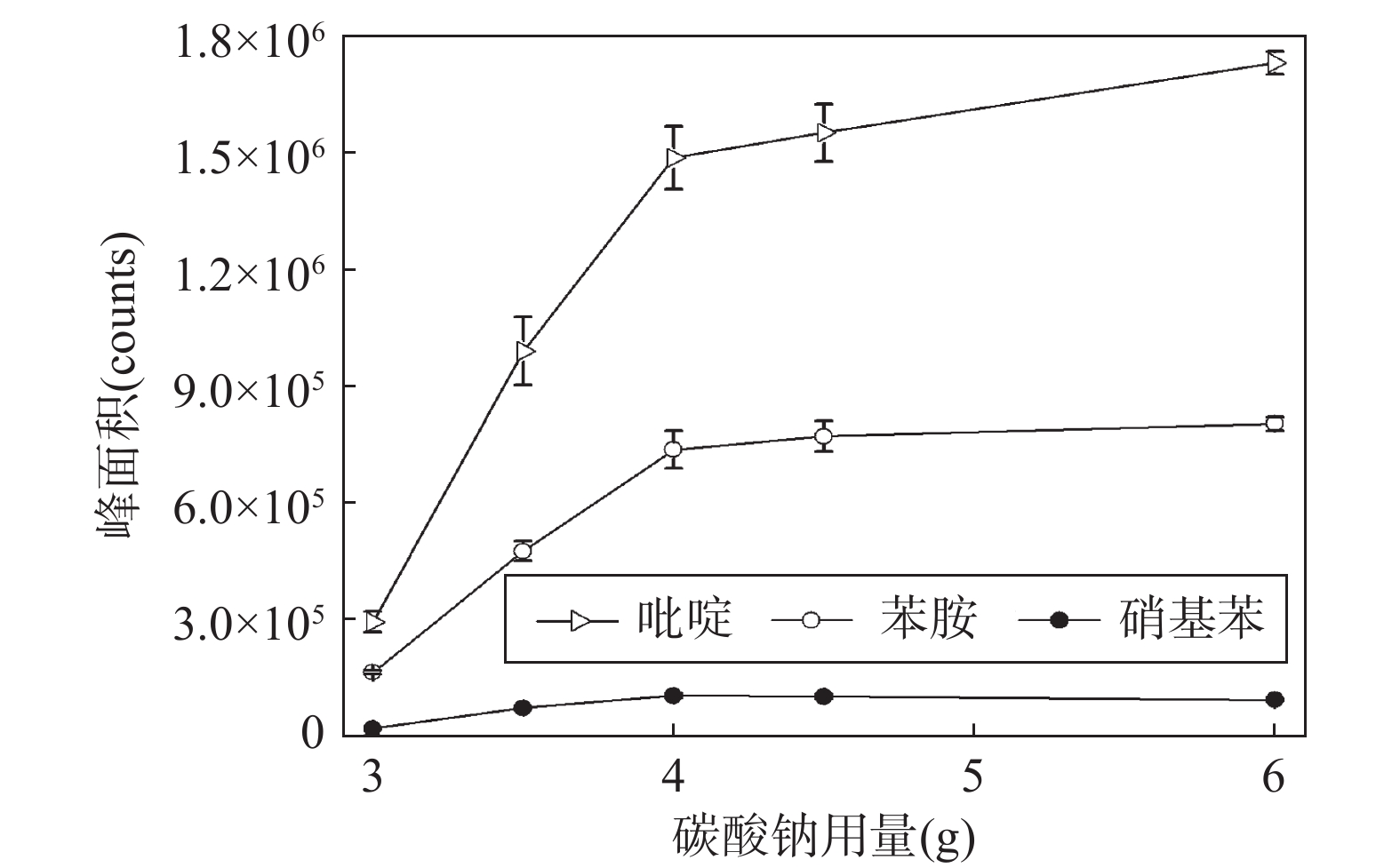
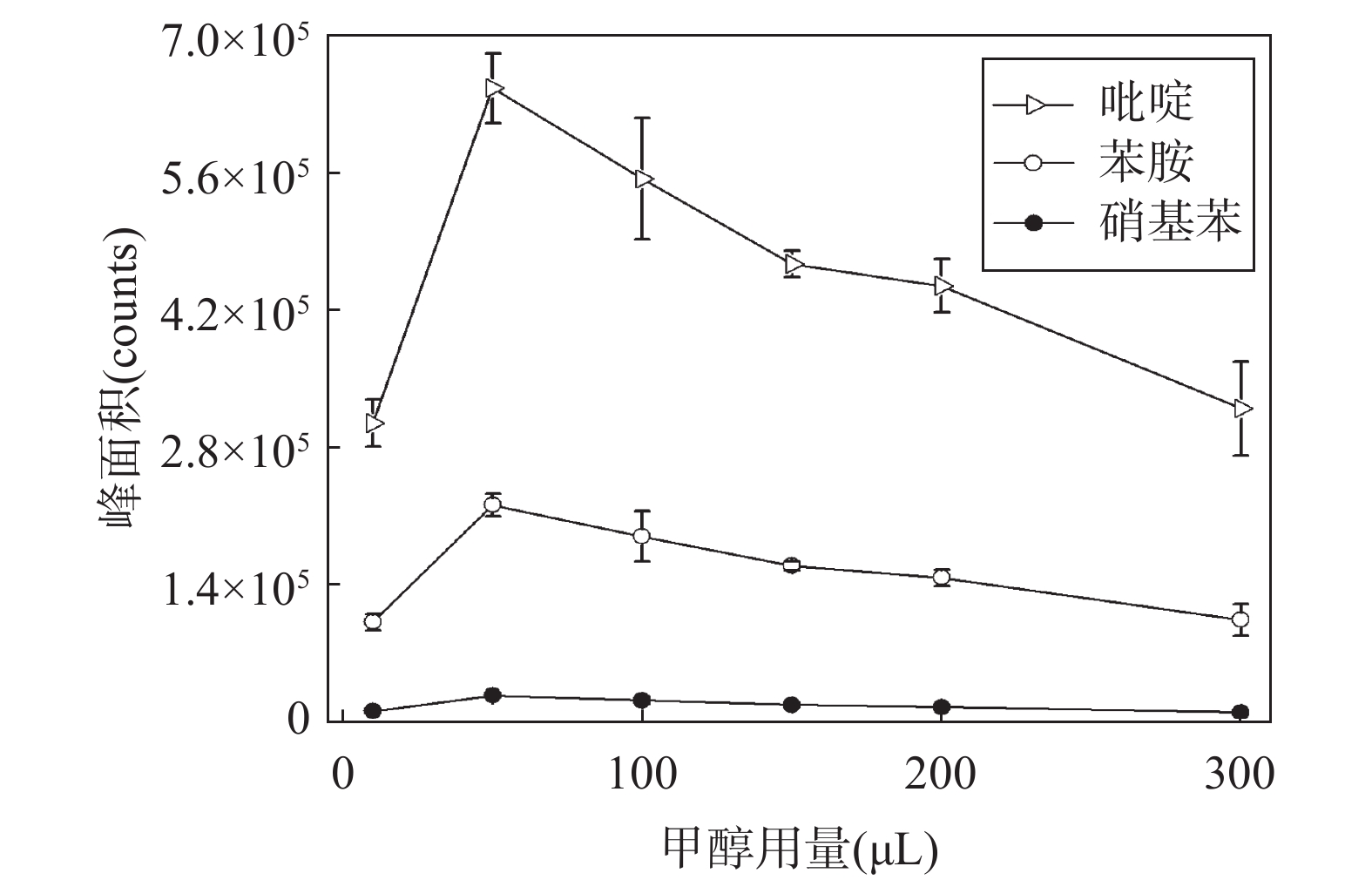
Simultaneous Determination of Pyridine, Aniline and Nitrobenzene in Printing and Dyeing Wastewater by Headspace Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
-
摘要:
吡啶、苯胺和硝基苯是重要的化工原料,因其低沸点、易挥发和极性强等特征,极易进入环境水体,并造成污染。基体复杂的印染废水含吡啶、苯胺和硝基苯等多种致癌的含氮有机污染物,排入外环境的印染废水将通过食物链影响人类健康,建立印染废水中三种化合物同时检测的方法对于保障工业外排水质安全至关重要。本文通过优化顶空条件等方法参数,建立了同时检测印染废水中吡啶、苯胺和硝基苯的顶空/气相色谱-质谱法(HS/GC-MS)。取10.0mL样品至预加有4.0g碳酸钠的20mL顶空瓶内,再加入总体积为50µL甲醇,在80℃顶空进样器中平衡60min,最后采用GC-MS检测和外标法定量。结果表明,吡啶(苯胺)和硝基苯的线性范围分别介于1.00~30.0µg/L和0.50~15.0µg/L,相关系数均大于0.992,检出限为0.15~0.93µg/L;对实验室空白和纺织产业园区污水处理厂排放的印染废水进行加标回收检测,平均回收率分别为73.6%~105.8%和67.2%~89.9%,相对标准偏差(RSD)分别为5.9%~14.2%(n=8)和2.2%~11.5%(n=6)。采用本方法检测纺织产业园区印染废水中吡啶、苯胺和硝基苯的浓度分别为1.10~1.13µg/L、1.71~5.36µg/L和未检出~0.19µg/L。该方法提出了有利于提高方法灵敏度的措施,例如加入适量的甲醇和碳酸钠,以及提高样品平衡温度,为印染废水中吡啶、苯胺和硝基苯的同时监控提供技术支撑。
-
关键词:
- 顶空/气相色谱-质谱法 /
- 吡啶 /
- 苯胺 /
- 硝基苯 /
- 印染废水
Abstract:BACKGROUND Pyridine, aniline, and nitrobenzene are important chemical raw materials with low boiling point and strong polarity. They are highly susceptible to enter environmental water and cause pollution. Printing and dyeing wastewater with a complex matrix contains various carcinogenic nitrogen-containing organic pollutants, such as pyridine, aniline, and nitrobenzene. Printing and dyeing wastewater discharging into the environment is harmful to human health through the food chain. The simultaneous detection method of pyridine, aniline, and nitrobenzene in environmental water is necessary.
OBJECTIVES To establish an analytical method based on headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of pyridine, aniline, and nitrobenzene in water.
METHODS The contents of pyridine, aniline, and nitrobenzene in the effluents from the wastewater treatment plants in the textile industry parks were detected and quantified by the external standard method with headspace gas chromatography-mass spectrometry method. Finally, the experiment conditions were optimized.
RESULTS The results showed that the linear ranges of pyridine and aniline were between 1.00µg/L and 30.0µg/L, and nitrobenzene was in the mass concentration range of 0.50-15.0µg/L, with the correlation coefficient above 0.992. The limits of detection were 0.15-0.93µg/L. The concentrations of pyridine, aniline and nitrobenzene in the effluents of the wastewater treatment plant in the textile industry parks were detected from 1.10µg/L to 1.13µg/L, from 1.71µg/L to 5.36µg/L and from ND to 0.19µg/L, respectively. The average recoveries of samples from laboratory blanks and wastewater treatment plant effluents at three levels of addition were 73.6% to 105.8% and 67.2% to 89.9%, respectively, with relative standard deviations of 5.9% to 14.2% (n=8) and 2.2% to 11.5% (n=6). The process and conditions of headspace are summarized as follows: 10.0mL of sample was placed into a 20mL headspace bottle containing 4.0g Na2CO3, and then 50µL methanol was added; the equilibration time of the headspace sampler was 60 min, and the equilibrium temperature was 80℃.
CONCLUSIONS Some measures are conductive to improving the sensitivity of the method, such as addition of methanol and sodium carbonate, and increasing the sample equilibrium temperature, in order to reduce the dissolved concentrations of the targets in the water and improve the precipitation effect of the targets. This method improves the detection efficiency, and is of significance for the simultaneous monitoring of pyridine, aniline, and nitrobenzene in printing and dyeing wastewater.
-

-
表 1 校准曲线强制过原点对实验室空白结果的影响
Table 1. Effects of forced through origin of the calibration curves on the results of blank samples.
实验室
空白吡啶(µg/L) 苯胺(µg/L) 硝基苯(µg/L) 非强制
过原点强制
过原点单点
校正非强制
过原点强制
过原点单点
校正非强制
过原点强制
过原点单点
校正第一次试验
(n=6)0.64a 0.63b 0.51 0.68aacc 0.11 0.14 — — — 第二次试验
(n=8)0.82 0.80 0.65 0.66aacc 0.09b 0.11 0.60aacc 0.05bb 0.08 第三次试验
(n=8)0.83a 0.81b 0.67 0.83aacc 0.26bb 0.32 0.56aacc 0.01 0.01 注:“—”表示无硝基苯的定量离子峰;a表示非强制过原点校准曲线的测定值与单点校正法(吡啶、苯胺和硝基苯的校正浓度分别为1.00、1.00和0.50µg/L,以下同)结果间存在显著性差异(P<0.05),aa表示他们间存在极显著性差异(P<0.01);b表示强制过原点校准曲线的测定值与单点校正法结果间存在显著性差异(P<0.05),bb表示它们之间存在极显著性差异(P<0.01);cc表示非强制过原点校准曲线的测定值与强制过原点校准曲线测定值间存在极显著性差异(P<0.01)。
表 2 优化后方法特性指标(n=10)
Table 2. The corresponding characteristic indexes of optimized methods (n=10).
化合物 配制浓度
(μg/L)测定值
(μg/L)标准偏差 检出限
(μg/L)检测下限
(μg/L)污染物排放限值
(μg/L)标准限值d
(μg/L)吡啶 2.00 3.06 0.329 0.93 3.72 100a,2000b 200 苯胺 2.00 2.38 0.171 0.49 1.96 500a,b 100 1000c 硝基苯 1.00 1.08 0.050 0.15 0.60 2000b 17 注:苯胺、硝基苯的污染物排放限值分别为苯胺类化合物和硝基苯类化合物的综合排放限值;a污染物排放限值来自《杂环类农药工业水污染物排放标准》(GB 21523—2008);b表示污染物排放限值来自《石油化学工业污染物排放标准》(GB 31571—2015);c表示污染物排放限值来自《纺织染整工业水污染物排放标准》(GB 4287—2012);d表示标准限值来自《地表水环境质量标准》(GB 3838—2002),其中苯胺和硝基苯的标准限值分别只针对苯胺和硝基苯。
表 3 实验室空白中3个水平下的加标样品准确度、精密度结果 (n=8)
Table 3. Accuracy and precision results of blank samples spiked with three levels (n=8).
化合物 配制浓度
(μg/L)测定值
(μg/L)回收率
(%)RSD
(%)吡啶 5.00 4.71 94.2 14.2 10.00 9.48 94.8 11.6 20.00 21.09 105.5 8.2 苯胺 5.00 4.16 83.2 12.8 10.00 8.94 89.4 11.5 20.00 21.15 105.8 8.8 硝基苯 2.50 1.84 73.6 13.0 5.00 4.19 83.8 10.6 10.00 9.97 99.7 5.9 表 4 汕头市潮阳区纺织印染环保综合处理中心污水处理厂排放印染废水中3个水平下的加标回收率 (n=6)
Table 4. Recoveries and RSDs of the three organic compounds at three levels in printing and dyeing wastewater from the wastewater treatment plant of the Textile Printing and Dyeing Environmental Protection Comprehensive Treatment Center in Chaoyang District, Shantou City (n=6).
化合物 本底浓度
(μg/L)加标浓度
(μg/L)测定值
(μg/L)回收率
(%)RSD
(%)吡啶 1.13 5.00 5.33 84.0 11.5 10.00 8.71 75.8 6.3 20.00 18.10 84.9 5.5 苯胺 5.36 5.00 9.73 87.4 9.9 10.00 12.47 71.1 6.9 20.00 22.32 84.8 4.2 硝基苯 ND 2.50 1.98 76.4 7.3 5.00 3.67 72.0 3.8 10.00 8.62 85.5 6.3 注:“ND”表示结果小于方法检出限。 表 5 汕头市潮南区纺织产业园区污水处理厂排放印染废水中3个水平下的加标回收率 (n=6)
Table 5. Recoveries and RSDs of the three organic compounds at three levels in printing and dyeing wastewater from Sewage Treatment Plant of the Textile Industrial Park,Chaonan District, Shantou City (n=6).
化合物 本底浓度
(μg/L)加标浓度
(μg/L)测定值
(μg/L)回收率
(%)RSD
(%)吡啶 1.10 5.00 4.76 73.2 3.8 10.00 9.24 81.4 10.9 20.00 18.43 86.7 3.7 苯胺 1.71 5.00 5.40 73.8 2.8 10.00 9.53 78.2 9.5 20.00 19.21 87.5 5.1 硝基苯 0.19 2.50 1.87 67.2 2.5 5.00 3.97 75.6 9.5 10.00 9.18 89.9 2.2 表 6 本研究与文献报道和标准检测方法的比较
Table 6. Comparison of this study with literature reports and standards.
化合物 样品前处理 分析检测方法 参考文献或
标准检测方法样品体积
(mL)前处理方法
及主要过程主要辅助试剂
及添加量方法名称 方法检出限
(µg/L)吡啶 10.0 顶空 碳酸钠(4.0g) GC-MS 0.93 本研究 10.0 顶空 氯化钠(4g) GC-FID 4.4 [24] 10.0 顶空 氯化钠(2g) GC-FID 16 [22] 10.0 顶空 氯化钠(3g) GC-FID 20 [25-26] 10.0 顶空 氯化钠(3g) GC-FID 26 [10] 10.0 顶空 氯化钠(4g) GC-FID 30 [8] 10.0 顶空 碳酸钠(4.0g) GC-FID 20 [21] 10.0 顶空 碳酸钠(5.0g) GC-MS 0.2 [23] 10.0 顶空 氯化钠(3g) GC-FID 30 HJ 1072—2019 苯胺 10.0 顶空 碳酸钠(4.0g) GC-MS 0.49 本研究 10.0 顶空 氢氧化钠(5g) GC-FID 2 [13] 20.0 顶空 氯化钠(10g) GC-MS 5.80 [27] 1000 液液萃取 二氯甲烷(145mL)+
正己烷(134mL)+
异丙醇(2.5mL)+
氯化钠(30g)GC-MS 0.057 HJ 822—2017 0.010 微孔滤膜过滤,
直接进样无 LC-TQMS 0.2 HJ 1048—2019 100 固相萃取 乙酸(5mL) LC-TQMS 0.02 HJ 1048—2019 硝基苯 10.0 顶空 碳酸钠(4.0g) GC-MS 0.15 本研究 40.0 顶空 无 GC-ECD <2.5 [28] 10.0 顶空 氯化钠(4.0g) GC-FID 10 [29] 10.0 顶空 氯化钠(4g) GC-MS 7.6 [30] 200 液液萃取 甲苯(40mL) GC-ECD 0.17 HJ 648—2013 1000 固相萃取 正己烷(7.5mL)+
丙酮(2.5mL)GC-ECD 0.032 HJ 648—2013 1000 液液萃取 二氯甲烷(89mL)+
正己烷(18mL)GC-MS 0.04 HJ 716—2014 1000 固相萃取 二氯甲烷(15mL) GC-MS 0.04 HJ 716—2014 注:GC-FID表示配氢火焰离子化检测器的气相色谱法;GC-ECD表示配电子捕获检测器的气相色谱法;LC-TQMS表示液相色谱-三重四极杆质谱法。
-
[1] 冯越, 陈丽丽, 张童, 等. 苯胺的健康效应研究进展[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2020, 54(2): 213−218.
Feng Y, Chen L L, Zhang T, et al. Research progress on health effects of aniline[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2020, 54(2): 213−218.
[2] 张琪, 刘玉香. 吡啶废水新型微生物法处理研究进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2021, 41(3): 17−22.
Zhang Q, Liu Y X. Research progress in the treatment of pyridine wastewater by novel microorganism method[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2021, 41(3): 17−22.
[3] Yin W, Wu J, Li P, et al. Experimental study of zero-valent iron induced nitrobenzene reduction in groundwater:The effects of pH, iron dosage, oxygen and common dissolved anions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 184(3): 198−204.
[4] Wei T, Hong M, Liu L. Study on the removal effect and influencing factors of nitrobenzene reduction by iron carbonate precipitates[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(27): 27112−27121. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2621-y
[5] 王鹏莺, 苏冰琴, 彭娅娅, 等. 过一硫酸盐直接氧化降解吡啶的反应条件和机制[J]. 中国给水排水, 2022, 38(13): 64−70. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2022.13.011
Wang P Y, Su B Q, Peng Y Y, et al. Reaction conditions and mechanism of peroxymonosulfate for direct oxidative degradation of pyridine[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2022, 38(13): 64−70. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2022.13.011
[6] 苏冰琴, 温宇涛, 林昱廷, 等. 改性活性炭纤维活化过硫酸盐深度处理焦化废水及降解吡啶[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(2): 576−591.
Su B Q, Wen Y T, Lin Y T, et al. Advanced treatment of coking wastewater and degradation of pyridine using modified activated carbon fiber activating peroxymonosulfate[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(2): 576−591.
[7] 冯尚华, 蒋波, 张建平, 等. 含苯胺废水处理技术进展[J]. 工业水处理, 2023, 43(6): 32−44. doi: 10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2021-0387
Feng S H, Jiang B, Zhang J P, et al. Progress in treatment of benzenamine wastewater[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2023, 43(6): 32−44. doi: 10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2021-0387
[8] 钱玉亭, 颜慧, 陆野. 顶空-毛细管柱气相色谱法测定水中吡啶[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2011, 36(9): 125−126,155.
Qian Y T, Yan H, Lu Y. Determination of pyridine in water by headspace-capillary GC-FID[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2011, 36(9): 125−126,155.
[9] 唐访良, 张明, 徐建芬. 直接进样-气相色谱法测定废水中5种含氮化合物[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2019, 55(5): 526−529.
Tang F L, Zhang M, Xu J F. GC determination of 5 nitrogenous compounds in wastewater with direct injection[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B:Chemical Analysis), 2019, 55(5): 526−529.
[10] 李海燕. 顶空-毛细管气相色谱法同步测定水中吡啶丙酮乙腈[J]. 中国环境监测, 2011, 27(2): 56−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2011.02.014
Li H Y. Headspace-capillary gas chromatography determination of pyridine[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2011, 27(2): 56−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2011.02.014
[11] 李少飞, 孙延康. 高效液相色谱法直接测定废水中苯胺含量[J]. 能源环境保护, 2017, 31(2): 63−64,22.
Li S F, Sun Y K. Direct determination of aniline in wastewater by HPLC[J]. Energy Environmental Protection, 2017, 31(2): 63−64,22.
[12] 李瑞琴. 高压液相色谱法测定废水中的苯胺和硝基苯胺[J]. 环境科学研究, 1998, 11(6): 34−36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.1998.06.011
Li R Q. Determination of aniline and nitroanilines in wastewater by HPLC[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 1998, 11(6): 34−36. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6929.1998.06.011
[13] 吴鹏, 缪建军, 於香湘. 顶空气相色谱法测定水中苯胺[J]. 中国环境监测, 2013, 29(6): 99−101.
Wu P, Miao J J, Yu X X. Determination of aniline in water with head-space gas-chromatography[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2013, 29(6): 99−101.
[14] 黄毅, 饶竹, 刘艳, 等. 超高效液相色谱法直接快速测定环境水样中硝基苯和苯胺[J]. 岩矿测试, 2012, 31(4): 666−671.
Huang Y, Rao Z, Liu Y, et al. Direct and rapid determination of nitrobenzene and aniline in environmental water by ultra performance liquid chromatography[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2012, 31(4): 666−671.
[15] 韩方岸, 陈钧, 将兆峰, 等. 中国沿海三省主要饮用水源有机物监测[J]. 中国环境监测, 2012, 28(1): 60−65.
Han F A, Chen J, Jiang Z F, et al. Monitoring the organic compounds of main source of drinking water in three coastal province of China[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2012, 28(1): 60−65.
[16] 宋权威, 赵兴达, 吴百春, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定炼化场地5种特征污染物[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(S2): 138−141. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.S2.021
Song Q W, Zhao X D, Wu B C, et al. Determination of five characteristic pollutants at the refinery by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(S2): 138−141. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.S2.021
[17] 万伟, 袁蕙, 马苏甜, 等. 吹扫捕集/气相色谱-质谱法测定石油炼制工艺废催化剂浸出液中挥发性有机物[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(11): 3695−3704. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021070807
Wan W, Yuan H, Ma S T, et al. Determination of volatile organic compounds in waste catalyst leaching liquor in petroleum refining process using P&T-GC-MS method[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(11): 3695−3704. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2021070807
[18] 刘玉龙, 邵志国, 张晓飞, 等. 顶空气相色谱-四极杆/静电场轨道阱高分辨质谱法测定复杂基体水样中挥发性有机物[J]. 分析化学, 2023, 51(4): 589−599.
Liu Y L, Shao Z G, Zhang X F, et al. Determination of volatile organic compounds in complex matrix waters by headspace-gas chromatography-quadrupole/orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2023, 51(4): 589−599.
[19] Tabbal S, El Aroussi B, Bouchard M, et al. A new headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous quantification of 21 microbial volatile organic compounds in urine and blood[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 296: 133901. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133901
[20] 陆国永, 吴悦, 赖永忠. 顶空固相微萃取法同时分析源水中5种极性挥发性有机物[J]. 中国给水排水, 2017, 33(12): 123−129.
Lu G Y, Wu Y, Lai Y Z. Simultaneous detection of 5 kinds of polar volatile organics in drinking source water with head space-solid phase microextraction[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2017, 33(12): 123−129.
[21] 缪建洋, 李丽. 顶空气相色谱法测定地表水中吡啶[J]. 环境保护科学, 2004, 30(6): 45−46. doi: 10.16803/j.cnki.issn.1004-6216.2004.06.015
Miu J Y, Li L. Determination of pyridine in surface water by head-space gas chromatography[J]. Environmental Protection Science, 2004, 30(6): 45−46. doi: 10.16803/j.cnki.issn.1004-6216.2004.06.015
[22] 李江, 陈华, 苏慕珂. 影响顶空-气相色谱法测定水中吡啶准确度的关键因素探讨[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2016, 28(2): 69−71.
Li J, Chen H, Su M K. Discussion on accuracy in determination of pyridine in water by headspace gas chromatography[J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2016, 28(2): 69−71.
[23] 王钊, 徐晓宇, 陈任翔, 等. 顶空气相色谱-质谱联用测定饮用水中吡啶[J]. 分析试验室, 2016, 35(12): 1386−1388. doi: 10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2016.0312
Wang Z, Xu X Y, Chen R X, et al. Determination of pyridine in drinking water by headspace gas chromatography with mass spectrometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2016, 35(12): 1386−1388. doi: 10.13595/j.cnki.issn1000-0720.2016.0312
[24] 郑锦辉, 李津津. 顶空气相色谱法测定水中乙醛、丙烯醛、丙烯腈和吡啶[J]. 贵州师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 34(3): 85−88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5570.2016.03.017
Zheng J H, Li J J. Determination of acetaldehyde, acrolein, acrylonitrile and pyridine in water with headspace gas chromatography[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University (Natural Sciences), 2016, 34(3): 85−88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5570.2016.03.017
[25] 罗毅, 姜建彪, 常青. 顶空-气相色谱法与吹扫捕集-气质联用法测定水中乙醛、丙烯醛、丙烯腈、吡啶的方法比较[J]. 河北工业科技, 2017, 34(3): 208−213.
Luo Y, Jiang J B, Chang Q. Comparison of headspace-GC with purge and trap-GC/MS methods in determination of acetaldehyde, acrolein, acrylonitrile and pyridine[J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology, 2017, 34(3): 208−213.
[26] 普学伟, 艾德平, 杨春涛, 等. 顶空-气相色谱法测定水中乙醛、丙烯醛、丙烯腈和吡啶[J]. 干旱环境监测, 2023, 37(1): 1−4,44.
Pu X W, Ai D P, Yang C T, et al. Determination of acetaldehyde, acrolein, acrylonitrile and pyridine in water by headspace-gas chromatography[J]. Arid Environmental Monitoring, 2023, 37(1): 1−4,44.
[27] 吕天峰, 王超, 滕恩江, 等. 便携式GC-MS快速测定水中苯胺[J]. 环境监测管理与技术, 2013, 25(6): 34−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2013.06.012
Lyu T F, Wang C, Teng E J, et al. Fast determination of aniline in water by the portable GC-MS[J]. The Administration and Technique of Environmental Monitoring, 2013, 25(6): 34−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2009.2013.06.012
[28] 韩长绵. 填充柱(ECD)-顶空气相色谱法测定水和废水中硝基苯、硝基甲苯和硝基氯苯[J]. 环境科学与技术, 1996, 19(2): 18−22.
Han C M. Determination of nitrobenzene, nitrotoluene, and nitrochlorobenzene in water and wastewater by packed column (ECD) headspace gas chromatography[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 1996, 19(2): 18−22.
[29] 张丰, 刘晓颖, 麦永乐. 顶空-气相色谱法测定水中苯系物和硝基苯类化合物[J]. 供水技术, 2015, 9(6): 49−53.
Zhang F, Liu X Y, Mai Y L. Determination of benzenes and nitrobenzenes in water by headspace gas chromatography[J]. Water Technology, 2015, 9(6): 49−53.
[30] 占美君, 赖永忠. 静态顶空-气相色谱/质谱法同时检测环境水体中59种挥发性有机物[J]. 分析测试技术与仪器, 2016, 22(4): 250−260. doi: 10.16495/j.1006-3757.2016.04.010
Zhan M J, Lai Y Z. Simultaneous determination of 59 volatile organic compounds in environmental water using headspace sampling method coupled to gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Analysis and Testing Technology and Instruments, 2016, 22(4): 250−260. doi: 10.16495/j.1006-3757.2016.04.010
[31] 熊茂富, 任敏, 杜伊, 等. 顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱联用法同时测定湖库水中12种氯苯甲醚的条件优化[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(6): 724−733. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201901210016
Xiong M F, Ren M, Du Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of 12 chloroanisoles in lake reservoir waters by headspace solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(6): 724−733. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201901210016
[32] 赖永忠. 顶空进样-固相微萃取测定饮用水源水中吡啶[J]. 岩矿测试, 2011, 30(5): 596−600. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.05.015
Lai Y Z. Determination of pyridine in drinking source water by head space sampling-solid phase microextraction[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2011, 30(5): 596−600. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2011.05.015
[33] 吴悦, 赖永忠, 陆国永, 等. 对水体中挥发性有机物分析的空白污染来源及解决措施的探讨[J]. 冶金分析, 2023, 43(2): 14−22. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.011894
Wu Y, Lai Y Z, Lu G Y, et al. Discussion on the sources and countermeasures of blank pollution in determination of volatile organic compounds in water samples[J]. Metallurgical Analysis, 2023, 43(2): 14−22. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1000-7571.011894
-




 下载:
下载: