Secondary consolidation characteristics and settlement calculation of soft soil treated by overload preloading
-
摘要:
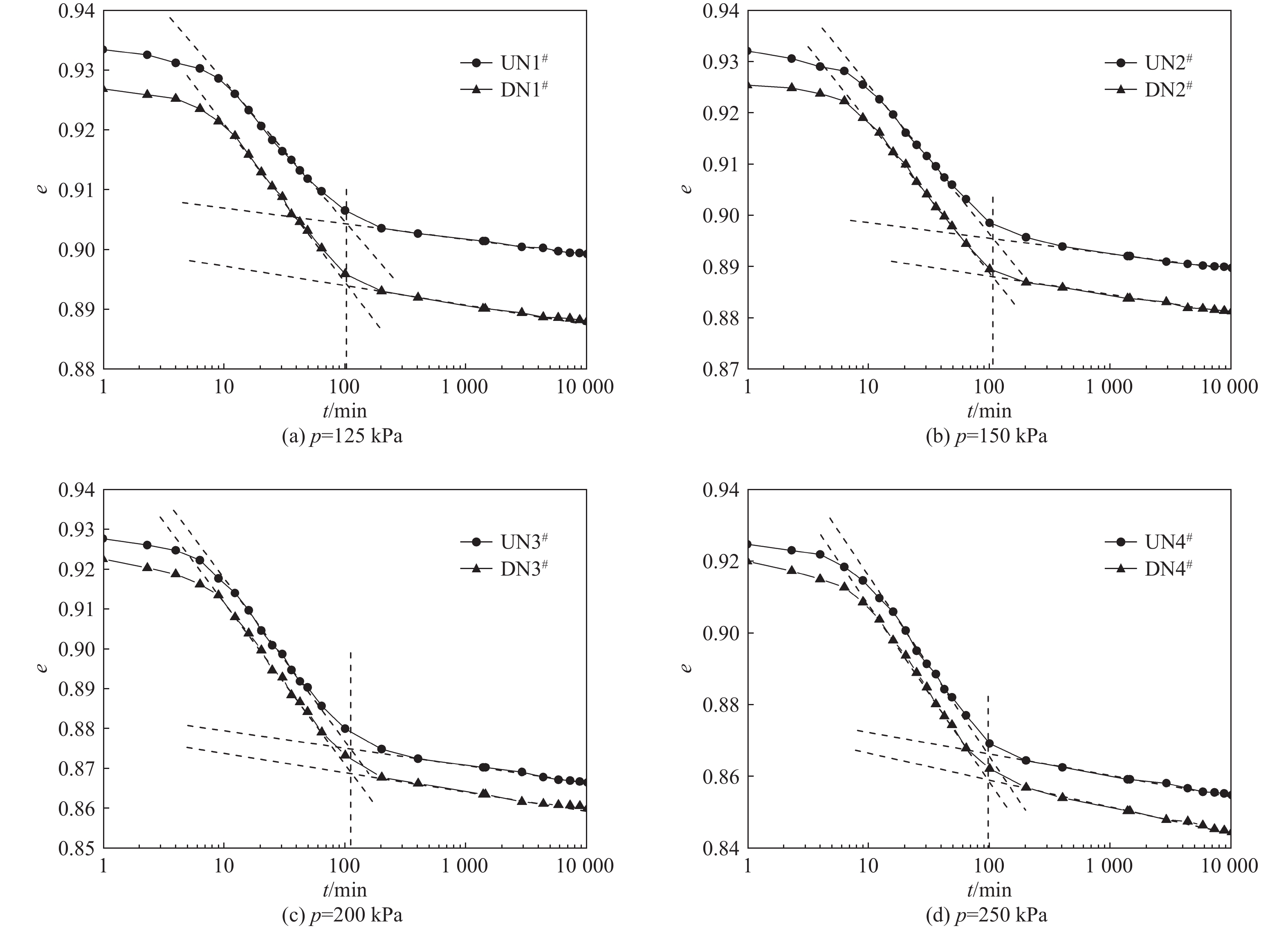
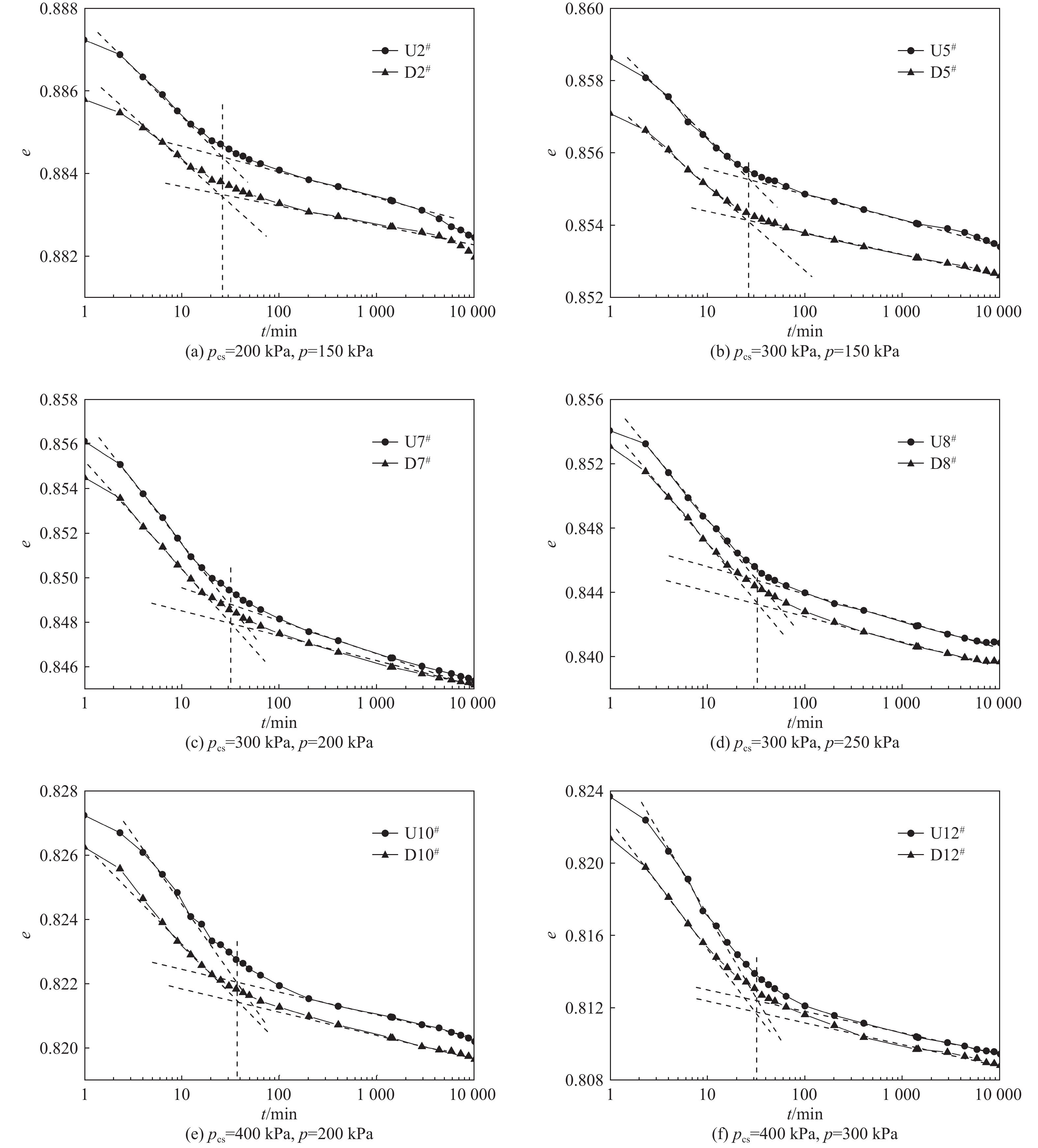
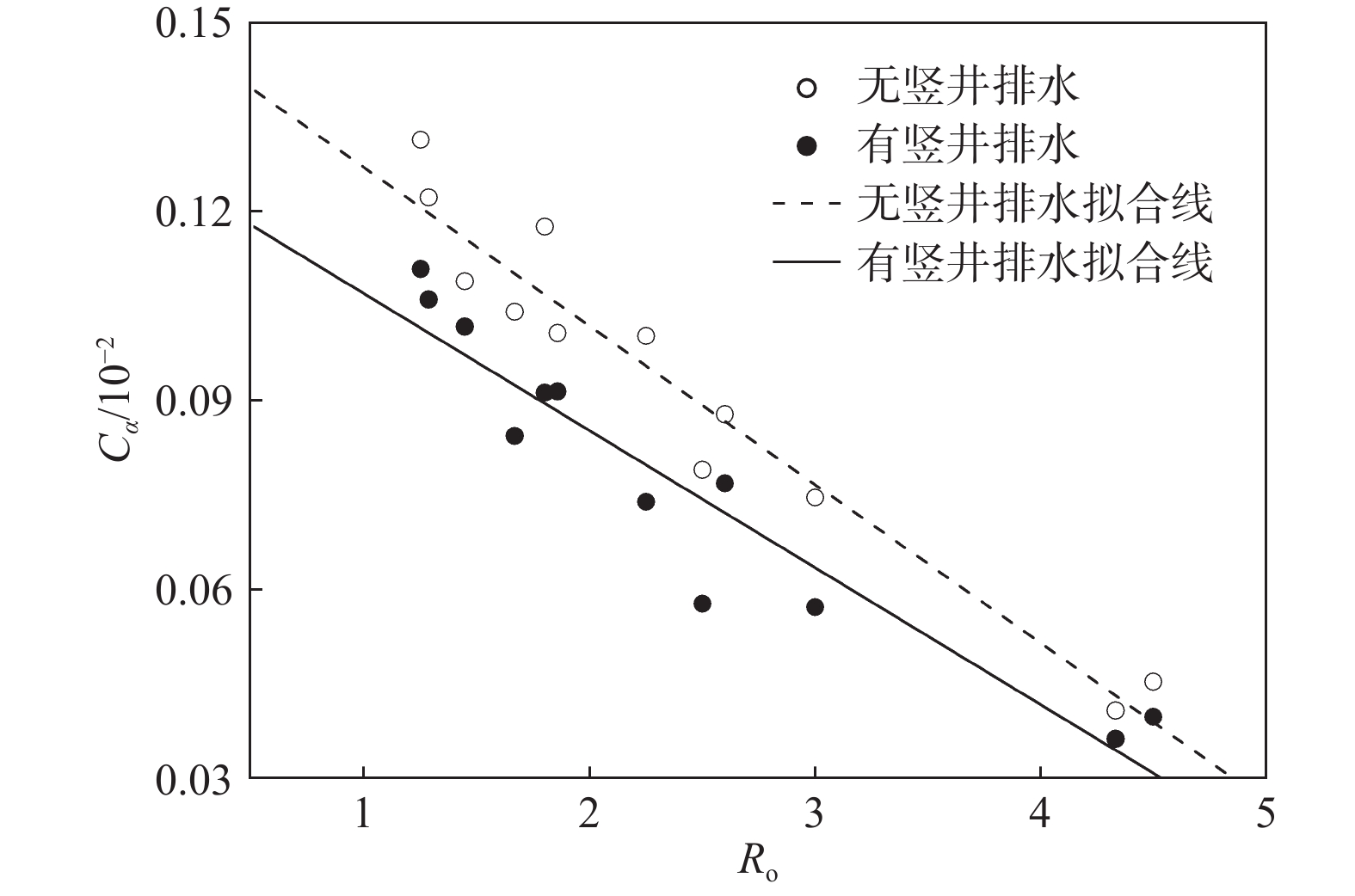
为了研究超载预压软土的次固结特征,分析超载预压处理软土地基的工后沉降,文章考虑应力历史对软土结构性的影响,模拟现场工况,对重塑洞庭湖软土试样进行超载预压后再压缩的一维固结蠕变试验。研究结果表明:经过超载预压的软土卸荷后再进行加载,压缩变形过程中主固结时间明显缩短,约为未经超载预压处理软土主固结时间的1/3,打设排水竖井对软土主固结时间几乎没影响;预压荷载越大,次固结系数越小,超载预压有利于消除软土的次固结沉降;随着建(构)筑物荷载的增加,次固结系数增大;打设排水竖井,未经预压处理软土的次固结系数略有增加,经过超载预压处理软土的次固结系数略有减小,但影响效果不是很明显。考虑应力历史,引入超载增量比,发现次固结系数与超载增量比呈线性递减关系,建立了相应的计算模型,提出了次固结沉降计算公式。试验及分析结果对预压处理地基的设计和施工具有一定的指导意义。
Abstract:In order to examine the secondary consolidation characteristics of the soft soil treated with overloading preloading and analyze the post-construction settlement of the soft soil foundation treated with overloading preloading, the soft soil of the Dongting Lake is remolded considering the influence of stress history on the structure of the soft soil. In the test, the field conditions are simulated, and the one-dimensional consolidation creep test of soft soil remolded samples is conducted after surcharge preloading and recompression. The results show that the main consolidation time of soft soil after unloading and loading after preloading is significantly shortened, which is about 1/3 that of soft soil without surcharge preloading, and the main consolidation time of soft soil is almost not affected by the construction of drainage shaft. Moreover, the higher the preloading, the smaller the secondary consolidation coefficient is, and the overloading preloading is helpful in eliminating the secondary consolidation settlement of soft soil. The secondary consolidation coefficient increases with the increasing building load. Furthermore, the secondary consolidation coefficient of soft soil without preloading increases slightly when the drainage shaft is set up, and that of soft soil after overload preloading decreases slightly, but the effect is not obvious. Considering the stress history and introducing the overload increment ratio, the relationship between the secondary consolidation coefficient and the overload increment ratio is found to be linearly decreasing. The corresponding calculation model is established, and the calculation formula of the secondary consolidation settlement is put forward. The results of the tests and analyses are of some guiding significance for the design and construction of precompression foundation.
-

-
表 1 试验土样基本物理力学性质指标
Table 1. Basic physical and mechanical properties of the test soil samples
力学指标 密度/(g·m−3) 含水量/% 土粒比重 孔隙比 压缩系数/MPa−1 液限/% 塑限/% 塑性指数 液性指数 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 取值 1.81 43.6 2.62 1.08 1.02 45.1 26.3 18.8 0.92 5.4 12.25 表 2 不同试验工况下的次固结系数
Table 2. Secondary consolidation coefficient under different test conditions
预压荷载
/kPa施加荷载
/kPa次固结系数 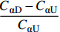 /%
/%
CαU/×10−2
(无竖井排水)CαD/×10−2
(有竖井排水)0 125 0.1916 0.2279 18.94 150 0.2641 0.2799 5.97 200 0.4269 0.4689 9.85 250 0.4887 0.5436 11.24 200 125 0.0790 0.0577 −27.01 150 0.1042 0.0844 −19.02 175 0.1316 0.1110 −15.66 300 125 0.0453 0.0397 −12.29 150 0.0746 0.0572 −23.36 175 0.1003 0.0739 −26.33 200 0.1177 0.0913 −22.45 250 0.1224 0.1061 −13.30 400 150 0.0407 0.0362 −11.16 200 0.0879 0.0769 −12.49 250 0.1008 0.0915 −9.22 300 0.1091 0.1018 −6.66 表 3 拟合参数
Table 3. Fitting parameters
排水条件 a b R2 无竖井排水 0.1529 0.0254 0.9365 有竖井排水 0.1289 0.0217 0.8933 -
[1] 龚晓南. 地基处理手册[M]. 3版. 北京: 中国建筑工出版社, 2008.
GONG Xiaonan. Foundation treatment manual[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Architecture Building Press, 2008.(in Chinese)
[2] 雷鸣, 王星华, 唐依民. 基于孔压实测资料的真空预压机理及沉降计算探讨[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2010,37(6):81 − 85. [LEI Ming, WANG Xinghua, TANG Yimin. Discussion of the mechanism of vacuum preloading and settlement calculation based on measured values of pore water pressure[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2010,37(6):81 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.06.016
[3] 刘景锦, 雷华阳, 卢海滨, 等. 真空预压法淤堵泥层形成机理及预测模型研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(3):61 − 71. [LIU Jingjin, LEI Huayang, LU Haibin, et al. A study of siltation mud formation mechanism and prediction model of vacuum preloading method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(3):61 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 周顺华, 许恺, 王炳龙, 等. 软土地基超载卸载再加荷的沉降研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2005,27(10):1226 − 1229. [ZHOU Shunhua, XU Kai, WANG Binglong, et al. Research on settlement of soft ground under overloading-unloading and reloading[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2005,27(10):1226 − 1229. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2005.10.024
[5] 李国维, 杨涛, 殷宗泽. 公路软基超载预压机理研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2006,28(7):896 − 901. [LI Guowei, YANG Tao, YIN Zongze. Study of mechanism about surcharge preloading method on the soft ground of highways[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2006,28(7):896 − 901. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.07.017
[6] 胡亚元. 考虑次压缩时分级超载预压时间的确定方法[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),2010,44(5):962 − 968. [HU Yayuan. Method of determining duration of stage constructed surcharge preloading with a view to second settlement[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2010,44(5):962 − 968. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2010.05.021
[7] 李国维, 盛维高, 蒋华忠, 等. 超载卸荷后再压缩软土的次压缩特征及变形计算[J]. 岩土工程学报,2009,31(1):118 − 123. [LI Guowei, SHENG Weigao, JIANG Huazhong, et al. Secondary compression characteristics and settlement calculation of soft clay under overloading-unloading and reloading[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2009,31(1):118 − 123. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.01.020
[8] XU G Z, YIN J. Compression behavior of secondary clay minerals at high initial water contents[J]. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology,2016,34(8):721 − 728.
[9] SHAHRIAR A R, JADID R. An experimental investigation on the effect of thixotropic aging on primary and secondary compression of reconstituted dredged clays[J]. Applied Clay Science,2018,162:524 − 533. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2018.05.023
[10] WU Z L, DENG Y F, CUI Y J, et al. Investigations on secondary compression behaviours of artificial soft sand-clay mixtures[J]. Soils and Foundations,2019,59(2):326 − 336. doi: 10.1016/j.sandf.2018.11.008
[11] 桂跃, 余志华, 刘海明, 等. 高原湖相泥炭土次固结特性及机理分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2015,37(8):1390 − 1398. [GUI Yue, YU Zhihua, LIU Haiming, et al. Secondary consolidation properties and mechanism of plateau lacustrine peaty soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015,37(8):1390 − 1398. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11779/CJGE201508005
[12] IMAI Y, AKAISHI M, HUANG W C, et al. Long-term settlement behavior of soft grounds and secondary compression[J]. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers,2017,40(5):361 − 369. doi: 10.1080/02533839.2017.1321971
[13] 朱向荣, 潘秋元. 超载卸除后地基变形的研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版),1991,25(2):246 − 257. [ZHU Xiangrong, PAN Qiuyuan. The deformation of subsoil after surcharge unloading[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Engineering Science),1991,25(2):246 − 257. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] MESRI G, STARK T D, AJLOUNI M A, et al. Secondary compression of peat with or without surcharging[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,1997,123(5):411 − 421. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(1997)123:5(411)
[15] ALONSO E E, GENS A, LLORET A. Precompression design for secondary settlement reduction[J]. Géotechnique,2000,50(6):645 − 656. doi: 10.1680/geot.2000.50.6.645
[16] 殷宗泽, 张海波, 朱俊高, 等. 软土的次固结[J]. 岩土工程学报,2003,25(5):521 − 526. [YIN Zongze, ZHANG Haibo, ZHU Jungao, et al. Secondary consolidation of soft soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2003,25(5):521 − 526. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2003.05.001
[17] 周秋娟, 陈晓平. 软土次固结特性试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2006,27(3):404 − 408. [ZHOU Qiujuan, CHEN Xiaoping. Test study on properties of secondary consolidation of soft soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2006,27(3):404 − 408. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.03.013
[18] 曾玲玲, 陈福全, 郭立群. 天然沉积结构性软土的超载预压变形性状试验[J]. 华侨大学学报(自然科学版),2012,33(4):435 − 439. [ZENG Lingling, CHEN Fuquan, GUO Liqun. Experimental study on deformation behavior of surcharge preloading for soft natural clays[J]. Journal of Huaqiao University(Natural Science),2012,33(4):435 − 439. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] CAI Y Q, HAO B B, GU C, et al. Effect of anisotropic consolidation stress paths on the undrained shear behavior of reconstituted Wenzhou clay[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,242:23 − 33. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.05.016
[20] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑地基处理技术规范: JGJ 79—2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2013.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Technical code for ground treatment of buildings: JGJ 79—2012[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2013. (in Chinese)
[21] 中华人民共和国水利部. 土工试验方法标准: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019.
Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for geotechnical testing method: GB/T 50123—2019[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[22] Methods of test for soils for civil engineering purposes —Part 5: Compressibility, permeability and durability tests: BS 1377—5:1990[S].
-




 下载:
下载: