mineralogical characteristics of Peru copper-sulphur ore dressing process by X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(2): 160−168. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201804130042
[20] 邱显扬, 梁冬云, 洪秋阳, 等. 难处理金矿石的工艺矿物学及可选冶特性分析[J]. 贵金属, 2020, 41(2): 36−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0676.2020.02.008
Qiu X Y, Liang D Y, Hong Q Y, et al. Process mineralogy and process improvement analysis of a refractory gold ore[J]. Precious Metals, 2020, 41(2): 36−44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0676.2020.02.008
[21] 胡欢, 王汝成, 车旭东, 等. 关键金属元素铍的原位分析技术研究进展[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(7): 1890−1900. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.07.05
Hu H, Wang R C, Che X D, et al. Research progress of in situ analysis technology of key metal element beryllium[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(7): 1890−1900. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.07.05
[22] 杨建文, 肖骏, 陈代雄, 等. 矿物解离分析仪在泥堡金尾矿金赋存状态分析中的应用[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(7): 2619−2624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.07.014
Yang J W, Xiao J, Chen D X, et al. Application of mineral liberation analyzer in the analysis of occurrences of gold in Nibao gold tailings[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(7): 2619−2624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.07.014
[23] 王俊萍, 武慧敏, 王玲. MLA在银的赋存状态研究中的应用[J]. 矿冶, 2015, 24(1): 77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2015.01.019
Wang J P, Wu H M, Wang L. Application of MLA in the study of silver occurrence status[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2015, 24(1): 77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2015.01.019
[24] 张然, 叶丽娟, 党飞鹏, 等. 自动矿物分析技术在鄂尔多斯盆地砂岩型铀矿矿物鉴定和赋存状态研究中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1): 61−73. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005130071
Zhang R, Ye L J, Dang F P, et al. Application of automatic mineral analysis technology to identify minerals and occurrences of elements in sandstone-type uranium deposits in the Ordos Basin[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(1): 61−73. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202005130071
[25] 余彬, 王礼珊, 赵立恒, 等. 铜冶炼渣工艺矿物学研究与磨浮流程优化方向探讨[J]. 矿冶, 2020, 29(5): 119−126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2020.05.023
Yu B, Wang L S, Zhao L H, et al. Study on process mineralogy of copper smelting slag and optimization direction of grinding flotation process[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2020, 29(5): 119−126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2020.05.023
[26] 温利刚, 曾普胜, 詹秀春, 等. 矿物表征自动定量分析系统(AMICS)技术在稀土稀有矿物鉴定中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(2): 121−129. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201708110129
Wen L G, Zeng P S, Zhan X C, et al. Application of the automated mineral identification and characterization system (AMICS) in the identification of rare earth and rare minerals[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(2): 121−129. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201708110129
[27] Yu J, Ke H Q, Pei C Z, et al. Process mineralogy of Dalucao rare earth ore and design of beneficiation process based on AMICS[J]. Rare Metals, 2020, 39(8): 959−966. doi: 10.1007/s12598-020-01446-w
[28] Luo L Q, Zhang H Q. Process mineralogy and characteristic associations of iron and phosphorus-based minerals on oolitic hematite[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(9): 1959−1967. doi: 10.1007/s11771-017-3604-8
[29] Liu T, Song W, Kynicky J, et al. Automated quantitative characterization REE ore mineralogy from the giant Bayan Obo deposit, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(4): 426. doi: 10.3390/min12040426
[30] Gottlieb P, Wilkie G, Sutherland D, et al. Using quantitative electron microscopy for process mineralogy applications[J]. Journal of Metals, 2000, 52(4): 24−25.
[31] Grammatikopoulos T, Mercer W, Gunning C. Mineralogical characterisation using QEMSCAN® of the Nechalacho heavy rare earth metal deposit, Northwest Territories, Canada[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2013, 52(3): 265−277. doi: 10.1179/1879139513Y.0000000090
[32] Rythoven A D V, Pfaff K, Clark J G. Use of QEMSCAN® to characterize oxidized REE ore from the Bear Lodge carbonatite, Wyoming, USA[J]. Ore and Energy Resource Geology, 2020, 2-3: 100005. doi: 10.1016/j.oreoa.2020.100005
[33] Hrstka T, Gottlieb P, Skála R, et al. Automated mineralogy and petrology—Applications of TESCAN integrated mineral analyzer (TIMA)[J]. Journal of Geosciences, 2018, 63(1): 47−63.
[34] Aylmore M G, Eksteen J J, Jones M G, et al. The mineralogy and processing potential of the commonwealth project in the Molong volcanic belt, central Eastern New South Wales, Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 111: 102976. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.102976
[35] Smythe D M, Lombard A, Coetzee L L. Rare earth element deportment studies utilising QEMSCAN technology[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2013, 52: 52−61. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2013.03.010
[36] Gilligan R, Nikoloski A N. Alkaline leaching of brannerite. Part 2:Leaching of a high-carbonate refractory uranium ore[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2017, 173: 224−231. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2017.08.019
[37] Aylmore M G, Merigot K, Quadir Z, et al. Applications of advanced analytical and mass spectrometry techniques to the characterisation of micaceous lithium-bearing ores[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 116: 182−195. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2017.08.004
[38] Aylmore M G, Merigot K, Rickard W, et al. Assessment of a spodumene ore by advanced analytical and mass spectrometry techniques to determine its amenability to processing for the extraction of lithium[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2018, 119: 137−148. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2018.01.010
[39] Breiter K, Badanina E, Uriová J, et al. Chemistry of quartz—A new insight into the origin of the Orlovka Ta-Li deposit, Eastern Transbaikalia, Russia[J]. Lithos, 2019, 348-349: 105206. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105206
[40] Ward I, Merigot K, Mcinnes B I A. Application of quantitative mineralogical analysis in archaeological micromorphology:A case study from Barrow Is. Western Australia[J]. Journal of Archaeological Method and Theory, 2017, 25(19-20): 1−24.
[41] Honeyands T, Manuel J, Matthews L, et al. Comparison of the mineralogy of iron ore sinters using a range of techniques[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(6): 333. doi: 10.3390/min9060333
[42] Juránek R, Výravský J, Kolář M, et al. Graph-based deep learning segmentation of EDS spectral images for automated mineral phase analysis[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2022: 105109.
[43] 谢小敏, 李利, 袁秋云, 等. 应用TIMA分析技术研究Alum页岩有机质和黄铁矿粒度分布及沉积环境特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(1): 50−60. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202007120103
Xie X M, Li L, Yuan Q Y, et al. Grain size distribution of organic matter and pyrite in Alum shales characterized by TIMA and its paleo-environmental significance[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(1): 50−60. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202007120103
[44] 钟祥, 陈福林, 史志新, 等. 矿物自动分析系统在攀西某矿区钒钛磁铁矿工艺矿物学上的应用[J]. 冶金分析, 2022, 42(7): 62−70.
Zhong X, Chen F L, Shi Z X, et al. Application of advanced mineral identification and characterization system in process mineralogy of vanadium-titanium magnetite in a mining area of Panxi[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2022, 42(7): 62−70.
[45] 温利刚, 贾木欣, 付强, 等. 矿物自动定量分析系统在金的赋存状态研究中的应用[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2022(4): 1−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2022.04.001
Wen L G, Jia M X, Fu Q, et al. Application of automated quantitative mineralogy system in the deportment study of low-grade and fine-grained gold[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2022(4): 1−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9492.2022.04.001
[46] 高倩倩, 刘杨, 杨艳芳, 等. MLA与偏光显微镜在工艺矿物学研究中的应用对比[J]. 矿业工程, 2018, 16(4): 39−40. doi: 10.16672/j.cnki.kygc.2018.04.013
Gao Q Q, Liu Y, Yang Y F, et al. The application comparison between MLA and polarizing microscope in process mineralogy study[J]. Mining Engineering, 2018, 16(4): 39−40. doi: 10.16672/j.cnki.kygc.2018.04.013
[47] 刘榕鑫, 朱坤, 谢海云, 等. 云南斑岩型多金属金矿的嵌布特征及赋存状态研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(4): 404−410. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201710200169
Liu R X, Zhu K, Xie H Y, et al. Study on the inlay characteristics and occurrences of Yunnan porphyry polymetallic gold deposits[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(4): 404−410. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201710200169
[48] 朱丹, 桂博艺, 王芳, 等. AMICS测试技术在铌矿中的应用——以竹溪铌矿为例[J]. 有色金属(选矿部分), 2021(3): 1−7.
Zhu D, Gui B Y, Wang F, et al. Application of AMICS test technology in Niobium ore—A case study of Zhuxi niobium ore[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Mineral Processing Section), 2021(3): 1−7.
[49] 庞建涛, 肖喆, 王灿霞, 等. MLA系统在磷块岩工艺矿物学研究中的应用[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2015, 44(10): 19−21.
Pang J T, Xiao Z, Wang C X, et al. Application of MLA system in process mineralogy research of phosphorite block[J]. Chemical Minerals and Processing, 2015, 44(10): 19−21.
[50] 方明山, 王明燕. AMICS 在铜矿伴生金银综合回收中的应用[J]. 矿冶, 2018, 27(3): 104−108.
Fang M S, Wang M Y. Application of AMICS in comprehensive recovery of associated gold and silver in a copper ore[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2018, 27(3): 104−108.
[51] 李波, 梁冬云, 张莉莉, 等. 自动矿物分析系统的统计误差分析[J]. 矿冶, 2018, 27(4): 120−123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2018.04.025
Li B, Liang D Y, Zhang L L, et al. The statistical deviation analysis of automatic process mineralogy analysis system[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2018, 27(4): 120−123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2018.04.025
[52] 付艳红, 李振, 周安宁, 等. 煤中矿物及显微组分解离特性的MLA研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(6): 1357−1363.
Fu Y H, Li Z, Zhou A N, et al. Liberation characterization of minerals and macerals in coal by using MLA[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2017, 46(6): 1357−1363.
[53] Xu C L, Zhong C B, Lu R L, et al. Process mineralogy of Weishan rare earth ore by MLA[J]. Journal of Rare Earth, 2019, 37(3): 334−338. doi: 10.1016/j.jre.2018.06.008
[54] Sampaio N P, Araújo F G, von Kruger F L. The formation of Brazilian minerals database for integrated SEM-EDS system applied to the gold ore characterization[J]. Holos, 2018, 3: 2−22. doi: 10.15628/holos.2018.6938
[55] Goodall W R, Scales P J, Butcher A R. The use of QEMSCAN and diagnostic leaching in the characterisation of visible gold in complex ores[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18(8): 877−886. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2005.01.018
[56] Benvie B, Chapman N M, Robinson D J, et al. A robust statistical method for mineralogical analysis in geometallurgical diagnostic leaching[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2013, 52: 178−183. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2013.06.010
[57] Schulz B, Merker G, Gutzmer J. Automated SEM mineral liberation analysis (MLA) with generically labelled EDX spectra in the mineral processing of rare earth element ores[J]. Minerals, 2019, 9(9): 527. doi: 10.3390/min9090527
[58] 王运, 胡宝群, 李佑国, 等. 邹家山铀矿石伴生稀土的EMPA和MLA研究[J]. 稀土, 2018, 39(3): 17−26.
Wang Y, Hu B Q, Li Y G, et al. Study of EMPA and MLA of associated rare earth in Zoujiashan uranium ore[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2018, 39(3): 17−26.
[59] Gaudin A M. Principles of mineral dressing[R]. New York: McGraw Hill, 1939: 1-554.
[60] McIvor R E, Finch J A. A guide to interfacing of plant grinding and flotation operations[J]. Minerals Engineering, 1991, 4(1): 9−23. doi: 10.1016/0892-6875(91)90114-B
-




 下载:
下载: