Determination of Nitrate Nitrogen and Nitrite Nitrogen in Brackish and Saline Waters by Flow Injection Analysis
-
摘要:
咸水、半咸水资源广布,是干旱、半干旱地区重要的替代水资源和锂、钾盐等国家战略性矿产资源的重要来源。对咸水、半咸水中硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐等关键指标进行监控,是实现水资源综合利用的重要前提。流动注射法集采样、富集、分离、检测于一体,能够实现在线检测分析,近年来被广泛应用于淡水和海水分析,但对盐度更高的咸水类样品,该法尚未开展深入研究。本文利用全自动流动注射分析仪,建立了适用于咸水和半咸水中硝酸盐氮和亚硝酸盐氮的分析测定方法。通过仪器工作参数、显色剂浓度和介质、缓冲溶液中氯化铵浓度和pH值等实验条件优化,确定了方法最佳试验参数。用纯水作载流,可以实现盐度为0~5%范围水样中硝酸盐氮和亚硝酸盐氮的准确测定。对于盐度大于5%的卤水样品,需采用载流盐度匹配的方式改善样品回收率,使该法对盐度的耐受范围扩展至24%左右。本法对硝酸盐氮和亚硝酸盐氮的检出限分别为0.002mg/L、0.001mg/L,测定范围分别为0~2.00mg/L、0~1.00mg/L。通过国家标准物质和实际样品分析表明,该法具有良好的精密度和正确度,自动化程度高,分析周期短,适用于大批量样品的分析测试。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Saline water and brackish water resources are widely distributed, which are important alternative water resources in arid and semi-arid areas. They are also important sources of national strategic mineral resources such as lithium and potassium salts. Monitoring the key indicators such as nitrate and nitrite in saline water and brackish water is an important prerequisite for the comprehensive utilization of water resources. There are various methods for determining nitrates and nitrites, including spectrophotometry, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, electrochemistry, chromatography, and flow injection analysis. Among them, chromatography and electrochemistry require expensive and complex instruments or reagent; while spectrophotometry, although using simple equipment, has complex manual operation. Flow injection analysis is an analytical method that integrates sampling, enrichment, separation, and detection and can be used to achieve online detection and analysis. It has been widely used in freshwater and seawater analysis, but for saline water samples with higher salinity, the method has not been studied in depth.
OBJECTIVES To establish an analytical method for the determination of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in saline water and brackish water using a fully automatic flow injection analyzer to expand the scope of application of the instrument and achieve simultaneous determination of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in saline water, brackish water and freshwater.
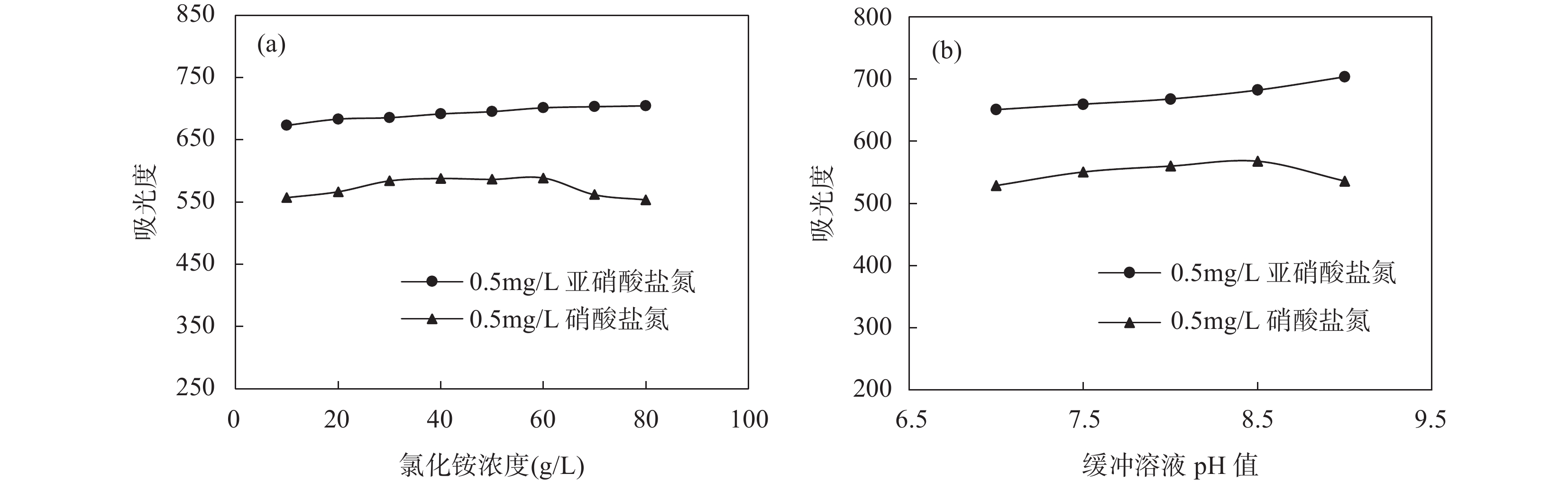
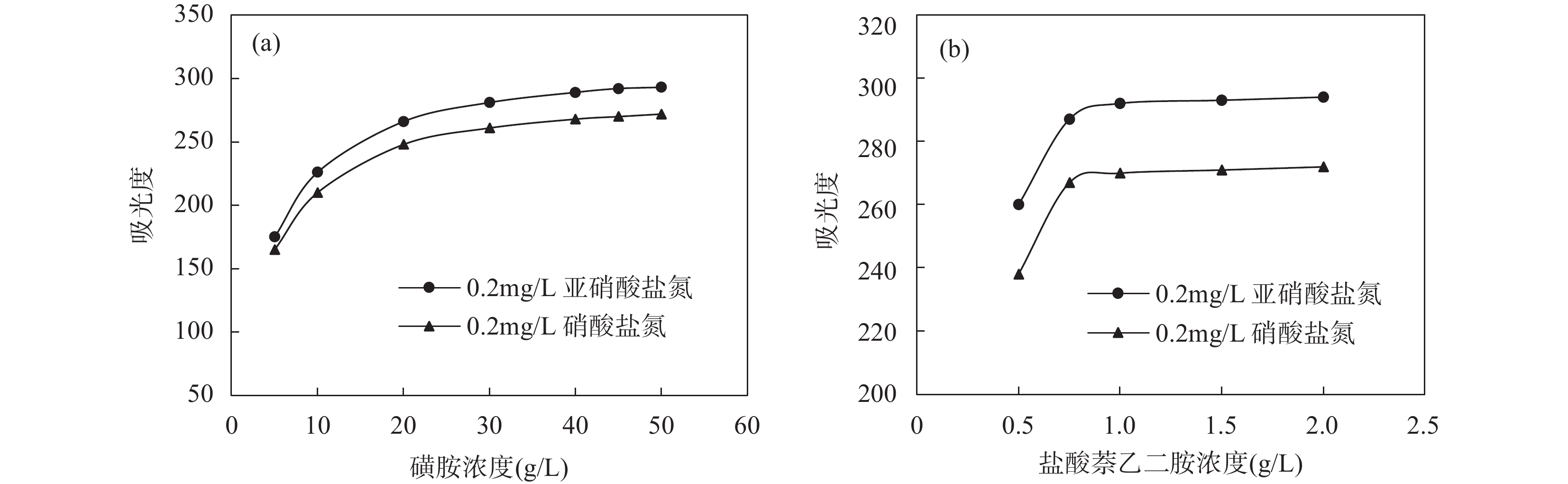
METHOD An analytical method suitable for the determination of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in saline and brackish water was established using a fully automatic flow injection analyzer after optimizing experimental conditions such as instrument working parameters, the affection of sulfonamide and N-(1-naphthyl) ethylenediamine concentration, the ammonium chloride concentration and pH value in buffer solution.
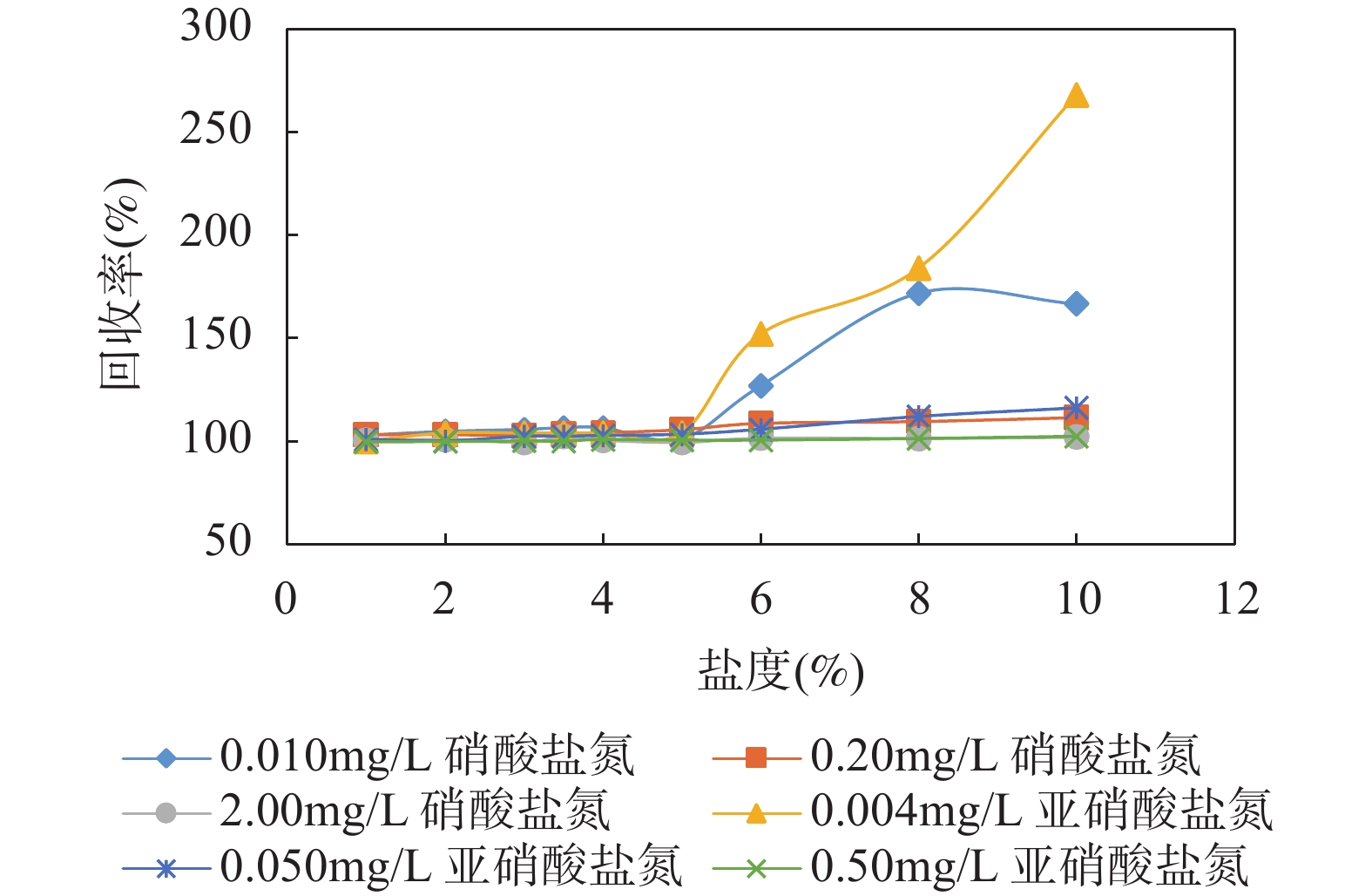
RESULTS The optimal instrumental operating conditions were selected through condition optimization experiments. The effects of chromogenic agent concentration and medium were investigated, as well as the buffer solution concentration and its pH value. Finally, sulfanilamide concentration was selected as 40g/L, hydrochloric acid-naphthyl ethylenediamine dihydrochloride concentration was selected as 1.0g/L as the optimal chromogenic concentration. Ammonium chloride concentration was selected as 60g/L, and the pH value was set to 8.5 to configure buffer solution. Under this condition, cadmium column had a reduction rate of more than 95% for nitrate nitrogen. Using pure water as carrier flow, this method can be used to accurately determine the content of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in water samples with salinity ranging from 0 to 5%. When the carrier flow was configured to have the same salinity as the sample to be tested, it effectively improved the recovery efficiency of high-salinity samples and extended the tolerance range of this method to about 24% salinity. The detection limits of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen were 0.002mg/L and 0.001mg/L, respectively, with measurement ranges of 0-2.00mg/L and 0-1.00mg/L. The analysis results of national standard substances and actual samples show that this method has good precision and accuracy, as well as a high degree of automation and short analysis cycle, which are suitable for the analysis of large quantities of samples.
CONCLUSION A method for the determination of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in saline water and brackish water samples was established. This method can be used to accurately determine the content of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in brackish water and saline water to achieve efficient online automation analysis.
-
Key words:
- saline water /
- brackish water /
- flow injection analysis /
- nitrate nitrogen /
- nitrite nitrogen
-

-
表 1 流动注射分析仪工作参数
Table 1. Working parameters of flow injection analyzer.
亚硝酸盐氮 硝酸盐氮 工作参数 设定值 工作参数 设定值 镉柱开关 关闭 镉柱开关 打开 测定波长 540nm 测定波长 540nm 洗针时间 10s 洗针时间 10s 出峰时间 10s 出峰时间 26s 进样时间 35s 进样时间 35s 峰宽 20s 峰宽 45s 进载流时间 20s 进载流时间 20s 到达阀时间 45s 到达阀时间 30s 积分时长 20s 积分时长 40s 注射时间 35s 注射时间 10s 蠕动泵转速 35r/min 蠕动泵转速 35r/min 样品周期时间 60s 样品周期时间 60s 表 2 镉柱对硝酸盐氮还原率的测试结果
Table 2. Reduction efficiency of Cd column for nitrate nitrogen.
测定参数 硝酸盐氮
峰面积亚硝酸盐氮
峰面积还原率
(%)测定平均值 285.6 297.6 96.0 标准偏差 1.34 1.11 / RSD(%) 0.47 0.37 / 表 3 载流盐度匹配后卤水样品中硝酸盐氮和亚硝酸盐氮测定结果
Table 3. Analytical results of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen after matching the same salinity with the carrier stream.
样品编号 盐度
(%)硝酸盐氮 亚硝酸盐氮 本底值
(mg/L)加标量
(mg/L)测定值
(mg/L)回收率
(%)本底值
(mg/L)加标量
(mg/L)测定值
(mg/L)回收率
(%)卤水1 7.2 0.030 0.10 0.133 103.9 0.083 0.05 0.136 106.8 卤水2 10.6 0.150 0.10 0.256 106.1 0.075 0.05 0.121 92.6 卤水3 13.8 0.027 0.10 0.129 102.7 0.067 0.05 0.117 101.0 卤水4 18.2 0.023 0.10 0.125 101.6 0.043 0.05 0.092 97.4 卤水5 24.1 0.041 0.10 0.146 105.3 0.058 0.05 0.103 91.0 卤水6 27.8 0.001 0.10 0.032 31.0 0.060 0.05 0.104 87.8 表 4 硝酸盐氮和亚硝酸盐氮的线性关系和方法检出限
Table 4. Regression analysis of calibration curves and quantification limits for nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen.
检测项目 线性关系 相关系数
(R2)方法检出限
(mg/L)线性范围
(mg/L)硝酸盐氮 y=0.0007x−0.0013 0.9999 0.002 0~2.00 亚硝酸盐氮 y=0.0007x+0.0007 0.9998 0.001 0~1.00 表 5 国家标准物质中硝酸盐氮和亚硝酸盐氮分析结果
Table 5. Analytical results of of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in the national standard substances.
样品类型 标准物质编号 标准值
(mg/L)测定平均值
(mg/L)RSD
(%)硝酸盐氮
标准物质GBW08636 0.140 0.141 1.19 GBW08637 0.210 0.212 0.97 GSB07-3166—2014(批次号200848) 0.900 0.917 0.30 亚硝酸盐氮
标准物质GBW08641 0.056 0.056 0.49 GBW08640 0.028 0.028 0.61 GSB07-3165—2014(批次号200641) 0.178 0.180 0.28 GSB07-3165—2014(批次号200639) 0.345 0.350 0.78 表 6 实际水样中硝酸盐氮和亚硝酸盐氮分析结果
Table 6. Analytical results of nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in water samples.
实际水样 硝酸盐氮 亚硝酸盐氮 本底值
(mg/L)加标量
(mg/L)测定值
(mg/L)回收率
(%)本底值
(mg/L)加标量
(mg/L)测定值
(mg/L)回收率
(%)威海海水1 0.600 0.5 1.120 103.3 0.014 0.05 0.068 108.0 威海海水2 0.573 0.5 1.087 102.5 0.030 0.05 0.084 108.2 威海海水3 0.584 0.5 1.088 100.8 0.028 0.05 0.082 108.4 秦皇岛海水4 0.096 0.5 0.602 101.3 0.046 0.05 0.100 107.2 秦皇岛海水5 0.312 0.5 0.811 99.8 0.047 0.05 0.100 106.6 青岛海水6 0.308 0.5 0.829 104.2 0.079 0.05 0.132 106.6 青岛海水7 0.317 0.5 0.839 104.6 0.081 0.05 0.135 109.0 西藏卤水8 0.454 0.5 0.922 93.6 0.030 0.05 0.079 98.8 西藏卤水9 12.41 10.0 21.98 95.7 0.055 0.05 0.108 106.6 青海卤水10 0.283 0.5 0.773 98.0 0.029 0.05 0.078 98.8 青海卤水11 0.098 0.5 0.581 96.6 0.030 0.05 0.084 106.6 -
[1] 《岩石矿物分析》编委会. 岩石矿物分析(第四版 第二分册)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011: 477.
The Editorial Committee of "Rock and Mineral Analysis". Rock and Mineral Analysis (The Fourth Edition, Volume Ⅱ)[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2011: 477.
[2] 张振龙, 孙慧, 苏洋, 等. 中国西北干旱地区水资源利用效率及其影响因素[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2017, 33(11): 961−967. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2017.11.001
Zhang Z L, Sun H, Su Y, et al. Water use efficiency and its influencing factors in arid areas of Northwest China[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2017, 33(11): 961−967. doi: 10.11934/j.issn.1673-4831.2017.11.001
[3] 李原园, 李云玲, 何君. 新发展阶段中国水资源安全保障战略对策[J]. 水利学报, 2021, 52(11): 1340−1346.
Li Y Y, Li Y L, He J. Strategic countermeasures for China’s water resources security in the new development stage[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2021, 52(11): 1340−1346.
[4] 陈佩, 王金涛, 董心亮, 等. 蔬菜咸水灌溉研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2022, 30(5): 799−808.
Chen P, Wang J T, Dong X L, et al. Review of research development associated with the application of saline water irrigation to vegetables[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30(5): 799−808.
[5] 孙宏勇, 张雪佳, 田柳, 等. 咸水灌溉影响耕地质量和作物生产的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2023, 31(3): 354−363.
Sun H Y, Zhang X J, Tian L, et al. Effects of saline water irrigation on soil quality and crop production: A review[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2023, 31(3): 354−363.
[6] 张妮, 左强, 石建初, 等. ANSWER模型评估新疆咸水灌溉棉花产量与效益[J]. 农业工程学报, 2023, 39(2): 78−89. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202209001
Zhang N, Zuo Q, Shi J C, et al. Estimating the yields and profits of saline water irrigated cotton in Xinjiang based on ANSWER model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(2): 78−89. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202209001
[7] 高会, 赵亮, 刘斌, 等. 河北滨海盐碱地浅层轻度咸水资源冬小麦灌溉安全利用研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2023, 31(7): 1102−1109.
Gao H, Zhao L, Liu B, et al. Study on shallow mild saline groundwater use safety in winter wheat irrigation based on the subsurface drainage system in the coastal area of Hebei Province in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2023, 31(7): 1102−1109.
[8] 阎文庆, 朱日来. 苦咸水、海水在国内外矿业中的应用[J]. 中国矿业, 2016, 25(10): 81−87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2016.10.017
Yan W Q, Zhu R L. Use of salt water in domestic and foreign mining industries[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2016, 25(10): 81−87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2016.10.017
[9] 王卓, 黄冉笑, 吴大天, 等. 盐湖卤水型锂矿基本特征及其开发利用潜力评价[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(1): 102−117. doi: 10.12029/gc20220808001
Wang Z, Huang R X, Wu D T, et al. The basic characteristics and development potential evaluation of salt lake brine-type lithium deposits[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(1): 102−117. doi: 10.12029/gc20220808001
[10] 余小灿, 刘成林, 王春连, 等. 江汉盆地大型富锂卤水矿床成因与资源勘查进展: 综述[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(1): 107−123.
Yu X C, Liu C L, Wang C L, et al. Genesis of lithium brine deposits in the Jianghan Basin and progress in resource exploration: A review[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(1): 107−123.
[11] 边绍菊, 刘鑫, 李东东, 等. 川东北普光地区深层富钾卤水钾资源提取研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(6): 171−178.
Bian S J, Liu X, Li D D, et al. Potassium extraction from potassium-rich brine in Puguang region, Northeastern Sichuan, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(6): 171−178.
[12] 雷风鹏, 朱朝梁, 卿彬菊, 等. 卤水提硼技术进展综述[J]. 无机盐工业, 2018, 50(7): 1−5.
Lei F P, Zhu C L, Qing B J, et al. Review of technology progress on extraction for boron from brine[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2018, 50(7): 1−5.
[13] 李东洋, 李先国, 冯丽娟, 等. 卤水中钾和镁的利用[J]. 无机盐工业, 2011, 43(11): 12−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2011.11.004
Li D Y, Li X G, Feng L J, et al. Utilization of potassium and magnesium resource in brine[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2011, 43(11): 12−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2011.11.004
[14] 张苏江, 张琳, 姜爱玲, 等. 中国盐湖资源开发利用现状与发展建议[J]. 无机盐工业, 2022, 54(10): 13−21.
Zhang S J, Zhang L, Jiang A L, et al. Current situation and development suggestions of development and utilization of salt lake resources in China[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(10): 13−21.
[15] 郭秀红, 郑绵平, 刘喜方, 等. 西藏盐湖卤水铯资源及其开发利用前景[J]. 盐业与化工, 2008(3): 8−13. doi: 10.16570/j.cnki.issn1673-6850.2008.03.010
Guo X H, Zheng M P, Liu X F, et al. Saline cesium resource and prospect of its exploitation and utilization in Xizang[J]. Journal of Salt and Chemical Industry, 2008(3): 8−13. doi: 10.16570/j.cnki.issn1673-6850.2008.03.010
[16] 余疆江, 郑绵平, 伍倩, 等. 卤水溴资源开发利用进展[J]. 现代化工, 2013, 33(4): 47−51. doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2013.04.039
Yu J J, Zheng M P, Wu Q, et al. Development and utilization progress of brine bromine resource[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2013, 33(4): 47−51. doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2013.04.039
[17] 陈景伟, 宋江涛, 赵庆令, 等. 薄膜吸附制样-波长色散X射线荧光光谱法测定卤水中的溴[J]. 岩矿测试, 2015, 34(5): 570−574.
Chen J W, Song J T, Zhao Q L, et al. Determination of bromine in brine by wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with film adsorption pretreatment[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(5): 570−574.
[18] 韩彬, 林法祥, 丁宇, 等. 海州湾近岸海域水质状况调查与风险评价[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(4): 429−437.
Han B, Lin F X, Ding Y, et al. Quality survey and risk assessment of the coastal waters of Haizhou Bay[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(4): 429−437.
[19] 李圣品, 李文鹏, 殷秀兰, 等. 全国地下水质分布及变化特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(6): 1−8.
Li S P, Li W P, Yin X L, et al. Distribution and evolution characteristics of national groundwater quality from 2013 to 2017[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(6): 1−8.
[20] 邢书才, 杨永, 岳亚萍. 分光光度法测定大气降水中亚硝酸盐方法的改进[J]. 中国测试, 2018, 44(11): 99−102. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2018.11.018
Xing S C, Yang Y, Yue Y P. The improvement of spectrophotometry for the determination of nitrite in atmospheric precipitation[J]. China Measurement & Test, 2018, 44(11): 99−102. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2018.11.018
[21] Cadeado A N S, Machado C C S, Costa M Q, et al. A palm-sized wireless device for colorimetric nitrite determination in water[J]. Microchemical Journal:Devoted to the Application of Microtechniques in All Branches of Science, 2022, 183: 108138.
[22] Masserini R T, Fanning K A. A sensor package for the simultaneous determination of nanamolar concentrations of nitrite, nitrate and ammonia in seawater by fluorescence detection[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2000, 68(3): 323−333.
[23] 窦宪民, 高岐, 石焱. 偶合化学发光法测定环境水样中的痕量亚硝酸根[J]. 分析试验室, 2002, 21(3): 43−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2002.03.014
Dou X M, Gao Q, Shi Y. Determination of trace nitrite in water samples by coupling chemiluminescence analysis[J]. Analytical Laboratory, 2002, 21(3): 43−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2002.03.014
[24] 郑冬云, 刘晓军, 朱珊莹, 等. 电化学传感法测定水中亚硝酸盐[J]. 中国环境监测, 2014, 30(4): 140−145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2014.04.024
Zheng D Y, Liu X J, Zhu S Y, et al. Detecting nitrite in water with electrochemical sensing method[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2014, 30(4): 140−145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2014.04.024
[25] 韩耀宗. 基于离子色谱法的水样中硝酸盐氮和亚硝酸盐氮含量测定[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(3): 1385, 1389. doi: 10.13989/j.cnki.0517-6611.2010.03.046
Han Y Z. Nitrate nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen content in the water sample based on ion chromatography method[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(3): 1385, 1389. doi: 10.13989/j.cnki.0517-6611.2010.03.046
[26] 左家信, 冯家力. 离子色谱法同时测定纯化水和饮用水中亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐[J]. 分析仪器, 2022(1): 42−46.
Zuo J X, Feng J L. Simultaneous determination of nitrite and nitrate in purified water and drinking water by ion chromatograph[J]. Analytical Instrumentation, 2022(1): 42−46.
[27] 佘小林, 孙伟, 叶晓勤, 等. 离子色谱法测定水果和蔬菜中硝酸盐[J]. 岩矿测试, 2007, 26(3): 233−234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.03.014
She X L, Sun W, Ye X Q, et al. Determination of nitrate in fruit and vegetable samples by ion chromatography[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2007, 26(3): 233−234. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.03.014
[28] 许丹丹. 采用流动注射分析仪总氮通道测定硝酸盐氮的探讨[J]. 工业水处理, 2023, 43(5): 158−161. doi: 10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2022-0688
Xu D D. Discussion on the determination of nitrate nitrogen by total nitrogen channel in flow injection analyzer[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2023, 43(5): 158−161. doi: 10.19965/j.cnki.iwt.2022-0688
[29] 李楠, 张新申, 高昊东, 等. 新型浓缩柱富集-流动注射法测定饮用水中痕量亚硝酸盐[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2015, 27(7): 1074−1077.
Li N, Zhang X S, Gao H D, et al. Research on enrichment of trace amounts of nitrite with new concentration column by flow injection analysis spectrophotometry[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2015, 27(7): 1074−1077.
[30] 陈灿云, 张志军, 梁高亮, 等. 连续流动分析仪测定环境水样中硝酸盐氮和亚硝酸盐氮[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2004, 40(10): 613−614.
Chen C Y, Zhang Z J, Liang G L, et al. Determination of nitrate and nitrite nitrogen in environmental water using continuous-flowing analyzer[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2004, 40(10): 613−614.
[31] 尚宝玉, 贺舒文, 洪滨, 等. 流动注射在线分析法测定海水中的亚硝酸盐氮[J]. 化学分析计量, 2022, 31(1): 10−12.
Shang B Y, He S W, Hong B, et al. Determination of nitrite nitrogen in seawater by on-line flow injection method[J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2022, 31(1): 10−12.
[32] 刘丽敏, 顾重武, 曾燕燕. 在线镉柱还原-连续流动注射法测定地表水和海水中硝酸盐氮[J]. 理化检验(化学分册), 2019, 55(2): 147−151.
Liu L M, Gu C W, Zeng Y Y. Determination of nitrate nitrogen in surface water and seawater by continuous flow injection method with on-line cadmium column reduction[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis (Part B: Chemical Analysis), 2019, 55(2): 147−151.
[33] 朱敬萍, 胡红美, 张小军, 等. 连续流动注射法同时测定海水中的硝酸盐和亚硝酸盐[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2015, 34(6): 543−547.
Zhu J P, Hu H M, Zhang X J, et al. Determination of nitrate and nitrite in seawater by continuous flow injection analysis[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2015, 34(6): 543−547.
[34] 胡浩光, 王耀, 谢翠美, 等. 连续流动分析法测定环境水样中痕量亚硝酸盐[J]. 现代仪器, 2010, 16(6): 68−70.
Hu H G, Wang Y, Xie C M, et al. Determination nitrite in environmental water samples by continuous flowing analysis[J]. Modern Instruments, 2010, 16(6): 68−70.
[35] 韩彬, 曹磊, 郑立, 等. 夹管电磁阀定量-流动注射分析系统测定海水中亚硝酸盐和硝酸盐氮[J]. 分析化学, 2010, 38(12): 1832−1837.
Han B, Cao L, Zheng L, et al. Determination of nitrite and nitrate-nitrogen in seawater by flow injection analysis based on quantificational pipe clamp solenoid valves[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2010, 38(12): 1832−1837.
-



 下载:
下载: