Sources and spatial distribution of heavy metals and arsenic in soils from Xiongan New Area, China
-
摘要:
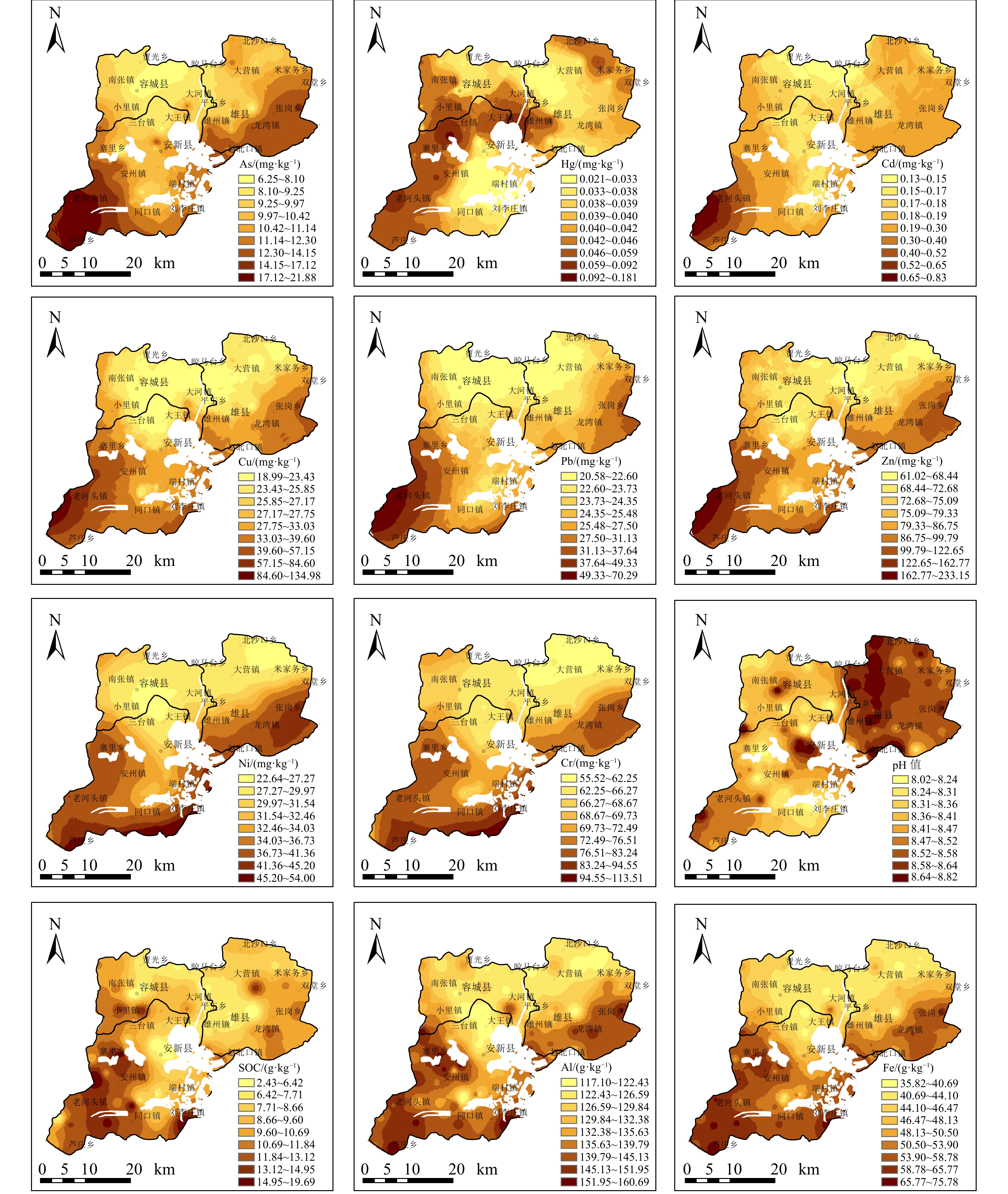
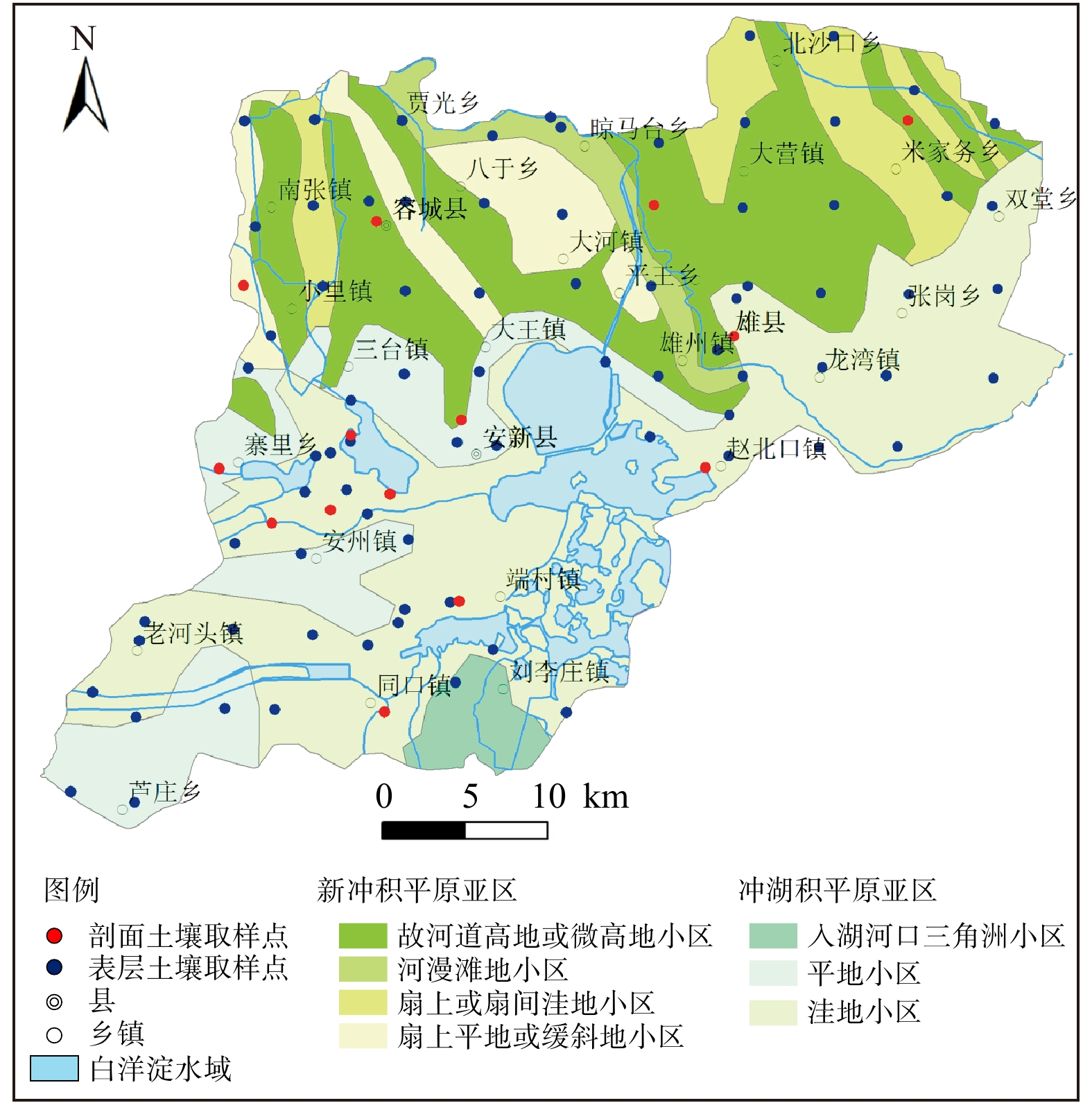
研究雄安地区土壤重金属和砷元素空间分布特征及其来源,对于支撑新区土地资源和环境管理具有重要意义。基于雄安新区土壤环境调查,运用地统计学方法和ArcGIS 技术分析模拟了土壤中As、Hg、Cd、Cu、Pb、Zn、Ni、Cr等8种元素空间分布特征,综合运用空间分析、多元统计学方法和正定因子矩阵模型解析这些元素的主要来源。结果表明:(1)区内土壤质量总体良好,4.35 %的土壤样品Cd和Cu含量超过农用地土壤污染风险筛选值,但均低于农用地土壤污染风险管控值;与河北省背景值相比,Cd、Cu、Pb、Zn和Hg存在不同程度中度和显著富集。(2)As、Cd、Cu、Pb、Zn、Ni、Cr含量呈现出由北部向南部逐渐增高的趋势,高值区主要分布在新区西南部;Hg元素分布分散,高值区主要分布在城镇及工业企业周边。(3)不同土地利用类型土壤剖面重金属和砷元素垂向分布受pH值、有机碳和铁铝氧化物等理化性质影响显著。(4)研究区土壤重金属和砷元素富集受人类活动影响明显,人为来源贡献率达67.12 %,Hg元素主要来源于人为排放的大气沉降富集,As元素富集受到废渣堆放和利用的影响,Cd、Cu、Pb和Zn元素富集受工业生产、污水灌溉以及尾气排放等活动影响。研究成果可为雄安新区合理制定土地资源开发利用和生态保护措施提供技术支撑。
Abstract:Conducting the soil environmental condition survey and accessing the distribution and potential sources of heavy metals and arsenic in soils in Xiongan New Area are of great significance for the land resources and environment management of the district. Based on the data of soil survey samples in the Xiongan New Area, spatial distributions of the elements (As, Hg, Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni and Cr) are analyzed and computed by using geostatistics and ArcGIS techniques. A combination of spatial analysis, multivariate statistical analysis, and positive matrix factorization model is used to assess the sources of these elements. The result show that the soil quality is good and the pollution risk is low. Approximately 4.35% of the soil samples for Cd and Cu have total concentrations higher than the risk screening values for soil contamination of agricultural land, and lower than the risk control values for soil contamination of agricultural land. However, moderate and significant enrichment in Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn and Hg in the surface soils was observed compared with their background values of Hebei province. The contents of As, Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni and Cr exhibite a gradually increasing trend from north to south. These elements principally concentrate in the southwest of the study area. The distribution of Hg is relatively dispersed, and the high-values are mainly located in the urban and industrial areas. The vertical distributions of heavy metals and arsenic in soils of different landuse types are dominantly controlled by physicochemical factors such as pH, organic carbon, and Fe/Al oxides. Anthropogenic sources contribute 67.12% of the heavy metal concentrations in soils, indicating the great influence on soil heavy metal accumulation. Hg is dominated by atmospheric deposition related to anthropogenic emissions such as coal combustion and smelting activities. As is principally affected by industrial activities. Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn are influenced by anthropogenic activities such as industrial production, sewage irrigation and vehicle emission.
-
Key words:
- Xiongan New Area /
- soil heavy metal /
- enrichment degree /
- spatial distribution /
- source apportionment
-

-
表 1 研究区表层土壤理化性质、重金属和砷元素统计
Table 1. Statistics of physical and chemical properties, heavy metals and arsenic in surface soils
元素 As Hg Cd Cu Pb Zn Ni Cr Al2O3 pH值 SOC Fe2O3 最小值 6.06 0.016 0.09 17.80 14.80 57.10 21.70 48.30 117.10 8.01 2.40 35.70 最大值 22.10 0.207 1.22 139.70 141.00 218.00 48.50 97.10 160.70 8.90 19.70 75.80 平均值 11.24 0.044 0.24 33.63 29.47 88.56 33.91 71.12 135.01 8.47 9.98 50.85 标准差 3.36 0.030 0.17 16.82 17.73 28.80 6.61 9.71 11.54 0.19 3.36 9.71 变异系数/% 29.91 57.15 68.15 50.01 60.18 32.52 19.49 13.65 8.55 2.19 33.68 19.10 偏度 1.01 4.35 3.69 3.60 5.01 2.56 0.41 0.40 0.27 0.02 0.33 0.57 峰度 1.11 24.22 16.06 18.13 27.85 8.45 −0.84 −0.40 −0.97 −0.33 0.15 −0.56 农用地筛选值[11] 25 3.4 0.6 100 170 300 190 250 农用地管控值[11] 100 6 4 − 1000 − − 1300 河北省土壤背景值[12] 13.6 0.036 0.094 21.8 21.5 78.4 30.8 68.3 127.30 富集系数(EF) 0.42~1.53 0.43~5.42 0.90~12.24 0.77~6.04 0.65~6.17 0.69~2.63 0.66~1.49 0.67~1.34 深圳市[13] 5.68 0.29 0.3 55 61.74 201.2 17.2 53.5 北京市[14] 8.14 0.398 0.204 32.2 40 107.5 23.7 57.5 上海市[15] 7.80 0.132 0.196 31.4 26.4 106.2 − 85.6 广州市[1] 13.62 0.12 0.21 18.02 45.36 104.55 14.53 48.81 石家庄市[6] 9.42 − 0.275 27.39 31 104.49 28.2 71.91 唐山市[2] 6.79 0.065 0.1 20.97 25.08 63.38 17.33 46.2 天津市[16] 11.426 0.043 0.138 31.584 27.667 85.338 34.279 74.849 重庆市[17] 6.3 0.08 0.34 27.08 28.06 88.53 35.57 75.89 承德市[18] 8.28 0.034 0.20 24.37 26.65 77.10 27.76 60.85 注:pH值无量纲,Al2O3、Fe2O3、SOC单位为g/kg,重金属和砷元素单位为mg/kg。EF为富集系数[4],以Al作为标准化元素,区域背景值作为地球化学背景,EF=(Ci/CAl)sample/(Ci/CAl)background,其中,Ci为元素i的浓度,CAl为标准元素Al的浓度;富集系数分级:EF<0为无富集,1~2之间为弱富集,2~5之间为中度富集,5~20之间为显著富集,20~40之间为高度富集,>40为极度富集。 表 2 表层土壤重金属和砷元素插值方法误差分析
Table 2. The error comparison of interpolation methods for heavy metal and arsenic in surface soils
元素 插值方法 误差分析 模型参数 最优插值方法 平均误差(ME) 均方根误差(RMSE) As 规则样条 径向基函数 −0.10589 2.14685 Hg 张力样条 径向基函数 −0.00015 0.01158 Cd P=3 普通Kriging −0.00118 0.04992 Cu P=2 普通Kriging −0.33838 10.65132 Pb P=2 普通Kriging 0.11714 4.77732 Zn P=3 普通Kriging 0.10838 14.36263 Ni P=2 普通Kriging 0.01220 5.07250 Cr 简单Kriging −0.10869 7.58289 表 3 土壤剖面重金属和砷元素统计分析
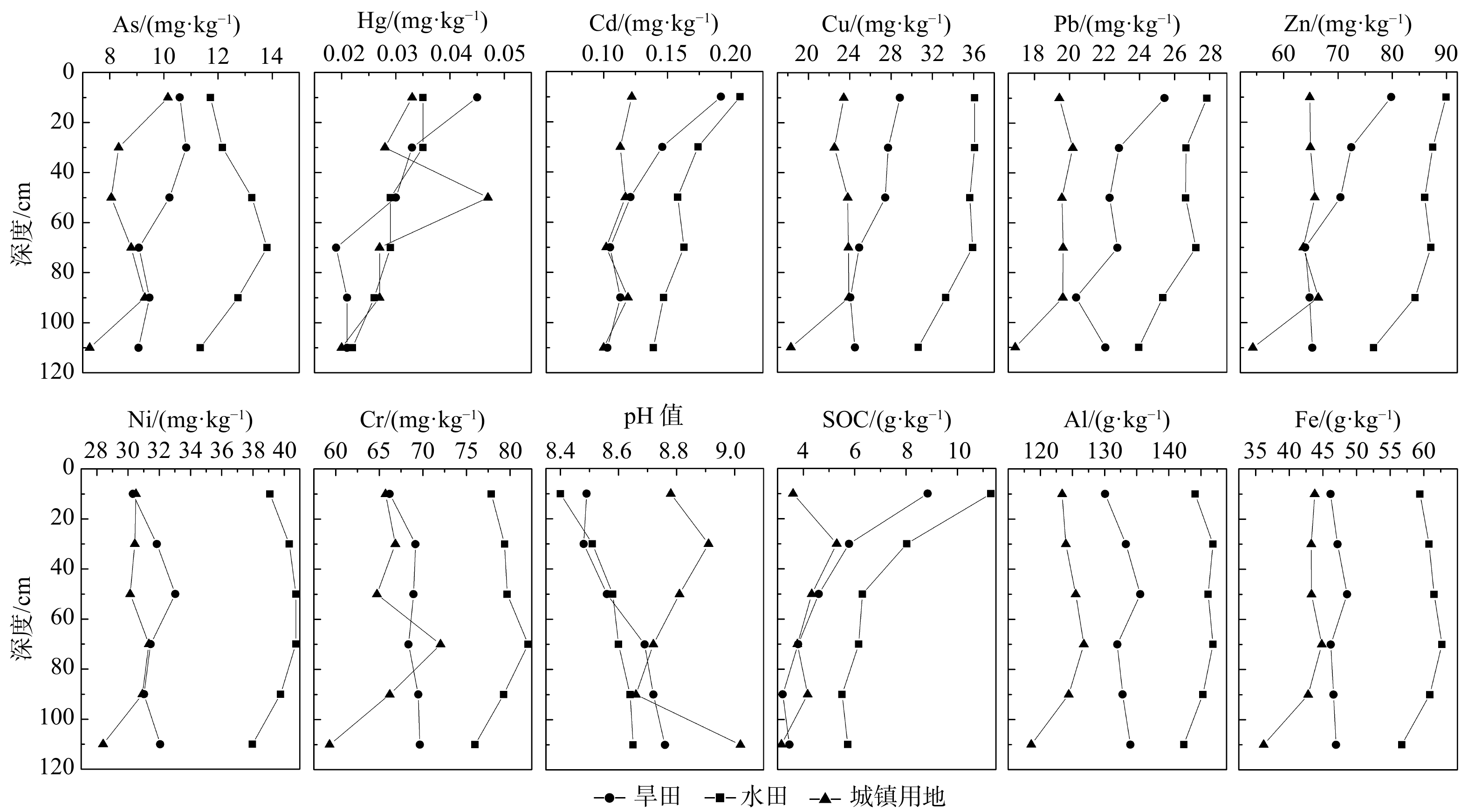
Table 3. Statistic analysis of heavy metals and arsenic in soil profiles
元素 剖面/cm 0~20 20~40 40~60 60~80 80~100 100~120 As 均值/(mg·kg−1) 10.98 10.86 11.05 11.05 10.83 9.93 标准差 2.33 2.53 3.02 3.84 3.06 2.62 变异系数/% 21.24 23.32 27.31 34.78 28.24 26.38 Hg 均值/(mg·kg−1) 0.04 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 标准差 0.015 0.009 0.014 0.011 0.009 0.010 变异系数/% 38.20 28.72 41.93 43.83 37.30 48.49 Cd 均值/(mg·kg−1) 0.18 0.15 0.14 0.13 0.13 0.12 标准差 0.05 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.04 变异系数/% 28.15 26.42 29.40 37.33 28.92 31.55 Cu 均值/(mg·kg−1) 30.80 30.19 30.17 29.40 27.99 26.73 标准差 9.42 8.95 8.79 11.15 9.32 9.83 变异系数/% 30.60 29.64 29.13 37.94 33.30 36.77 Pb 均值/(mg·kg−1) 25.17 23.90 23.57 23.99 22.34 22.45 标准差 5.43 4.61 5.28 6.59 5.39 4.74 变异系数/% 21.57 19.27 22.39 27.46 24.14 21.10 Zn 均值/(mg·kg−1) 80.93 77.27 76.09 73.80 73.44 69.40 标准差 16.52 14.82 16.62 22.11 19.21 18.29 变异系数/% 20.42 19.19 21.84 29.96 26.16 26.35 Ni 均值/(mg·kg−1) 34.11 35.18 35.72 35.41 34.75 34.41 标准差 6.89 6.63 7.56 9.95 8.67 9.41 变异系数/% 20.21 18.85 21.17 28.09 24.94 27.35 Cr 均值/(mg·kg−1) 71.09 73.05 72.64 75.03 72.98 71.59 标准差 10.61 9.57 12.66 15.06 11.28 13.53 变异系数/% 14.92 13.10 17.43 20.07 15.45 18.90 表 4 表层土壤重金属和砷元素相关系数
Table 4. Correlation coefficient of heavy metals and arsenic in surface soils
As Hg Cd Cu Pb Zn Ni Cr As 1 Hg 0.201 1 Cd 0.619** 0.441** 1 Cu 0.735** 0.413** 0.781** 1 Pb 0.691** 0.464** 0.811** 0.917** 1 Zn 0.730** 0.404** 0.800** 0.944** 0.909** 1 Ni 0.697** 0.221* 0.624** 0.875** 0.761** 0.854** 1 Cr 0.569** 0.261* 0.592** 0.834** 0.748** 0.815** 0.937** 1 注:**. 在 0.01 水平(双侧)上显著相关;*.在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关。 表 5 表层土壤重金属和砷元素含量因子载荷系数表
Table 5. Rotated component matrix for heavy metals and arsenic in surface soils
元素 主成分 PC1 PC2 PC3 As 0.779 0.41 −0.118 Hg 0.197 0.057 0.963 Cd 0.924 0.179 0.228 Cu 0.763 0.542 0.221 Pb 0.876 0.285 0.275 Zn 0.811 0.487 0.214 Ni 0.376 0.911 0.021 Cr 0.292 0.936 0.089 特征值 3.74 2.52 1.17 方差贡献/% 46.68 31.51 14.64 累积贡献/% 46.68 78.19 92.83 表 6 PMF解析表层土壤重金属和砷元素来源及贡献率
Table 6. Source contribution as estimated by the PMF model for heavy metals and arsenic in surface soils
元素 源成分谱/(mg·kg−1) 贡献率/% 因子 1 因子 2 因子 3 因子 4 因子 1 因子2 因子 3 因子 4 As 2.45 1.02 5.70 2.07 21.77 9.10 50.74 18.39 Hg 0.00 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.08 62.57 18.02 19.34 Cd 0.06 0.03 0.00 0.15 24.67 12.03 0.01 63.29 Cu 13.37 3.67 2.88 12.40 41.37 11.36 8.91 38.37 Pb 10.70 3.70 1.67 12.71 37.17 12.85 5.81 44.17 Zn 36.59 10.66 12.86 28.00 41.53 12.09 14.59 31.78 Ni 16.20 3.66 9.18 4.78 47.90 10.81 27.14 14.15 Cr 34.59 9.00 18.42 9.25 48.55 12.62 25.85 12.98 总贡献率 − − − − 32.88 17.93 18.88 30.31 -
[1] 陈丹青, 谢志宜, 张雅静, 等. 基于PCA/APCS和地统计学的广州市土壤重金属来源解析[J]. 生态环境学报,2016,25(6):1014 − 1022. [CHEN Danqing, XIE Zhiyi, ZHANG Yajing, et al. Source apportionment of soil heavy metals in Guangzhou based on the PCA/APCS model and geostatistics[J]. Ecology and Environment Sciences,2016,25(6):1014 − 1022. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 牛彦斌, 等. 唐山城市土壤重金属污染及潜在生态危害评价[J]. 中国地质,2011,38(5):1379 − 1386. [CUI Xingtao, LUAN Wenlou, NIU Yanbin, et al. An assessment of the heavy metal pollution and potential ecological hazards in urban soil of Tangshan City[J]. Geology in China,2011,38(5):1379 − 1386. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2011.05.024
[3] 王茜, 张光辉, 田言亮, 等. 农田表层土壤中重金属潜在生态风险效应研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(4):165 − 172. [WANG Qian, ZHANG Guanghui, TIAN Yanliang, et al. Research on the potential ecological risk of farmland top-soil of heavy metals[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(4):165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] LIU H W, ZHANG Y, ZHOU X, et al. Source identification and spatial distribution of heavy metals in tobacco-growing soils in Shandong Province of China with multivariate and geostatistical analysis[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2017,24(6):5964 − 5975. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-8229-1
[5] 吕建树, 何华春. 江苏海岸带土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 环境科学,2018,39(6):2853 − 2864. [LÜ Jianshu, HE Huachun. Identifying the origins and spatial distributions of heavy metals in the soils of the Jiangsu Coast[J]. Environmental Science,2018,39(6):2853 − 2864. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 宋泽峰, 等. 石家庄城市土壤重金属空间分布特征及源解析[J]. 中国地质,2016,43(2):683 − 690. [CUI Xingtao, LUAN Wenlou, SONG Zefeng, et al. A study of the spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in urban soil in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Geology in China,2016,43(2):683 − 690. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.02.027
[7] 黄华斌, 林承奇, 胡恭任, 等. 基于PMF模型的九龙江流域农田土壤重金属来源解析[J]. 环境科学,2020,41(1):430 − 437. [HUANG Huabin, LIN Chengqi, HU Gongren, et al. Source appointment of heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Jiulong river basin based on positive matrix factorization[J]. Environmental Science,2020,41(1):430 − 437. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张秀芝, 郭海全, 李宏亮, 等. 河北省白洋淀洼地环境地球化学物源判断[J]. 地学前缘,2008,15(5):90 − 96. [ZHANG Xiuzhi, GUO Haiquan, LI Hongliang, et al. Distinguishing origins of elements in environmental geochemistry of Baiyangdian billabong of Hebei Province, North China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2008,15(5):90 − 96. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.05.010
[9] 张丽红, 徐慧珍, 于青春, 等. 河北清苑县及周边农田土壤及农作物中重金属污染状况与分析评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2010,29(11):2139 − 2146. [ZHANG Lihong, XU Huizhen, YU Qingchun, et al. The investigation and evaluation of the heavy metal pollution in farmland soil and crop in the QingYuan of Hebei, China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2010,29(11):2139 − 2146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 邢洪连, 郭华明, 王轶, 等. 河北保定市安新—清苑县土壤重金属形态分布及风险评估[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(2):140 − 146. [XING Honglian, GUO Huaming, WANG Yi, et al. Fraction distribution and risk assessment of soil heavy metals in Anxin—Qingyuan County in Baoding of Hebei[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(2):140 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 中华人民共和国国家标准: 土壤环境质量 农用地土壤污染风险管控标准 GB 15618—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
Ministry of Ecological Environment, State Administration for Market Regulation. National Standard (Mandatory) of the People's Republic of China: Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land. GB 15618—2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018.(in Chinese)
[12] 中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990.
Environmental Monitoring of China. Background values of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environment Science Press, 1990.(in Chinese)
[13] 张静. 深圳市土壤重金属特征分析及研究[J]. 长春工程学院学报(自然科学版),2018,19(3):121 − 125. [ZHANG Jing. The characteristics analysis and research on heavy metal pollution in Shenzhen City China[J]. Journal of Changchun Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2018,19(3):121 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 安永龙, 黄勇, 刘清俊, 等. 北京城区表层土壤多元素分布特征及重金属元素污染评价[J]. 地质通报,2016,35(12):2111 − 2120. [AN Yonglong, HUANG Yong, LIU Qingjun, et al. The distribution of surface soil elements and the pollution as-sessment of heavy metal elements in Beijing[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2016,35(12):2111 − 2120. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.12.019
[15] 孟飞, 刘敏, 史同广. 上海农田土壤重金属的环境质量评价[J]. 环境科学,2008,29(2):428 − 433. [MENG Fei, LIU Min, SHI Tongguang. Evaluation on environmental quality of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Shanghai[J]. Environmental Science,2008,29(2):428 − 433. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2008.02.026
[16] 李炜, 周笑白, 王斌, 等. 天津市不同土地利用方式下土壤重金属污染特征及评价[J]. 水土保持通报,2018,38(6):200 − 205. [LI Wei, ZHOU Xiaobai, WANG Bin, et al. Pollution characteristics and assessment of heavy metal in different land-use types in Tianjin City[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,38(6):200 − 205. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] LI Siyue, JIA Zhongmin. Heavy metals in soils from a representative rapidly developing megacity (SW China): Levels, source identification and apportionment[J]. Catena,2018,163:414 − 423. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.12.035
[18] 安永龙, 万利勤, 李霞, 等. 承德市土壤重金属空间结构与分布特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):119 − 131. [AN Yonglong, WAN Liqin, LI Xia, et al. Spatial structure and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in the soil in Chengde[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):119 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] WANG S, TANG C, SONG X, et al. The impacts of a linear wastewater reservoir on groundwater recharge and geochemical evolution in a semi-arid area of the Lake Baiyangdian watershed, North China Plain[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2014,482/483:325 − 335. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.130
[20] 周国华, 马生明, 喻劲松, 等. 土壤剖面元素分布及其地质、环境意义[J]. 地质与勘探,2002,38(6):70 − 75. [ZHOU Guohua, MA Shengming, YU Jinsong, et al. Vertical distribution of elements in soil profiles and their significance for geological and environmental[J]. Geology and Prospecting,2002,38(6):70 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 陈子扬, 孙孝龙. 土壤中有机质与重金属关系的研究进展[J]. 环境与发展,2017,29(8):141 − 142. [CHEN Ziyang, SUN Xiaolong. Research progress on the relationship between organic matter and heavy metals in soils[J]. Environment and Development,2017,29(8):141 − 142. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 王兆苏, 王新军, 陈学萍, 等. 微生物铁氧化作用对砷迁移转化的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2011,31(2):328 − 333. [WANG Zhaosu, WANG Xinjun, CHEN Xueping, et al. The effect of microbial iron oxidation on arsenic mobility and transformation[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2011,31(2):328 − 333. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: