Predicting seismic landslide hazard in the Batang fault zone of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau
-
摘要:
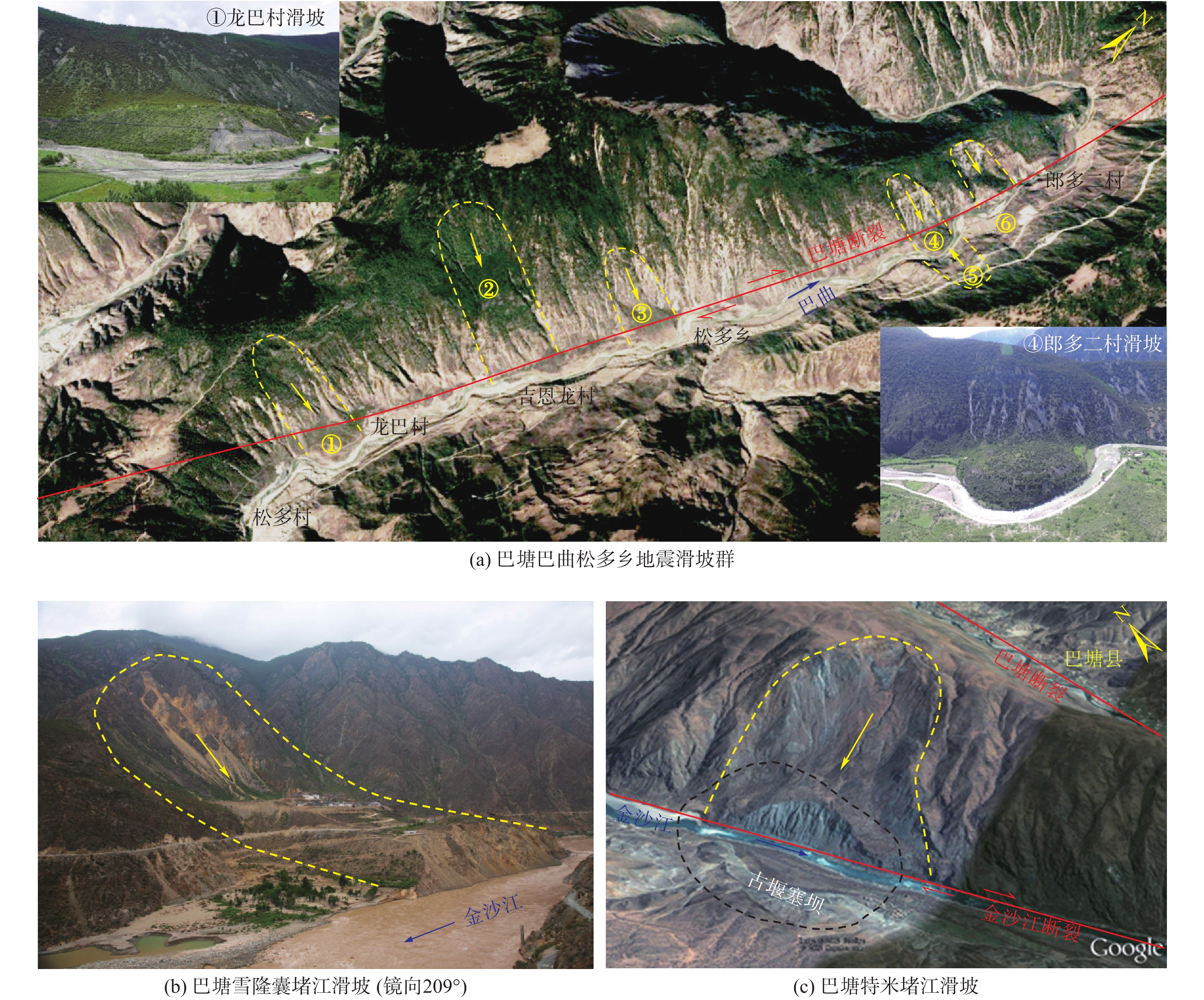
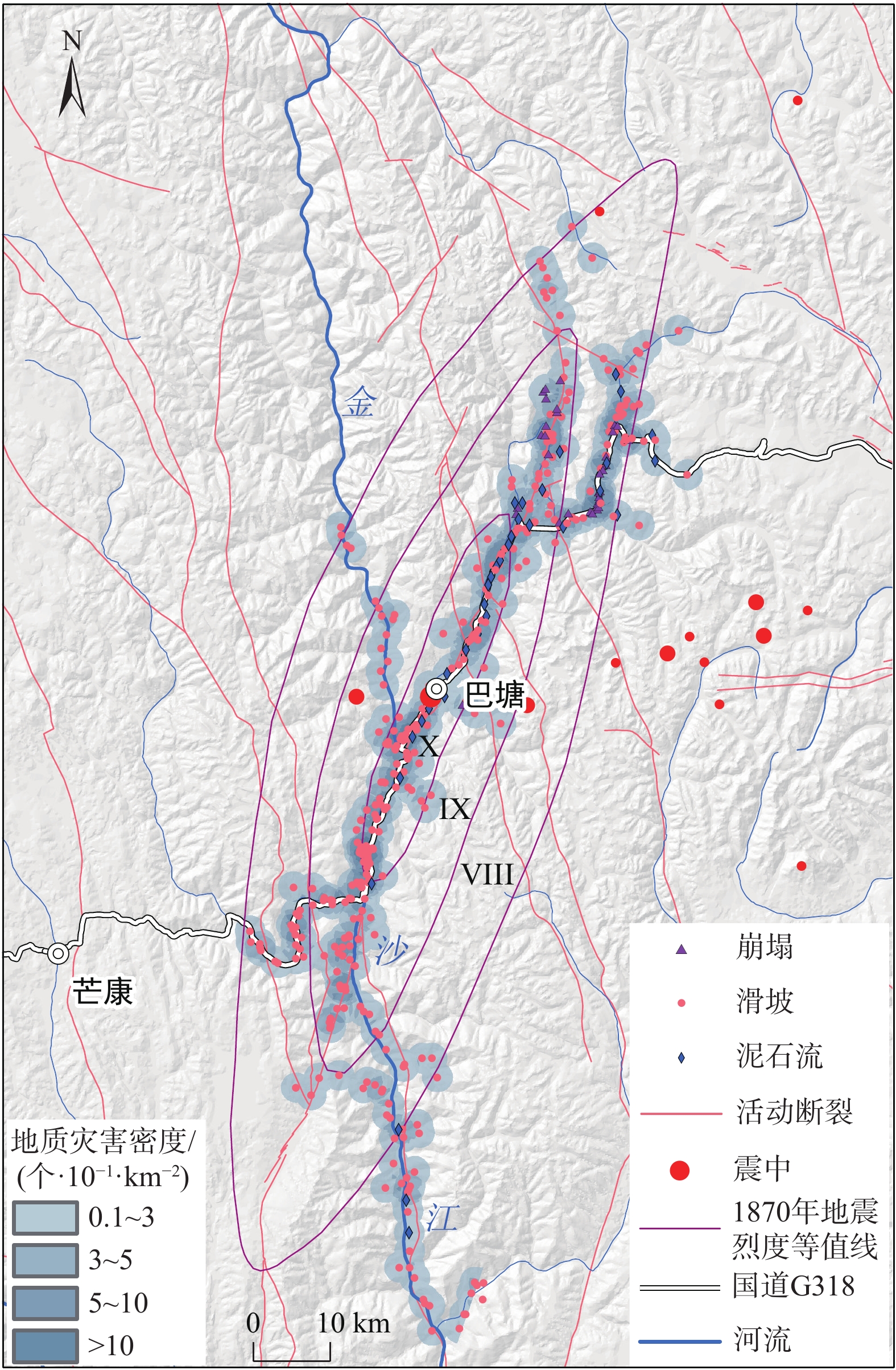
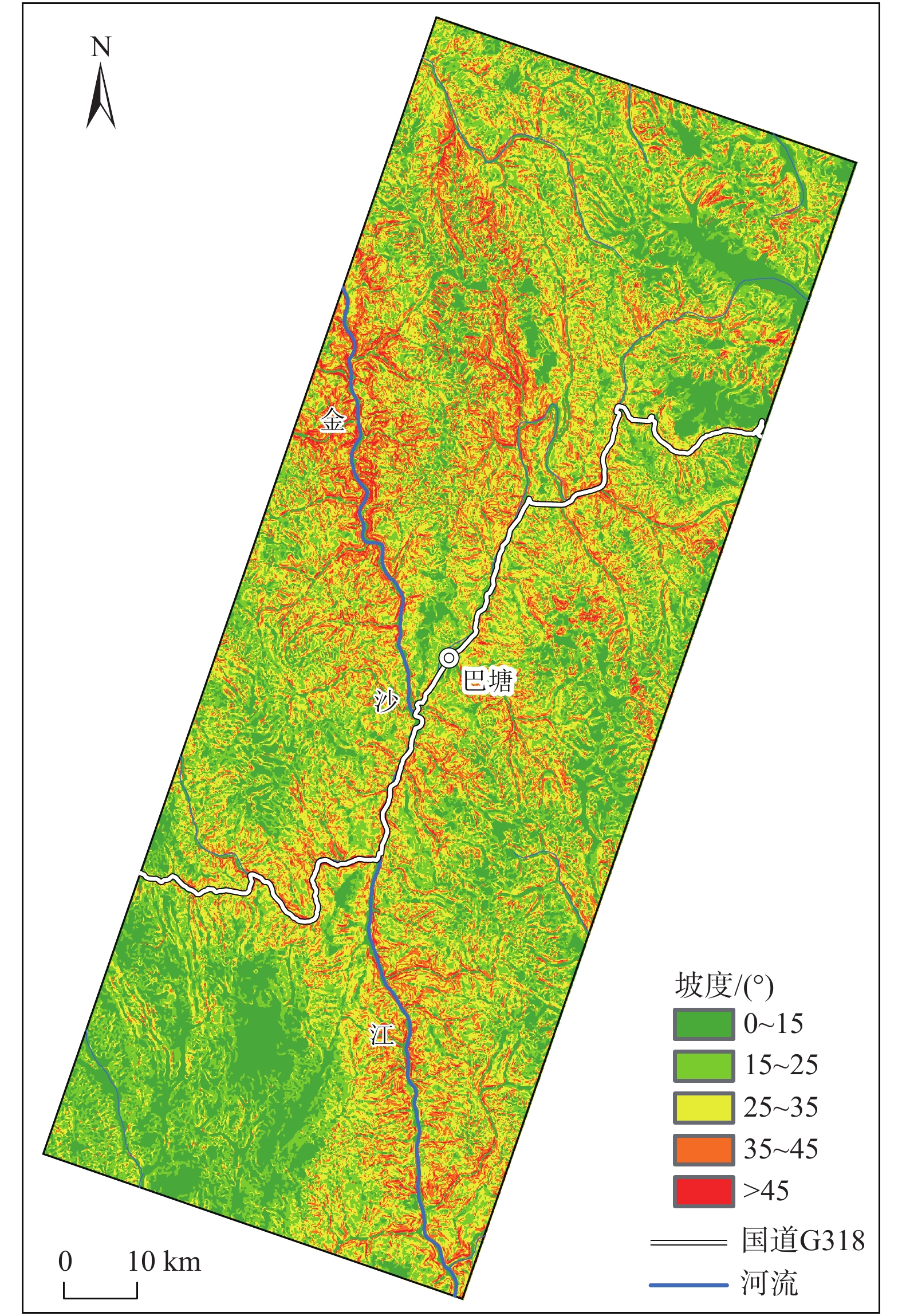
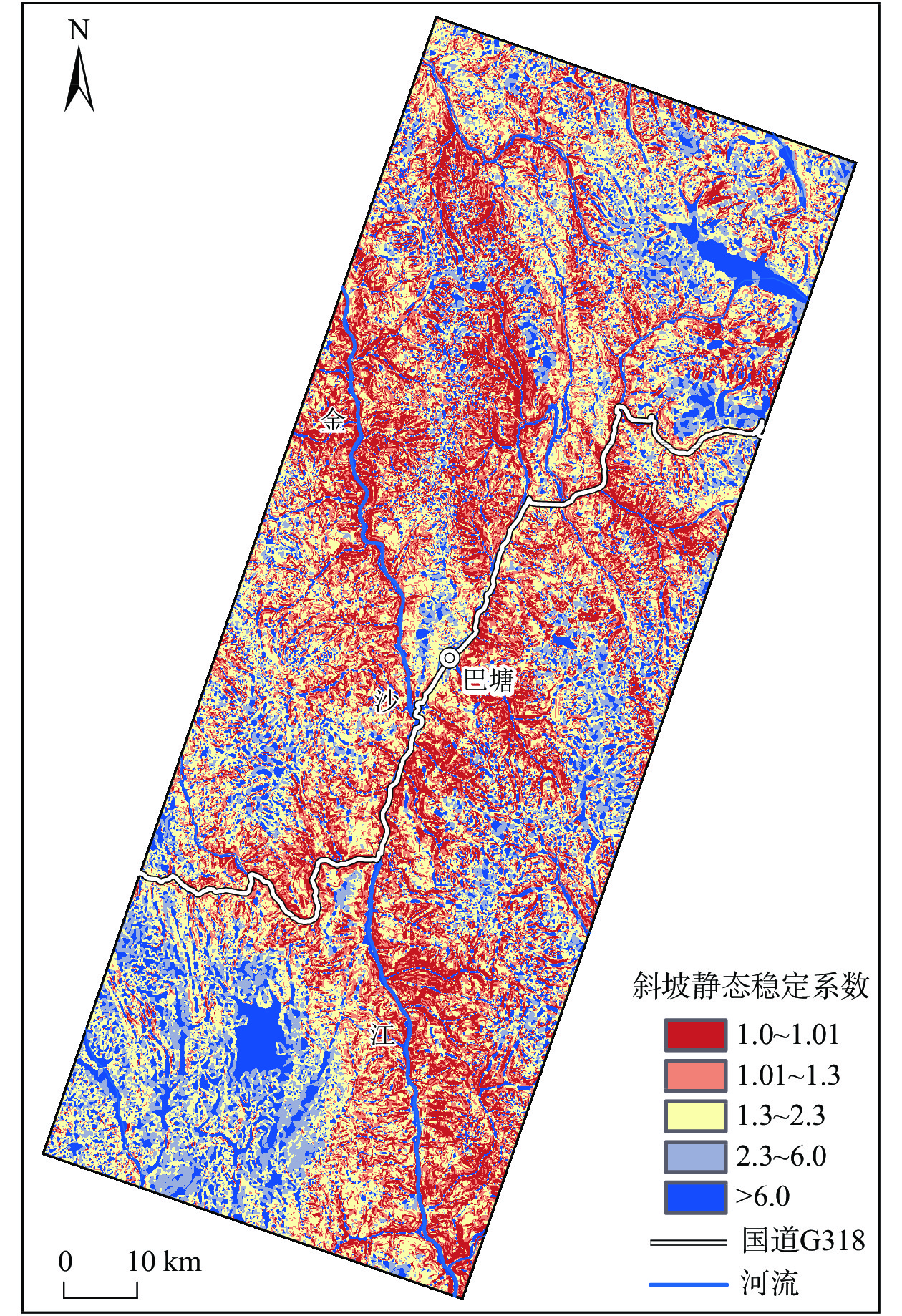
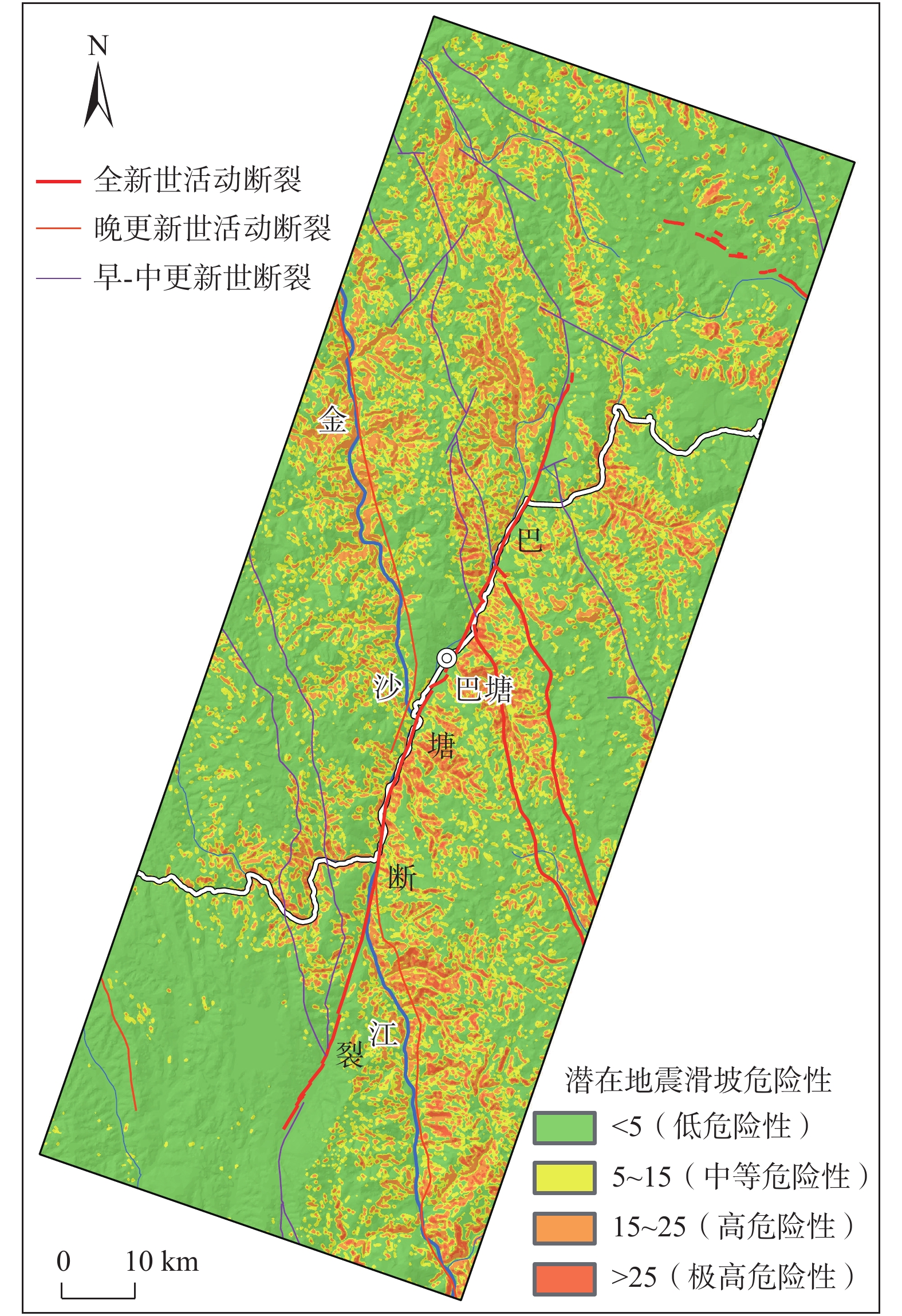
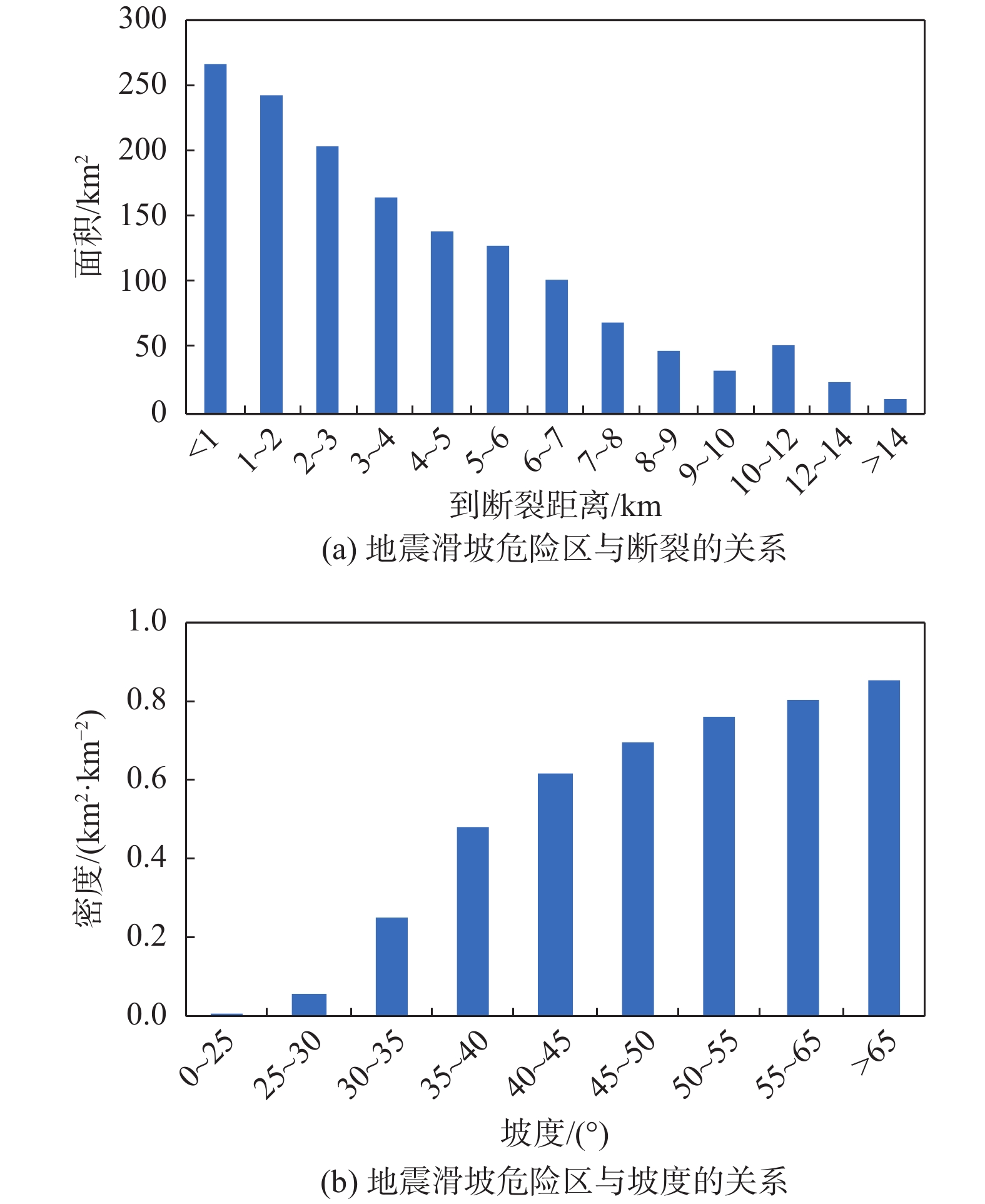
全新世以来青藏高原东部巴塘断裂带活动强烈,地形地貌和地质构造复杂,历史地震频发,并诱发大量滑坡灾害。基于巴塘断裂带地震滑坡长期防控的需要,在分析区域地质灾害成灾背景和发育分布特征的基础上,采用Newmark模型完成了巴塘断裂带50年超越概率10%的潜在地震滑坡危险性预测评价,并完成地震滑坡危险性区划。结果表明:巴塘断裂带及其临近的金沙江断裂带区域、金沙江及其支流沿岸具有较高的潜在地震滑坡危险性,地震滑坡危险区具有沿断裂带和大江大河等峡谷区分布的总体趋势,受活动断裂和地形地貌影响显著;距离断层越近、坡度越大的斜坡,地震滑坡危险性越高;规划建设中的川藏铁路经巴塘县德达乡、白玉县沙马乡,向西北延伸,跨越金沙江,可以穿越较少的地震滑坡危险区,金沙江水电工程规划建设需加强潜在地震滑坡危害研判及防控。巴塘断裂带潜在地震滑坡危险性评价结果可为区域城镇开发和重大工程规划建设的地震滑坡长期防控提供科学参考。
Abstract:The Batang fault on the eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau has strong activity since the Holocene, where the geomorphology and geological structure is complex, and the historical earthquakes occurred frequently, which induced abundant landslides. For the long-term prevention of regional earthquake landslides in the Batang fault zone, based on analyzing the geological background and development characteristics of regional landslides, the Newmark model was used to complete the seismic landslide hazard assessment with exceeding probability 10% of 50 years in the Batang fault zone. The results show that the Batang fault zone and its adjacent Jinshajiang fault zone, the Jinsha River and its tributaries coast have the high seismic landslide hazard. The potential seismic landslide hazard zone has a general distribution trend of along the fault zone and the river canyons, which is significantly affected by the active faults and topography. The closer the slope to the fault is and the greater the slope angle is, the higher the seismic landslide hazard is. The Sichuan-Xizang Railway line under planning and construction extends from the Deda Town and Shama Town to the northwest and crosses the Jinsha River, and can traverse fewer zones with potential seismic landslide hazard. The planning and construction of Jinsha River hydropower project needs to strengthen the assessment and prevention of potential seismic landslide hazard. The potential seismic landslide hazard assessment results in the Batang fault zone can provide a scientific reference for the long-term prevention and control of earthquake landslides in the regional urban development and major engineering planning and construction.
-

-
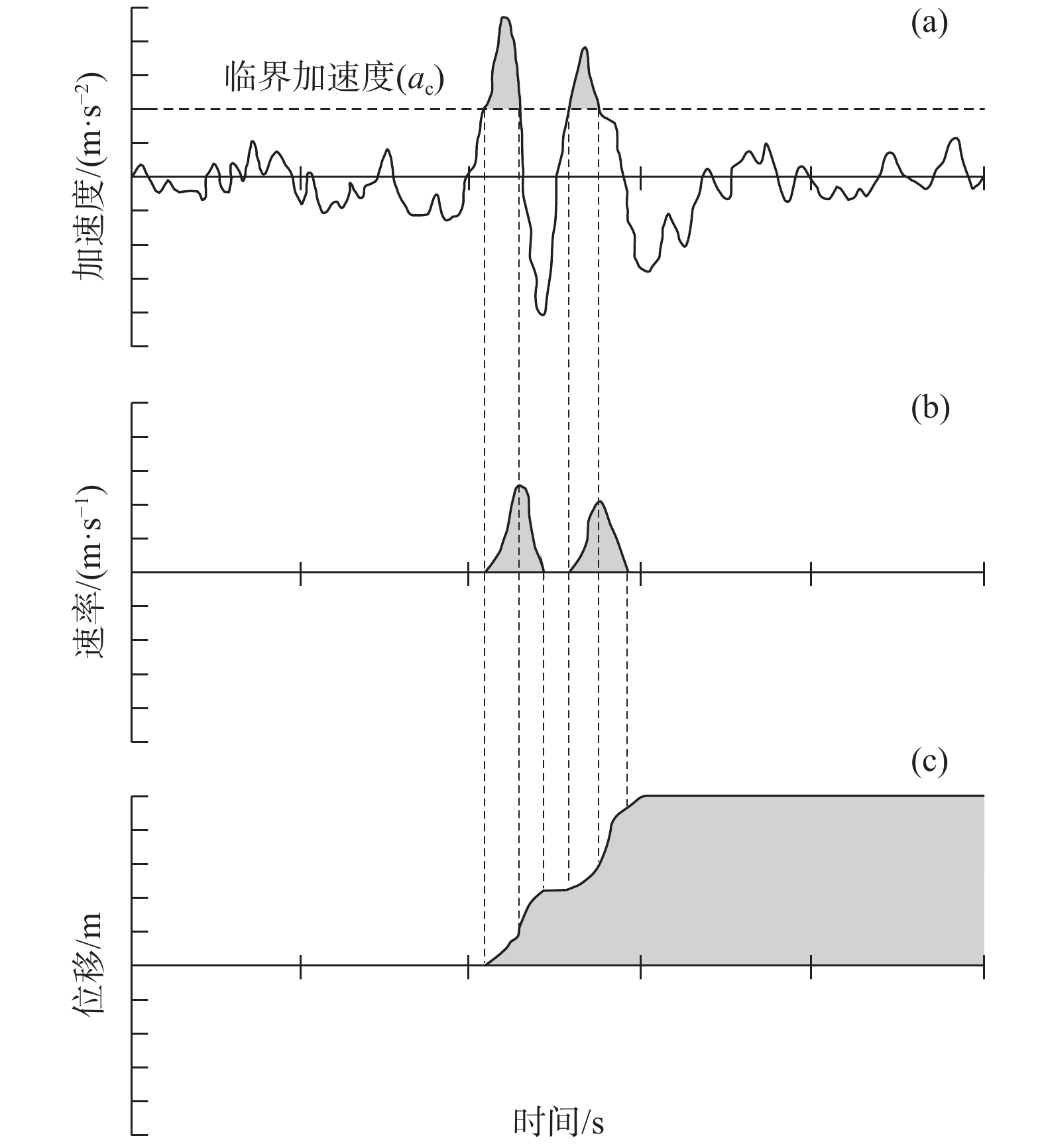
图 4 Newmark累积位移计算过程示意图[15]
Figure 4.
表 1 巴塘断裂带工程地质岩组物理力学性质
Table 1. Physical and mechanical properties of engineering geological groups in the Batang fault zone
ID 工程地质岩组 c′/kPa φ′/(°) γ/(kN·m−3) 1 坚硬的厚层状砂岩岩组 26 33 26 2 较坚硬-坚硬的中-厚层状砂
岩夹砾岩、泥岩、板岩岩组25 32 25 3 软硬相间的中-厚层状砂岩、泥岩
夹灰岩、泥质灰岩及其互层岩组23 30 24 4 软弱-较坚硬薄-中厚层状砂岩、
泥岩及砾岩、泥岩互层岩组22 28 23 5 软弱的薄层状泥岩、页岩岩组 20 27 21 6 坚硬的中-厚层状灰岩及
白云岩岩组24 31 25 7 较坚硬的薄-中厚层状灰岩、
泥质灰岩岩组23 30 24 8 软硬相间的中-厚层状灰岩、
白云岩夹砂岩、泥岩、千枚岩、板岩岩组22 29 23 9 较坚硬-坚硬薄-中厚层状板岩、
千枚岩与变质砂岩互层岩组21 28 22 10 较弱-较坚硬的薄-中厚层状千枚岩、
片岩夹灰岩、砂岩、火山岩岩组20 26 21 11 坚硬的块状玄武岩为主的岩组 27 34 29 12 坚硬块状花岗岩、安山岩、闪长岩岩组 26 33 28 13 软质散体结构岩组 15 25 18 注:ID与图5中的工程地质岩组编号一致,c′为有效黏聚力,φ′为有效内摩擦角,γ为岩土体重度。 -
[1] 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957 − 966. [XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, LI Weile. Integrated Space-Air-Ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 殷跃平. 汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2008,16(4):433 − 444. [YIN Yueping. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2008,16(4):433 − 444. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2008.04.001
[3] ZHANG Y S, DONG S W, HOU C T, et al. Geohazards induced by the Lushan Ms7.0 earthquake in Sichuan Province, southwest China: typical examples, types and distributional characteristics[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(- English Edition),2013,87(3):646 − 657. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12076
[4] KEEFER D K. Statistical analysis of an earthquake-induced landslide distribution - the 1989 Loma Prieta, California event[J]. Engineering Geology,2000,58(3/4):231 − 249.
[5] 乔建平, 黄栋, 杨宗佶, 等. 汶川大地震诱发滑坡的震中距[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(2):1 − 7. [QIAO Jianping, HUANG Dong, YANG Zongji, et al. The landslide epicenter distance triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(2):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] TANG H M, LIU X, HU X L, et al. Evaluation of landslide mechanisms characterized by high-speed mass ejection and long-run-out based on events following the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Engineering Geology,2015,194:12 − 24. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.01.004
[7] 张永双, 成余粮, 姚鑫, 等. 四川汶川地震-滑坡-泥石流灾害链形成演化过程[J]. 地质通报,2013,32(12):1900 − 1910. [ZHANG Yongshuang, CHENG Yuliang, YAO Xin, et al. The evolution process of Wenchuan earthquake-landslide-debris flow geohazard chain[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2013,32(12):1900 − 1910. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 张永双, 郭长宝, 姚鑫, 等. 青藏高原东缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究[J]. 地球学报,2016,37(3):277 − 286. [ZHANG Yongshuang, GUO Changbao, YAO Xin, et al. Research on the geohazard effect of active fault on the eastern margin of the Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2016,37(3):277 − 286. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2016.03.03
[9] KAMP U, GROWLEY B J, KHATTAK G A, et al. GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping for the 2005 Kashmir earthquake region[J]. Geomorphology,2008,101(4):631 − 642. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.03.003
[10] 郭长宝, 张永双, 蒋良文, 等. 川藏铁路沿线及邻区环境工程地质问题概论[J]. 现代地质,2017,31(5):877 − 889. [GUO Changbao, ZHANG Yongshuang, JIANG Liangwen, et al. Discussion on the environmental and engineering geological problems along the Sichuan-Xizang Railway and its adjacent area[J]. Geoscience,2017,31(5):877 − 889. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.05.001
[11] 邹强, 蒋良文, 游勇, 等. 川藏铁路山地灾害信息化管理平台及其应用[J]. 长江科学院院报,2020,37(10):177 − 182. [ZOU Qiang, JIANG Liangwen, YOU Yong, et al. Information management system of mountain hazards along Sichuan-Xizang Railway[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2020,37(10):177 − 182. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.2019158382
[12] 周荣军, 陈国星, 李勇, 等. 四川西部理塘—巴塘地区的活动断裂与1989年巴塘6.7级震群发震构造研究[J]. 地震地质,2005,27(1):31 − 43. [ZHOU Rongjun, CHEN Guoxing, LI Yong, et al. Research on active faults in Litang-Batang region, western Sichuan province, and the seismogenic structures of the 1989 Batang M6.7 earthquake swarm[J]. Seismology and Geology,2005,27(1):31 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2005.01.004
[13] 徐锡伟, 张培震, 闻学泽, 等. 川西及其邻近地区活动构造基本特征与强震复发模型[J]. 地震地质,2005,27(3):446 − 461. [XU Xiwei, ZHANG Peizhen, WEN Xueze, et al. Features of active tectonics and recurrence behaviors of strong earthquakes in the western Sichuan province and its adjacent regions[J]. Seismology and Geology,2005,27(3):446 − 461. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2005.03.010
[14] NEWMARK N M. Effects of earthquakes on dams and embankments[J]. Géotechnique,1965,15(2):139 − 160.
[15] JIBSON R W, HARP E L, MICHAEL J A. A method for producing digital probabilistic seismic landslide hazard maps[J]. Engineering Geology,2000,58(3/4):271 − 289.
[16] ROMEO R. Seismically induced landslide displacements: a predictive model[J]. Engineering Geology,2000,58(3/4):337 − 351.
[17] WANG E, BURCHFIEL B C, ROYDEN L H, et al. Late Cenozoic Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang, Red river, and Dali fault systems of southwestern Sichuan and central Yunnan, China[C]//Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1998, 327.
[18] 程佳. 川西地区现今地壳运动的大地测量观测研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 2008.
CHENG Jia. Present-day crustal deformation of western Sichuan inferred from geodetic observations[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 陈立春. 地壳稳定性、活动断裂及对铁路影响评价专题研究报告[R]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所, 2019.
CHEN Lichun. Crust stability, active faults, and their impact evaluation on railway[R]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, 2019. (in Chinese)
[20] 王新民. 1870年四川巴塘地震的烈度及等震线特征[J]. 四川地震,1990(4):89 − 94. [WANG Xinmin. Characteristics of intensity and isoseismic of the 1870 Sichuan Batang earthquake[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan,1990(4):89 − 94. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 郭劲, 张庆云, 袁灿林. 巴塘6.7级强震群灾害及其影响[J]. 四川地震,1990(1):43 − 47. [GUO Jin, ZHANG Qingyun, YUAN Canlin. Disaster and its impact of Batang M6.7 strong earthquake swarm[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan,1990(1):43 − 47. (in Chinese)
[22] 何玉林, 张绪奇, 郭劲. 1996年12月21日四川白玉、巴塘间5.5级地震烈度考察[J]. 四川地震,1997,2(2):46 − 53. [HE Yulin, ZHANG Xuqi, GUO Jin. Investigation on intensity distribution of the 1996 M5.5 Baiyu-Batang earthquake[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan,1997,2(2):46 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 白永健, 郑万模, 李明辉, 等. 川藏公路茶树山滑坡特征及成因机制分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(6):862 − 866. [BAI Yongjian, ZHENG Wanmo, LI Minghui, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of Chashushan landslide on Sichuan-Xizang highway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(6):862 − 866. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.06.008
[24] 任三绍, 郭长宝, 张永双, 等. 川西巴塘茶树山滑坡发育特征及形成机理[J]. 现代地质,2017,31(5):978 − 989. [REN Sanshao, GUO Changbao, ZHANG Yongshuang, et al. Development characteristics and formation mechanism of Chashushan landslide in Batang, western Sichuan[J]. Geoscience,2017,31(5):978 − 989. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.05.009
[25] 陈剑, 崔之久. 金沙江上游雪隆囊古滑坡堰塞湖溃坝堆积体的发现及其环境与灾害意义[J]. 沉积学报,2015,33(2):275 − 284. [CHEN Jian, CUI Zhijiu. Discovery of outburst deposits induced by the Xuelongnang paleolandslide-dammed lake in the upper Jinsha river, China and its environmental and hazard significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2015,33(2):275 − 284. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] YANG Z H, LAN H X, GAO X, et al. Urgent landslide susceptibility assessment in the 2013 Lushan earthquake-impacted area, Sichuan province, China[J]. Natural Hazards,2015,75(3):2467 − 2487. doi: 10.1007/s11069-014-1441-8
[27] 王涛, 吴树仁, 石菊松, 等. 地震滑坡危险性概念和基于力学模型的评估方法探讨[J]. 工程地质学报,2015,23(1):93 − 104. [WANG Tao, WU Shuren, SHI Jusong, et al. Concepts and mechanical assessment method for seismic landslide hazard: a review[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2015,23(1):93 − 104. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] ZHANG Y S, YANG Z H, GUO C B, et al. Predicting landslide scenes under potential earthquake scenarios in the Xianshuihe fault zone, southwest China[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2017,14(7):1262 − 1278. doi: 10.1007/s11629-017-4363-6
[29] JIBSON R W. Predicting earthquake-induced landslide displacements using Newmark’s sliding block analysis[J]. Transportation Research Record,1993,1411:9 − 17.
[30] MILES S B, HO C L. Rigorous landslide hazard zonation using Newmark’s method and stochastic ground motion simulation[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,1999,18(4):305 − 323. doi: 10.1016/S0267-7261(98)00048-7
[31] 王涛, 吴树仁, 石菊松, 等. 基于简化Newmark位移模型的区域地震滑坡危险性快速评估: 以汶川Ms8.0级地震为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2013,21(1):16 − 24. [WANG Tao, WU Shuren, SHI Jusong, et al. Case study on rapid assessment of regional seismic landslide hazard based on simplified Newmark displacement model: Wenchuan M s 8.0 earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2013,21(1):16 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.01.003
[32] 冯卫, 唐亚明, 赵法锁, 等. 考虑基质吸力作用的Newmark改进模型在地震滑坡风险评价中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(5):154 − 160. [FENG Wei, TANG Yaming, ZHAO Fasuo, et al. Application of Newmark improved model considering matrix suction in earthquake landslide risk assessment[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(5):154 − 160. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 《工程地质手册》编委会. 工程地质手册[M].4版. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2007.
Engineering geology manual Editorial Board. Engineering geology manual[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2007. (in Chinese)
[34] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 工程岩体分级标准: GB/T 50218—2014[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2015.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Standard for engineering classification of rock mass: GB/T 50218—2014[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
[35] WILSON R C, KEEFER D K. Dynamic analysis of a slope failure from the 6 August 1979 Coyote lake, California, earthquake[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,1983,73(3):863 − 877.
[36] JIBSON R W. Regression models for estimating coseismic landslide displacement[J]. Engineering Geology,2007,91(2/3/4):209 − 218.
-




 下载:
下载: