A study of anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility of cohesive soil under unconfined compression
-
摘要:
近年来基坑、隧洞等开挖工程活动中的卸载导致黏性土体发生过大侧向变形,引起的工程事故越来越多。目前多采用测斜仪对基坑周围土体变形进行水平位移监测,然而由于软土的特殊工程性质,在监测中软土无法带动测斜仪一起变形,往往监测效果不尽人意,不能准确给出实际软土的真实变形。因此,需要加强开挖卸荷工程施工中土体的侧向变形监测技术研究工作。本文基于磁性矿物受荷载变形具有定向性特征,运用磁组构试验对无侧限压缩后的黏性土试样进行磁各向异性研究,同时与有侧限压缩试验变形测试结果进行比较,分析试验轴向应力、土样含水率对无侧限压缩条件下磁各向异性的影响规律,以及主磁化率值与应变的数学关系,探讨了由黏性土磁各向异性推求其受力变形规律的可行性。研究成果表明,受力作用的黏性土变形与其磁性矿物定向性具有较好的一致性。这一认识对于有效监测软土地区卸荷工程周围软土变形情况具有重要的理论意义和实际应用价值。
Abstract:In recent years, the unloading of excavation engineering activities such as foundation pits and tunnels has caused excessive lateral deformation of cohesive soil, which result in more and more engineering accidents. At present, the inclinometer is often used to monitor the horizontal displacement of the soil around the foundation pit. However, due to the special engineering properties of soft soil, the inclinometer cannot be driven to deform with the soft soil during monitoring. The effect of monitoring is often unsatisfactory and inaccurate to reflect the true deformation. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the research of lateral deformation monitoring technology of soil in the construction of excavation unloading engineering. In this paper, based on the directional characteristics of the deformation of magnetic minerals under loading, the magnetic fabric test is used to study the magnetic anisotropy of the cohesive soil sample after unconfined compression test and then to compare with the results of the confined one. The paper then discusses the mathematical relationship between the main magnetic susceptibility value and the strain as the consequence of the analysis of the influence of the axial stress and the moisture content of soil on the magnetic anisotropy under unconfined compression. Finally, the feasibility of the calculation of the law of force and the deformation from the magnetic anisotropy of the cohesive soil is explored. The research results show that the deformation of the cohesive soil under force has good consistency with its orientation of magnetic mineral. This understanding has important theoretical significance and practical application value for effectively monitoring the deformation of soft soil around unloading projects in soft soil areas.
-
Key words:
- unconfined compression /
- lateral deformation /
- moisture content /
- magnetic anisotropy
-

-
表 1 软土的物理力学性质指标
Table 1. Physical parameters of the soil
天然含
水率w/%天然
孔隙比e重度
γ/(kN·m−3)液性
指数IL内摩
擦角φ/(°)黏聚力
c/kPa39.9 1.130 17.7 1.68 5.4 11.9 表 2 粒径分布
Table 2. Particle size distribution
粒径/mm 0.075~0.25 0.05~0.075 0.005~0.05 0.002~0.005 <0.002 含量/% 6.8 9.5 60.3 9.3 14.2 表 3 不同含水率无侧限压缩试样加载方案
Table 3. Loading scheme of soil samples with different moisture contents
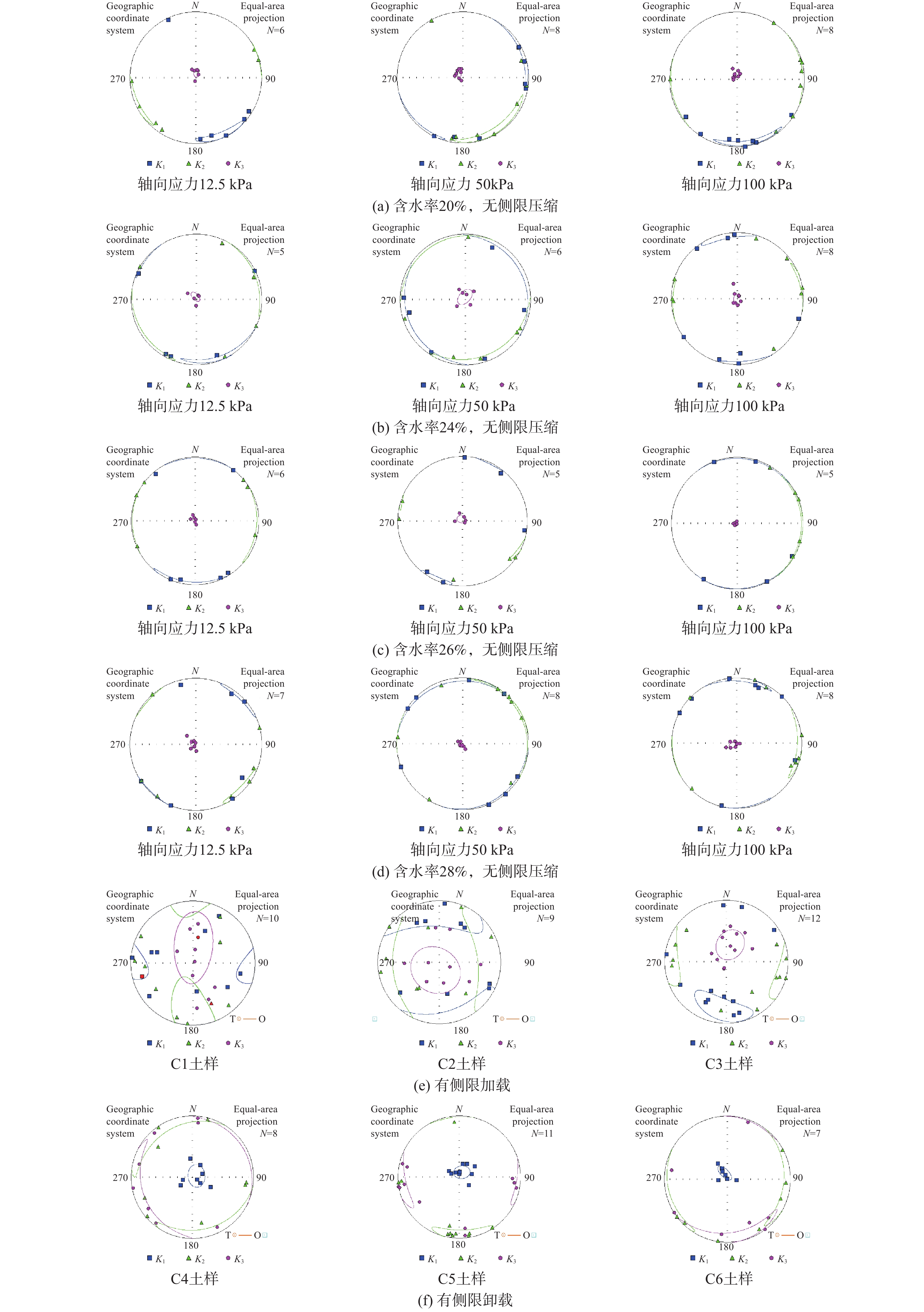
试样编号 含水率/% 轴向应力/ kPa 1-1 20 12.5 1-2 12.5—50 1-3 12.5—50—100 2-1 24 12.5 2-2 12.5—50 2-3 12.5—50—100 3-1 26 12.5 3-2 12.5—50 3-3 12.5—50—100 4-1 28 12.5 4-2 12.5—50 4-3 12.5—50—100 表 4 有侧限压缩试样加载方案
Table 4. Loading scheme of soil samples under confined compression conditions
试样编号 加载方式/kPa 有侧限加载 C1 25—50—100—200—400 C2 25—50—100—200—400—800 C3 25—50—100—200—400—800—1600 有侧限卸载 C4 25—50—100—200—400—800—1600—200 C5 25—50—100—200—400—800—1600—400 C6 25—50—100—200—400—800—1600—800 表 5 无侧限压缩试样磁各向异性基本参数
Table 5. Parameters of magnetic anisotropy for soil samples under unconfined compression
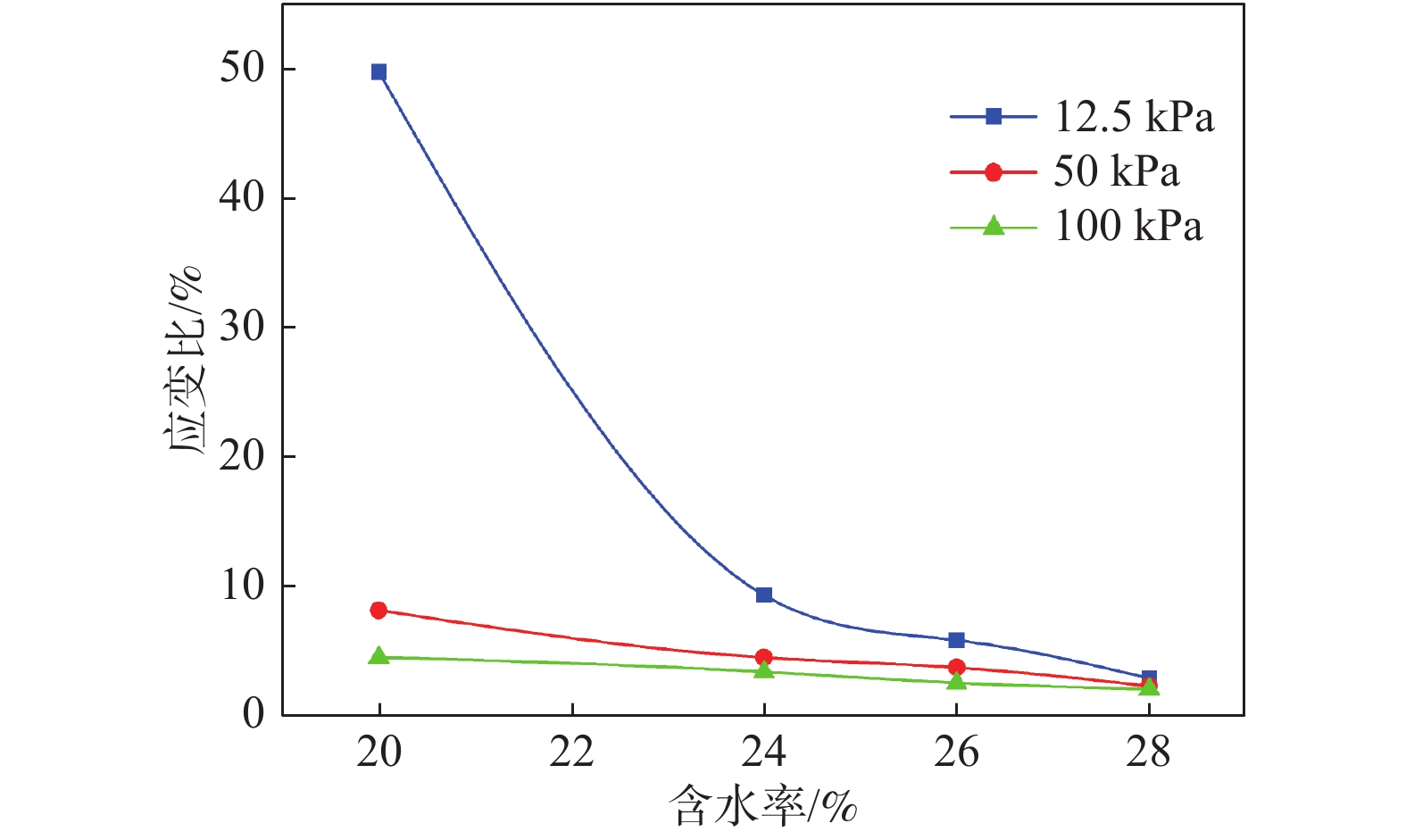
含水率/% 轴向应力/kPa 磁各向异性度Pj 磁线理度L 磁面理度F 形状参数T 20 12.5 1.023 1.001 1.019 0.853 50.0 1.026 1.001 1.022 0.894 100.0 1.028 1.001 1.024 0.910 24 12.5 1.024 1.003 1.019 0.747 50.0 1.031 1.001 1.025 0.950 100.0 1.037 1.001 1.031 0.907 26 12.5 1.027 1.001 1.023 0.898 50.0 1.033 1.003 1.027 0.818 100.0 1.040 1.001 1.034 0.952 28 12.5 1.038 1.002 1.032 0.905 50.0 1.042 1.001 1.036 0.944 100.0 1.044 1.002 1.037 0.901 表 6 幂指数α
Table 6. Power exponent (α) values
含水率/% 轴向应力/kPa K1/K3 L1/L3 α 20 12.5 1.018 49.749 0.0046 50 1.021 8.166 0.0099 100 1.023 4.547 0.0150 24 12.5 1.016 9.334 0.0071 50 1.024 4.514 0.0157 100 1.030 3.414 0.0240 26 12.5 1.022 5.856 0.0123 50 1.024 3.75 0.0179 100 1.033 2.565 0.0344 28 12.5 1.030 2.926 0.0275 50 1.035 2.315 0.0409 100 1.035 2.084 0.0468 -
[1] 谭儒蛟, 焦宇杰, 徐文杰. 天津滨海软土蠕变参数及路基沉降效应分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(4):67 − 73. [TAN Rujiao, JIAO Yujie, XU Wenjie. Tests on the creep parameters of the soft soil in Tianjin coastal region and analysis on the effect of subgrade settlement deformation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(4):67 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 刘浩旭, 朱剑锋, 饶春义, 等. 盾构施工与波浪荷载耦合作用后软土力学特性[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):97 − 103. [LIU Haoxu, ZHU Jianfeng, RAO Chunyi, et al. Mechanical properties of soft clay after coupling between shield construction and wave loading[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):97 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 杜晨翔. 开挖引起的深厚淤泥质软土桩基变形试验研究[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学, 2016.
DU Chenxiang. Experiment study on the deformation of pile foundation by excavation in thick mucky soft soil[D]. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, 2016.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] RATHORE J S, BECKE M. Magnetic fabric analyses in the Gail Galley (Carinthia, Austria) for the determination of the sense of movements along this region of the Periadriatic Line[J]. Tectonophysics,1980,69(3/4):349 − 368.
[5] HENRY B, PLENIER G, CAMPS P. Post-emplacement tilting of lava flows inferred from magnetic fabric study: the example of Oligocene lavas in the Jeanne D’Arc Peninsula (Kerguelen Islands)[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,2003,127(1/2):153 − 164.
[6] CIFELLI F, ROSSETTI F, MATTEI M, et al. An AMS, structural and paleomagnetic study of quaternary deformation in eastern Sicily[J]. Journal of Structural Geology,2004,26(1):29 − 46. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(03)00092-0
[7] 张淑伟, 杨振宇, 王喜生, 等. 磁化率各向异性的原理及应用实例[J]. 地质力学学报,2017,23(1):135 − 140. [ZHANG Shuwei, YANG Zhenyu, WANG Xisheng, et al. Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility: theory and case studies[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2017,23(1):135 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.01.009
[8] 顾延生, 管硕, 马腾, 等. 江汉盆地东部第四纪钻孔地层与沉积环境[J]. 地球科学,2018,43(11):3989 − 4000. [GU Yansheng, GUAN Shuo, MA Teng, et al. Quaternary sedimentary environment documented by borehole stratigraphical records in eastern Jianghan basin[J]. Earth Science,2018,43(11):3989 − 4000. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 霍斐斐, 邵瑞琦, 姜南, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘中新生代地层的磁组构特征及其沉积—构造学意义[J]. 地球物理学报,2020,63(2):583 − 596. [HUO Feifei, SHAO Ruiqi, JIANG Nan, et al. Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility of Mesozoic and Cenozoic sediments in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin and its sedimentary-tectonic significance[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2020,63(2):583 − 596. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg2020N0038
[10] 刘彩彩, 王伟涛, 张培震, 等. 祁连盆地第三纪沉积物磁性地层和岩石磁组构初步研究[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(8):2965 − 2978. [LIU Caicai, WANG Weitao, ZHANG Peizhen, et al. Magnetostratigraphy and magnetic anisotropy of the Neogene sediments in the Qilian Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2016,59(8):2965 − 2978. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg20160820
[11] 艾可可, 季军良. 准噶尔西北部山地晚新生代以来隆升过程:来自沉积学和磁组构的证据[J]. 地球科学,2015,40(3):535 − 547. [AI Keke, JI Junliang. Tectonic uplift of mountains in northwestern Junggar since late Cenozoic: evidences from sedimentology and magnetic fabric in heshituoluogai basin[J]. Earth Science,2015,40(3):535 − 547. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 谢兴俊, 常秋芳, 孔祥辉. 洛川红黏土-黄土记录的风向变化及磁组构与磁化率对气候变化的敏感性对比[J]. 地球环境学报, 2020, 11(1): 66 − 71.
XIE Xingjun, CHANG Qiufang, KONG Xianghui. Changes of the wind direction recorded by red clay and loess in Luochuan and comparation of the sensitivity of magnetic fabric and magnetic susceptibility to climate change[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2020, 11(1): 66 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 唐锐枰, 葛俊逸, 庞海娇, 等. 泥河湾黑土沟剖面磁组构特征及古湖水文环境变化[J]. 科学通报,2020,65(11):1027 − 1045. [TANG Ruiping, GE Junyi, PANG Haijiao, et al. Paleohydro-climatic changes revealed by anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility at the Heitugou section, Nihewan Basin, and its influences on human's occupation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2020,65(11):1027 − 1045. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.1360/TB-2019-0737
[14] CARMICHAEL R S. Stress control of magnetization in magnetite and nickel, and implications for rock magnetism[J]. Journal of Geomagnetism and Geoelectricity,1968,20(3):187 − 196. doi: 10.5636/jgg.20.187
[15] SUN W W, KODAMA K P. Magnetic anisotropy, scanning electron microscopy, and X ray pole figure goniometry study of inclination shallowing in a compacting clay-rich sediment[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth,1992,97(B13):19599 − 19615. doi: 10.1029/92JB01589
[16] BORRADAILE G J, HENRY B. Tectonic applications of magnetic susceptibility and its anisotropy[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,1997,42(1/2):49 − 93.
[17] RUF A S, NARUK S J, BUTLER R F, et al. Strain and magnetic fabric in the Santa Catalina and Pinaleno Mountains Metamorphic Core Complex Mylonite Zones, Arizona[J]. Tectonics,1988,7(2):235 − 248. doi: 10.1029/TC007i002p00235
[18] 刘羊, 孙茜, 阎长虹. 含水量对软土无侧限变形影响的试验研究[J]. 土工基础,2018,32(4):455 − 460. [LIU Yang, SUN Qian, YAN Changhong. Evaluation of moisture content on the unconfined compressive strength of soft soils[J]. Soil Engineering and Foundation,2018,32(4):455 − 460. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 孙茜.无侧限压缩条件下重塑土变形机制研究[D].南京: 南京大学, 2019.
SUN Qian. Study on deformation mechanism of remolding soil under unconfined compression[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] CABALLERO-MIRANDA C I, TORRES-HERNÁNDEZ J R, ALVA-VALDIVIA L M. Anisotropy of magnetic susceptibility analysis of the Cantera Ignimbrite, San Luis Potosi, México: flow source recognition[J]. Earth, Planets and Space,2009,61(1):173 − 182. doi: 10.1186/BF03352897
-



 下载:
下载: