A study of the potential of field-scale of CO2 geological storage and enhanced water recovery in the eastern Junggar area of Xinjiang
-
摘要:
二氧化碳地质封存联合深部咸水开采技术(CO2-EWR)被认为是有效的碳减排途径之一。在新疆准东地区率先开展CO2-EWR技术,可在实现CO2减排的同时获得咸水,在一定程度上缓解当地的水资源短缺问题,取得环境经济双重效益。以往研究大多以概化模型为主,缺乏工程实践依托,根据准噶尔盆地东部CO2源汇匹配适宜性评价结果,基于我国首个CO2-EWR野外先导性工程试验场地资料,构建拟选CO2-EWR场地西山窑组三维(3D)非均质模型开展了场地尺度CO2-EWR技术潜力研究。研究表明,拟选场地CO2理论封存量为1.72×106(P50)t,动态封存量为2.14×106 t。采用CO2-EWR技术可实现CO2动态封存量11.18×106 t,较单独CO2地质封存提升5.22倍,同时可增采咸水资源10.17×106 t,CO2采水比率为1∶0.91。同时,该技术可有效缓解因CO2大量注入引起的储层压力累积,提高CO2封存效率,增加咸水开采潜力。本研究可为新疆准东地区实施规模化CO2地质封存联合深部咸水开采工程提供理论依据和技术支撑。
-
关键词:
- 深部咸水层 /
- 二氧化碳联合深部咸水开采 /
- 场地尺度 /
- 潜力评估 /
- 准噶尔盆地
Abstract:CO2 geological storage combined with saline recovery (CO2-EWR) is considered to be one of the effective storage methods. Taking the lead in carrying out CO2-EWR technology in the eastern Junggar of Xinjiang can achieve CO2 emission reduction and mean while produce saline water, which can alleviate the local water resources shortage problem to a certain extent, and obtain dual benefits of environment and economy. Previous research mainly focused on generalized models, and the support of engineering practices is lacking. Based on the evaluation results of the suitability of CO2 source - sink matching in the eastern Junggar Basin and the geological data of the first CO2-EWR field pilot test site in China, a 3D heterogeneous model of the Xishanyao Formation of the CO2-EWR test site in the eastern Junggar Basin is constructed to study the potential of the CO2-EWR technology. The results show that the the oretical storage capacity of CO2 at the test site is 1.72 × 106 (P50) tons, and the dynamic storage capacity is 2.14 × 106 tons. When the CO2-EWR technology is adopted, the CO2 dynamic storage capacity can reach 11.18 × 106 tons, which is 5.22 times the CO2 geological storage only, and may increase the production of the saline water resources by 10.17 × 106 tons with a mass ratio of 1 to 0.91 of CO2 sweeping out saline water. Meanwhile, the CO2-EWR technology can effectively slow down the accumulation of reservoir pressure caused by the massive injection of CO2, improve the efficiency of CO2 storage, and increase the saline water production potential. This study can provide theoretical basis and technical support for the implementation of large-scale CO2 geological storage combined with deep saline water production project in the eastern Junggar of Xinjiang.
-
Key words:
- deep saline aquifers /
- CO2-EWR /
- field-scale /
- potential assessment /
- Junggar Basin
-

-
表 1 基于静态地质建模的CO2埋存量
Table 1. CO2 storage capacity from static geological modeling
计算参数 P10 P50 P90 封存系数 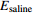 /%[32]
/%[32]1.2 2.4 4.1 封存体积/(106 m3) 1.22 2.43 4.16 封存质量/(106 t) 0.86 1.72 2.94 注:基于蒙特卡罗模型计算的深部咸水层CO2有效封存系数可信度为90%时定义为P10,CO2有效封存系数可信度为50%时定义为P50,CO2有效封存系数可信度为10%时定义为P90。不同的可信度对应不同的CO2有效封存系数。 -
[1] BACHU S, ADAMS J J. Sequestration of CO2 in geological media in response to climate change: capacity of deep saline aquifers to sequester CO2 in solution[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2003,44(20):3151 − 3175. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(03)00101-8
[2] SCOTT V, GILFILLAN S, MARKUSSON N, et al. Last chance for carbon capture and storage[J]. Nature Climate Change,2013,3(2):105 − 111. doi: 10.1038/nclimate1695
[3] CHAUDHRY R, FISCHLEIN M, LARSON J, et al. Policy stakeholders' perceptions of carbon capture and storage: a comparison of four US states[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2013,52:21 − 32. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.02.002
[4] DALGAARD T, OLESEN J E, PETERSEN S O, et al. Developments in greenhouse gas emissions and net energy use in Danish agriculture - How to achieve substantial CO2 reductions?[J]. Environmental Pollution,2011,159(11):3193 − 3203. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2011.02.024
[5] TOLÓN-BECERRA A, PÉREZ-MARTÍNEZ P, LASTRA-BRAVO X, et al. A methodology for territorial distribution of CO2 emission reductions in transport sector[J]. International Journal of Energy Research,2012,36(14):1298 − 1313. doi: 10.1002/er.1871
[6] MC GEOUGH E J, LITTLE S M, JANZEN H H, et al. Life-cycle assessment of greenhouse gas emissions from dairy production in Eastern Canada: a case study[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2012,95(9):5164 − 5175. doi: 10.3168/jds.2011-5229
[7] 李小春, 刘延锋, 白冰, 等. 中国深部咸水含水层CO2储存优先区域选择[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(5):963 − 968. [LI Xiaochun, LIU Yanfeng, BAI Bing, et al. Ranking and screening of CO2 saline aquifer storage zones in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2006,25(5):963 − 968. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.05.015
[8] BACHU S, BONIJOLY D, BRADSHAW J, et al. CO2 storage capacity estimation: Methodology and gaps[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2007,1(4):430 − 443. doi: 10.1016/S1750-5836(07)00086-2
[9] XU T F, PRUESS K, APPS J. Numerical studies of fluid-rock interactions in EnhancedGeothermal Systems (EGS) with CO2 as working fluid[EB/OL]. 2008.
[10] 张二勇. 澳大利亚Otway盆地二氧化碳地质封存示范工程[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2012,39(2):131 − 137. [ZHANG Eryong. Introduction to the CO2 geosequestration demonstration project in the Otway basin in Australia[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2012,39(2):131 − 137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] TAPIA J F D, LEE J Y, OOI R E H, et al. Optimal CO2 allocation and scheduling in enhanced oil recovery (EOR) operations[J]. Applied Energy,2016,184:337 − 345. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.09.093
[12] DE SILVA P N K, RANJITH P G. A study of methodologies for CO2 storage capacity estimation of saline aquifers[J]. Fuel,2012,93:13 − 27. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.07.004
[13] 张炜, 吕鹏. 二氧化碳地质封存中“对流混合”过程的研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2013,40(2):101 − 107. [ZHANG Wei, LV Peng. Density-driven convection in carbon dioxide geological storage: a review[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2013,40(2):101 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] BERGMO P E S, GRIMSTAD A A, LINDEBERG E. Simultaneous CO2 injection and water production to optimise aquifer storage capacity[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2011,5(3):555 − 564. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.09.002
[15] 李琦, 魏亚妮. 二氧化碳地质封存联合深部咸水开采技术进展[J]. 科技导报,2013,31(27):65 − 70. [LI Qi, WEI Yani. Progress in combination of CO2 geological storage and deep saline water recovery[J]. Science & Technology Review,2013,31(27):65 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2013.27.010
[16] 杨国栋, 李义连, 马鑫, 等. 超临界CO2增强热卤水开采模型研究[J]. 地质科技情报,2014,33(6):233 − 240. [YANG Guodong, LI Yilian, MA Xin, et al. Modeling study of enhanced thermal brine extraction using supercritical CO2[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2014,33(6):233 − 240. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] LI Q, WEI Y N, LIU G Z, et al. Combination of CO2 geological storage with deep saline water recovery in Western China: insights from numerical analyses[J]. Applied Energy,2014,116:101 − 110. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.11.050
[18] HEATH J E, MCKENNA S A, DEWERS T A, et al. Multiwell CO2 injectivity: impact of boundary conditions and brine extraction on geologic CO2 storage efficiency and pressure buildup[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(2):1067 − 1074.
[19] BUSCHECK T A, SUN Y W, HAO Y, et al. Combining brine extraction, desalination, and residual-brine reinjection with CO2 storage in saline formations: Implications for pressure management, capacity, and risk mitigation[J]. Energy Procedia,2011,4:4283 − 4290. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2011.02.378
[20] FANG Q, LI Y L. Exhaustive brine production and complete CO2 storage in Jianghan Basin of China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2014,72(5):1541 − 1553. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3059-2
[21] LIU D Q, AGARWAL R, LI Y L. Numerical simulation and optimization of CO2-enhanced water recovery by employing a genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2016,133:994 − 1007. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.023
[22] MA X, LI X F, YANG G D, et al. Study on field-scale of CO2 geological storage combined with saline water recovery: a case study of east Junggar basin of Xinjiang[J]. Energy Procedia,2018,154:36 − 41. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2018.11.007
[23] 万青山, 赵辉, 喻高明. 彩南油田彩9井区西山窑组油藏井间动态连通性研究[J]. 石油化工应用,2013,32(2):41 − 43. [WAN Qingshan, ZHAO Hui, YU Gaoming. Research on interwell dynamic connectivity for Xishanyao reservoir wellblock Cai-9 Cainan oilfield[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application,2013,32(2):41 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2013.02.011
[24] 董雪梅, 徐怀民, 马迪娜·马吾提, 等. 彩9井区西山窑组特低渗油藏高含水期加密调整试验[J]. 新疆石油地质,2014,35(5):558 − 561. [DONG Xuemei, XU Huaimin, MADINA Mawutihan, et al. Well infill adjustment test of Xishanyaoultra-low permeability reservoir in high water cutstage in wellblock Cai-9 of Cainan oilfield, Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2014,35(5):558 − 561. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 李旭峰, 刁玉杰, 马鑫, 等. 准噶尔等盆地二氧化碳地质储存综合地质调查成果报告[R]. 北京: 中国地质调查局, 2019.
LI Xufeng, DIAO Yujie, MA Xin, et al. Report on comprehensive geological survey of carbon Dioxide storage in Junggar Basin[R]. Beijing: China Geological Survey, 2019. (in Chinese)
[26] LI Y K, NGHIEM L X. Phase equilibria of oil, gas and water/brine mixtures from a cubic equation of state and henry's law[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering,1986,64(3):486 − 496. doi: 10.1002/cjce.5450640319
[27] PENG D Y, ROBINSON D B. A new two-constant equation of state[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals,1976,15(1):59 − 64.
[28] PENG D Y, ROBINSON D B. Two- and three-phase equilibrium calculations for coal gasification and related processes[C]//Thermodynamics of Aqueous Systems with Industrial Applications. WASHINGTON, D. C.: AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY, 1980: 393-414.
[29] COREY A T. The interrelation between gas and oil relative permeabilities[J]. Producers Monthly,1954,19:38 − 41.
[30] AHMED T K, NASRABADI H. Case study on combined CO2 sequestration and low-salinity water production potential in a shallow saline aquifer in Qatar[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2012,109:27 − 32.
[31] GOODMAN A, HAKALA A, BROMHAL G, et al. U.S. DOE methodology for the development of geologic storage potential for carbon dioxide at the national and regional scale[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2011,5(4):952 − 965. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2011.03.010
[32] BACHU S. Review of CO2 storage efficiency in deep saline aquifers[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2015,40:188 − 202. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.01.007
[33] WEN D G, MA X, WANG L Q, et al. Combined study of static and dynamic reservoir modelling for the CO2 storage project in deep saline aquifer in Zhundong, Xinjiang, China[J]. Social Science Electronic Journal,2019:1 − 8.
[34] DEMPSEY D, O’MALLEY D, PAWAR R. Reducing uncertainty associated with CO2 injection and brine production in heterogeneous formations[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2015,37:24 − 37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2015.03.004
[35] HOSSEINI S A, NICOT J P. Scoping analysis of brine extraction/re-injection for enhanced CO2 storage[J]. Greenhouse Gases: Science and Technology,2012,2(3):172 − 184. doi: 10.1002/ghg.1283
[36] 许志刚, 陈代钊, 曾荣树. CO2地质埋存渗漏风险及补救对策[J]. 地质论评,2008,54(3):373 − 386. [XU Zhigang, CHEN Daizhao, ZENG Rongshu. The leakage risk assessment and remediation options of CO2 geological storage[J]. Geological Review,2008,54(3):373 − 386. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.03.011
[37] 马鑫, 李义连, 杨国栋, 等. 盖层不确定性对CO2地质封存安全性的影响[J]. 安全与环境工程,2013,20(4):45 − 50. [MA Xin, LI Yilian, YANG Guodong, et al. Impact of the uncertainties of caprocks on the security of CO2 geological storage[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2013,20(4):45 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2013.04.011
[38] YASUNISHI A, YOSHIDA F. Solubility of carbon dioxide in aqueous electrolyte solutions[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data,1979,24(1):11 − 14.
-




 下载:
下载:










