Determination of granite deformation and failure stages using the long short term memory neural network
-
摘要:
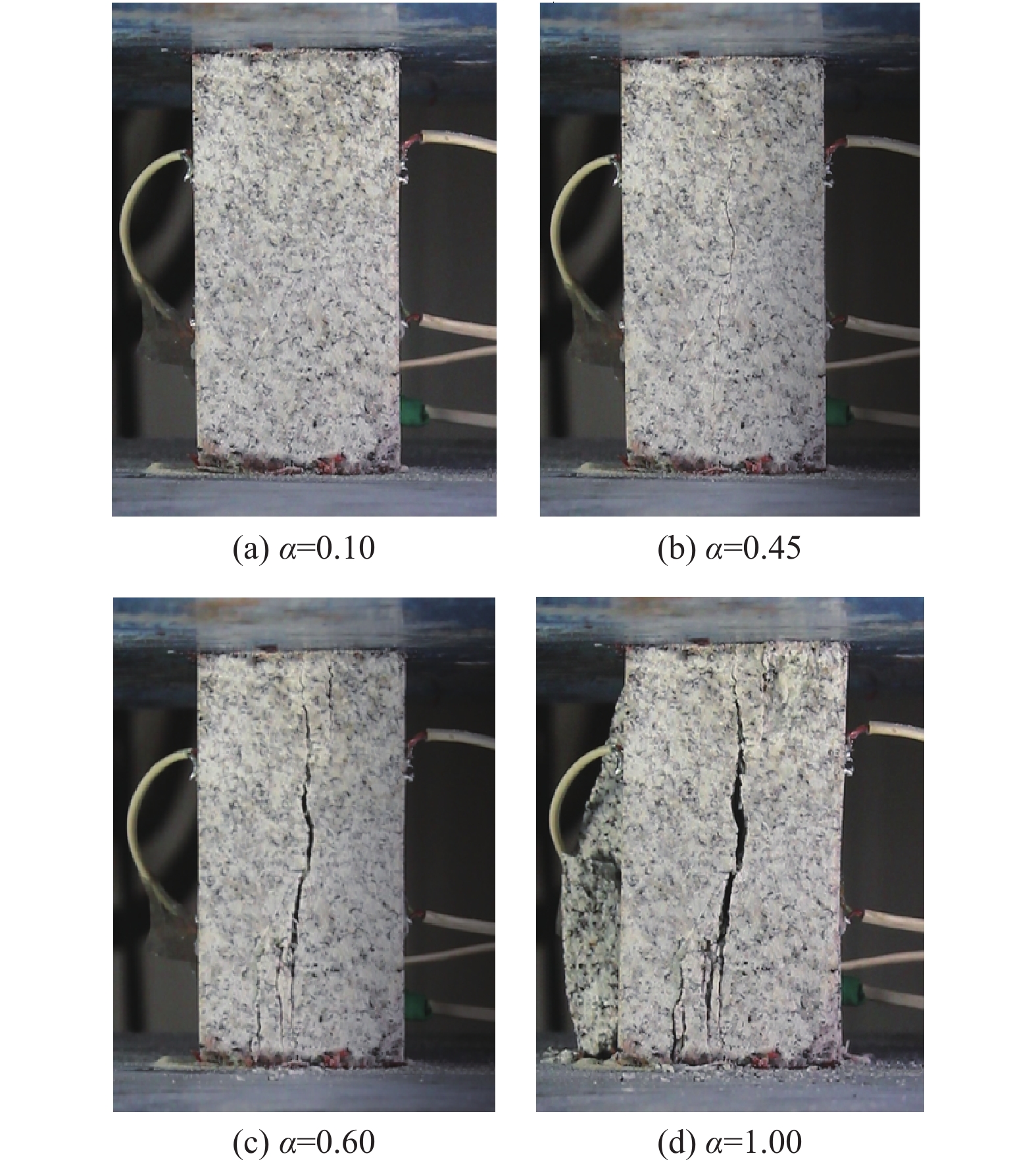
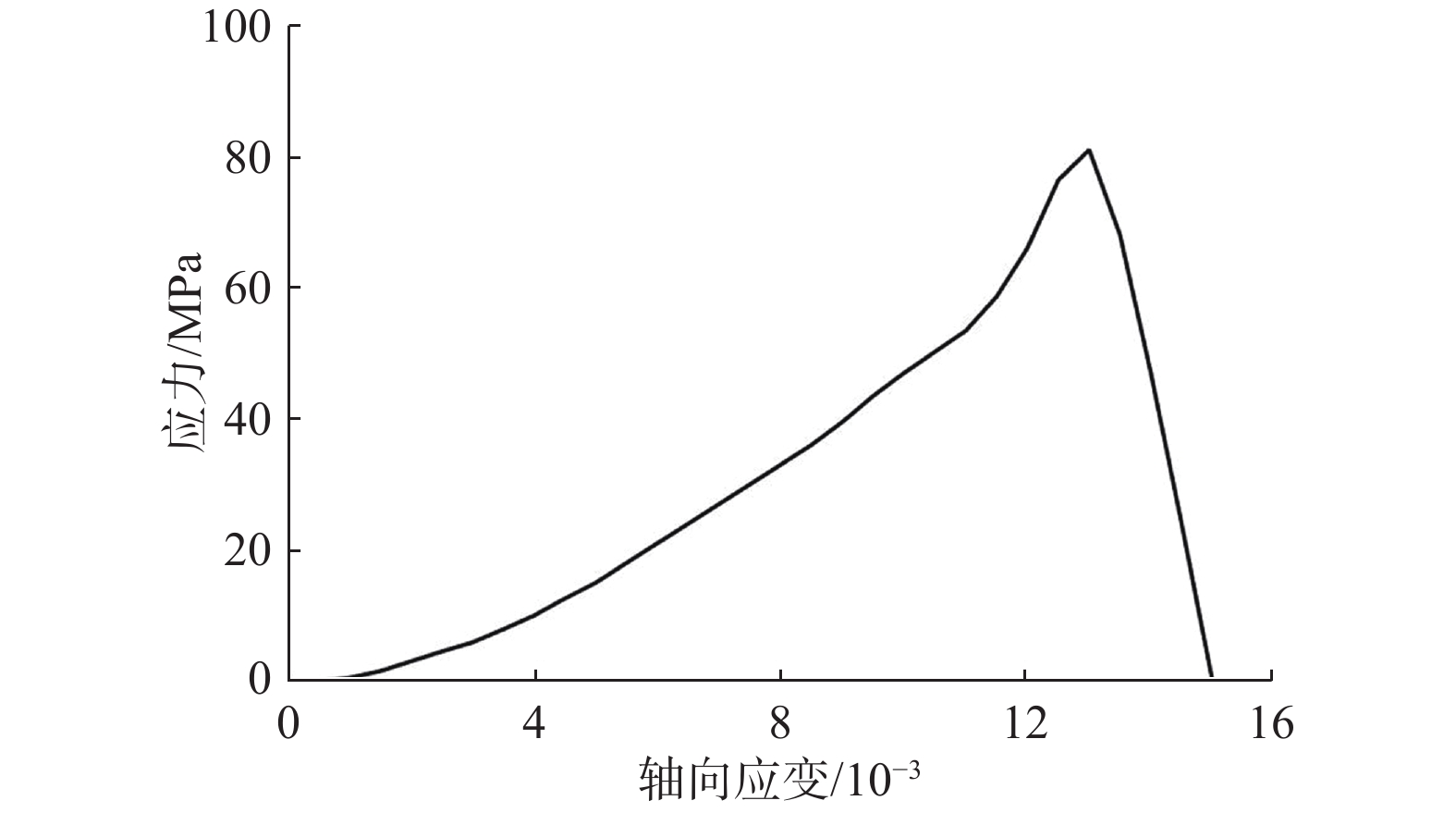
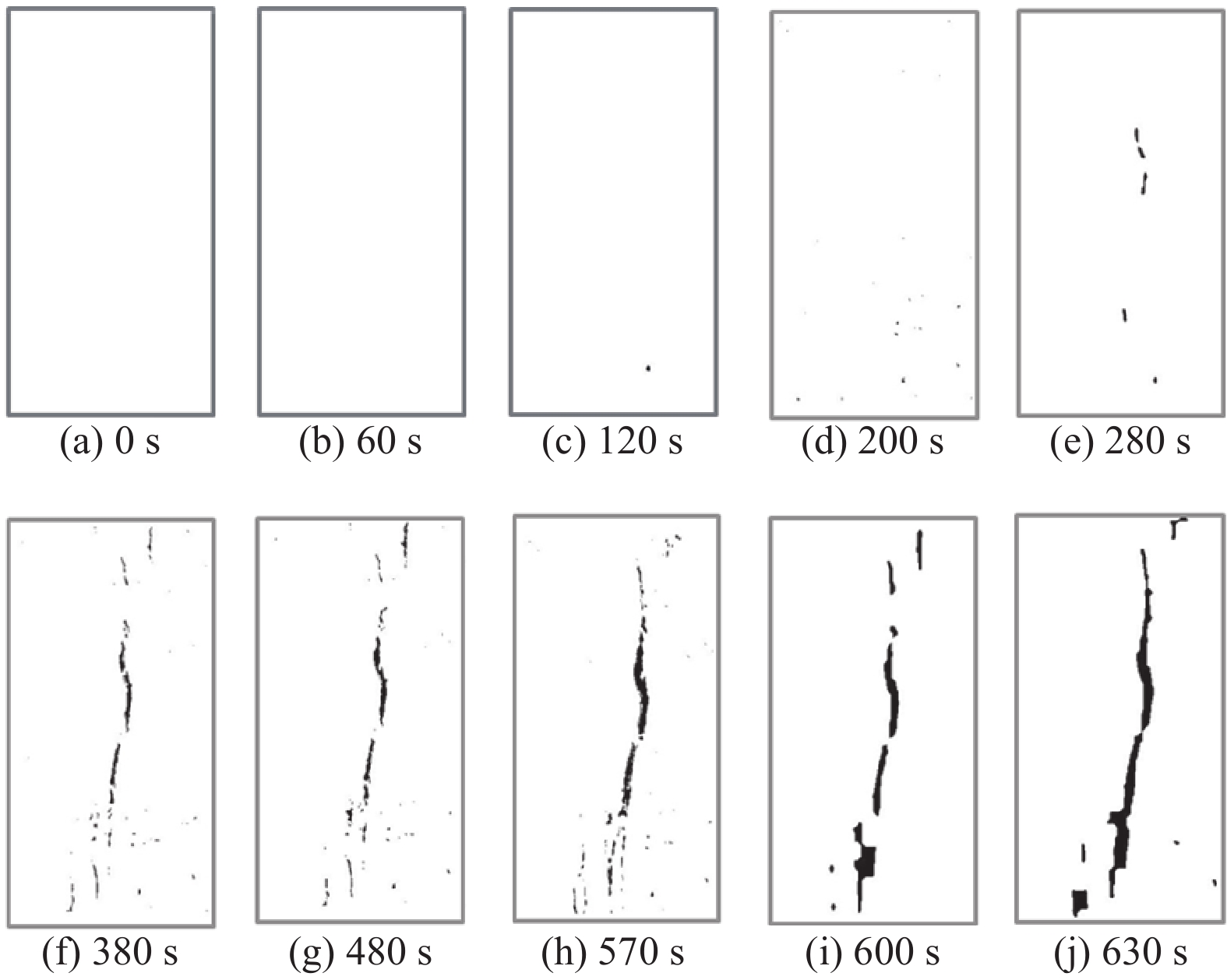
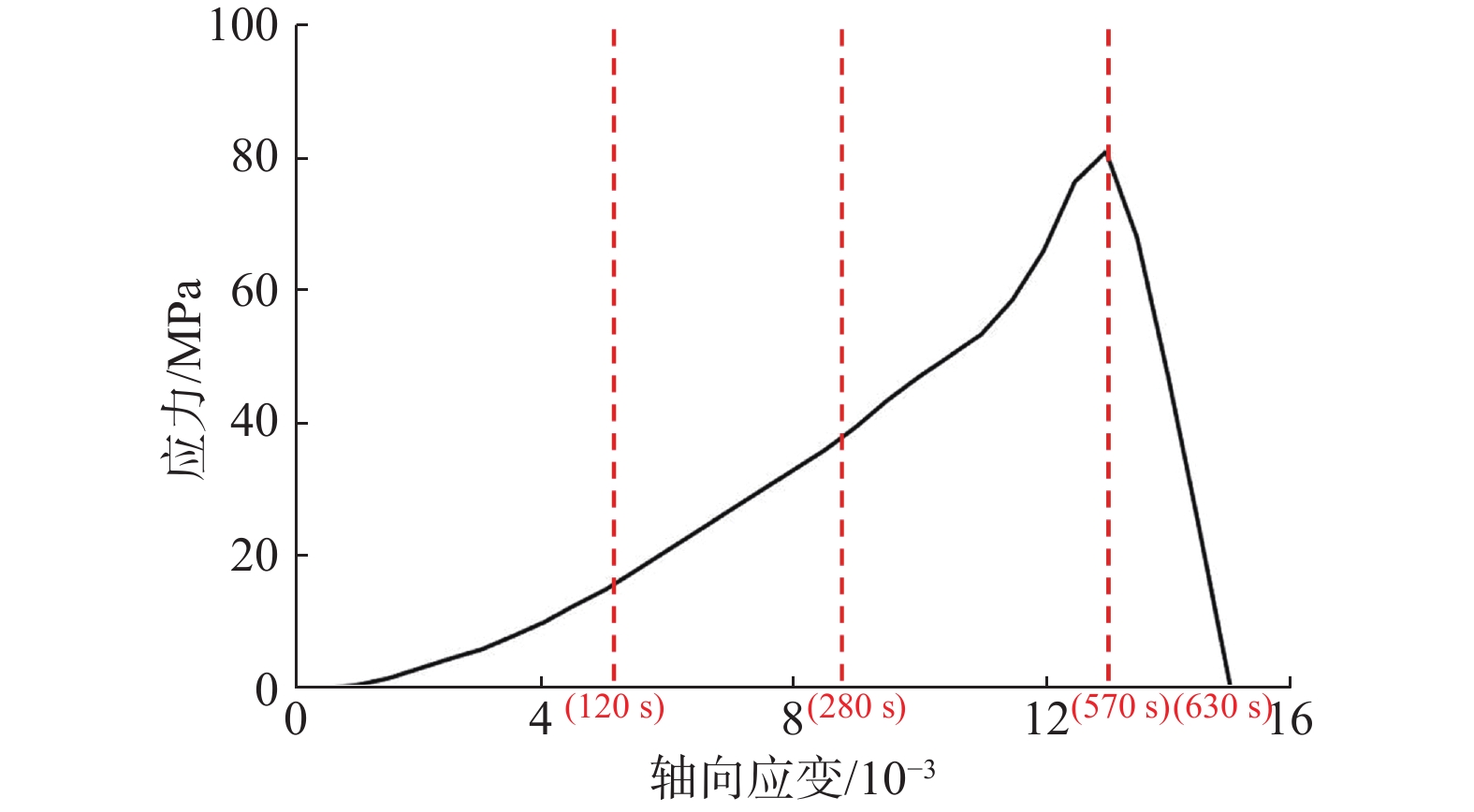
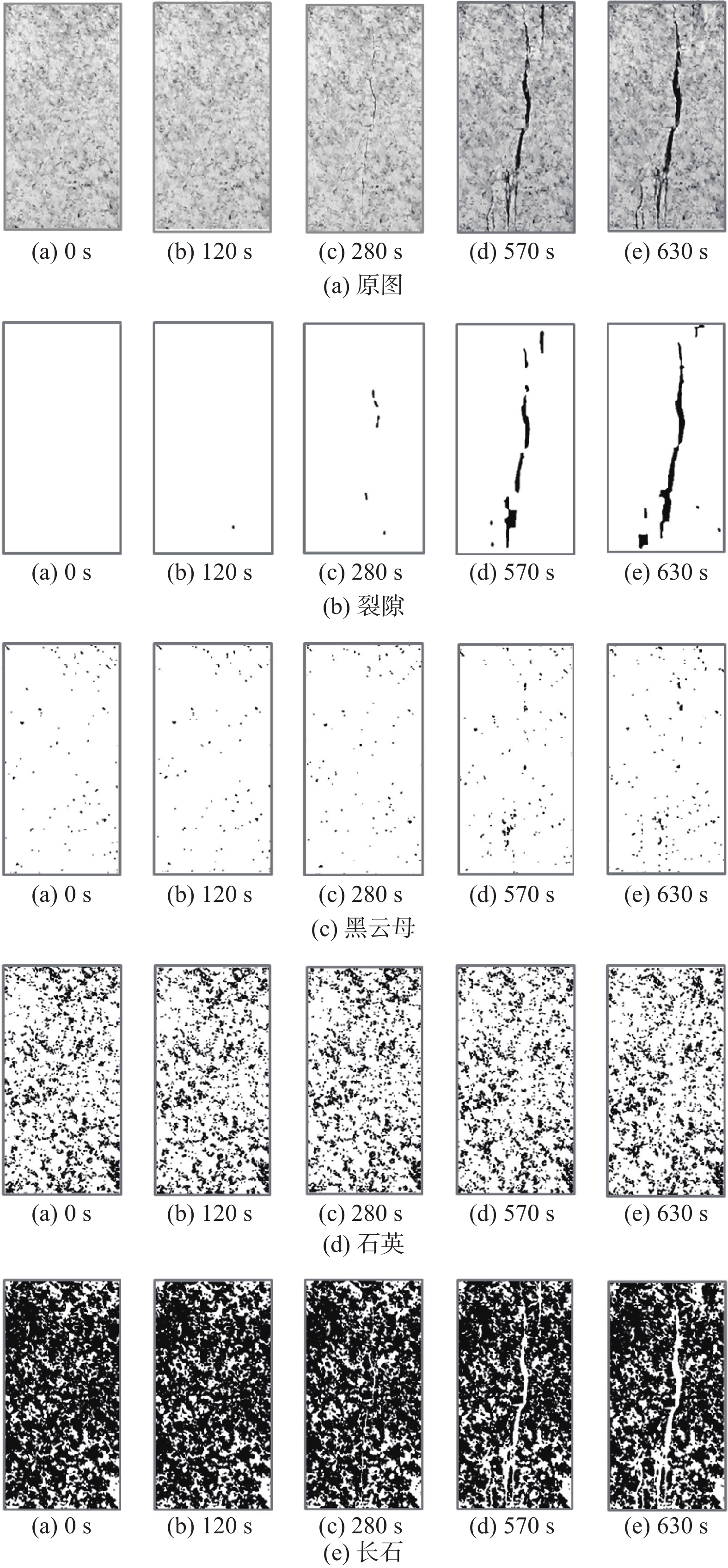
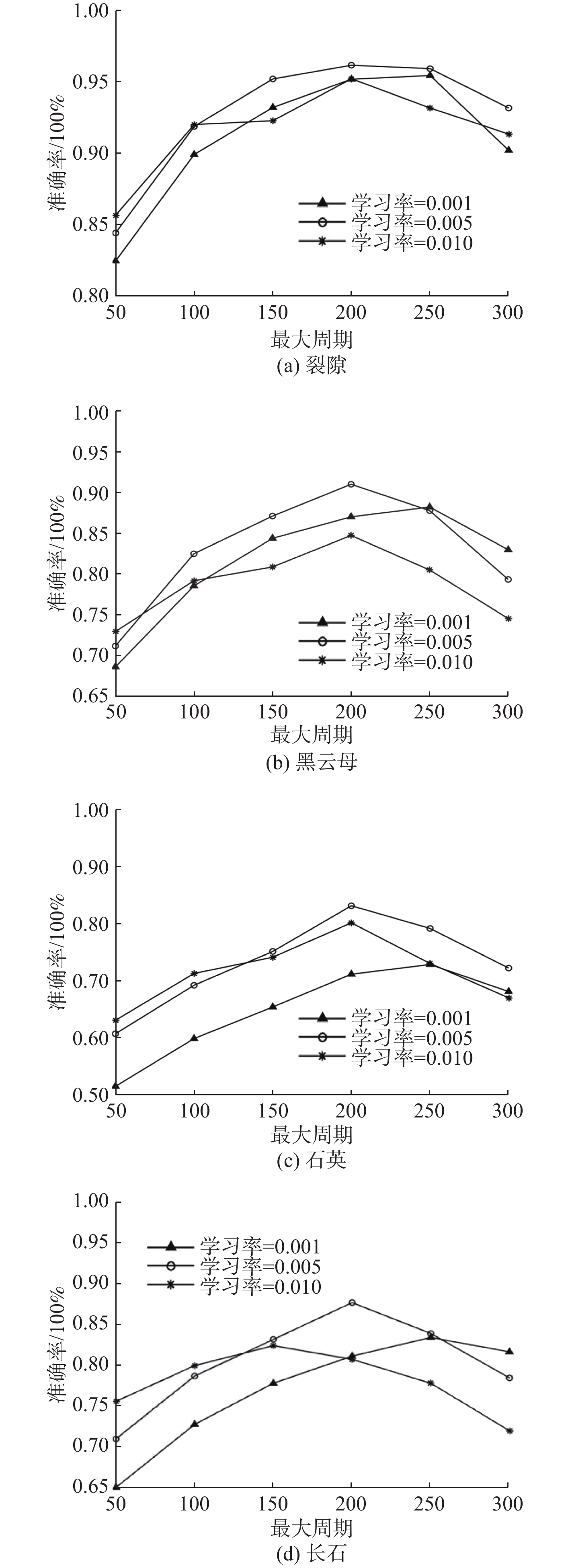
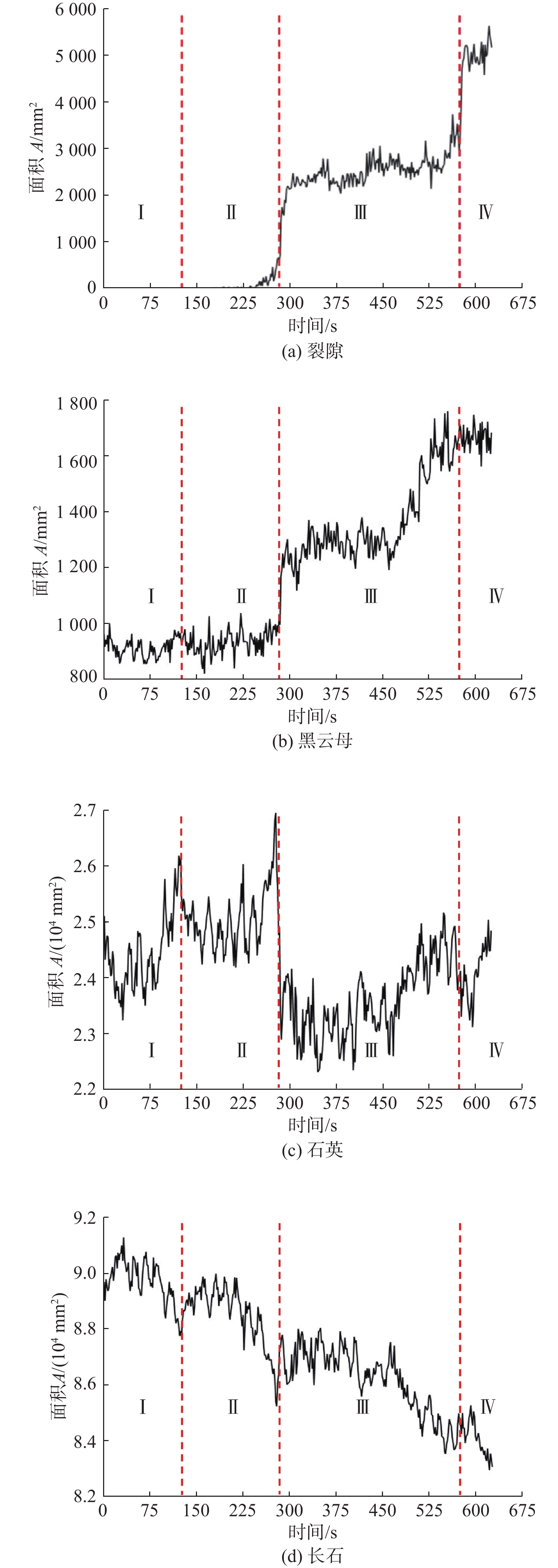
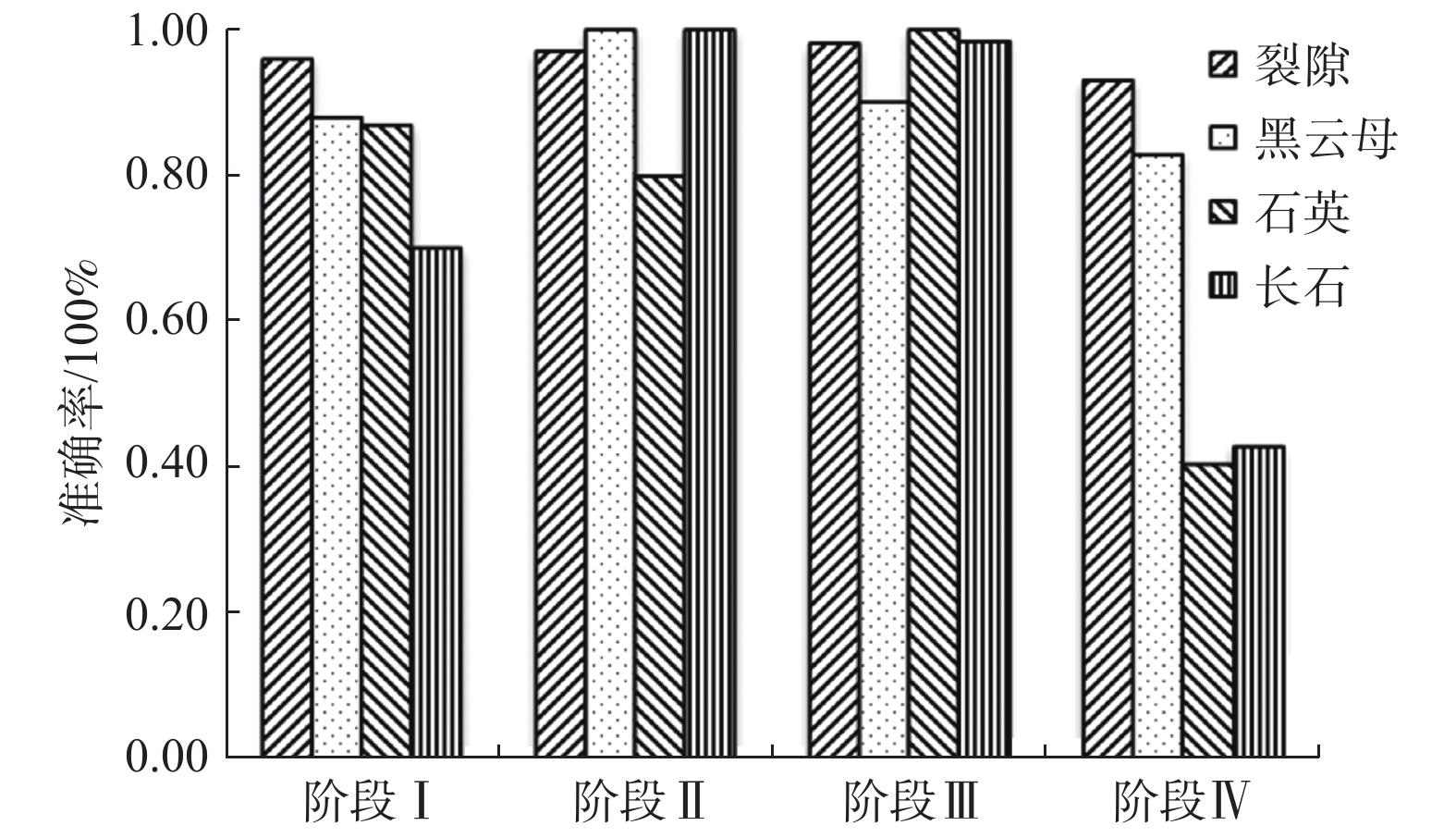
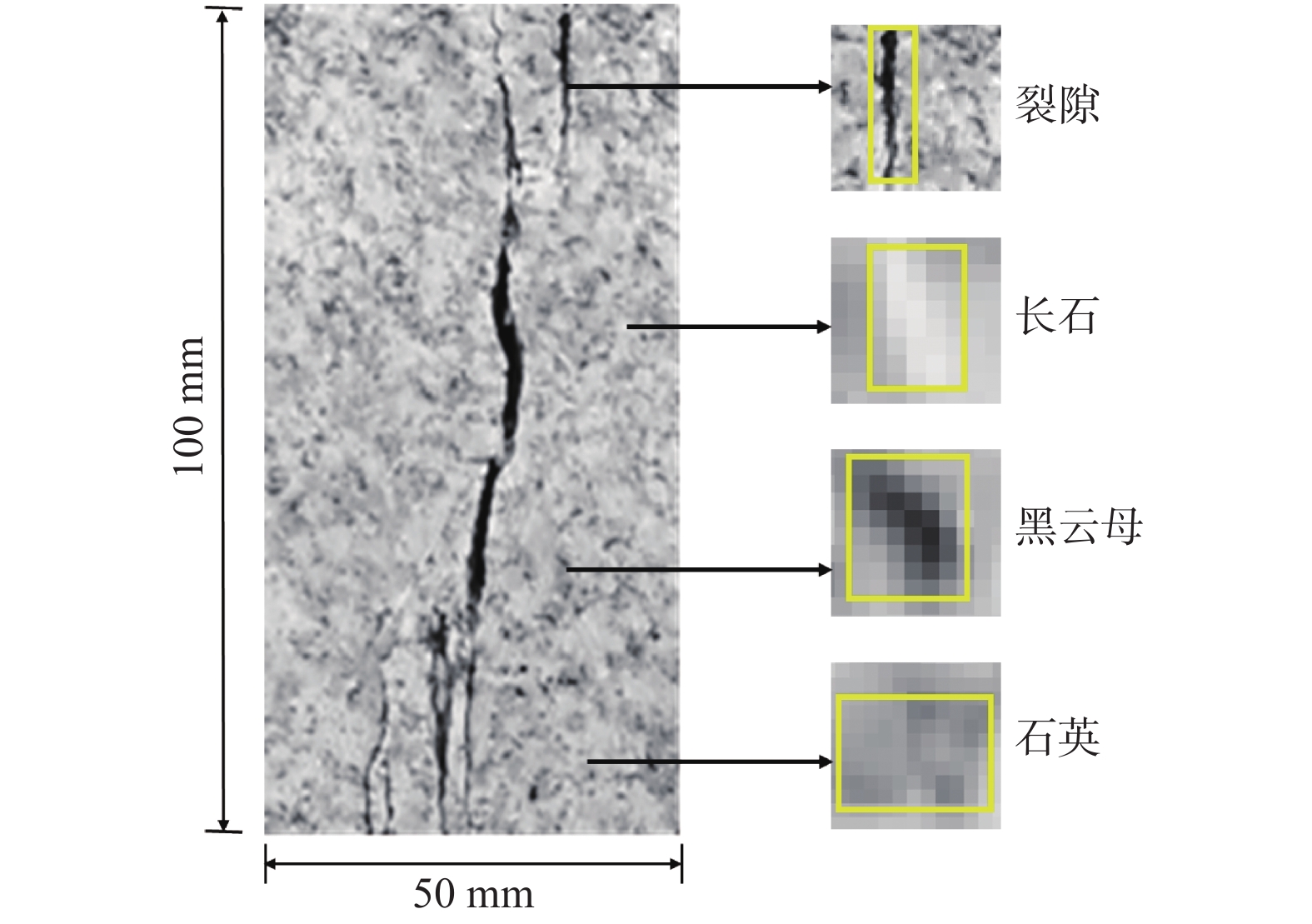
判别岩石所处的变形破坏阶段是分析岩石变化过程的重要基础。由于室内试验视频数据具有很好的等时距分布特征,可以使用基于长短期记忆的神经网络(LSTM-NN)模型判别外荷作用下岩石的变形破坏阶段。本文根据花岗岩室内单轴压缩试验所得应力-应变曲线和试验视频图像中裂隙的分布情况,将岩石变形破坏过程分成岩石压密阶段、弹性变形阶段、裂隙扩展阶段、整体破坏阶段,在提取不同阶段不同组分主要数字特征参数(面积)基础上,建立了基于LSTM-NN模型的岩石变形破坏阶段分类网络,分析了模型主要参数(学习率和最大周期等)对分类准确性的影响,使用所建模型对岩石所处变形破坏阶段进行了判别。结果表明,在LSTM-NN模型参数中,学习率和最大周期对变形破坏阶段判别准确率的影响较大,二者分别为0.005和200时的判别准确率达到最高;对于整个变形破坏阶段来说,LSTM-NN模型对裂隙扩展阶段预测的判别效果最好、对整体破坏阶段预测的判别效果最差;对于花岗岩中不同组分来说,LSTM-NN模型对变形破坏阶段预测准确性高低的顺序是裂隙、黑云母、长石、石英。
Abstract:Determination of deformation and failure stages is a fundamental issue in analyzing the movement processes of a rock. Due to the data distribution with an isochronous interval of the laboratory test video image, the long short term memory neural network (LSTM-NN) may be used to determine the deformation and failure stages of the rock under the external load. In this study, the stress-strain curve and the fissure distributions in the test video images photographed during the laboratory uniaxial compression tests of the granite specimen are used, and the deformation and failure stages of the rock are divided into compression deformation, elasticity deformation, fissure propagation, and complete failure stages. After extracting the main digital features (area) corresponding to these stages, a classification network for dividing the deformation and failure stages of the rock is established based on the LSTM-NN model. The influences of the main parameters (including learning ratio and maximum epoch) in the model on the classification precision are also examined. The determination of deformation and failure stages are furthermore performed using the model. The results shows that among the parameters of the LSTM-NN model, the learning ratio and the maximum epoch have a relatively great influence on the determination precision for the deformation and failure stages with the maximum precision if 0.005 and 200 are set respectively for these two parameters. As for the whole deformation and failure stages, the LSTM-NN model has the best and worst precisions respectively to determinate the fissure propagation and complete failure stages. As for the various compositions included in the rock, the great-to-small order of the determination precision for the deformation and failure stages is fissure, biotite, feldspar, and quartz.
-

-
表 1 6个试样不同变形破坏阶段的历时
Table 1. Time interval of deformation and failure stages of 6 test videos
/s 视频编号 阶段I 阶段II 阶段III 阶段IV 1号 0~120 120~280 280~570 570~630 2号 0~135 135~290 290~570 570~640 3号 0~140 140~280 280~560 560~620 4号 0~140 140~300 300~590 590~670 5号 0~130 130~290 290~590 590~640 6号 0~120 120~260 260~550 550~610 表 2 各组分分类的准确率和平均准确率
Table 2. Precision rate and average accuracy of each composition classification
花岗岩各组分 准确率/% 平均准确率/% 裂隙 96.89 90.83 黑云母 91.49 石英 86.77 长石 88.17 -
[1] 陈中一, 徐金明, 刘芳. 花岗岩中多条裂隙的萌生扩展过程研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(5):96 − 101. [CHEN Zhongyi, XU Jinming, LIU Fang. Investigation of the initiation and propagation of multi-cracks in granite[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(5):96 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] RIGOPOULOS I, TSIKOURAS B, POMONIS P, et al. Petrographic investigation of microcrack initiation in mafic ophiolitic rocks under uniaxial compression[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering,2013,46(5):1061 − 1072. doi: 10.1007/s00603-012-0310-6
[3] LIN Q, LABUZ J F. Fracture of sandstone characterized by digital image correlation[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2013,60:235 − 245. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.12.043
[4] AKESSON U, HANSSON J, STIGH J. Characterisation of microcracks in the Bohus granite, western Sweden, caused by uniaxial cyclic loading[J]. Engineering Geology,2004,72(1/2):131 − 142.
[5] 孙皓, 徐金明, 吴红斌. 使用试验视频图像研究花岗岩中不同矿物成分的变化特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(5):44 − 49. [SUN Hao, XU Jinming, WU Hongbin. An investigation of mineral composition changes on granite surface using video images from uniaxial compression test[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(5):44 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张岩, 徐金明, 张文清. 使用图像分析方法研究单轴压缩条件下花岗岩中细观组分的定向性变化[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2012,39(2):66 − 73. [ZHANG Yan, XU Jinming, ZHANG Wenqing. Orientation of meso-components in granite under uniaxial compression using image analysis[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2012,39(2):66 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] HAN H, DING Y S, HAO K R. Collaborative associated particle filter for interactive multi-target tracking in video surveillance[J]. Control Theory and Applications,2013,30(9):1185 − 1191.
[8] 徐金明, 韩娜娜, 李岩松. 石灰岩局部化变形的图像特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2010,29(10):2110 − 2115. [XU Jinming, HAN Nana, LI Yansong. Image features of localized deformation of limestone[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2010,29(10):2110 − 2115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 刘希康, 徐金明. 使用相对熵研究花岗岩的损伤演化特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):105 − 111. [LIU Xikang, XU Jinming. A study of damage evolutions of granites by using relative entropy[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):105 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 刘雪燕, 王成钢, 雷军明. 基于LSTM和注意力机制的安全事故等级分类[J]. 信息技术与信息化,2019(10):190 − 192. [LIU Xueyan, WANG Chenggang, LEI Junming. Classification of safety accident level based on LSTM and attention mechanism[J]. Information Technology and Informatization,2019(10):190 − 192. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9528.2019.10.060
[11] 曲星宇, 曾鹏, 李俊鹏. 基于RNN-LSTM的磨矿系统故障诊断技术[J]. 信息与控制,2019,48(2):179 − 186. [QU Xingyu, ZENG Peng, LI Junpeng. Fault diagnosis technology of grinding system based on RNN-LSTM[J]. Information and Control,2019,48(2):179 − 186. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.5755/j01.itc.48.2.21390
[12] RASHID K M, LOUIS J. Times-series data augmentation and deep learning for construction equipment activity recognition[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics,2019,42:100944. doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2019.100944
[13] ZHANG X, ZOU Z X, WANG K W, et al. A new rail crack detection method using LSTM network for actual application based on AE technology[J]. Applied Acoustics,2018,142:78 − 86. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2018.08.020
[14] 付文秀, 李弘扬, 靳东明. 基于LSTM的列车测速测距设备故障诊断[J]. 北京交通大学学报,2020,44(2):9 − 16. [FU Wenxiu, LI Hongyang, JIN Dongming. Fault diagnosis of train speed and ranging equipment based on LSTM[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University,2020,44(2):9 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] GAO X J, SHI M L, SONG X G, et al. Recurrent neural networks for real-time prediction of TBM operating parameters[J]. Automation in Construction,2019,98:225 − 235. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2018.11.013
[16] ZHOU C, XU H C, DING L Y, et al. Dynamic prediction for attitude and position in shield tunneling: a deep learning method[J]. Automation in Construction,2019,105:102840. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2019.102840
[17] HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation,1997,9(8):1735 − 1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
[18] 韩伟, 吴艳兰, 任福. 基于全连接和LSTM神经网络的空气污染物预测[J]. 地理信息世界,2018,25(3):34 − 40. [HAN Wei, WU Yanlan, REN Fu. The prediction of air pollutants based on full connection and LSTM neural network[J]. Geomatics World,2018,25(3):34 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2018.03.007
[19] RUMELHART D E, HINTON G E, WILLIAMS R J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors[J]. Nature,1988,323(6088):696 − 699.
[20] TIELEMAN T, HINTON G. Lecture 6.5-rmsprop: Divide the gradient by a running average of its recent magnitude[J]. COURSERA: Neural networks for machine learning,2012,4(2):26 − 31.
[21] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. 2014: arXiv: 1412.6980[cs.LG]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
[22] HINTON G E, OSINDERO S, TEH Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets[J]. Neural Computation,2006,18(7):1527 − 1554. doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527
-



 下载:
下载: