Determination of 42 Trace Elements in Silicate Glass Reference Materials by High Spatial Resolution LA-ICP-MS
-
摘要:
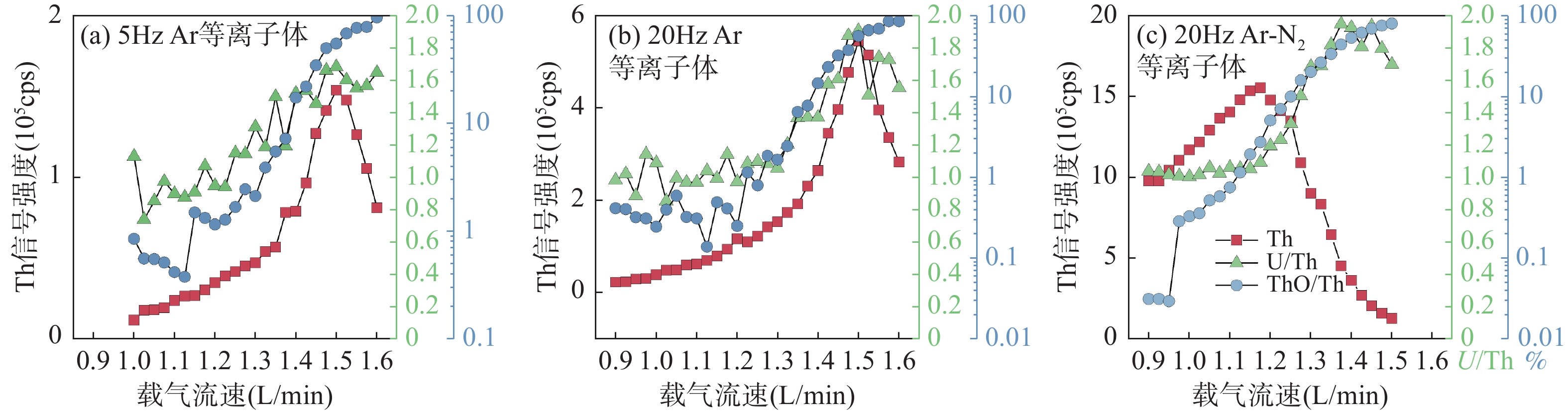
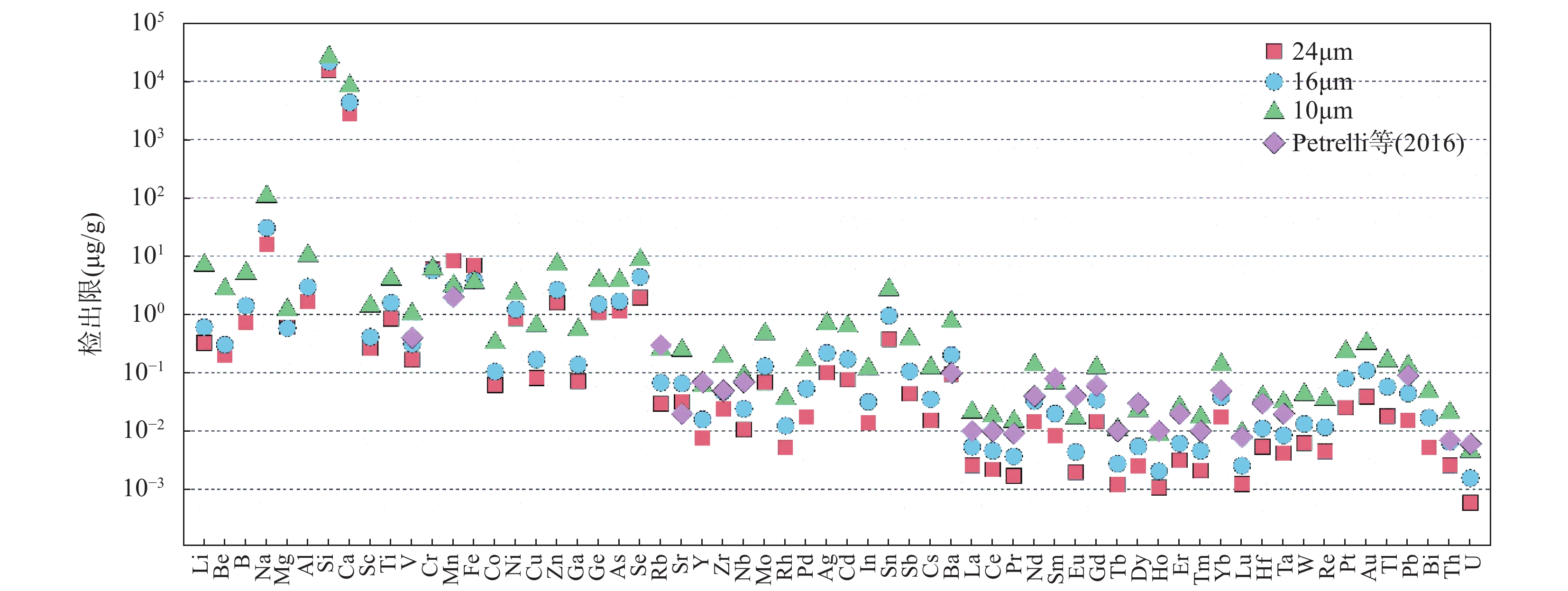
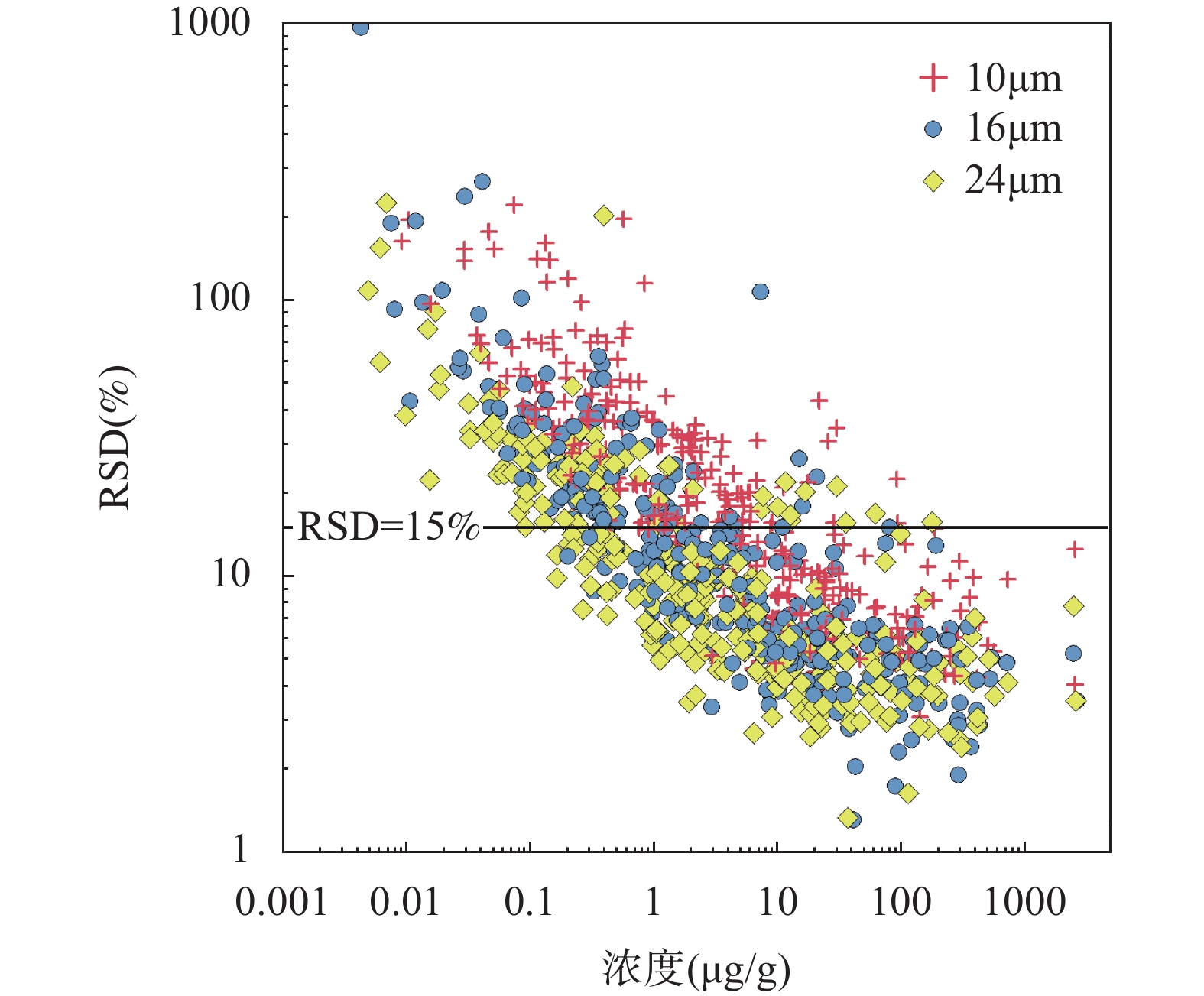
近年来,随着人们对关键金属(稀有金属、稀土金属、稀散金属和稀贵金属)的成矿机制、分布规律和绿色利用等研究日益加深,建立原位测定地质样品中关键金属元素(如REEs、Cr、Co、Ga、Ag、Cd、In、W、Tl等)分析方法对于研究关键金属元素的地球化学行为、分布规律和成矿机制具有重要意义。由于关键金属在地壳中丰度极低(一般为ng/g~μg/g级别),赋存矿物非常细小(粒径μm级别),因此需要建立高空间分辨率微区原位分析技术实现低含量(ng/g~μg/g)微量元素的定量。本文提出了高频剥蚀模式与Ar-N2等离子体技术相结合提升LA-ICP-MS对微量元素的检出能力,使之能够满足地质样品中关键金属元素的检测需求。结果表明:在Ar-N2等离子体条件下,采用高频(20Hz)剥蚀模式,LA-ICP-MS分析中大部分元素灵敏度提升了1.5~9倍。在使用高灵敏度X型截取锥时,高频剥蚀模式与氮气增敏技术相结合可以显著减小氧化物产率和降低U-Th分馏,获得更宽的载气流速区间(0.9~1.08L/min)以满足测试的仪器分析条件(ThO+/Th+<0.5%和U/Th=1)。本研究开发的高空间分辨率LA-ICP-MS关键金属分析方法具有较低的检出限(在剥蚀束斑24μm条件下,30种元素的检出限<0.02μg/g),在高空间分辨率(10~24μm)条件下,通过对8种国际硅酸盐玻璃标准物质中42种微量元素进行定量分析,34种微量元素的测试结果的准确度优于10%,精密度优于15%,实现了在高空间分辨率条件下对微量元素的准确定量分析。
Abstract:BACKGROUND Critical metal elements are a group of metal elements including rare metal elements (e.g., Li, Be, Rb, Cs, Nb, Ta, Zr, Hf, W), rare earth elements (REEs), rare disperse elements (e.g., Ga, Ge, Se, Cd, In, Te, Re, Tl) and rare precious elements (e.g., PGE, Cr and Co), which are important for the development of emerging industries. In recent years, the critical metal elements have shown great economic characteristics in emerging industries such as advanced materials, new energy resources and national defense and military industry uses, which is important strategic significance for the development of the national economy and technology. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the geochemical properties and metallogenic mechanism of critical metal elements. How to accurately determine trace elements in geological materials is a prerequisite for these investigations. Critical metal elements in geological materials can be determined by conventional chemical wet digestion methods. However, chemical wet digestion methods can only obtain an average chemical composition without spatial distribution information of critical metal elements. Compared to digestion methods, in situ microanalysis technology can obtain micrometer scale elemental distribution in silicate minerals, omit tedious chemical processing processes and avoid the use of a large amount of chemical reagents. However, the abundance of critical metal elements in the crust is low (μg/g level) and the carrier minerals containing critical metal elements are at the micrometer scale. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a high spatial resolution in situ analysis technique to determine trace elements in geological materials.
OBJECTIVES To improve sensitivity of LA-ICP-MS for the determination of critical metal elements (ng/g-μg/g level) in silicate minerals by high-frequency ablation mode combined with Ar-N2 mixed plasma technique.
METHODS Experiments were carried out using a single collector ICP-MS (Element XR Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany) in combination with a 193nm excimer laser ablation system (GeoLas 2005, Lambda Physik, Gttingen, Germany) at the Ministry of Natural Resources Key Laboratory of Gold Mineralization Processes and Resources Utilization. The X skimmer cone was used to improve sensitivity of ICP-MS. To obtain high sensitivity and reduce oxide interference, a small amount (0-10mL/min) of nitrogen was added into the carried gas, downstream from the ablation cell by a T junction. The ablation frequency was 5Hz or 20Hz. The ablation spot size was 10-24μm. Each measurement consisted of 18s of acquisition of the background signal, followed by 10s ablation signal acquisition. The washing time was 20s between each measurement. The standard reference materials NIST 610, NIST612 and NIST614 were used as calibration standards. The comparison of signal intensity, sensitivity, oxide yield and U/Th ratio in LA-ICP-MS were investigated at low and high frequency ablation modes in Ar plasma or Ar-N2 mixed plasma. Before testing, the signal of 232Th and 238U were higher than 1×106cps when ablating NIST 612 at 24μm. Moreover, U/Th was close to 1 and ThO+/Th+ was lower than 0.5%. At optimum condition, an in situ elemental quantitative method with high spatial resolution (10-24μm) was established to determine 42 trace elements in MPI-DING and USGS silicate glass reference materials.
RESULTS Sensitivity in LA-ICP-MS is the primary factor for the elemental quantitative analysis with high spatial resolution. Compared to Ar plasma, sensitivities of most elements were improved by a factor of 1.5-9 when using Ar-N2 mixed plasma at high-frequency (20Hz) ablation mode. In LA-ICP-MS analysis, analytical results can be influenced by oxide yield and elemental fractionation. When using X skimmer cone in SF-ICP-MS, the oxide yield and elemental fractionation was significantly reduced in Ar-N2 mixed plasma at high-frequency (20Hz) ablation mode. There was a wide range of carrier flow rate (0.9-1.075L/min) for obtaining good analysis conditions (ThO+/Th+<0.5% and U/Th=1). The limits of detection for 30 trace elements were lower than 0.02μg/g when ablation spot and ablation frequency were at 24μm and 20Hz, respectively. At optimum conditions (ablation spot 10-24μm and ablation frequency 20Hz), 42 trace elements in MPI-DING and USGS silicate glass reference materials were analyzed by LA-ICP-MS in Ar-N2 mixed plasma. The accuracy of analytical results for 34 trace elements was better than 10% and the precision was better than 15%, which suggested high-frequency ablation mode combined with Ar-N2 mixed plasma technique can be used to achieve the determination of critical metal elements (ng/g-μg/g level) in silicate minerals with high spatial resolution.
CONCLUSIONS Compared to low-frequency ablation mode, high-frequency ablation mode combined with Ar-N2 mixed plasma technique can improve sensitivity and reduce oxide yield and elemental fractionation. Moreover, the analysis time of high-frequency ablation mode is very short, which can improve the analysis efficiency of LA-ICP-MS. Due to the high sensitivity and high spatial resolution of LA-ICP-MS at high-frequency ablation mode, LA-ICP-MS can be applied to quantify trace elements and complex internal chemical compositions in micrometer level minerals, such as distribution of trace elements in mineral growth zones. Furthermore, this high-frequency ablation mode may also be applied to the development of in situ accessory mineral dating and isotope ratio analysis.
-

-
表 1 LA-ICP-MS仪器参数
Table 1. Instrumental operating conditions
高分辨电感耦合等离子体质谱
(Thermo Scientific Element XR)激光剥蚀系统
(Geolas 2005准分子激光器)参数 工作条件 参数 工作条件 RF 功率 1200W 波长 193nm 冷却气(Ar)流速 16.00L/min 脉冲宽度 15ns 辅助气(Ar)流速 0.8L/min 能量密度 14J/cm2 载气(Ar)流速 0.9~1.5L/min 剥蚀束斑(直径) 10μm、16μm、24μm 采样锥和截取锥类型 标准采样锥+X型截取锥 剥蚀频率 5Hz、20Hz 分辨率 M/ΔM=300 载气(He)流速 0.54L/min 检测器模式 Triple 同位素个数 79 每个元素积分时间 0.010s 总积分时间 1.2s -
[1] 蒋少涌, 温汉捷, 许成, 等. 关键金属元素的多圈层循环与富集机理: 主要科学问题及未来研究方向[J]. 中国科学基金, 2019, 33(2): 111−118.
Jiang S Y, Wen H J, Xu C, et al. Earth sphere cycling and enrichment mechanism of critical metals: Major scientific issues for future research[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2019, 33(2): 111−118.
[2] 翟明国, 王汝成, 吴福元, 等. 战略性关键金属矿产资源: 现状与问题[J]. 中国科学基金, 2019, 33(2): 106−111.
Zhai M G, Wang R C, Wu F Y, et al. Critical metal mineral resources: Current research status and scientific issues[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2019, 33(2): 106−111.
[3] Cobelo-Garcia A, Filella M, Croot P, et al. COST action TD1407: Network on technology-critical elements (NOTICE)—From environmental processes to human health threats[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(19): 15188−15194. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5221-0
[4] Watari T, Nansai K, Nakajima K. Review of critical metal dynamics to 2050 for 48 elements[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2020, 155: 104669. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104669
[5] 李超, 王登红, 屈文俊, 等. 关键金属元素分析测试技术方法应用进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(5): 658−669. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201907310115
Li C, Wang D H, Qu W J, et al. A review and perspective on analytical methods of critical metal elements[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(5): 658−669. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.201907310115
[6] 刘勇胜, 屈文俊, 漆亮, 等. 中国岩矿分析测试研究进展与展望(2011—2020)[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(3): 515−539.
Liu Y S, Qu W J, Qi L, et al. Advances and perspectives of researches on rock and mineral analyses in China (2011—2020)[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(3): 515−539.
[7] Chu Z. Analytical methods for Os isotope ratios and Re-PGE mass fractions in geological samples[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry, 2020, 8: 615839.
[8] Braukmüller N, Wombacher F, Bragagni A, et al. Determination of Cu, Zn, Ga, Ag, Cd, In, Sn and Tl in geological reference materials and chondrites by isotope dilution ICP‐MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2020, 44(4): 733−752. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12352
[9] Wang W, Ma L, Evans R D, et al. Quantification of Re and four other trace elements (Ag, Cd, Pd, Zn) in certified reference materials and natural waters[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2022, 37(7): 1471−1483. doi: 10.1039/D2JA00073C
[10] Albrecht M, Derrey I T, Horn I, et al. Quantification of trace element contents in frozen fluid inclusions by UV-fs-LA-ICP-MS analysis[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2014, 29(6): 1034−1041. doi: 10.1039/C4JA00015C
[11] Michaliszyn L, Ren T, Röthke A, et al. A new method for the SI-traceable quantification of element contents in solid samples using LA-ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2020, 35(1): 126−135. doi: 10.1039/C9JA00296K
[12] 赵令浩, 詹秀春, 曾令森, 等. 磷灰石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年直接校准方法研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(5): 744−753.
Zhao L H, Zhan X C, Zeng L S, et al. Direct calibration method for LA-HR-ICP-MS apatite U-Pb dating[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(5): 744−753.
[13] 张雅, 李全忠, 闫峻, 等. LA-ICP-MS独居石U-Th-Pb测年方法研究[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(5): 637−649. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101130005
Zhang Y, Li Q Z, Yan J, et al. Analytical conditions for U-Th-Pb dating of monazite by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(5): 637−649. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202101130005
[14] 谭细娟, 郭超, 凤永刚, 等. 激光剥蚀系统气体流速变化对LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年精度的影响[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(4): 554−563. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202110020140
Tan X J, Guo C, Feng Y G, et al. Effect of gas flow rates in laser ablation system on accuracy and precision of zircon U-Pb dating analysis by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(4): 554−563. doi: 10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202110020140
[15] Caulfield J T, Tomlinson E L, Chew D M, et al. Microanalysis of Cl, Br and I in apatite, scapolite and silicate glass by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 557: 119854. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119854
[16] Jenner F E, Arevalo R D. Major and trace element analysis of natural and experimental igneous systems using LA-ICP-MS[J]. Elements, 2016, 12(5): 311−316. doi: 10.2113/gselements.12.5.311
[17] Jochum K P, Stoll B, Weis U, et al. Non-matrix-matched calibration for the multi-element analysis of geological and environmental samples using 200nm femtosecond LA-ICP-MS: A comparison with nanosecond lasers[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2014, 38(3): 265−292. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2014.12028.x
[18] Bao Z A, Yuan H L, Zong C L, et al. Simultaneous determination of trace elements and lead isotopes in fused silicate rock powders using a boron nitride vessel and fsLA-(MC)-ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2016, 31(4): 1012−1022. doi: 10.1039/C5JA00410A
[19] Zhang L, Han B F, Gu L B, et al. A comparison of zircon Hf isotope analyses by MC-ICP-MS and LA-MC-ICP-MS[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(2): 510−512.
[20] Zhang W, Hu Z C, Günther D, et al. Direct lead isotope analysis in Hg-rich sulfides by LA-MC-ICP-MS with a gas exchange device and matrix-matched calibration[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2016, 948: 9−18. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2016.10.040
[21] Martin C, Ponzevera E, Harlow G. In situ lithium and boron isotope determinations in mica, pyroxene, and serpentine by LA-MC-ICP-MS[J]. Chemical Geology, 2015, 412: 107−116. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.07.022
[22] Tong X R, Liu Y S, Hu Z C, et al. Accurate determination of Sr isotopic compositions in clinopyroxene and silicate glasses by LA-MC-ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2016, 40(1): 85−99. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2015.00315.x
[23] Gray A L. Solid sample introduction by laser ablation for inductively coupled plasma source-mass spectrometry[J]. Analyst, 1985, 110(5): 551−556. doi: 10.1039/an9851000551
[24] Scheffler G L, Pozebon D. Advantages, drawbacks and applications of mixed Ar-N2 sources in inductively coupled plasma-based techniques: An overview[J]. Analytical Methods, 2014, 6(16): 6170−6182. doi: 10.1039/C4AY00178H
[25] Hu Z C, Gao S, Liu Y S, et al. Signal enhancement in laser ablation ICP-MS by addition of nitrogen in the central channel gas[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2008, 23(8): 1093−1101. doi: 10.1039/b804760j
[26] Guillong M, Heinrich C A. Sensitivity enhancement in laser ablation ICP-MS using small amounts of hydrogen in the carrier gas[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2007, 22(12): 1488−1494. doi: 10.1039/b709489b
[27] Newman K. Effects of the sampling interface in MC-ICP-MS: Relative elemental sensitivities and non-linear mass dependent fractionation of Nd isotopes[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2012, 27(1): 63−70. doi: 10.1039/C1JA10222B
[28] He T, Ni Q, Miao Q, et al. Effects of cone combinations on the signal enhancement by nitrogen in LA-ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2018, 33(6): 1021−1030. doi: 10.1039/C7JA00376E
[29] Hu Z C, Liu Y S, Li M, et al. Results for rarely determined elements in MPI-DING, USGS and NIST SRM glasses using laser ablation ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2009, 33(3): 319−335. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2009.00030.x
[30] Petrelli M, Laeger K, Perugini D. High spatial resolution trace element determination of geological samples by laser ablation quadrupole plasma mass spectrometry: Implications for glass analysis in volcanic products[J]. Geosciences Journal, 2016, 20: 851−863. doi: 10.1007/s12303-016-0007-z
[31] 冯彦同, 张文, 胡兆初, 等. 激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱仪新分析模式及其在地球科学中的应用[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2022, 52(1): 98−121.
Feng Y T, Zhang W, Hu Z C, et al. A new analytical mode and application of the laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer in the Earth sciences[J]. Science China: Earth Science, 2022, 52(1): 98−121.
[32] Kimura J I, Chang Q. Origin of the suppressed matrix effect for improved analytical performance in determination of major and trace elements in anhydrous silicate samples using 200nm femtosecond laser ablation sector-field inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2012, 27(9): 1549−1559. doi: 10.1039/c2ja10344c
[33] Zou Z Q, Wang Z C, Cheng H, et al. Comparative determination of mass fractions of elements with variable chalcophile affinities in geological reference materials with and without HF-desilicification[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2020, 44(3): 501−521. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12328
[34] Gaschnig R M, Rudnick R L, McDonough W F. Determination of Ga, Ge, Mo, Ag, Cd, In, Sn, Sb, W, Tl and Bi in USGS whole-rock reference materials by standard addition ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2015, 39(3): 371−379. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-908X.2014.00330.x
[35] Belgrano T M, Milton J A, Teagle D A H. Determination of ultra-trace Au, Ag, As, Pt and Re mass fractions in volcanic glasses and rock powders by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2022, 46(4): 621−644. doi: 10.1111/ggr.12452
[36] Wang Z, Becker H, Wombacher F. Mass fractions of S, Cu, Se, Mo, Ag, Cd, In, Te, Ba, Sm, W, Tl and Bi in geological reference materials and selected carbonaceous chondrites determined by isotope dilution ICP-MS[J]. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 2014, 39(2): 185−208.
-




 下载:
下载: