APPLICATION OF DOUBLE-WIDTH SEISMIC DATA TO FRACTURE PREDICTION IN R GASFIELD OF XIHU SAG
-
摘要:
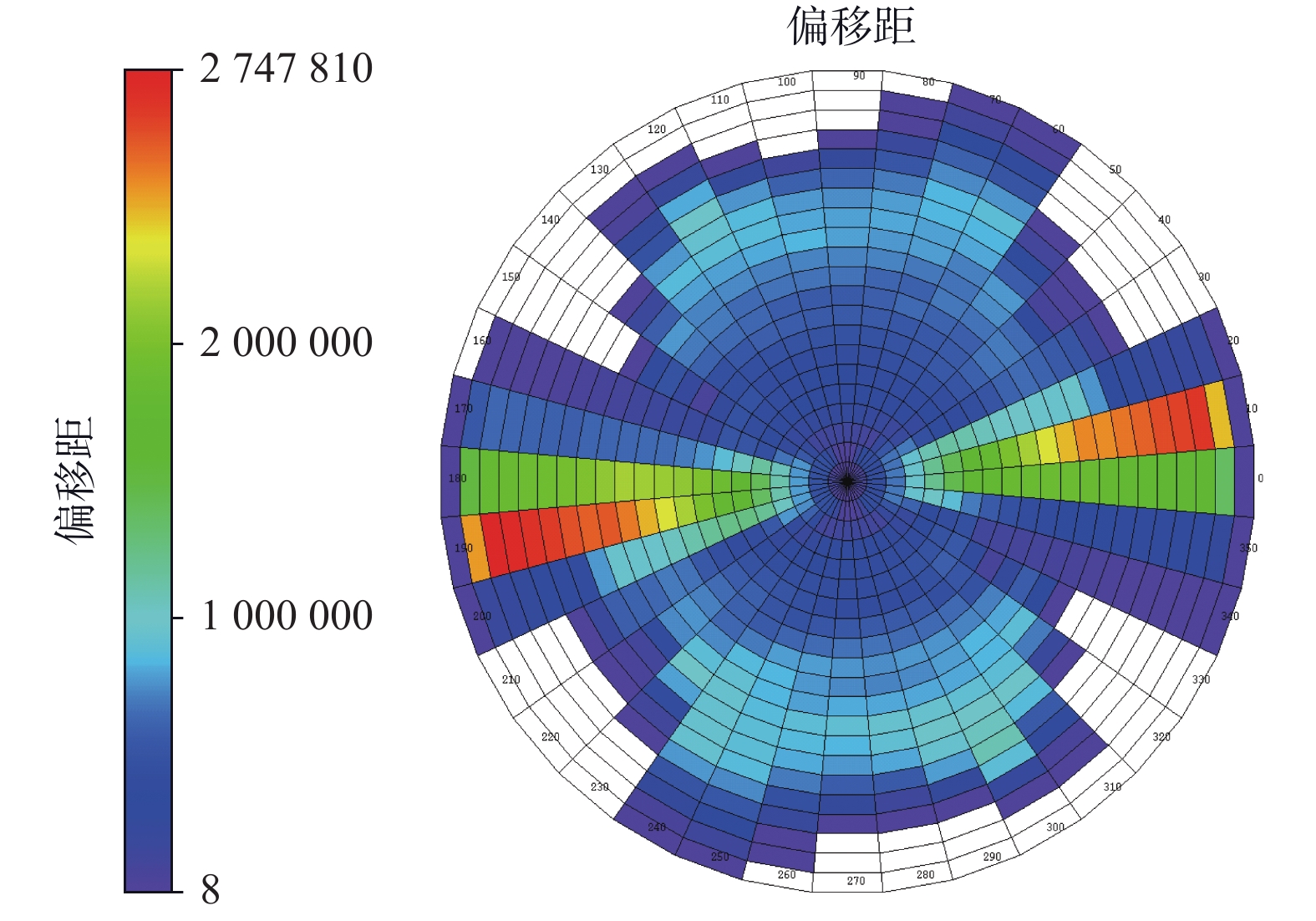
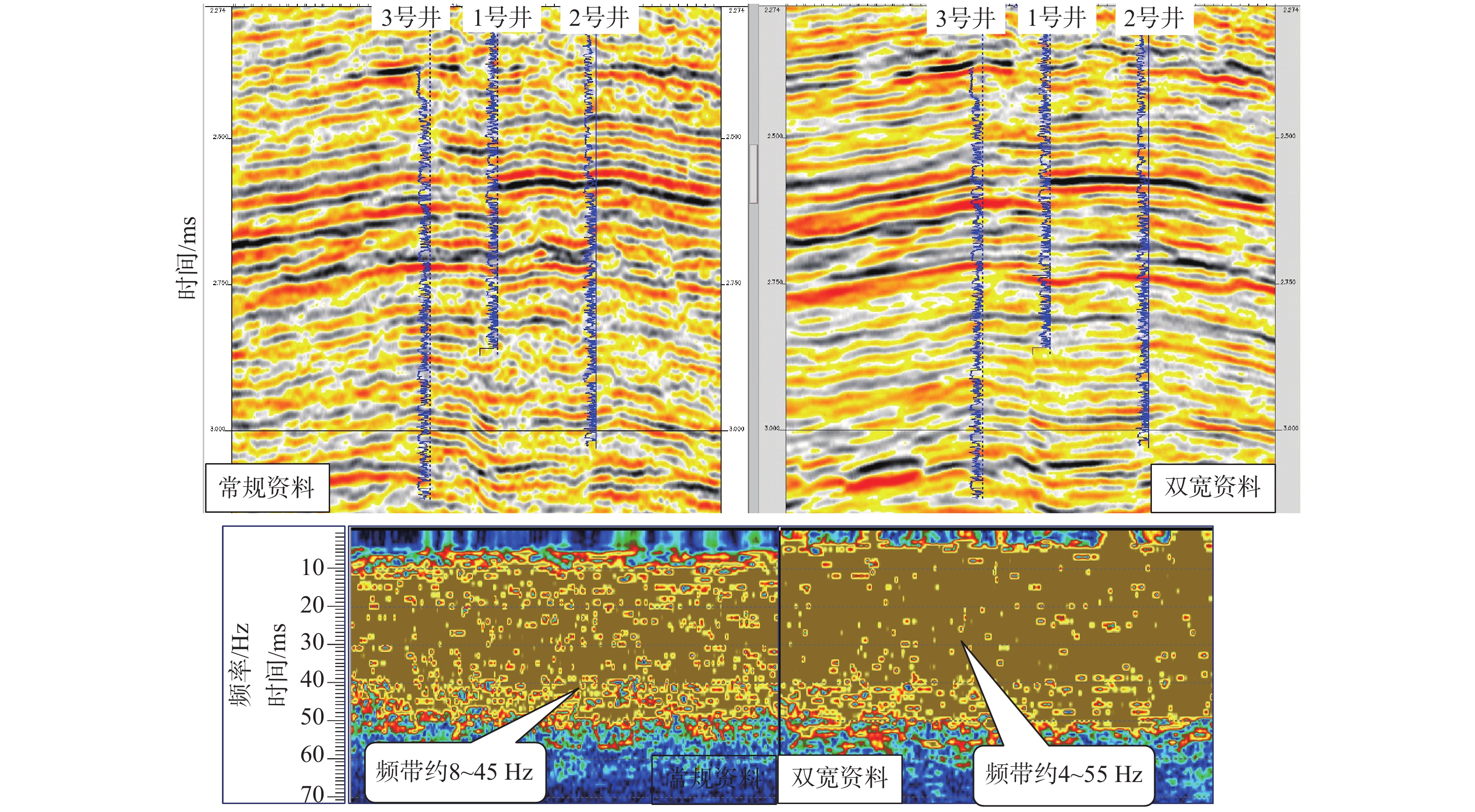
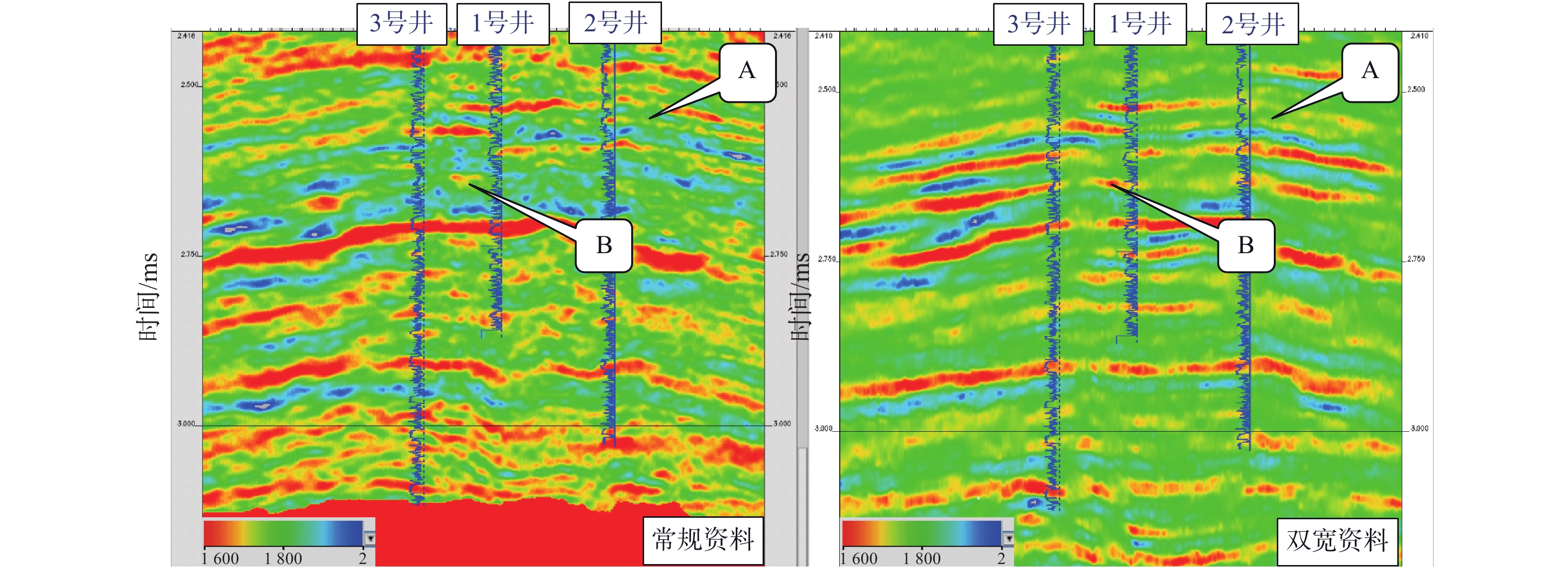
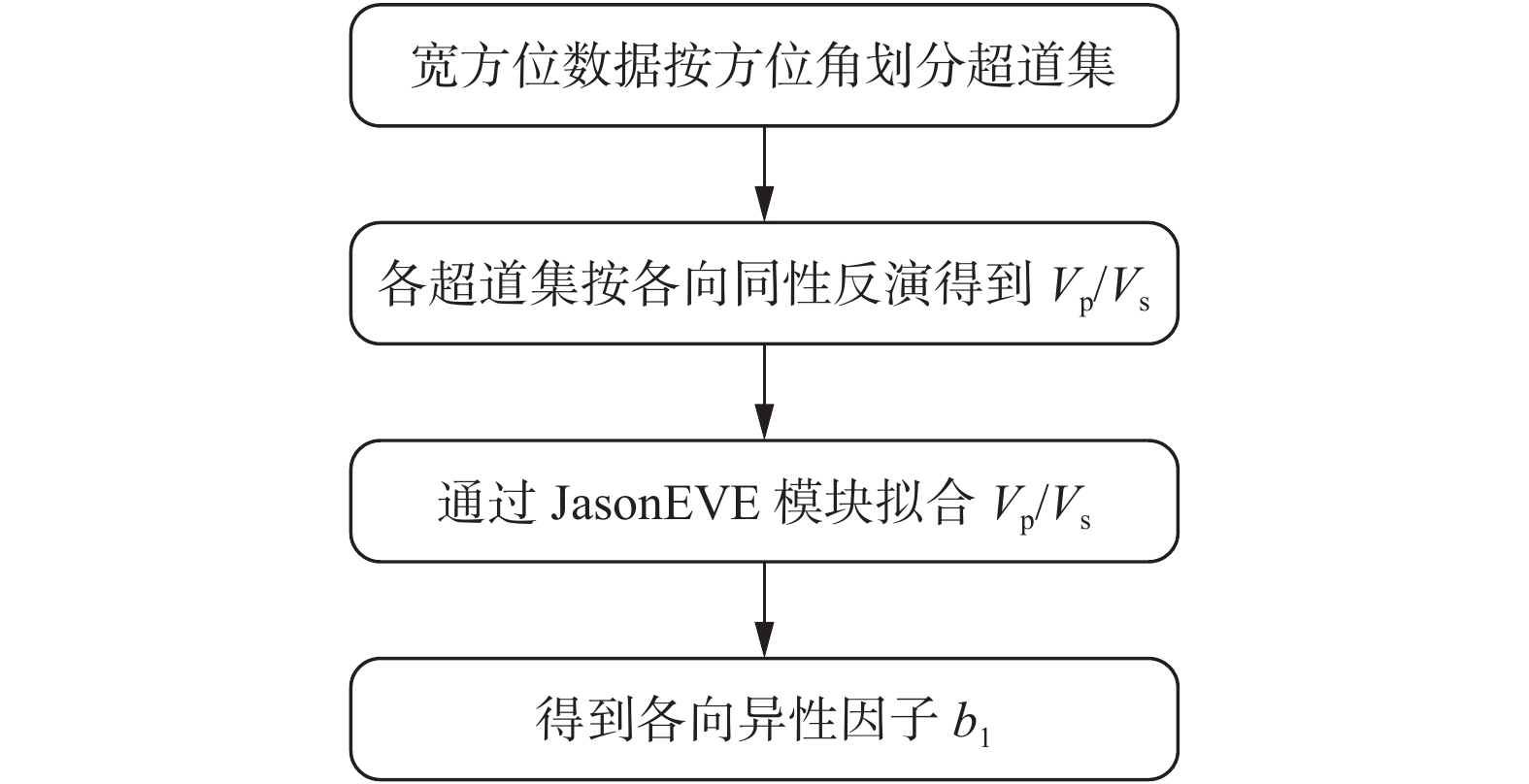
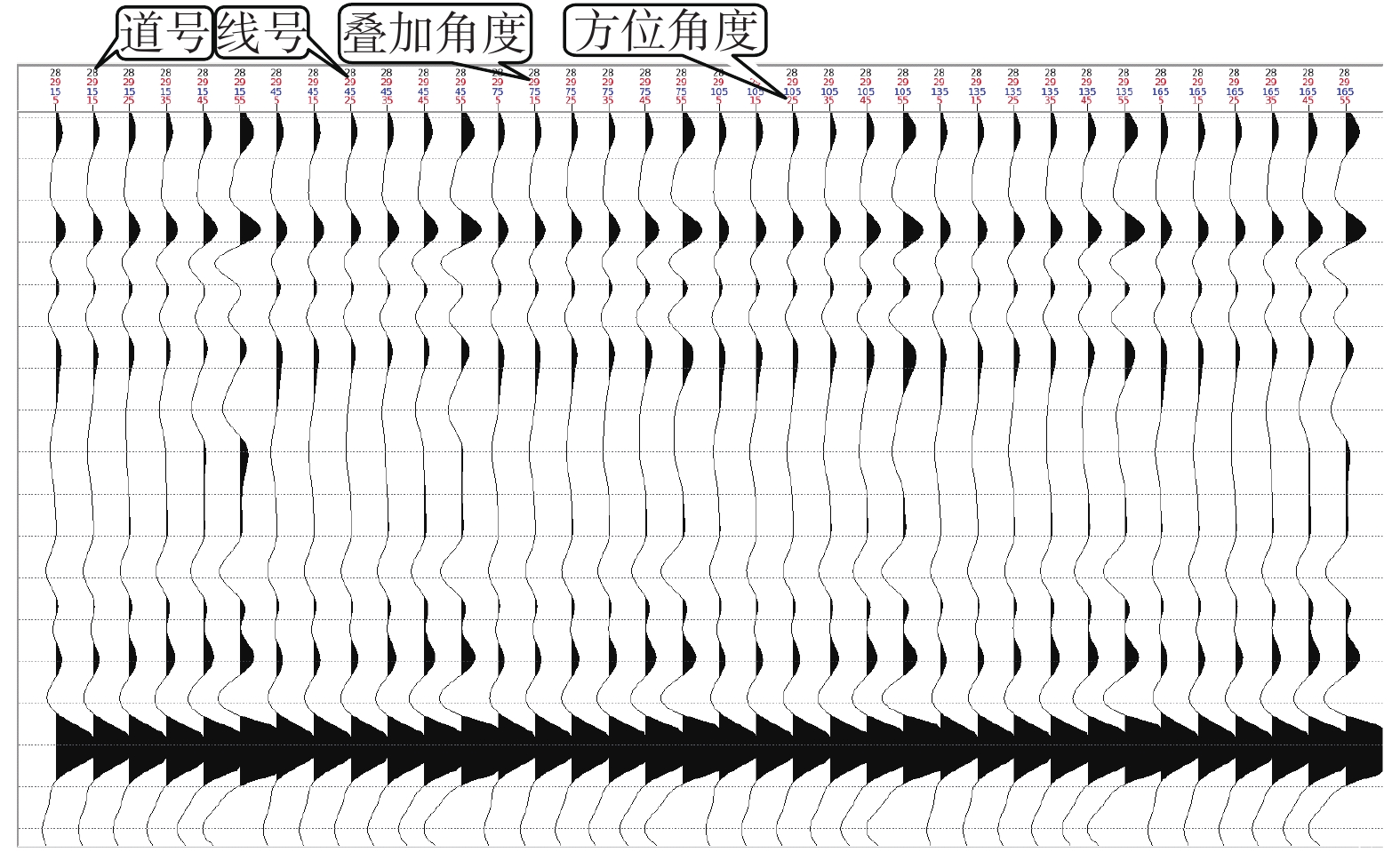
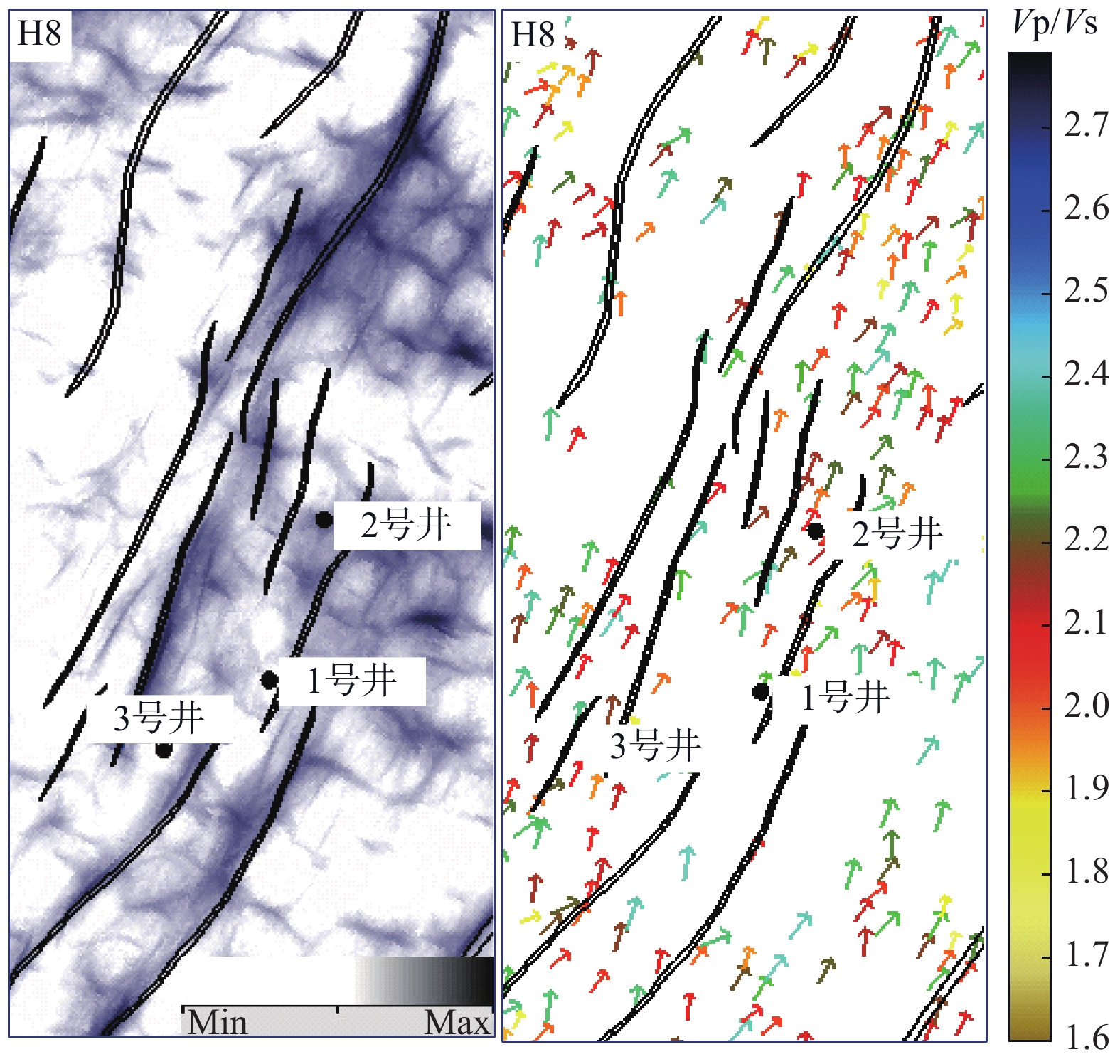
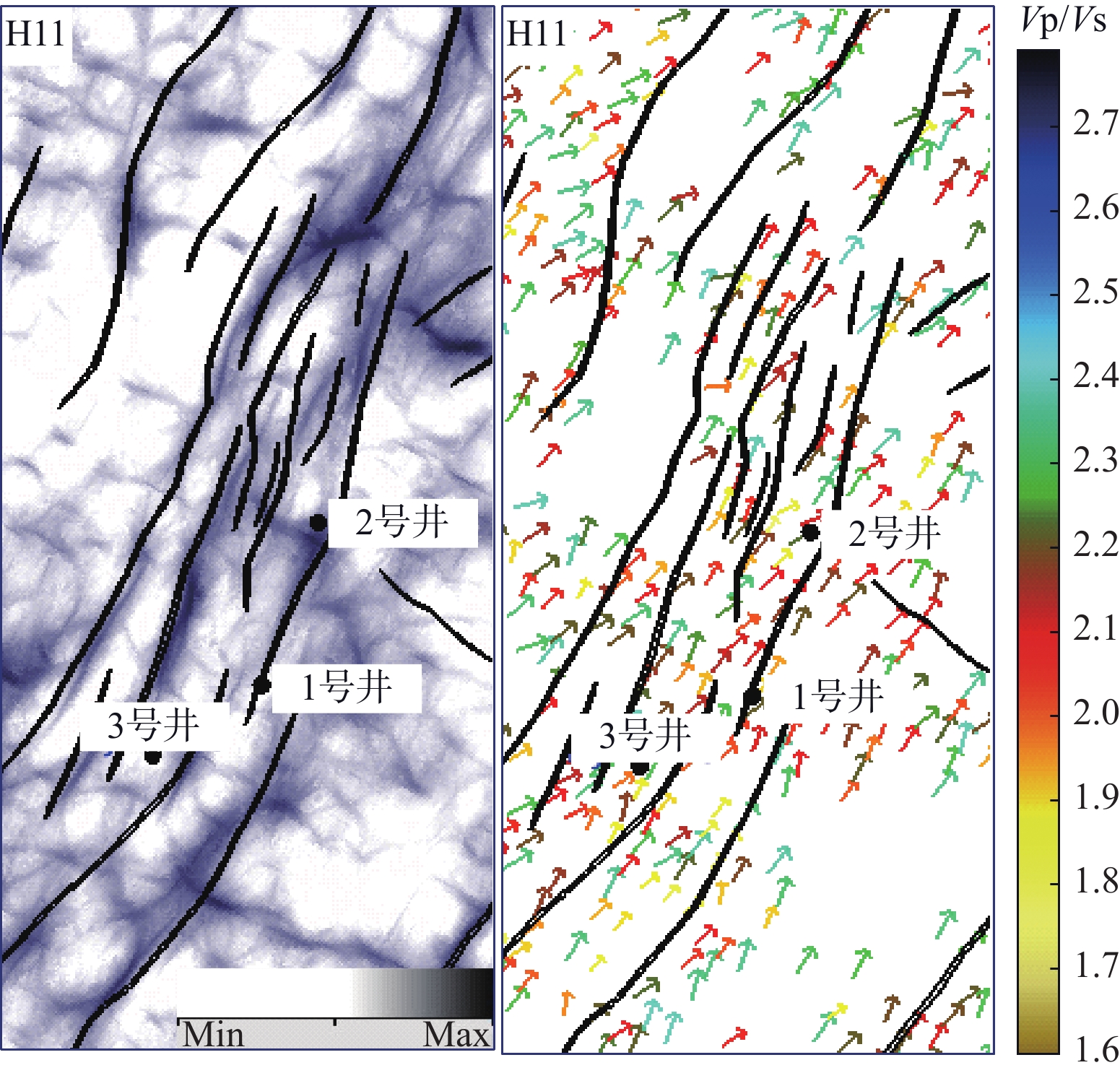
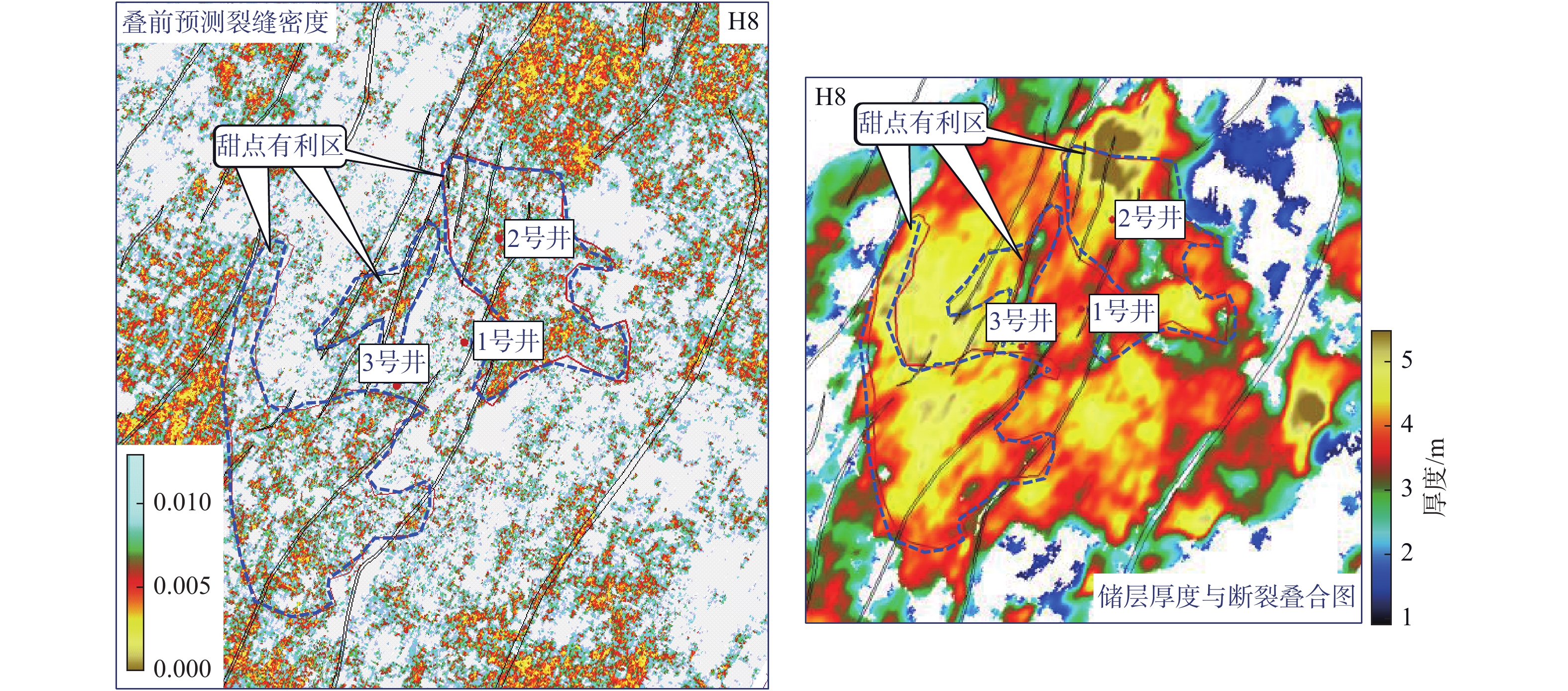
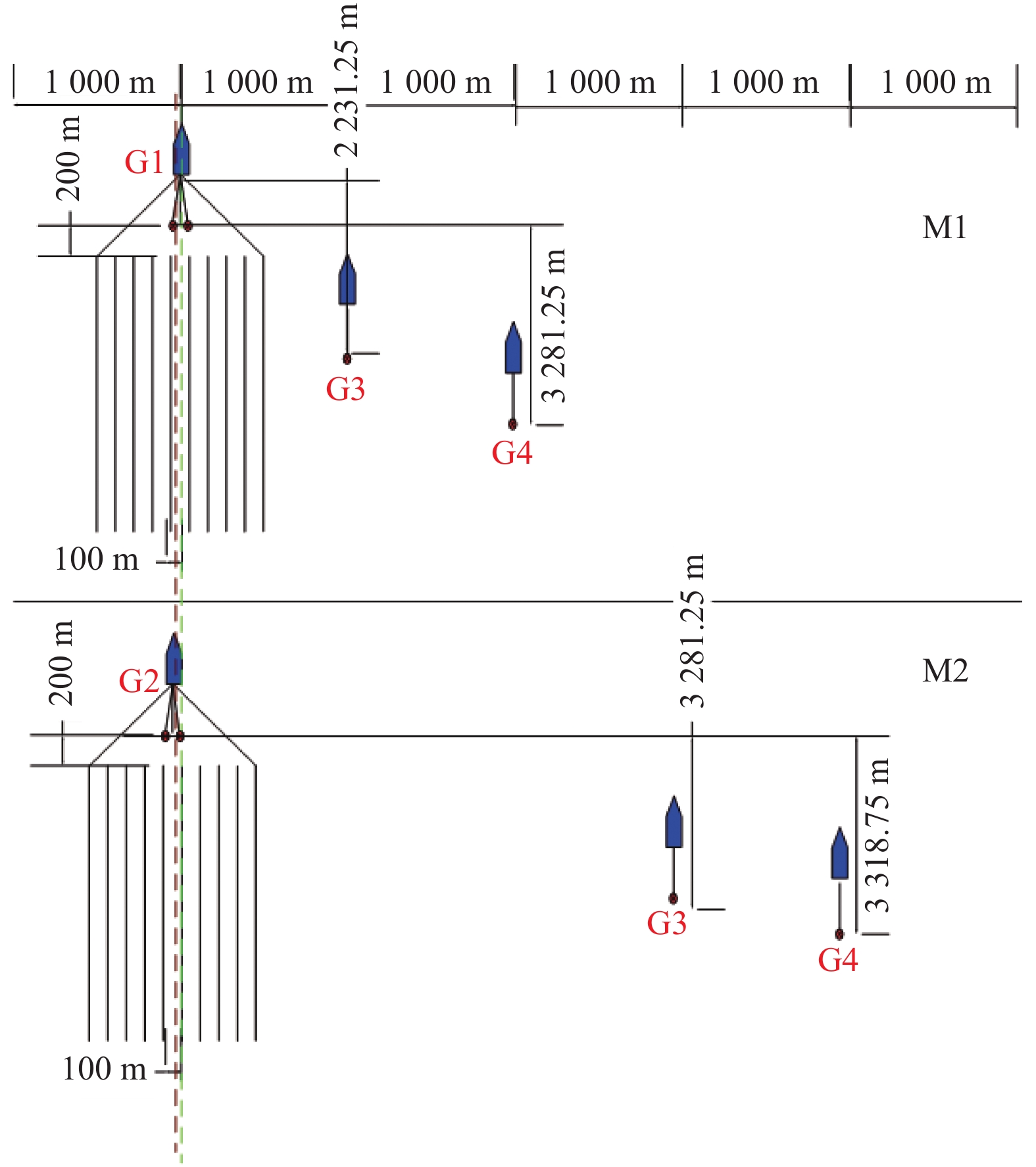
西湖凹陷R气田由于埋藏深、地震资料品质差,常规地震资料处理效果不理想。2016年,通过斜缆宽频+多船宽方位的采集方式得到了高质量的双宽地震资料,分析认为,双宽地震资料具有高信噪比、高分辨率、高保真度的优势。由于R气田H7层以下主要受裂缝控制,裂缝预测的准确性关系到H7层以下油气层的开发效果。以往预测裂缝的方法只能通过地震属性和相干体定性预测,精度往往不高;通过应用双宽地震资料开展裂缝预测,可以得到较为精确的各向异性因子,从而得到裂缝密度的分布,通过裂缝密度可以表征裂缝的发育程度和方向。从预测结果来看,H7层以下裂缝较发育,且裂缝方向与解释大断层方向一致,其中H11层比H8层断裂更加发育,可以很好的解释H11砂体比H8薄但产能比H8高的矛盾;通过求取的裂缝密度,也可以预测甜点的有利发育区。
Abstract:Seismic data acquired from the R Gasfield of the Xihu Sag is poor in quality due to its deep buried depth and the conventional seismic data processing is not efficient enough to meet the requirement of exploration. In 2016, high-quality double-width seismic data were acquired with the method of variable-depth atreamer broadband and multi-vessel wide-azimuth acquisition. Because the oil reservoir below the Layer H7 in the R Gasfield is controlled by fractures, the accuracy of fracture prediction is of significance to the production of oil and gas from the reservoirs below the Layer H7. In the past, the fracture prediction could only be performed with seismic attributes and seismic coherent bodies, and the accuracy was often not so high. By using double-width seismic data to predict fracture now, we can get more accurate anisotropy factor and the distribution of fracture density, which can be used to indicate the development status and direction of fractures. The prediction results prove that the fractures are well developed below the Layer H7, and the extending direction of the fractures is consistent with that of the large fault. Fractures in the Layer H11 are more developed than those in the Layer H8, which can well explain why the productivity of H11 is higher than the H8 but the sand body is thinner. By calculating the density of the fracture, we can also make better prediction of more sweet areas.
-
Key words:
- double-width data /
- wide-azimuth acquisition /
- anisotropic strength /
- fracture density /
- Xihu Sag
-

-
[1] 叶云飞,刘春成,刘志斌,等. 海上宽频地震反演方法及其在南海深水区的应用[J]. 中国海上油气,2018,30(2):65-70.
[2] 张建军,刘红星,孙 强,等. “两宽一高”地震采集技术在鄂东缘致密砂岩气藏勘探中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2018,53(2):1-7.
[3] 刘依谋,印兴耀,张三元,等. 宽方位地震勘探技术新进展[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2014,49(3):596-610.
[4] 张保庆,周 辉,左黄金,等. 宽方位地震资料处理技术及应用效果[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2011,46(3):396-406.
[5] 凌云研究小组. 宽方位角地震勘探应用研究[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2003,38(4):350-358. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2003.04.003
[6] 张振波,李东方. 斜缆宽频地震勘探技术在珠江口盆地的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2014,49(3):451-456.
[7] 肖 曦,张益明,王志华,等. 宽频数据在致密砂岩储层预测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展,2019,34(1):1-10. doi: 10.6038/pg2019CC0028
[8] 秦德文,高红艳,钟 韬,等. 东海低渗气藏储层改造区“甜点”预测技术研究与应用[J]. 海洋石油,2017,37(2):45-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2017.02.045
[9] 连小翠. 东海西湖凹陷深层低渗-致密砂岩气成藏的地质条件与模式[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2018,34(2):23-30.
[10] 姜 雨,陈 华,姚 刚,等. 海上变深电缆宽频宽方位地震采集现场作业难点及解决方案[J]. 海洋石油,2016,36(4):8-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2016.04.008
[11] 余本善. 海上宽频地震采集技术新进展[J]. 石油科技论坛,2015(1):41-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-302x.2015.01.008
[12] 谢玉洪,李 列,袁全社. 海上宽频地震勘探技术在琼东南盆地深水区的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2012,47(3):430-436.
[13] 潘仁芳,金吉能. 断层和裂缝尺度识别的地球物理方法探讨[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版),2011,8(3):16-18.
[14] 熊金红,陈 岑,曹占元,等. 基于叠前地震全方位各向异性预测裂缝发育——以普光气田须家河组为例[J]. 地质力学学报,2017,23(2):280-287. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.02.011
[15] 凌 云,高 军,孙德胜,等. 裂缝储层的地震预测技术与应用实例[J]. 石油地球物理勘探,2015,50(1):91-102.
[16] Thomsen L. Elastic anisotropy duo to aligned crachs in porous rock[J]. Geophysics Prospecting,1995,43(6):805-829. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.1995.tb00282.x
[17] Hall S A. Fractured reservoir characterization using P-wave AVOA analysis of 3D OBC data[J]. The Leading Edge,2002,21(8):777-781. doi: 10.1190/1.1503183
[18] Hall S A. Fractured characterization at Valhall:application of P-wave amplitude variation with offset and azimuth(AVOV) analysis to a 3D ocean-bottom dataset[J]. Geophysics,2003,68(4):1150-1160. doi: 10.1190/1.1598107
[19] 夏亚良,魏小东,王中凡,等. OVT域方位各向异性技术在中非花岗岩裂缝预测中的应用研究[J]. 石油物探,2018,57(1):140-147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2018.01.018
-



 下载:
下载: