Monitoring of dangerous rock mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir area based on the terrestrial laser scanning method
-
摘要:
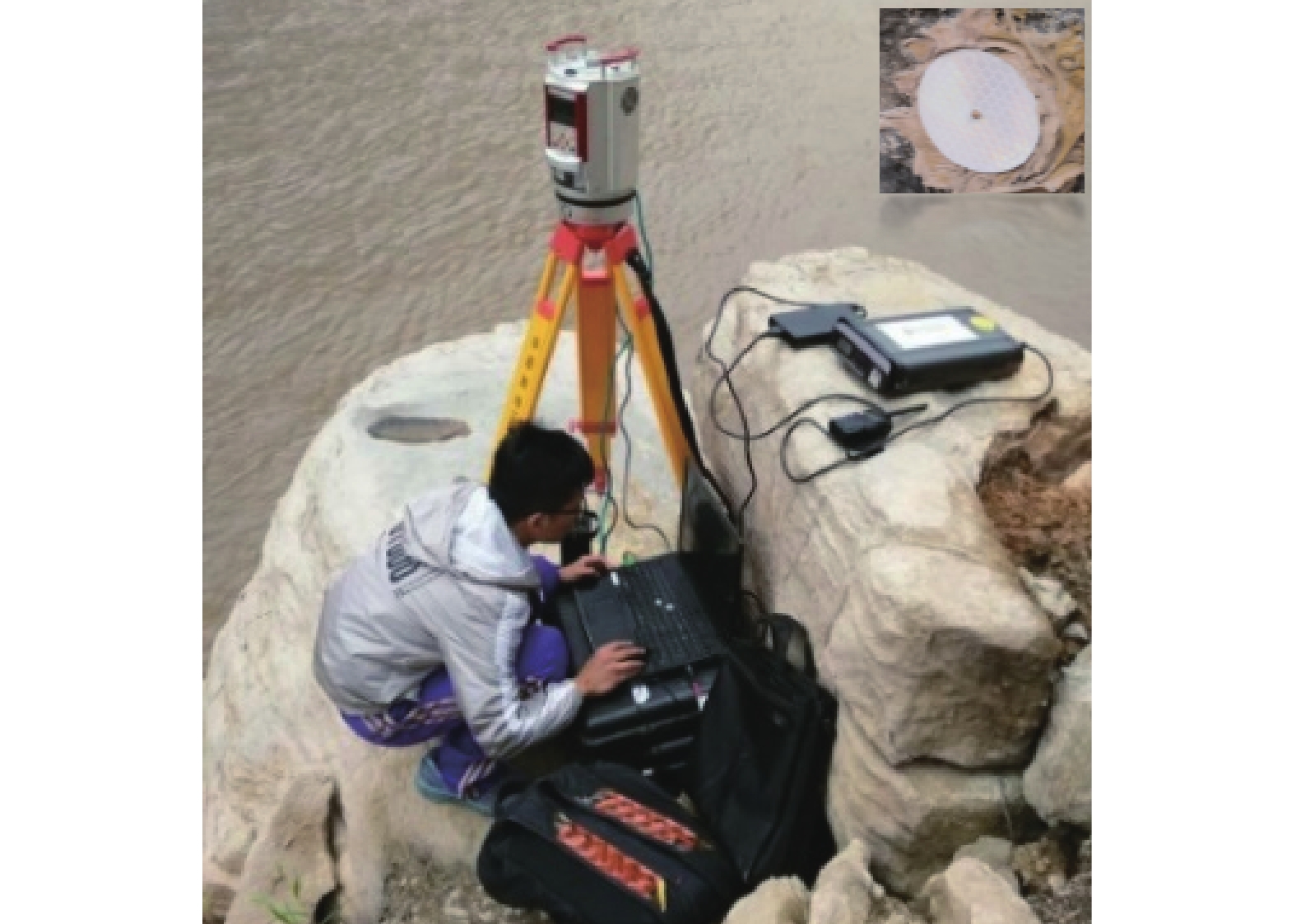
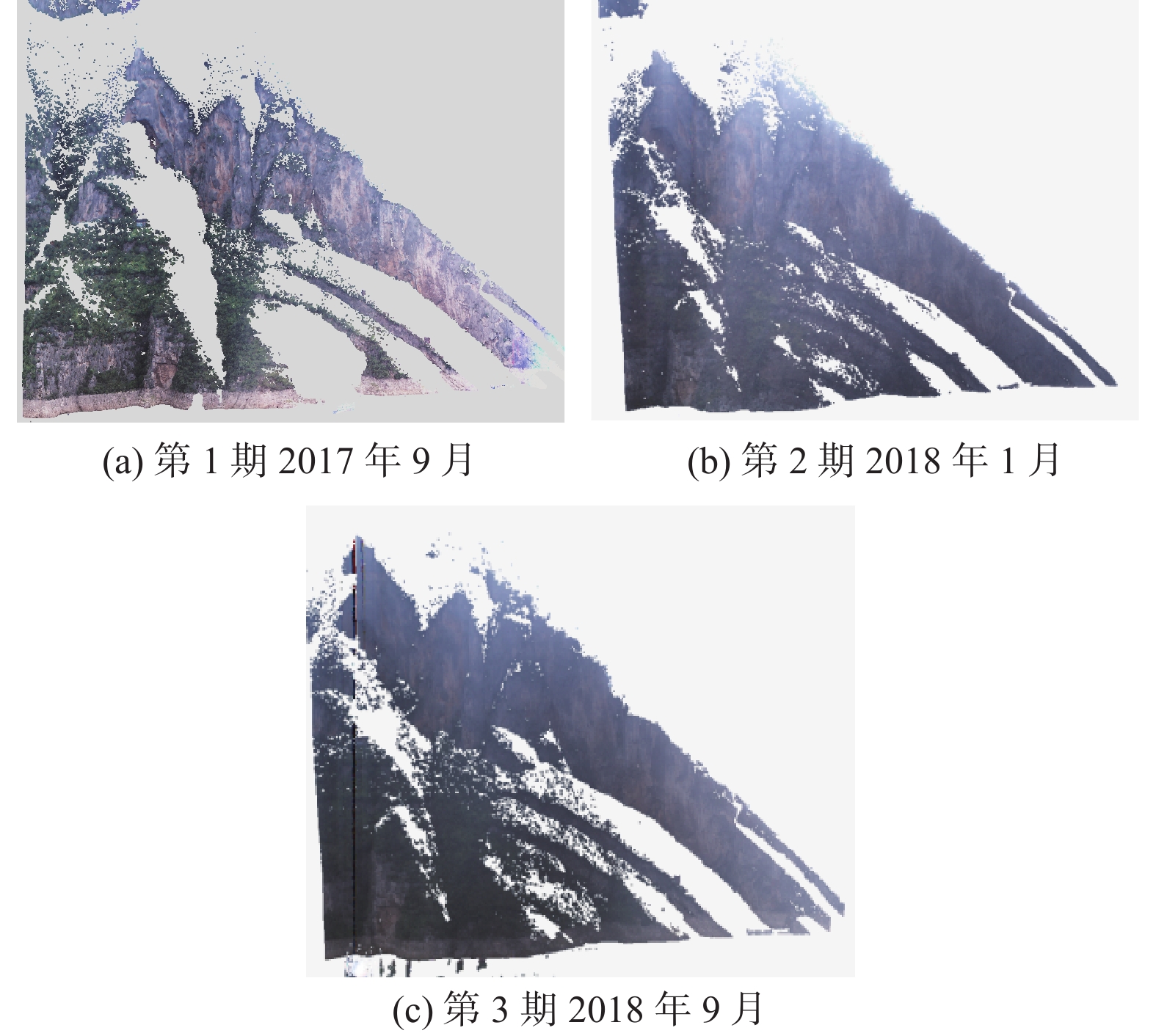
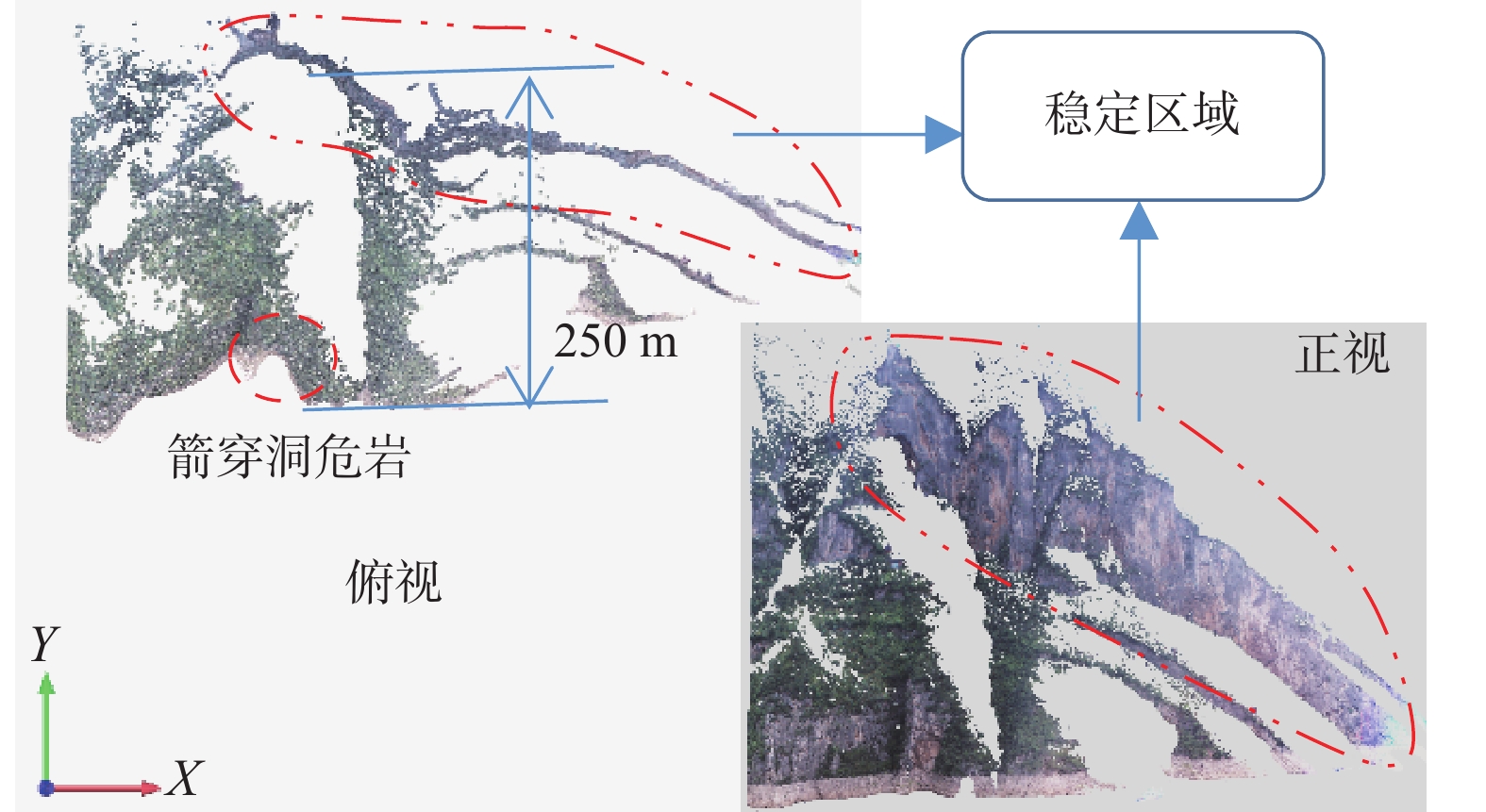
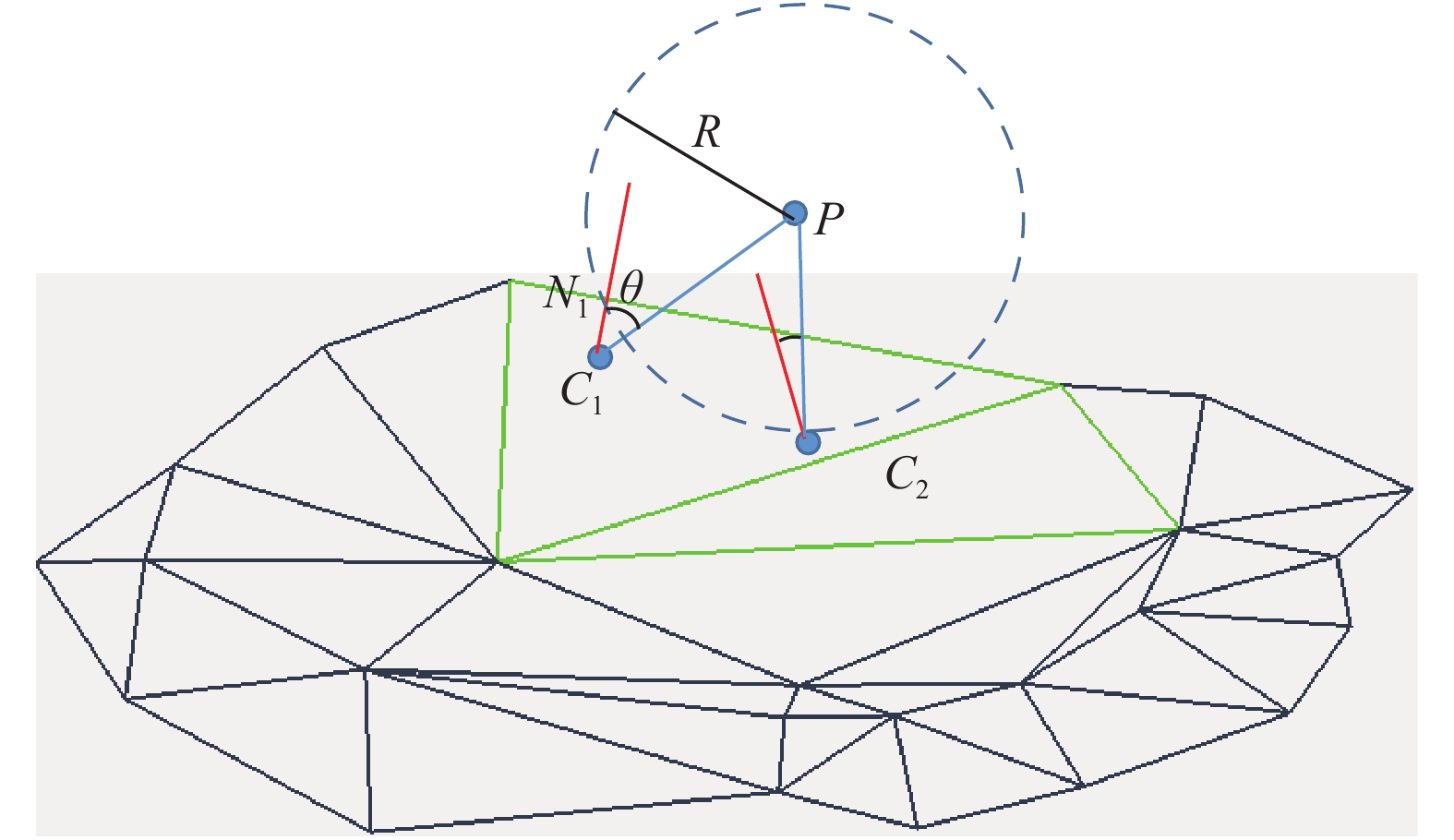
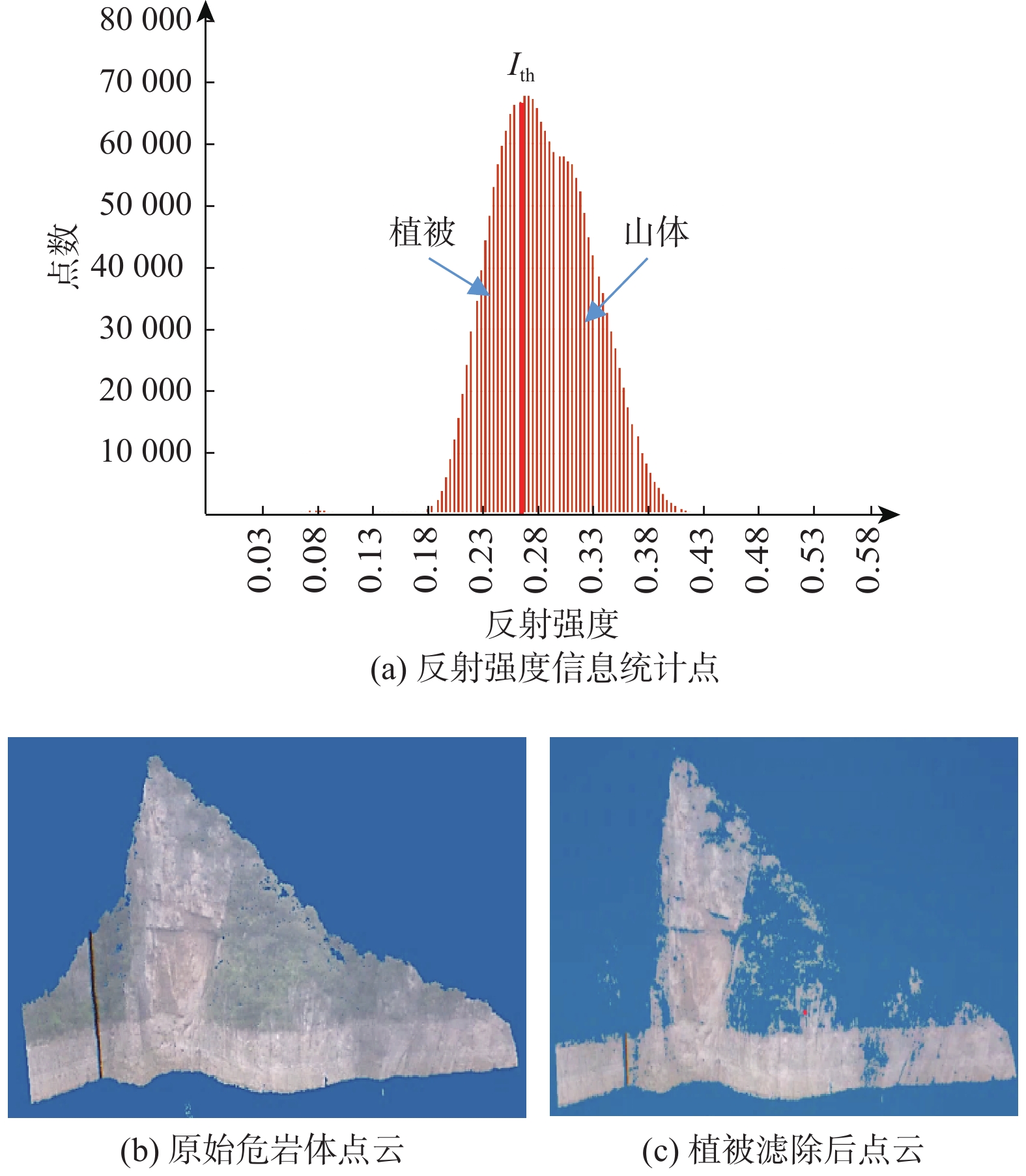
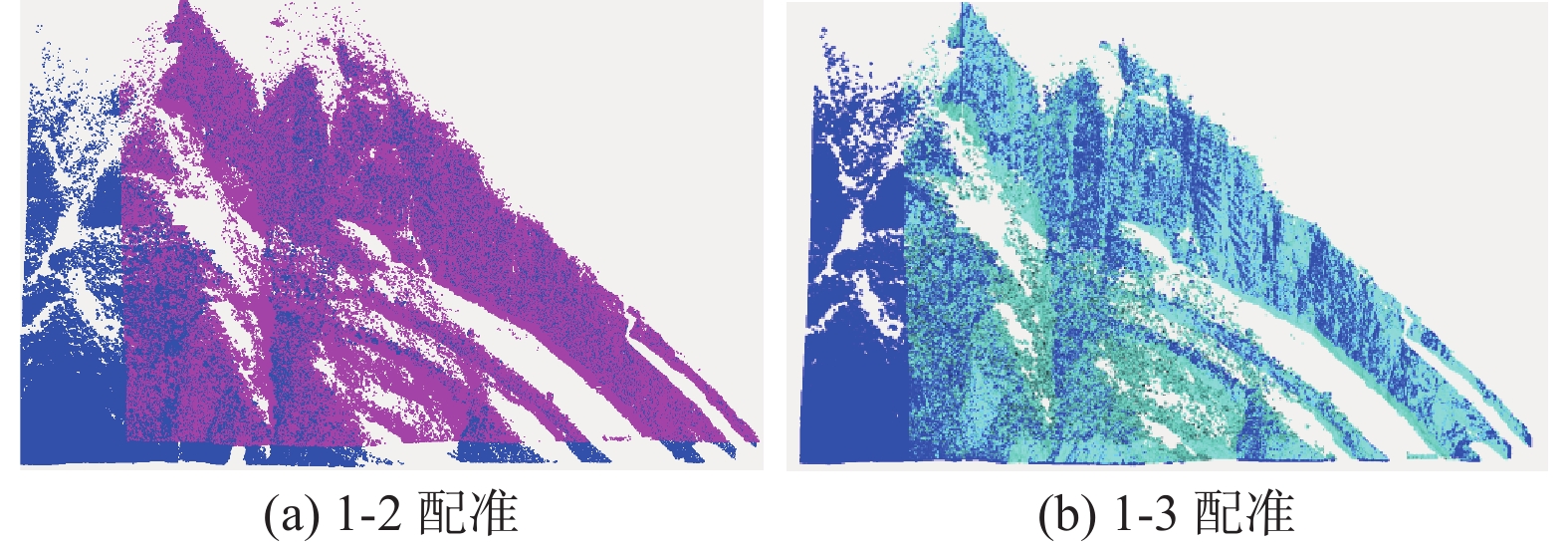
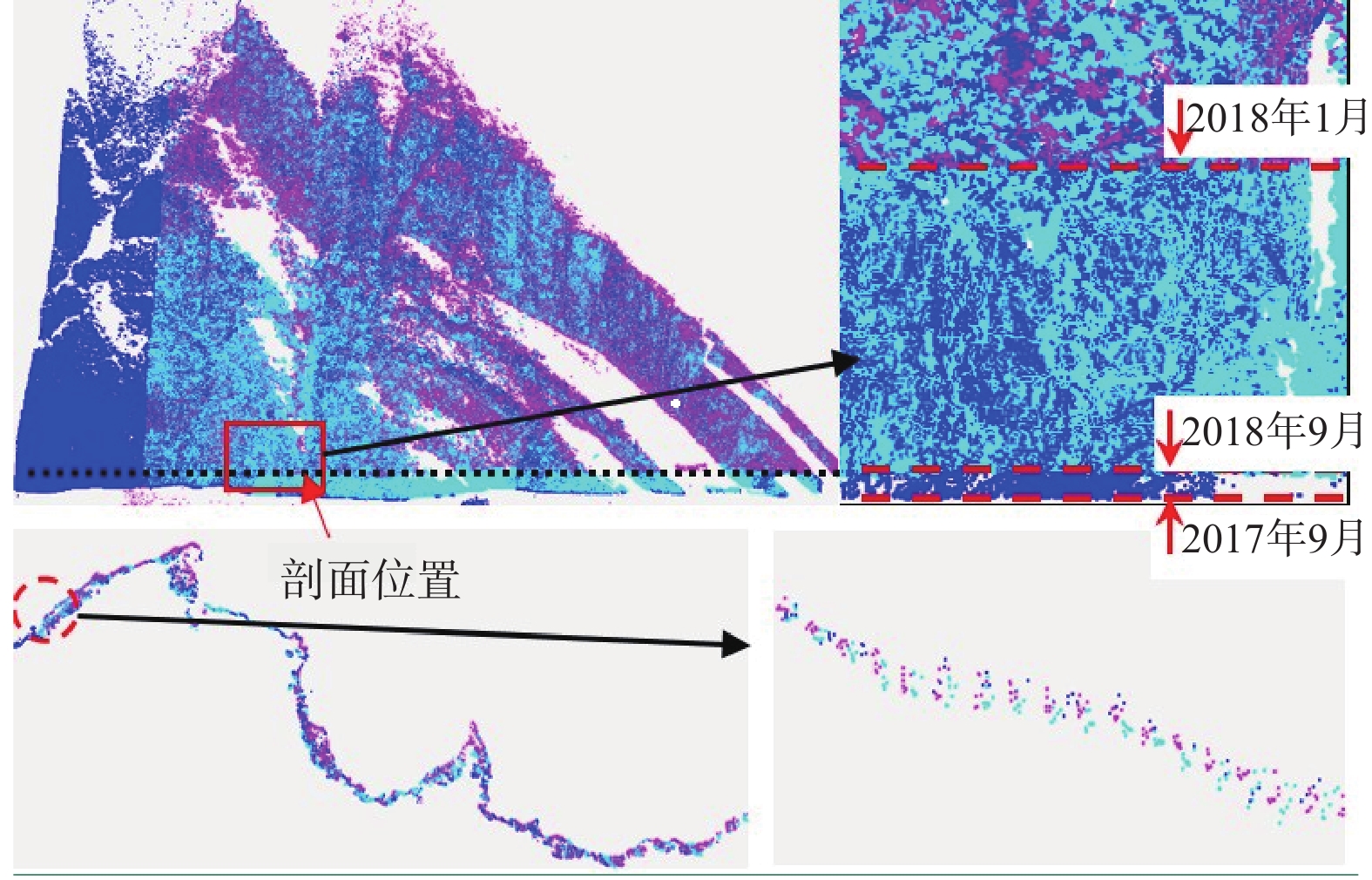
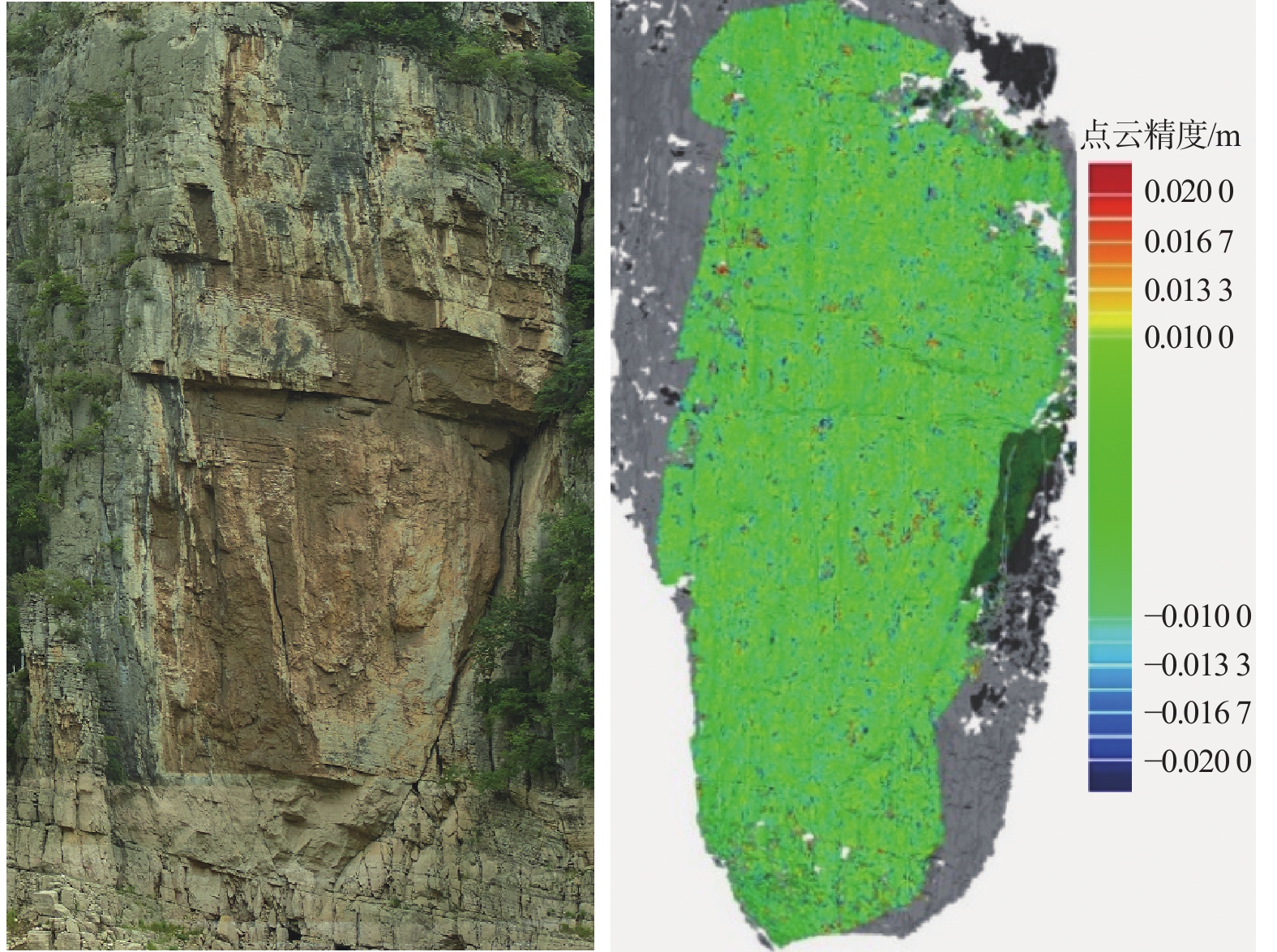
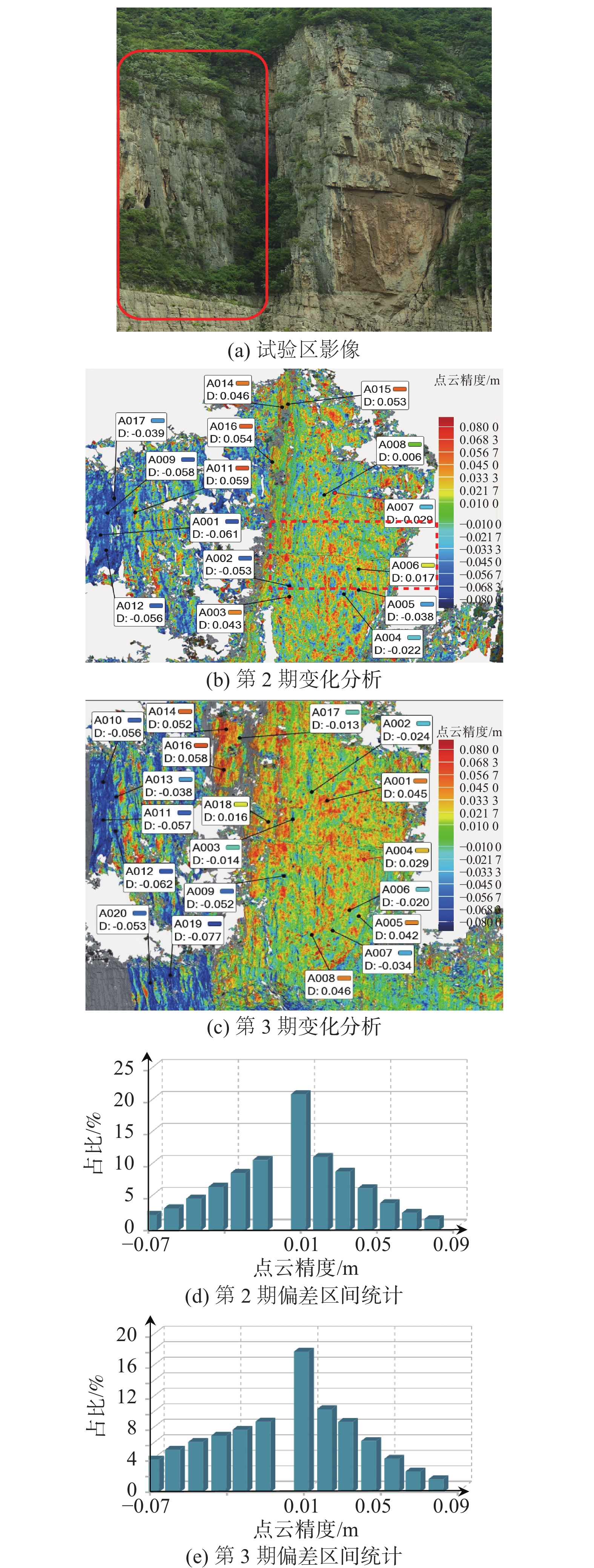
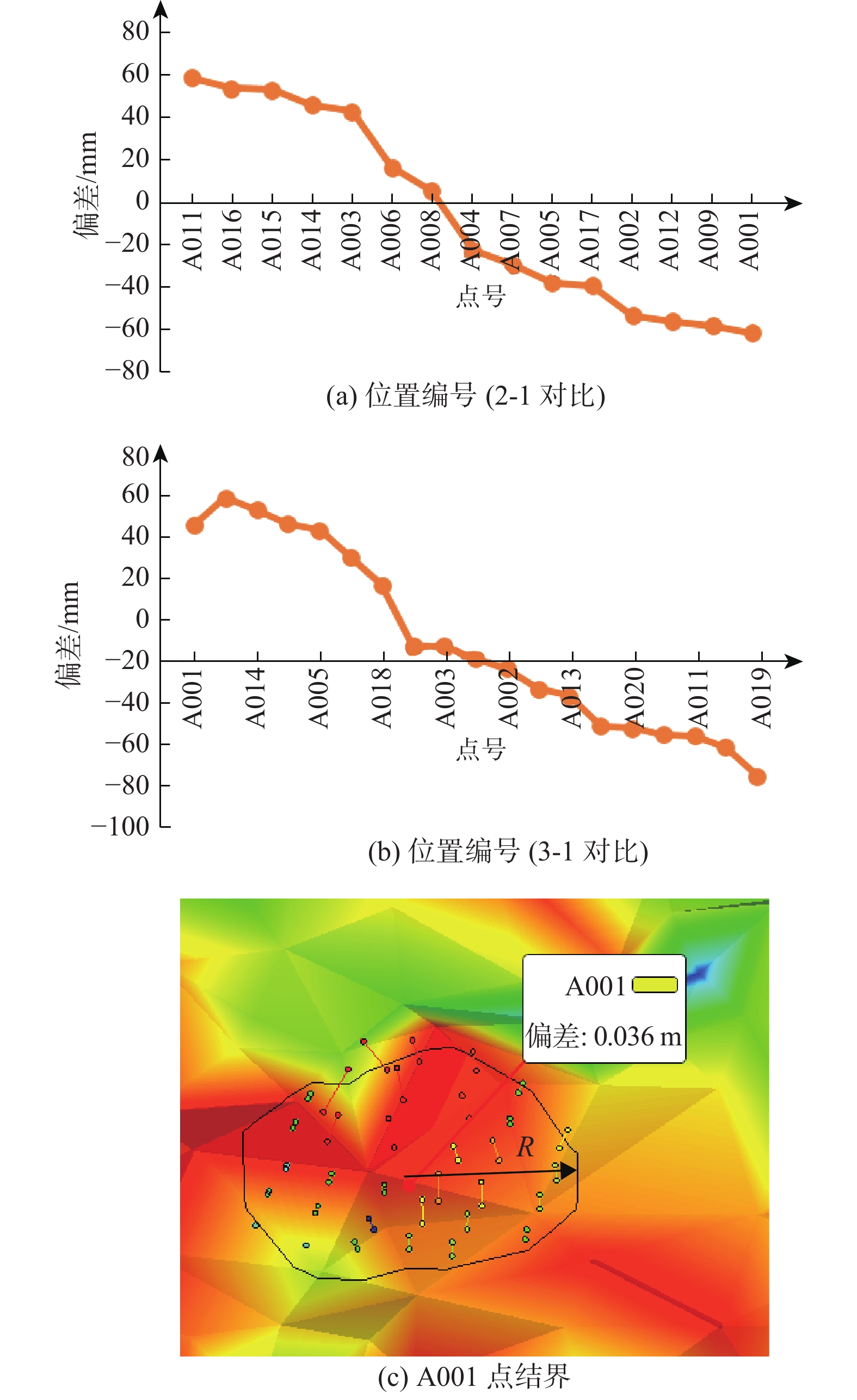
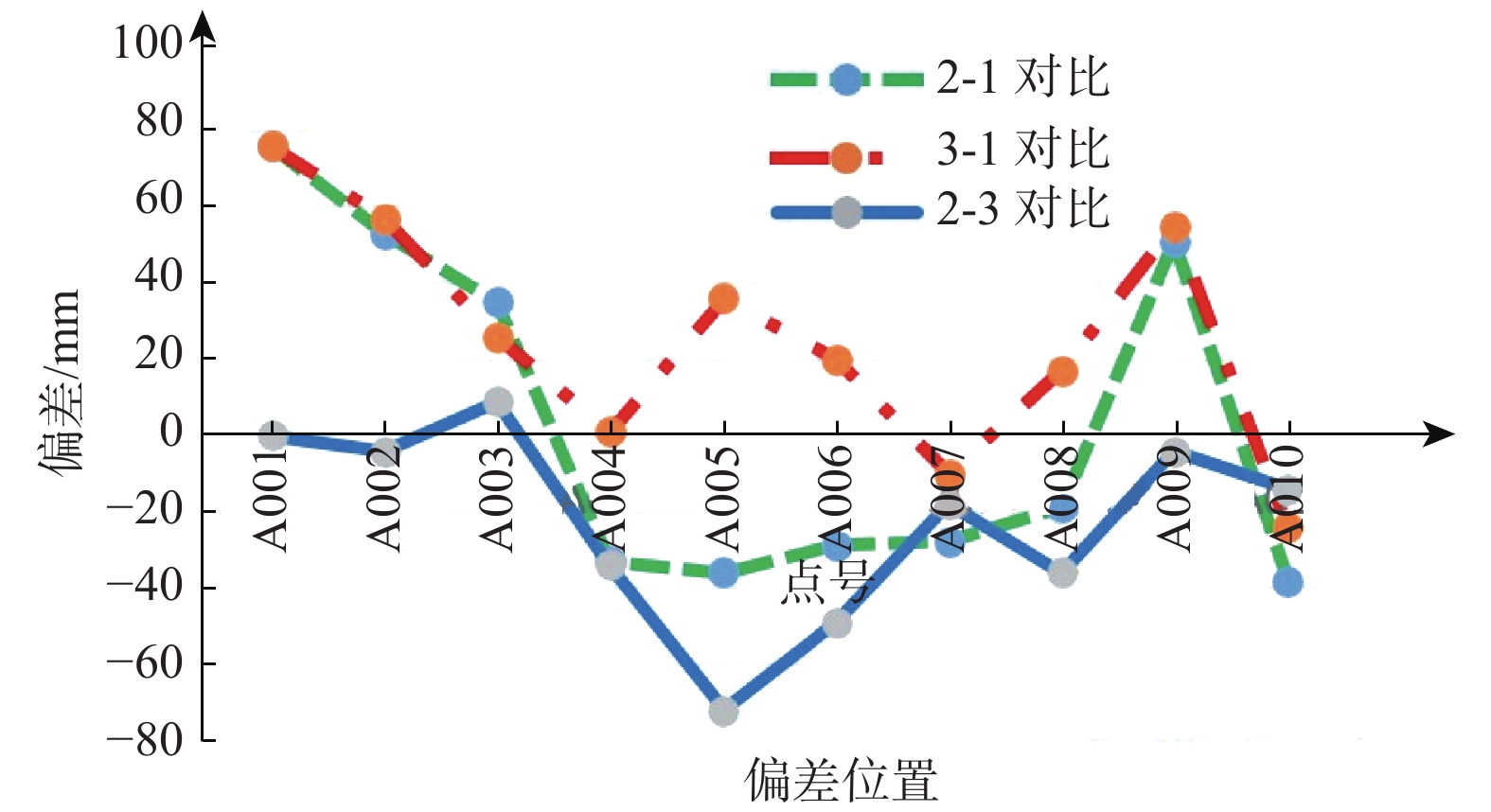
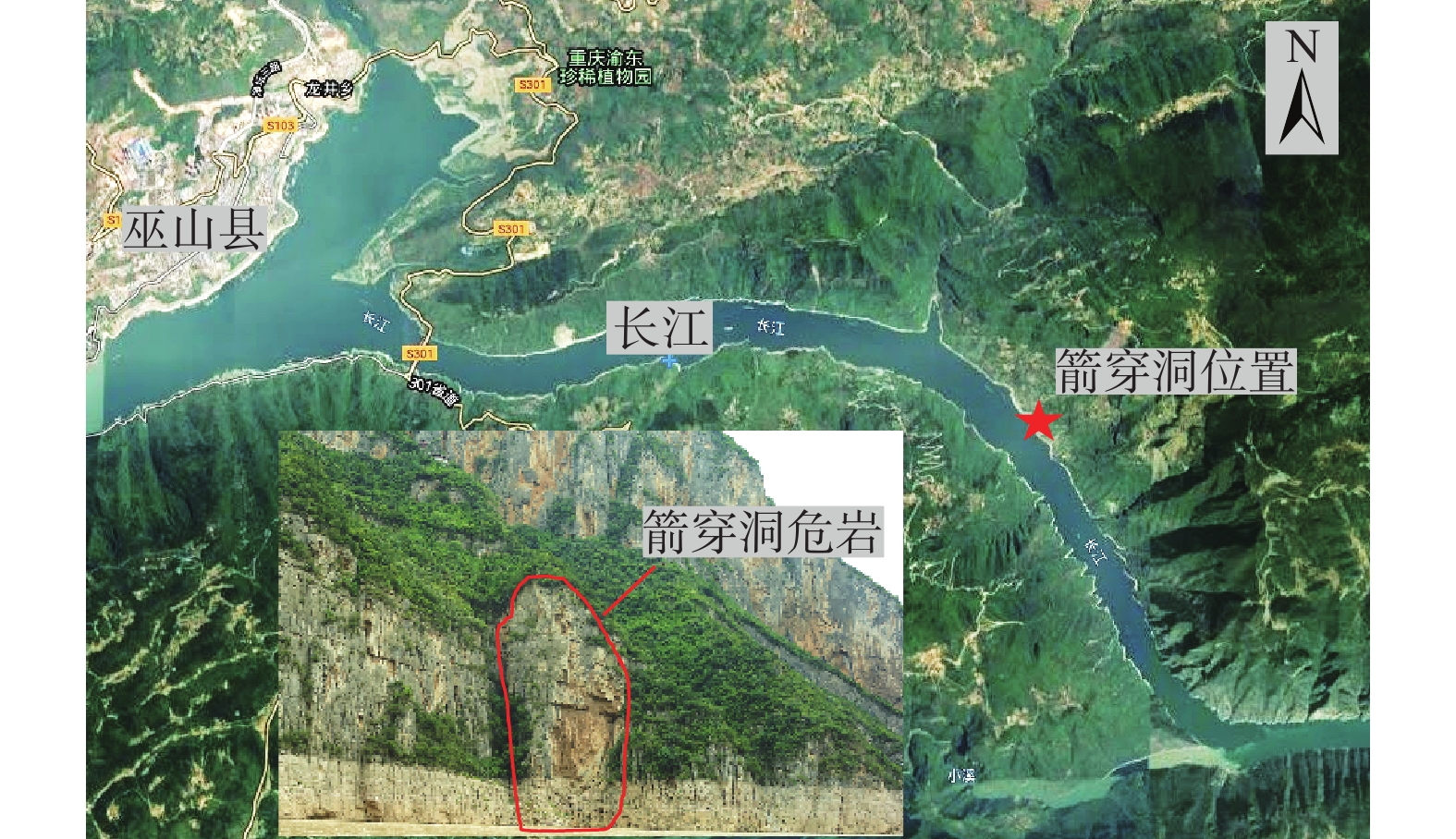
三峡水库周期性蓄水改变了岸坡内的地下水渗流场和应力场,降低岩土体的剪切强度,对库岸边坡、岩体稳定性影响很大。以往库区岸坡岩体形变监测主要通过设置固定点进行观测,难以发现岩体整体变化情况。地面三维激光扫描方法能获取岩体整体表面厘米精度的点云数据,具有无需接触目标、获取速度快、精度高等特点,非常适合库区高陡危岩体表面三维形变监测。以巫山箭穿洞危岩体为例,采用地面三维激光扫描方法对箭穿洞危岩体进行了为期2年(2017—2018年)共3期监测,以第一期观测目标周围稳定岩体数据为基准,对数据进行重叠点云迭代配准,点云配准精度优于±2.7 cm。针对箭穿洞危岩体在观测时段内的变化情况,构建危岩体区域的基准不规则三角网模型,以点到基准面最近距离法结合危岩体变化区间分析其变形。通过对比分析箭穿洞危岩体3期观测数据,发现相对于2017年,2018年箭穿洞危岩体左侧岩体有变形趋势;在库区蓄水阶段,危岩体局部多处存在明显凹陷变化,局部因蓄水影响发生约−0.03~−0.07 m变形。结果证明三维激光扫描技术在库岸高陡边坡形变监测中的有效性,为三峡库区高陡危岩体形变监测及地质灾害防治工作提供了参考。
Abstract:Changes in water level of the Three Gorges Reservoir are easy to induce the deformation and failure of the reservoir slope. Periodic impoundment changes in the groundwater seepage field and stress field in the reservoir slope reduce the shear strength of rock and soil mass, and have a great impact on the stability of the reservoir bank slope and rock mass. It is urgent for the deformation monitoring of bank slopes in the reservoir area. It is difficult to find out the overall change of rock mass by setting fixed observation points, and the terrestrial laser scanning method (TLS) can obtain the point cloud data of the overall rock mass surface with centimeter accuracy, which is very suitable for the monitoring of rock mass of characteristics of no contact with the target, fast acquisition speed and high precision. In this paper, the terrestrial laser scanning method is used to monitor the dangerous rock mass of Jianchuandong in Wuxia county for two years (2017—2018) and three periods data are acquired. The stable rock mass data around the observation target of the first period is selected as datum and the iterative closest point registration (ICP) is carried out with the overlapping point cloud. The registration accuracy of the point cloud is better than ± 2.7 cm, which realizes the accurate alignment of multi-period data. According to the change of dangerous rock mass in the observation period, the datum TIN model of dangerous rock body area is constructed, and the deformation of dangerous rock mass is analyzed with the nearest distance method from point to reference surface combined with the change range of dangerous rock mass. Through the comparative analysis of the 3 periods observation data of the Jianchuandong dangerous rock mass, it is found that the dangerous rock mass has the expansion trend in 2018 compared with the left rock mass in 2017. In the reservoir water storage stage, there are obvious sag changes in some parts of the dangerous rock body, and the local deformation is about 30-70 mm due to the influence of water storage. The experiment proves the correctness and validity of the proposed monitoring method, which provides reference for the monitoring of dangerous rock state and the prevention and control of geological disasters in the Three Gorges Reservoir area.
-

-
表 1 Riegl VZ-1000激光扫描仪主要技术指标
Table 1. Main technical indexes of Riegl VZ-1000
性能指标 参数 测程 1.5 ~ 1200.0+ m 点位精度 5 mm@ 100 m 扫描视角 360° (H) × 100° (V) 角度分辨率 1.8 arcsec 激光等级 Class1 表 2 危岩体典型位置测量
Table 2. Typical position measurement of dangerous rock mass
/m 对比期数 位置1 位置2 位置3 位置4 位置5 2-1 −0.017 −0.012 −0.028 −0.010 −0.013 3-1 −0.002 0.005 0.012 0.027 0.010 2-3 −0.015 −0.017 −0.040 −0.037 −0.023 -
[1] 王尚庆, 徐进军. 滑坡灾害短期临滑预报监测新途径研究[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版),2006,28(5):385 − 388. [WANG Shangqing, XU Jinjun. New method to monitor and forecast landslide disaster in short-term[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences),2006,28(5):385 − 388. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 徐进军, 王海城, 罗喻真, 等. 基于三维激光扫描的滑坡变形监测与数据处理[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(7):2188 − 2191. [XU Jinjun, WANG Haicheng, LUO Yuzhen, et al. Deformation monitoring and data processing of landslide based on 3D laser scanning[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(7):2188 − 2191. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2010.07.027
[3] JABOYEDOFF M, OPPIKOFER T, ABELLÁN A, et al. Use of LIDAR in landslide investigations: a review[J]. Natural Hazards,2012,61(1):5 − 28.
[4] 褚宏亮, 殷跃平, 曹峰, 等. 大型崩滑灾害变形三维激光扫描监测技术研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(3):128 − 134. [CHU Hongliang, YIN Yueping, CAO Feng, et al. Research on deformation monitoring of large collapses and landslides based on 3D laser scanning technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(3):128 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 刘明坤, 段奇三, 赵晨曦, 等. 三维激光扫描在滑坡灾害变形中的监测应用[J]. 测绘通报,2016(2):147 − 149. [LIU Mingkun, DUAN Qisan, ZHAO Chenxi, et al. Application of 3D laser scanning in monitoring landslide deformation[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2016(2):147 − 149. (in Chinese)
[6] HOBBS P, HUMPHREYS B, REES J, et al. Monitoring the role of landslides in ‘soft cliff’ coastal recession[C]// International Conference on Instability, Planning & Management. Ventnor: Thomas Telford, 2002: 589−600.
[7] 董秀军, 黄润秋. 三维激光扫描技术在高陡边坡地质调查中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(增刊2):3629 − 3635. [DONG Xiujun, HUANG Runqiu. Application of 3D laser scanning technology to geologic survey of high and steep slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2006,25(Sup2):3629 − 3635. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] ABELLÁN A, VILAPLANA J M, CALVET J, et al. Rockfall monitoring by terrestrial laser scanning-case study of the basaltic rock face at Castellfollit de la Roca(Catalonia, Spain)[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2011,11(3):829 − 841. doi: 10.5194/nhess-11-829-2011
[9] 谢谟文, 胡嫚, 杜岩, 等. TLS技术及其在滑坡监测中的应用进展[J]. 国土资源遥感,2014,26(3):8 − 15. [XIE Mowen, HU Man, DU Yan, et al. Application of TLS technique to landslide monitoring: Summarization and prospect[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources,2014,26(3):8 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 裴东东, 官云兰, 张勇峰, 等. 基于车载三维激光扫描系统的滑坡变形监测方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2016,27(1):71 − 76. [PEI Dongdong, GUAN Yunlan, ZHANG Yongfeng, et al. Landslide deformation monitoring method based on vehicular laser scanning system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2016,27(1):71 − 76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 王文沛, 李滨, 黄波林, 等. 三峡库区近水平厚层斜坡滑动稳定性研究—以重庆巫山箭穿洞危岩为例[J]. 地质力学学报,2016,22(3):725 − 731. [WANG Wenpei, LI Bin, HUANG Bolin, et al. Stability analysis of sub-horizontal thick-bedded slope in Three Gorges Reservoir Area: A Case study of Jianchuandong dangerous rock mass in Wushan, Chongqing[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2016,22(3):725 − 731. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2016.03.026
[12] WANG G, PHILIPS D, JOYCE J, et al. The integration of TLS and continuous GPS to study landslide deformation: A case study in Puerto Rico[J]. Journal of Geodetic Science,2011,1(1):25 − 34.
[13] 朱海雄, 隋立春, 鲁凯翔. 三维激光扫描技术在危岩体变形监测中的应用[J]. 测绘通报,2017(11):68 − 71. [ZHU Haixiong, SUI Lichun, LU Kaixiang. Application of terrestrial 3D laser scanning technology in deformation monitoring of dangerous rock mass[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2017(11):68 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 方良斌, 张宏魏, 詹建勇, 等. 基于移动平均法的危岩点云数据处理及变形分析[J]. 人民长江,2019,50(4):152 − 156. [FANG Liangbin, ZHANG Hongwei, ZHAN Jianyong, et al. Point cloud data processing of dangerous rock and deformation analysis based on moving average method[J]. Yangtze River,2019,50(4):152 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 徐寿志, 程鹏飞, 张玉, 等. 地面三维激光扫描仪的检校与测量精度评定[J]. 测绘通报,2016(2):79 − 83. [XU Shouzhi, CHENG Pengfei, ZHANG Yu, et al. Calibration and accuracy evaluation of terrestrial laser scanner[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping,2016(2):79 − 83. (in Chinese)
[16] MAT ZAM P M, FUAD N A, YUSOFF A R, et al. Evaluating the performance of terrestrial laser scanning for landslide monitoring[C]//Int Arch Photogramm Remote Sens Spatial Inf Sci, 2018: 35-55.
[17] OPPIKOFER T, JABOYEDOFF M, BLIKRA L, et al. Characterization and monitoring of the Aknes rockslide using terrestrial laser scanning[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2009(9):1003 − 1019.
[18] ABELLÁN A, JABOYEDOFF M, OPPIKOFER T, et al. Detection of precursory deformation using a TLS application to spatial prediction of rockfalls[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2009(9):365 − 372.
-



 下载:
下载: