Route selection of deep-lying and hard rock tunnel in the Sichuan-Xizang Railway based on rock burst risk assessment
-
摘要:
川藏铁路穿越区域地形起伏大,区域地质构造作用强烈,隧道建设中面临的高地应力问题异常复杂,特别是深埋硬岩隧道中的岩爆灾害问题,成为制约选线、设计乃至施工建设的难题。由于隧道工程地质条件复杂,如果岩爆评价指标针对性不强,往往会造成评价结果与实际偏差较大。通过综合分析影响岩爆的关键因素,选取岩石单轴抗压强度与洞壁最大主应力比、洞壁最大切向应力与岩石单轴抗压强度比、岩石强度脆性系数、岩石弹性能指数及岩体完整性系数建立了岩爆评价指标体系。根据熵权法确定各指标权重,基于理想点的基本理论及计算规则,构建了一种岩爆危险性评价模型。通过计算各里程段与理想点的距离,对新建川藏铁路某隧道的3种线路方案进行岩爆风险评估的综合比选。研究结果表明B线路总岩爆段落占比24.9%,其中不可控岩爆段落占比13.4%,比另外两条比选方案低4%左右,综合对比B线路为最优方案。该方法可为深埋硬岩隧道地质综合选线提供必要的科学依据和技术支撑。
Abstract:The large terrain undulations and strong regional geological structures are the typical characteristics along the Sichuan-Xizang Railway. The high ground stress problem in tunnel construction is extremely complex, especially the rockburst problem in deep-lying and hard rock tunnels, which restricts route selection schemes and becomes a major difficult problem of construction. Because of the complex geological conditions of the tunnel engineering, the evaluation results often deviate from the actual situation if the rockburst evaluation index is not pertinent. The key factors of rockburst is considering comprehensively, and five factors are selected as the evaluation indexes, including the ratio of the uniaxial compressive strength of rock to the maximum main stress of the surrounding cave wall, the ratio of the maximum tangential stress of the surrounding cave wall to the uniaxial compressive strength of rock, the ratio of compressive to the tensile strength of rock, the elastic strain energy index, and the intactness index of rock mass. The entropy weight method is used to determine the weight of each index, and a rock burst risk assessment model is constructed based on the basic theory and calculation rules of the ideal point method. By calculating the distance between each mileage section and the ideal point, a comprehensive comparison of rock burst risk assessment is carried out on three route plans of a tunnel on the Sichuan-Xizang Railway. The results show that the total rock burst sections of route B is 24.9%, and the uncontrollable rock burst sections account for 13.4%. The route B is about 4% lower than the other two alternative schemes. The route B is determined as the optimal plan according to the impact of rock burst disasters. This method can provide a new scientific basis and technical support for the comprehensive geological selection of deep-lying and hard rock tunnels.
-

-
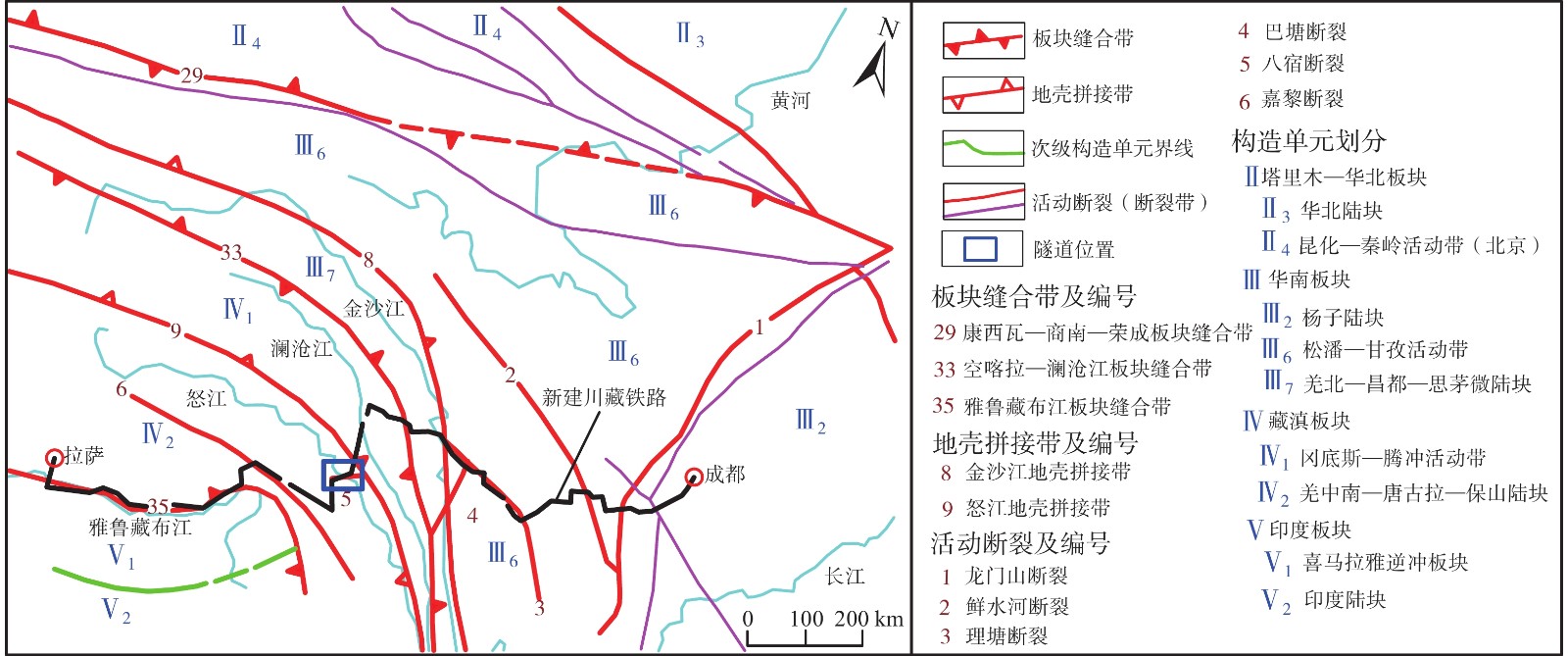
图 1 新建川藏铁路沿线构造纲要[24]
Figure 1.
表 1 岩爆与各评价指标的关系
Table 1. Relationship between rock burst and various evaluation indexes
评价指标 无 轻微 中等 强烈 σc/σmax ≥7 [4, 7) [2, 4) <2 σθ/σc <0.20 [0.20, 0.30) [0.30, 0.55) ≥0.55 σc/σt ≥40.0 [26.7, 40.0) [14.5, 26.7) <14.5 Kv <0.55 [0.55, 0.65) [0.65, 0.75) ≥0.75 Wet <2.0 [2.0, 3.5) [3.5, 5.0) ≥5.0 表 2 岩石物理力学参数一览表
Table 2. Physical and mechanical parameters of rocks
岩性 单轴抗压强度
σc/MPa抗拉强度
σt /MPa静弹性
模量E/GPa静泊松
比v密度ρ/
(g·cm−3)横波波速
vp/(m·s−1)纵波波速
vs/(m·s−1)动弹性模量
Ed/GPa动泊松
比vd二长花岗岩 118.2 5.83 30.12 0.21 2.69 3054.62 5233.84 61.32 0.24 123.7 6.33 32.36 0.22 2.66 2643.39 5694.83 54.72 0.25 103.4 5.34 28.79 0.21 2.76 3018.19 5450.18 64.19 0.28 花岗闪长岩 145.6 6.92 36.16 0.23 2.65 3123.32 4998.11 60.98 0.18 151.4 7.57 35.78 0.25 2.68 3131.55 5163.69 63.48 0.21 137.5 7.31 35.62 0.21 2.75 2643.39 5694.83 52.27 0.36 表 3 实测钻孔地应力数据
Table 3. Measured borehole stress data
钻孔
编号埋深/m 主应力值/MPa 最大主应力方向 SH Sh Sv CD-1# 178~622 6.25~17.55 5.32~13.35 4.66~16.20 N42°—
52°E表 4 线路部分里程的应力资料
Table 4. Stress data of route partial mileage
线路方案 里程编号 SH/MPa Sh/MPa Sv/MPa A A1 39.6 16.8 19.6 A2 42.9 19.3 22.9 A3 50.3 26.1 33.2 A4 51.2 22.3 29.3 B B1 33.7 14.3 23.7 B2 35.6 12.1 20.6 B3 47.9 23.1 31.9 B4 43.5 19.7 26.5 C C1 35.2 12.5 21.6 C2 36.1 16.3 24.6 C3 48.6 23.6 32.8 C4 45.1 20.6 28.4 表 5 线路部分里程的岩爆分析资料
Table 5. Rock burst analysis data of route partial mileage
线路方案 里程编号 σc /MPa σmax/MPa σθ/MPa A A1 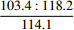
39.6 47.4 A2 42.9 59.5 A3 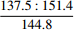
50.3 86.2 A4 51.2 77.4 B B1 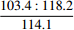
33.7 45.2 B2 35.6 42.8 B3 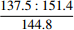
47.9 75.7 B4 43.5 68.1 C C1 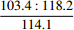
35.2 49.6 C2 36.1 65.2 C3 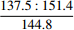
48.6 85.5 C4 45.1 78.1 注:单轴抗压强度中,横线上为最小值∶最大值,横线下为平均值。 表 6 各评价指标值
Table 6. Each evaluation index values
线路方案 里程编号 σc/σmax σθ/σc σc/σt Wet Kv A A1 2.91 0.41 19.74 0.62 3.60 A2 2.69 0.52 19.74 0.62 3.60 A3 2.88 0.60 18.35 0.81 4.30 A4 2.83 0.53 19.92 0.71 4.00 B B1 3.42 0.39 19.74 0.62 3.60 B2 3.23 0.37 19.74 0.62 3.60 B3 3.02 0.52 19.92 0.62 4.00 B4 3.33 0.47 18.35 0.81 4.30 C C1 3.27 0.43 19.74 0.62 3.60 C2 3.19 0.57 19.74 0.62 3.60 C3 2.98 0.59 18.35 0.81 4.30 C4 3.21 0.54 19.92 0.71 4.00 表 7 各评价指标权重系数
Table 7. Entropy weight of each evaluation index
评价指标 σc/σmax σθ/σc σc/σt Wet Kv 熵值ej 0.992 0.837 0.997 0.931 0.985 偏差度1−ej 0.008 0.163 0.003 0.069 0.015 权重系数w 0.032 0.631 0.013 0.267 0.056 表 8 岩爆危险性评价结果示例
Table 8. Examples of rock burst risk assessment results
线路方案 里程
编号岩性 埋深/m 围岩级别 H=2(欧氏距离) 岩爆判
别结果无 轻微 中等 强烈 A A1 二长花岗岩 783~809 Ⅲ级 2.701 1.312 0.428 0.480 中等 A2 二长花岗岩 792~813 Ⅲ级 3.478 2.131 0.516 0.386 强烈 A3 花岗闪长岩 1195~1215 Ⅱ级 4.164 2.969 0.786 0.252 强烈 A4 花岗闪长岩 893~912 Ⅲ级 3.657 2.346 0.354 0.217 强烈 B B1 二长花岗岩 780~801 Ⅲ级 2.553 1.155 0.440 0.540 中等 B2 二长花岗岩 806~815 Ⅲ级 2.405 0.995 0.459 0.551 中等 B3 花岗闪长岩 1176~1192 Ⅲ级 3.544 2.188 0.519 0.404 强烈 B4 花岗闪长岩 973~995 Ⅱ级 3.237 2.083 0.588 0.335 强烈 C C1 二长花岗岩 753~767 Ⅲ级 2.835 1.456 0.427 0.487 中等 C2 二长花岗岩 780~796 Ⅲ级 3.883 2.554 0.628 0.420 强烈 C3 花岗闪长岩 1183~1191 Ⅱ级 4.125 2.932 0.775 0.261 强烈 C4 花岗闪长岩 936~965 Ⅲ级 3.693 2.385 0.371 0.268 强烈 -
[1] 严健, 何川, 汪波, 等. 雅鲁藏布江缝合带深埋长大隧道群岩爆孕育及特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(4):769 − 781. [YAN Jian, HE Chuan, WANG Bo, et al. Inoculation and characters of rockbursts in extra-long and deep-lying tunnels located on Yarlung Zangbo suture[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(4):769 − 781. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 何怡帆, 李天斌, 曹海洋. 隧道施工期岩爆危险性评价的属性识别模型及工程应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(2):102 − 111. [HE Yifan, LI Tianbin, CAO Haiyang. Attribute recognition model of fatalness assessment of rockburst in tunnel construction and its application[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(2):102 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 刘国锋, 李志强, 王晓明, 等. 深埋隧道岩爆规模现场快速估算方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(1):57 − 64. [LIU Guofeng, LI Zhiqiang, WANG Xiaoming, et al. Field rapid estimation method for the scale of rockburst in deep tunnels[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(1):57 − 64. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 吴光, 肖道坦, 蒋良文, 等. 复杂山区高等级铁路选线工程地质的若干问题[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2010,45(4):527 − 532. [WU Guang, XIAO Daotan, JIANG Liangwen, et al. Problems about engineering geology of high-grade railway route selection in complicated mountainous areas[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2010,45(4):527 − 532. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2010.04.007
[5] 罗圆, 朱颖, 张小强, 等. 基于大地震风险的川藏铁路线路方案评价模型[J]. 铁道工程学报,2018,35(4):34 − 38. [LUO Yuan, ZHU Ying, ZHANG Xiaoqiang, et al. Evaluation model of Sichuan-Xizang Railway scheme based on large earthquake risk[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2018,35(4):34 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2018.04.007
[6] 张永双, 任三绍, 郭长宝, 等. 活动断裂带工程地质研究[J]. 地质学报,2019,93(4):763 − 775. [ZHANG Yongshuang, REN Sanshao, GUO Changbao, et al. Research on engineering geology related with active fault zone[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2019,93(4):763 − 775. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 杨宗佶, 丁朋朋, 王栋, 等. 川藏铁路(康定至林芝段)沿线滑坡风险分析[J]. 铁道学报,2018,40(9):97 − 103. [YANG Zongji, DING Pengpeng, WANG Dong, et al. Landslide risk analysis on Sichuan-Xizang Railway (Kangding to Nyingchi section)[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society,2018,40(9):97 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2018.09.014
[8] 钟卫, 李秀珍, 崔云, 等. 崩塌滑坡灾害对川藏铁路康定—昌都段选线的影响[J]. 铁道标准设计,2018,62(1):34 − 38. [ZHONG Wei, LI Xiuzhen, CUI Yun, et al. The influence of landslide and collapse hazards on railway alignment in Kangding-Changdu section of Sichuan-Xizang Railway[J]. Railway Standard Design,2018,62(1):34 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 林奎. 冰川泥石流地区铁路线路方案综合优选研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016.
LIN Kui. Research on comprehensive optimization in route scheme of railway in the glacial debris flow area[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University , 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李雯. 岩溶地区铁路选线风险评估研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2014.
LI Wen. The risk assessment research on railway location in karst region[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 李国和, 李桂芳. 采空区铁路工程地质选线研究[J]. 铁道工程学报,2012,29(10):15 − 20. [LI Guohe, LI Guifang. Geological route selection of railway in mining district[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2012,29(10):15 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2012.10.004
[12] 黄润秋, 王贤能. 深埋隧道工程主要灾害地质问题分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1998,25(4):3 − 5. [HUANG Runqiu, WANG Xianneng. Analysis of the main geological hazards in deep lying tunnels[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1998,25(4):3 − 5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 徐林生. 地下工程岩爆发生条件研究[J]. 重庆交通学院学报,2005,24(3):31 − 34. [XU Linsheng. Research of rockburst formation condition in underground engineering[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University,2005,24(3):31 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 何川, 汪波, 吴德兴. 苍岭隧道岩爆特征与影响因素的相关性及防治措施研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2007,34(2):25 − 28. [HE Chuan, WANG Bo, WU Dexing. Research of relativity between rockburst character and influence factor and prevention measure in Cangling tunnel[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2007,34(2):25 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2007.02.006
[15] 张镜剑, 傅冰骏. 岩爆及其判据和防治[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(10):2034 − 2042. [ZHANG Jingjian, FU Bingjun. Rockburst and its criteria and control[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(10):2034 − 2042. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.10.010
[16] 邱道宏, 李术才, 张乐文, 等. 基于隧洞超前地质探测和地应力场反演的岩爆预测研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(7):2034 − 2040. [QIU Daohong, LI Shucai, ZHANG Lewen, et al. Rockburst prediction based on tunnel geological exploration and ground stress field inverse analysis[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(7):2034 − 2040. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 邢军, 王建斌, 蒋蕾, 等. 圭嘎拉高速公路隧道地应力特征及岩爆预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(2):170 − 178. [XING Jun, WANG Jianbin, JIANG Lei, et al. In-situ stress characteristics and rock burst prediction of the Guigala Expressway tunnel[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(2):170 − 178. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 徐俊帅, 徐金明, 涂齐亮. 基于地应力和岩体强度的岩爆预判[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):52 − 58. [XU Junshuai, XU Jinming, TU Qiliang. Prediction of rock based on field geostress and rock mass strength[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):52 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] ZHOU J, LI X B, MITRI H S. Evaluation method of rockburst: State-of-the-art literature review[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2018,81:632 − 659.
[20] 王元汉, 李卧东, 李启光, 等. 岩爆预测的模糊数学综合评判方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,1998,17(5):493 − 501. [WANG Yuanhan, LI Wodong, LI Qiguang, et al. Method of fuzzy comprehensive evaluations for rockburst prediction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,1998,17(5):493 − 501. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.1998.05.003
[21] ZHOU H, CHEN S K, LI H R, et al. Rockburst prediction for hard rock and deep-lying long tunnels based on the entropy weight ideal point method and geostress field inversion: a case study of Sangzhuling Tunnel[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2021,80(5):3885 − 3902. doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02175-9
[22] 周航, 陈仕阔, 张广泽, 等. 基于功效系数法和地应力场反演的深埋长大隧道岩爆预测研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(6):1386 − 1396. [ZHOU Hang, CHEN Shikuo, ZHANG Guangze, et al. Efficiency coefficient method and ground stress field inversion for rockburst predicition in deep and long tunnel[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(6):1386 − 1396. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 卞爽, 于志泉, 龚俊峰, 等. 青藏高原近南北向裂谷的时空分布特征及动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报,2021,27(2):178 − 194. [BIAN Shuang, YU Zhiquan, GONG Junfeng, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution and geodynamic mechanism of the nearly NS-trending rifts in the Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2021,27(2):178 − 194. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 宋章, 张广泽, 蒋良文, 等. 川藏铁路工程地质特征及地质选线原则[J]. 铁道建筑,2017,57(2):142 − 145. [SONG Zhang, ZHANG Guangze, JIANG Liangwen, et al. Engineering geological features and geological route selection principle of Sichuan-Xizang Railway[J]. Railway Engineering,2017,57(2):142 − 145. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2017.02.35
[25] 郭长宝, 吴瑞安, 蒋良文, 等. 川藏铁路雅安—林芝段典型地质灾害与工程地质问题[J]. 现代地质,2021,35(1):1 − 17. [GUO Changbao, WU Rui’an, JIANG Liangwen, et al. Typical geohazards and engineering geological problems along the Ya'an-Linzhi section of the Sichuan-Xizang Railway, China[J]. Geoscience,2021,35(1):1 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 陈兴强. 基于地应力侧压系数的青藏高原东南缘区域性岩爆预测研究[J]. 铁道标准设计,2020,64(7):44 − 49. [CHEN Xingqiang. Prediction of regional rock burst in southeastern Qinghai-Xizang plateau based on in-situ stress lateral pressure coefficient[J]. Railway Standard Design,2020,64(7):44 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 霍欣. 某铁路怒江至伯舒拉岭段主要工程地质问题及地质选线[J]. 铁道标准设计,2020,64(11):7 − 13. [HUO Xin. Major engineering geological problems and geological route selection of Nujiang-Bershulla section of a railway[J]. Railway Standard Design,2020,64(11):7 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 工程岩体分级标准: GB/T 50218—2014[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2014.
Standard for engineering classification of rock mass: GB/T 50218—2014[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2014. (in Chinese)
-



 下载:
下载:








