Pollution assessment and source tracking of heavy metals in surface sediments of Xinyanggang River
-
摘要:
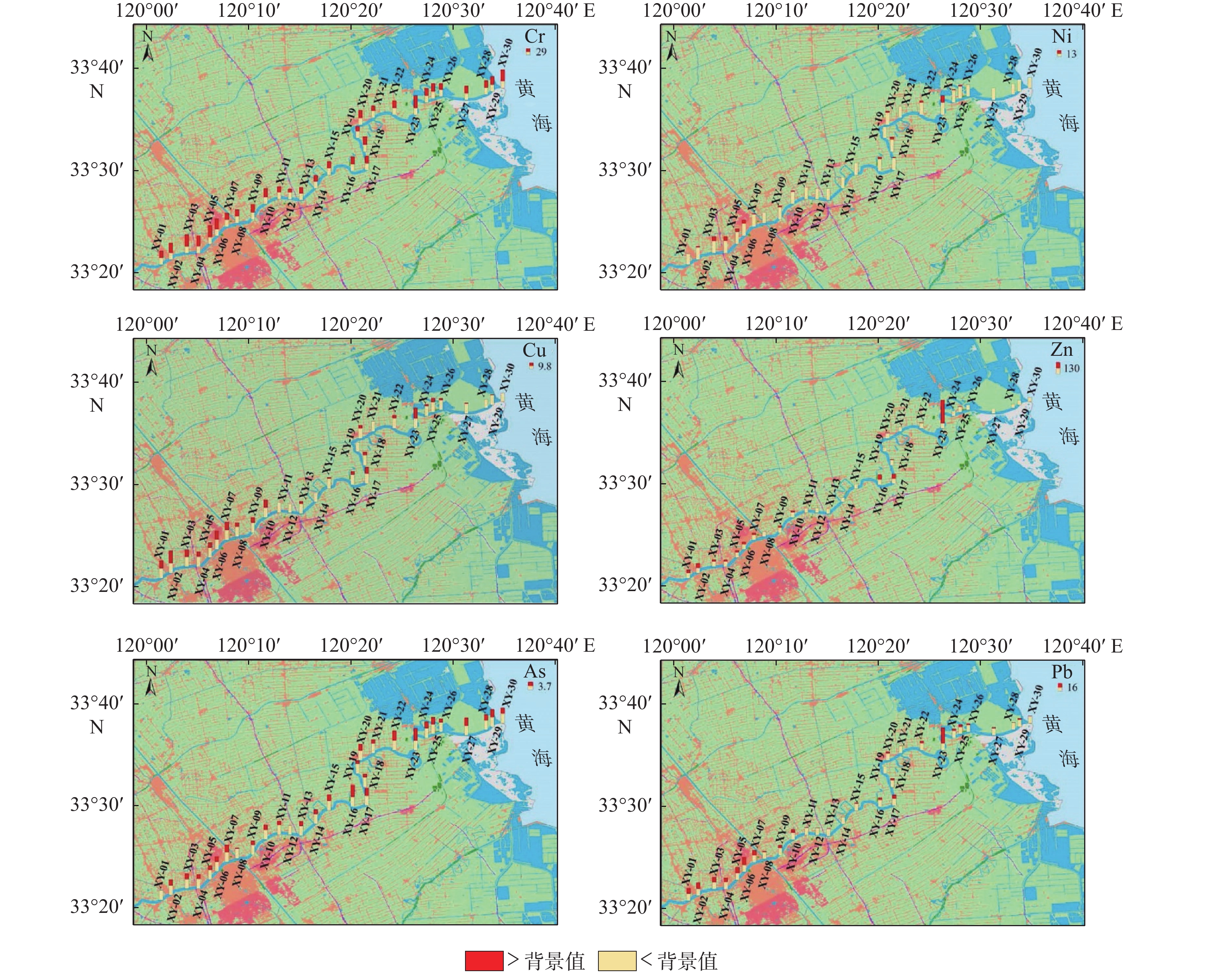
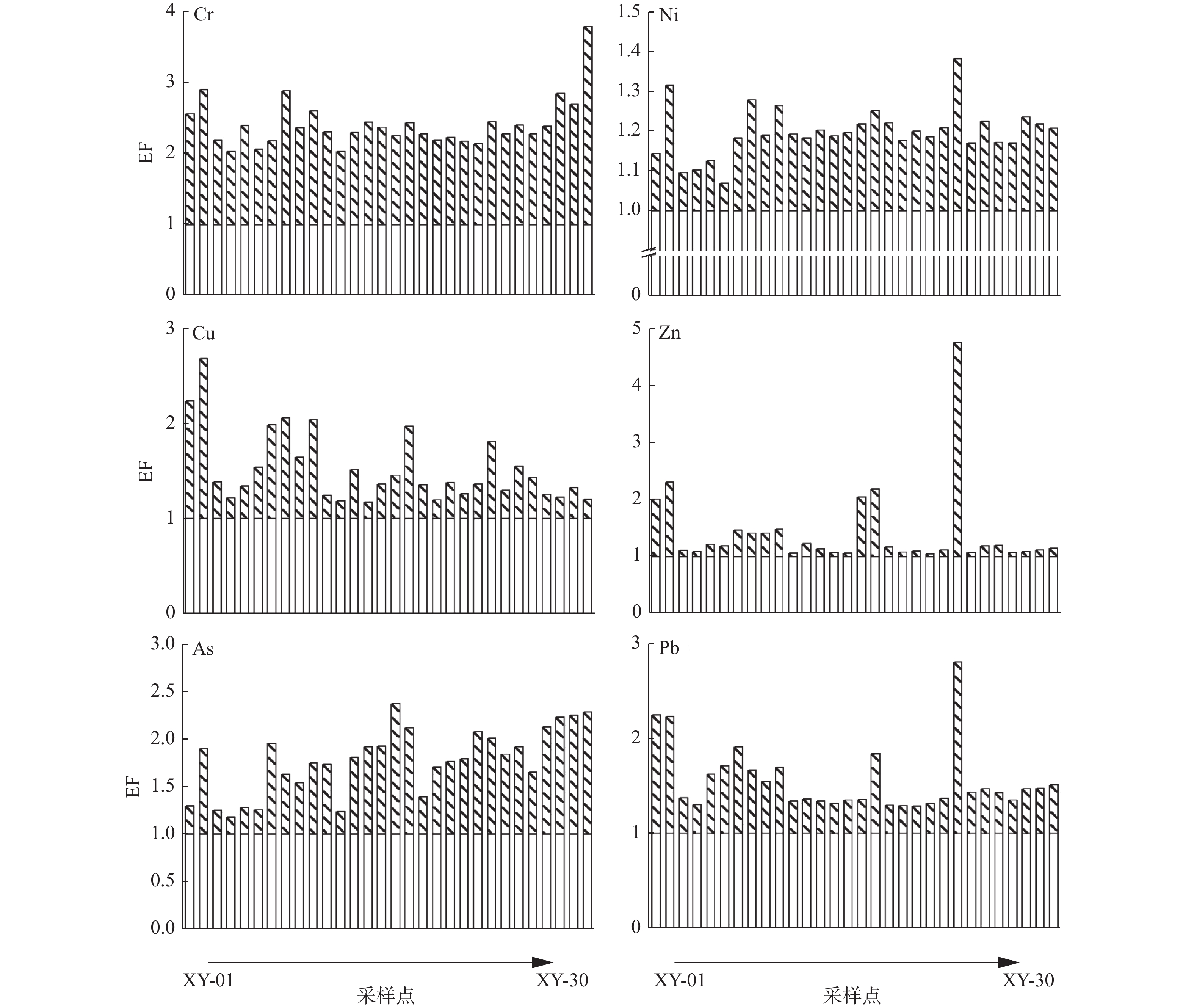
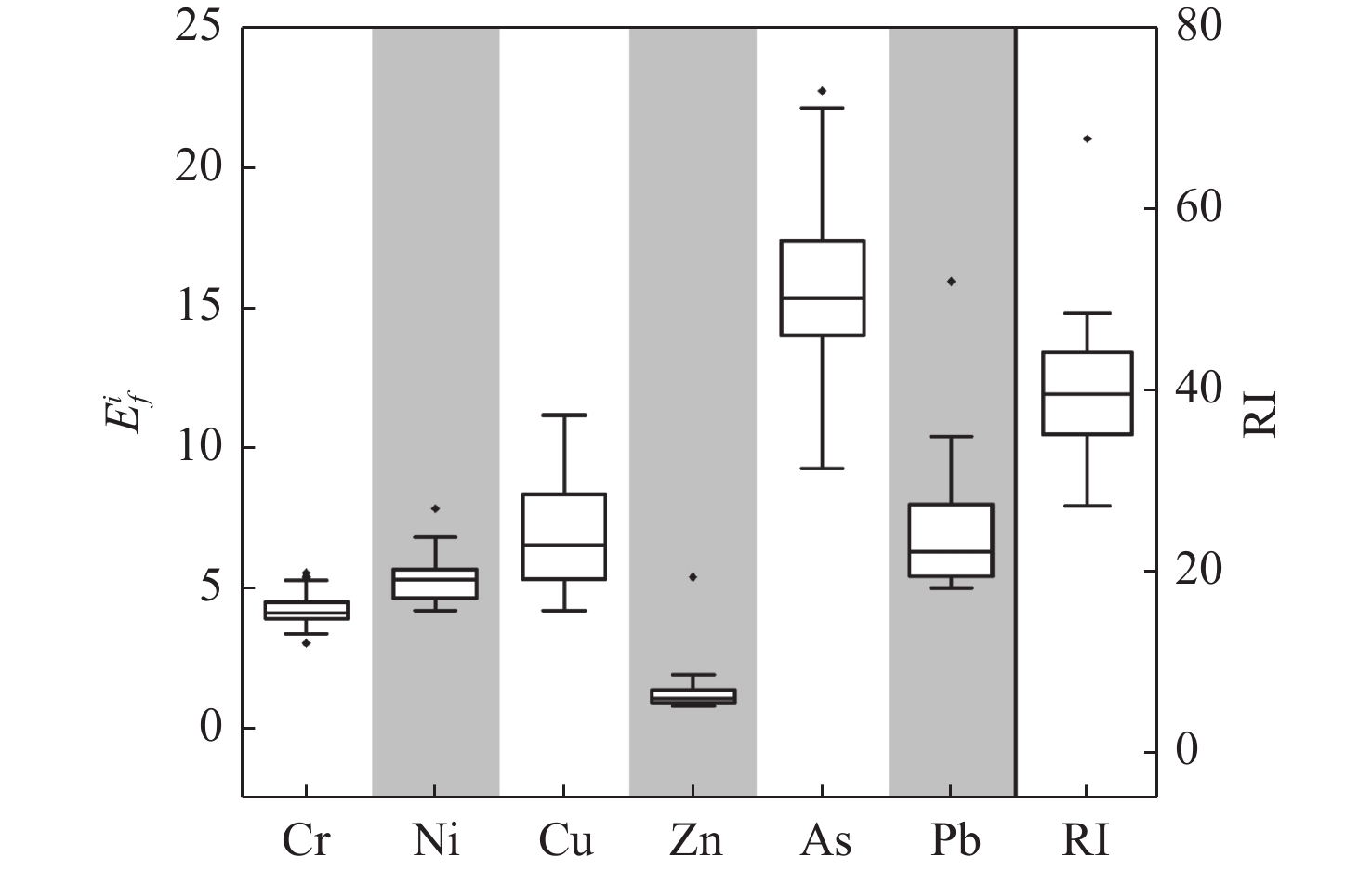
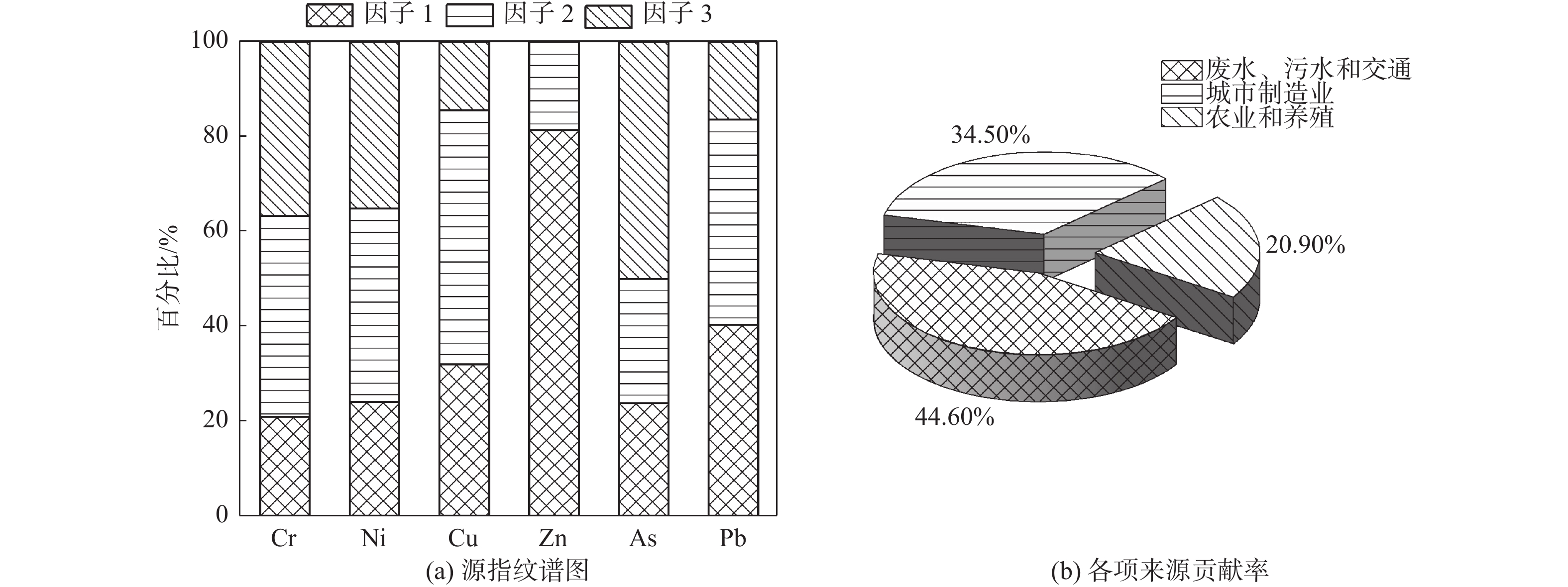
以盐城市新洋港河表层沉积物为研究对象,运用富集系数法和潜在生态风险指数法对6种重金属进行污染评价,结合多变量分析方法和正定矩阵因子分解模型(PMF)进行来源解析。研究结果表明,新洋港河表层沉积物重金属Cr、Ni、Cu、Zn、As、Pb的平均浓度分别为70.63 、27.73、21.60、21.60 、9.01、20.38 mg/kg,其平均浓度顺序为Zn>Cr>Ni>Cu>Pb>As,多数表层沉积物样品中6种重金属数样点处于轻度—中度富集水平,潜在生态风险指数评价结果表明研究区域整体处于轻度生态风险。重金属按照来源大致分为3类:①第1类为Cu、Zn和Pb,主要来自工业废水、城市生活污水和城市交通(贡献率占44.60%);②第2类为Cr和Ni,主要来自城市制造业(贡献率占34.50%);③第3类为As,主要来源农业污染和养殖(贡献率占20.90%)。
Abstract:The ecological risk of six heavy metals (Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Pb) in the surface sediments collected from the Xinyanggang River in Yancheng, Jiangsu, East China was evaluated using the enrichment coefficient method and potential ecological risk indexing, combined with multivariate analysis method and positive matrix factorization model (PMF) for source analysis. Results show that: (1) The average concentrations of the heavy metals were Cr (70.63 mg/kg), Ni (27.73 mg/kg), Cu (21.60 mg/kg), Zn (21.60 mg/kg), As (9.01 mg/kg), and Pb (20.38 mg/kg). The average levels of metals are in the order of Zn > Cr > Ni > Cu > Pb > As. Six heavy metals in most of the samples were at the levels of low and moderate enrichment. The potential ecological risk index indicated low ecological risk in the whole study area. The sources of heavy metals were divided into three categories. Cu, Zn, and Pb were derived from industrial wastewater, urban domestic sewage, and urban traffic (44.60%); Cr and Ni mainly came from the emission of urban manufacturing operations (34.50%); and As was mainly from agriculture and breeding pollution (20.90%).
-
Key words:
- heavy metals /
- pollution evaluation /
- source analysis /
- sediment /
- Xinyanggang River
-

-
表 1 新洋港河与江苏其他入海河流表层沉积物重金属浓度对比
Table 1. Comparison of heavy metal contents in surface sediments of Xinyanggang River and other rivers in Jiangsu Province
研究区域 参数 Cr Ni Cu Zn As Pb 数据来源 新洋港河 浓度最小值/(mg/kg) 50.52 21.88 13.34 47.06 5.35 14.52 本研究 浓度最大值/(mg/kg) 92.12 40.67 35.54 323.66 13.14 46.34 浓度平均值/(mg/kg) 70.63 27.73 21.60 77.61 9.01 20.38 标准偏差 10.39 4.41 5.93 50.55 1.72 6.54 变异系数/% 14.71 15.90 27.45 65.13 19.09 32.09 灌河入海河段 平均浓度/(mg/kg) 75.40 / 31.10 127.00 16.60 27.00 文献[23] 射阳河流域 41.47 62.34 66.91 799.85 / 46.25 文献[24] 韩口河 22.76 13.25 9.67 35.29 / 8.87 龙王河 26.28 16.50 13.79 44.83 / 11.28 文献[25] 兴庄河 35.39 23.59 16.06 49.44 / 15.13 沙王河 45.81 30.83 27.20 262.71 / 23.44 青口河 29.14 19.85 16.66 62.19 / 15.26 文献[25] 临洪河 44.56 29.16 23.28 78.65 / 19.08 表 2 新洋港河表层沉积物重金属变量之间的Pearson相关矩阵
Table 2. The Pearson correlation matrix between heavy metal variables in surface sediments of Xinyanggang River
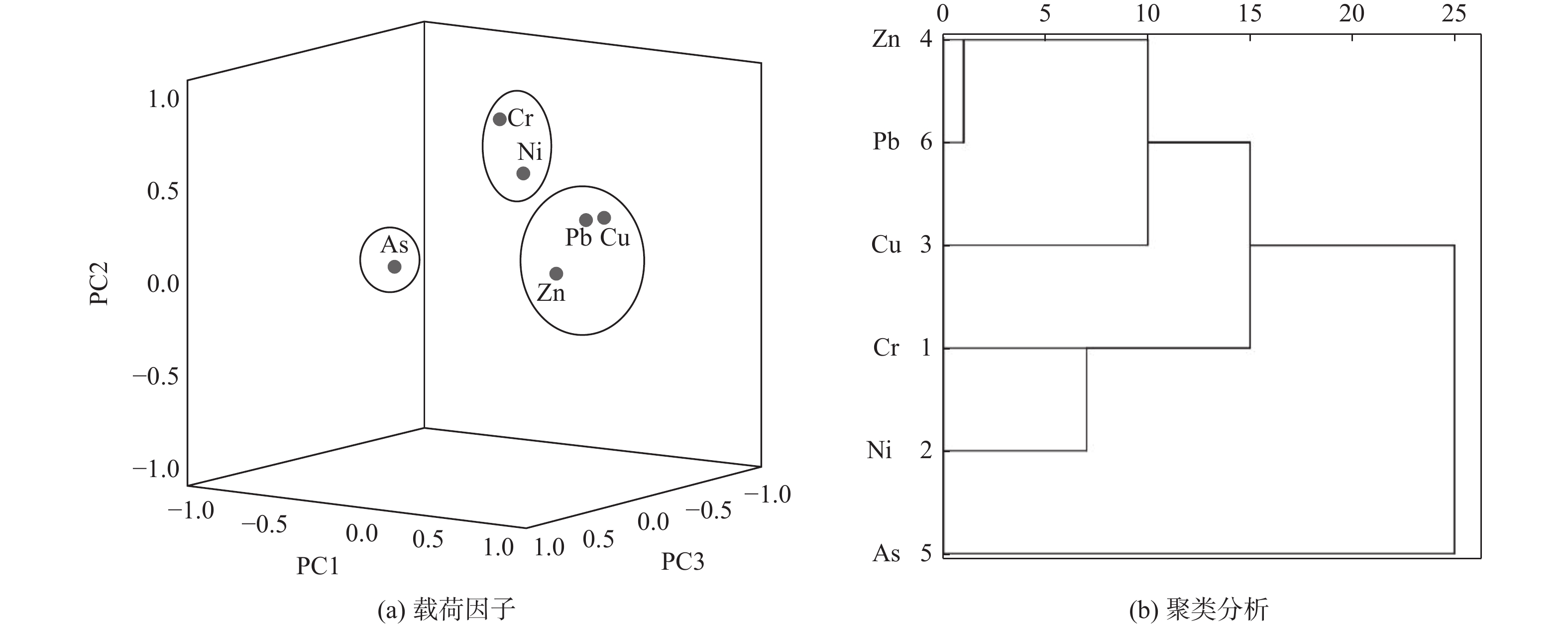
Cr Ni Cu Zn As Pb Cr 1 Ni 0.73** 1 Cu 0.56** 0.65** 1 Zn 0.51** 0.68** 0.63** 1 As 0.38* 0.48** 0.22 0.50** 1 Pb 0.68** 0.79** 0.82** 0.89** 0.37* 1 注:**表示在0.01水平(双尾)上显著相关,*表示在0.05水平(双尾)上显著相关。 表 3 新洋港河表层沉积物重金属变量载荷矩阵
Table 3. Variable loading matrix of heavy metals in surface sediments of Xinyanggang River
重金属元素 PC1 PC2 PC3 Cr 0.30 0.91 0.18 Ni 0.55 0.66 0.32 Cu 0.82 0.39 −0.06 Zn 0.84 0.15 0.42 As 0.15 0.20 0.95 Pb 0.87 0.42 0.19 特征值 2.55 1.64 1.25 变量解释/% 42.51 27.28 20.27 累积/% 42.51 69.79 90.60 注:PC为各个主成分。 -
[1] MAJID A,FAMIL H,SATTAR M,et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in coastal sediments of the western Caspian Sea[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2020,192(8):500. doi: 10.1007/s10661-020-08401-3
[2] FANG X H,PENG B,WANG X,et al. Distribution,contamination and source identification of heavy metals in bed sediments from the lower reaches of the Xiangjiang River in Hunan Province,China[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019(689):557-570.
[3] KHAN M H R,LIU J G,LIU S F,et al. Anthropogenic effect on heavy metal contents in surface sediments of the Bengal Basin river system,Bangladesh[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2020,27(6):19688-19702.
[4] ZHU A M,LIU J H,QIAO S Q,et al. Distribution and assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Bohai Sea of China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2020(153):110901.
[5] SUN X S,FAN D J,LIU M,et al. Source identification,geochemical normalization and influence factors of heavy metals in Yangtze River Estuary sediment[J]. Environmental Pollution,2018(241):938-949.
[6] 冯晓博,肖凯,李海龙,等. 广东海陵岛北部海域表层沉积物重金属分布特征与污染评价[J]. 海洋环境科学,2021,40(4):507-514. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20200162
[7] 盐城市统计局. 盐城统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2015-2021.
[8] 郑江鹏,矫新明,方南娟,等. 江苏近岸海域沉积物重金属来源及风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学,2017,37(4):1514-1522. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.04.039
[9] LIU N,ZHANG D L,CEN K,et al. Influence of anthropogenic activities on the temporal and spatial variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the sediments of Jiangsu coastal zone,China[J]. Continental Shelf Research,2018(170):11-20.
[10] 袁红明,赵广明,李雪,等. 江苏盐城大丰滨海湿地表层沉积物重金属空间分布特征及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2018,34(9):51-59.
[11] 赵雪琴,赵善道,左平,等. 江苏盐城原生湿地表层沉积物中的重金属污染评价[J]. 环境保护科学,2010,36(1):64-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-6216.2010.01.020
[12] 盐城市地方志办公室. 盐城年鉴[M]. 北京: 方志出版社, 2020.
[13] 李明亮,杨旸,项明,等. 新洋港河口悬沙特征与再悬浮过程[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学),2014,50(5):666-678.
[14] JIANG S Y,ZHAO H X,CHEN Y Q,et al. Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of phosphate nodules from the lower Cambrian black shale sequence in the Mufu Mountain of Nanjing,Jiangsu Province,China[J]. Chemical Geology,2007,224(3):584-604.
[15] MÜLLER G. Schwermetalle in den sedimenten des Rheins-Veraänderungen seit 1971[J]. Umschau,1979,79(24):778-783.
[16] 吕利云,董树刚,刘阳,等. 南黄海近岸海域表层沉积物重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2013,35(4):101-110. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2013.04.017
[17] LU S Y,ZHU M Y. The background value of chemical elements in the Huanghai Sea sediment[J]. Acta Oceanological Sinica,1987,6(4):558-567.
[18] 廖启林,刘聪,许艳,等. 江苏省土壤元素地球化学基准值[J]. 中国地质,2011,38(5):1363-1378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.05.023
[19] HAKANSON L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control:a sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research,1980,14(8):975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[20] PAATERO P,TAPPER U. Positive matrix factorization:a non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values[J]. Environmetrics,1994,5(2):111-126.
[21] PAATERO P. Least squares formulation of robust non-negative factor analysis[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems,1997,37(1):23-35.
[22] 李悦昭,陈海洋,孙文超. “河-湖”沉积物重金属环境特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(6):2646-2652. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201910215
[23] 宋晓娟,贺心然,陈斌林,等. 灌河口海域表层沉积物中重金属的污染变化及潜在生态危害[J]. 海洋科学,2013,37(5):25-32.
[24] 吴姗姗. 射阳河流域沉积物重金属环境地球化学研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2017.
[25] DENG X Q,WU Y L,LIANG Y,et al. Source apportionment of heavy metals in sediments of the urban rivers flowing into Haizhou Bay,Eastern China:using multivariate statistical analyses and Pb-Sr isotope fingerprints[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(27):36354-36366.
[26] 肖彩玲,陈路锋,李雁宾. 胶州湾沉积物重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 中国科技论文,2017,12(9):1079-1086. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2017.09.019
[27] 曹郁,赵文伟,伍婧怡,等. 盐城新洋港河流表层沉积物重金属污染评价[J]. 亚热带资源与环境学报,2020,15(3):39-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7105.2020.03.007
[28] 卢霞,范礼强,包诗玉,等. 海州湾连岛周边海域沉积物重金属污染评价[J]. 海洋环境科学,2020,39(4):570-575. doi: 10.12111/j.mes.20190011
[29] LV J S,LIU Y,ZHANG Z L,et al. Distinguishing anthropogenic and natural sources of trace elements in soils undergoing recent 10-year rapid urbanization:a case of Donggang,Eastern China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2015,22(14):10539-10550. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4213-4
[30] 孟昆,徐敏,徐文健,等. 海州湾北部沉积物重金属来源解析及污染评价[J]. 南京师大学报(自然科学版),2018,41(2):99-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4616.2018.02.018
[31] XIA F,ZHANG C,QU L Y,et al. A comprehensive analysis and source apportionment of metals in riverine sediments of a rural-urban watershed[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020(381):121230.
[32] LV J S,LIU Y,ZHANG Z L,et al. Factorial kriging and stepwise regression approach to identify environmental factors influencing spatial multi-scale variability of heavy metals in soils[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2013(261):387-397.
[33] 中国海洋生态环境状况公报[R]. 北京: 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2021.
[34] 代静,赵玉强,李欣,等. 小清河济南段表层沉积物重金属和营养盐污染现状评价与来源分析[J]. 环境化学,2021,40(6):1795-1807. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020020403
[35] 滕彦国,倪师军,林学钰,等. 城市环境地球化学研究综述[J]. 地质论评,2005,51(1):64-76. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2005.01.009
[36] 盐城市农业农村局办公室. 盐城农业农村信息[EB/OL]. [2020-04-09]. http://snw.yancheng.gov.cn/art/2020/4/9/art_915_3352612.html.
[37] 许东升,黄淑玲,李琦. 安徽省泗县池塘底泥As含量分布特征及污染评价[J]. 光谱实验室,2012,29(2):1233-1237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8138.2012.02.136
-




 下载:
下载: