Research on the identification and engineering characteristics of recently deposited soils in the Tianjin Binhai New Area
-
摘要:
基于古海岸线及测年试验分析,对滨海新区上部陆相沉积土的形成年代进行研究,确定了该区新近沉积土的划分原则,并根据成因类型及沉积环境,进一步划分了新近沉积土的类别;根据土层厚度及底板埋深,查清了滨海新区新近沉积土的发育分布规律,并分析评价了该类土的工程特性。结果表明:滨海新区上部陆相沉积土形成年代小于4 000年,应将其划归为新近沉积土,与原新近沉积土共同组成该区新近沉积层;新划分原则下新近沉积土可分为洪泛新近沉积土、古河道新近沉积土及上部陆相新近沉积土三类,其厚度一般在1~2 m,底板埋深一般在3~4 m,工程性质较差,表现为较高含水量、较大孔隙比、较低抗剪强度、较高压缩性,地基承载力普遍在100 kPa左右。
Abstract:Based on the analyses of the paleocoast line and the dating test, the formation age of the upper terrestrial sedimentary soil in the Binhai New Area is studied, the principle of the recently deposited soils in the area is determined, and the classification of the recently deposited soils is further divided according to the genetic type and sedimentary environment. Based on the thickness of the soil layer and the depth of the floor, the development and distribution of the recently deposited soils in the Binhai New Area is investigated, and the engineering characteristics of this type of soil are analyzed and evaluated. The results show that formation age of the upper terrestrial sedimentary soil in the Binhai New Area is less than 4000 years. Consequently, the soil should be classified as recently deposited soil. Together with the original recently deposited soil, the recently deposited layer formed in the area. According to new classification principle, the recently deposited soils can be divided into three types: flooded recently deposited soil, ancient channel recently deposited soil and upper terrestrial recently deposited soil. The thickness of the recently deposited layer generally ranges from 1 to 2 m, and the floor depth generally ranges from 3 to 4 m. The engineering properties are poor, and are characterized by higher water content, larger void ratio, lower shear strength and higher compressibility, and the foundation bearing capacity is generally 100 kPa or so.
-

-
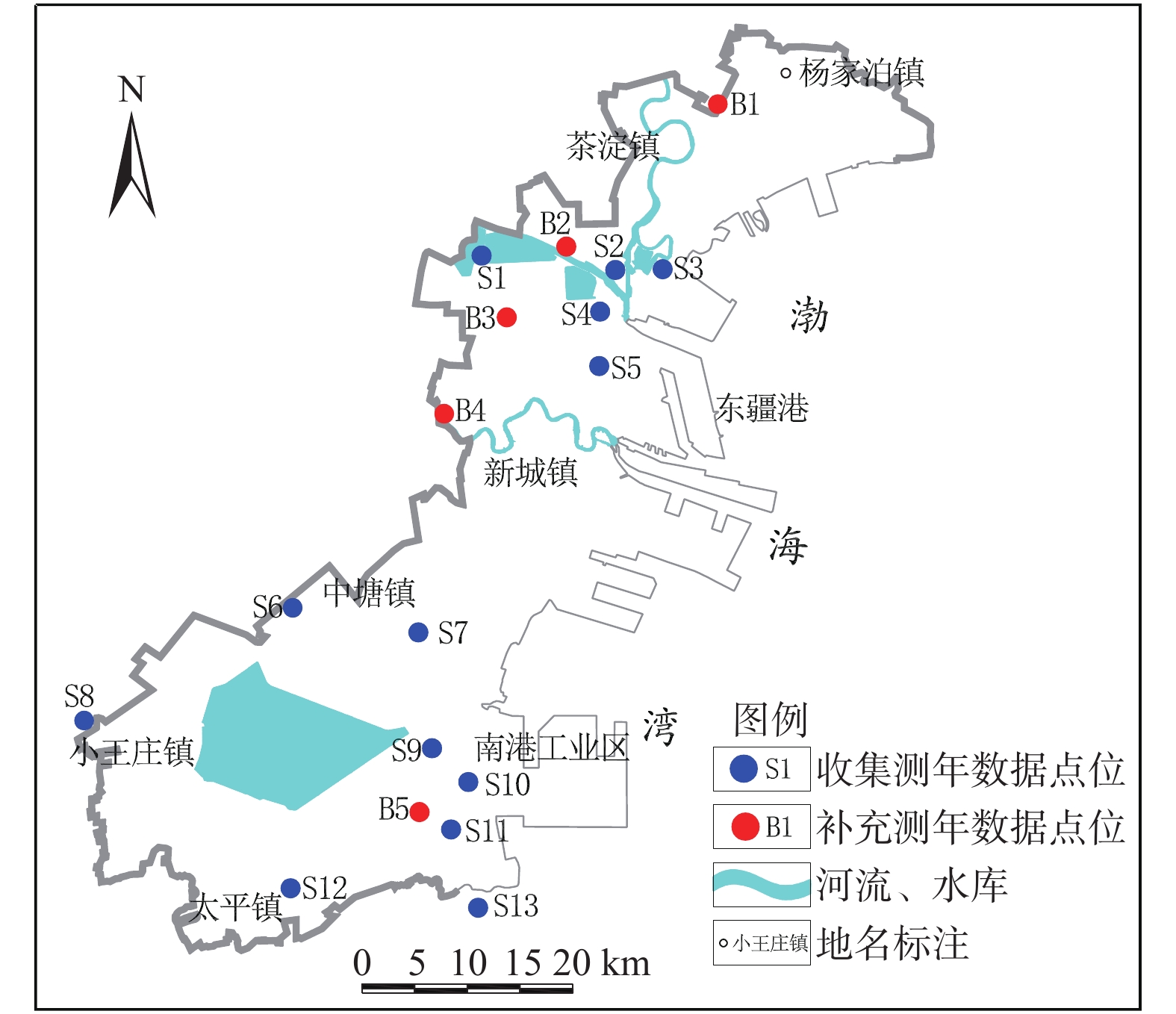
表 1 收集的测年成果数据
Table 1. Collected dating results
编号 测年材料 取样深度/m 测定值/a BP 数据来源 S1 C.gigas 3.0 2 130±80 文献[14] C.gigas 4.2 2 240±80 文献[14] S2 贝壳 − 2 130±80 ● S3 贝壳 − 1 350±65 文献[15] S4 C.gigas 1.0~2.0 975±85 文献[16] S5 有机质泥 3.5 9 070±200 文献[16] S6 黏土 2.0 2 200±200 ● S7 贝壳 1.3~1.5 2 030±150 文献[17] 贝壳 − 2 290±120 文献[17] S8 贝壳 − 7 920±655 文献[16] S9 贝壳 3.87 1 170±120 ● S10 贝壳 4.0 220±200 ● S11 贝壳 − 2 660±115 文献[16] S12 M..quadrangularis − 3 060±100 文献[16] S13 贝壳 0.3~0.4 1 480±65 文献[18] 贝壳 1.2 2 000±70 文献[18] 注:1. C.gigas为长牡蛎,M..quadrangularis为四角蛤蜊;
2. ●数据来源于天津地质矿产研究所、天津地质调查中心等单位。表 2 补充测年数据
Table 2. Supplementary dating data
编号 样品 测定值(14C年代BP) 误差 B1 贝壳 3 950 20 B2 贝壳 现代碳 − B3 贝壳 1 720 20 B4 贝壳 2 240 30 B5 贝壳 2 375 20 注:所用14C半衰期为5 568年,BP为距1950年的年代。 表 3 物理性状对比
Table 3. Comparison of physical properties
地区 土层 颜色 结构 强度 滨海新区 上部陆相沉积土 褐黄 结构性差,受扰动后
原始结构显著变软低 市区 新近沉积土 褐灰 结构性差 低 上部陆相沉积土 灰黄 结构稳定 高 表 4 黏土物理力学指标统计表
Table 4. Statistics of physical and mechanical indexes of clay
指标 统计项目 市区 滨海地区 上部陆相沉积土 新近沉积土 上部陆相沉积土 ω/% 平均值 31.2 32.2 35.8 变异系数 0.11 0.10 0.11 γ/(kN·m−3) 平均值 19.0 18.8 18.4 变异系数 0.02 0.03 0.02 e 平均值 0.91 0.94 1.03 变异系数 0.09 0.10 0.09 IP 平均值 18.51 18.81 19.40 变异系数 0.11 0.14 0.12 IL 平均值 0.50 0.54 0.69 变异系数 0.23 0.20 0.22 a/MPa−1 平均值 0.42 0.46 0.58 变异系数 0.18 0.23 0.24 Es1-2/MPa 平均值 4.60 4.20 3.70 变异系数 0.23 0.20 0.23 N/击 平均值 4.10 3.20 2.90 变异系数 0.26 0.22 0.26 表 5 粉质黏土物理力学指标统计
Table 5. Statistics of physical and mechanical indexes of silty clay
指标 统计项目 市区 滨海地区 上部陆相沉积土 新近沉积土 上部陆相沉积土 ω/% 平均值 27.8 29.3 30.5 变异系数 0.10 0.08 0.10 γ/(kN·m−3) 平均值 19.3 19.1 19.1 变异系数 0.02 0.02 0.03 e 平均值 0.80 0.84 0.84 变异系数 0.05 0.10 0.10 IP 平均值 12.50 12.30 13.50 变异系数 0.18 0.08 0.20 IL 平均值 0.84 0.99 0.87 变异系数 0.19 0.20 0.16 a/MPa−1 平均值 0.28 0.33 0.41 变异系数 0.22 0.25 0.27 Es1-2/MPa 平均值 6.60 5.80 4.90 变异系数 0.18 0.21 0.20 N/击 平均值 5.00 3.40 3.40 变异系数 0.23 0.27 0.28 表 6 淤泥质土物理力学指标统计
Table 6. Statistics of physical and mechanical indexes of silty soil
指标 统计项目 市区 滨海地区 上部陆相沉积土 新近沉积土 上部陆相沉积土 ω/% 平均值 − 38.1 42.4 变异系数 − 0.06 0.10 γ/(kN·m−3) 平均值 − 18.1 17.8 变异系数 − 0.02 0.02 e 平均值 − 1.07 1.19 变异系数 − 0.09 0.09 IP 平均值 − 15.70 18.40 变异系数 − 0.12 0.13 IL 平均值 − 1.02 1.15 变异系数 − 0.13 0.08 a/MPa−1 平均值 − 0.59 0.81 变异系数 − 0.23 0.18 Es1-2/MPa 平均值 − 3.30 2.80 变异系数 − 0.12 0.13 N/击 平均值 − 2.10 1.70 变异系数 − 0.28 0.25 表 7 粉土物理力学指标统计
Table 7. Statistics of physical and mechanical indexes of silt
指标 统计项目 市区 滨海地区 上部陆相沉积土 新近沉积土 上部陆相沉积土 ω/% 平均值 26.8 27.3 26.9 变异系数 0.07 0.05 0.08 γ/(kN·m−3) 平均值 19.7 19.3 19.4 变异系数 0.01 0.02 0.02 e 平均值 0.77 0.78 0.76 变异系数 0.06 0.05 0.07 IP 平均值 8.90 9.20 9.20 变异系数 0.08 0.06 0.08 IL 平均值 0.80 0.86 0.67 变异系数 0.22 0.24 0.22 a/MPa−1 平均值 0.12 0.13 0.16 变异系数 0.22 0.21 0.19 Es1-2/MPa 平均值 14.5 13.9 11.2 变异系数 0.16 0.15 0.18 N/击 平均值 11.00 7.30 6.30 变异系数 0.21 0.28 0.27 表 8 物理指标统计表
Table 8. Statistics of physical index
指标 统计项目 黏性土 (③1) 粉土 (③2) 淤泥质土 (③3) 粉质黏土 (③4) ω/% 最小值 25.0 22.4 34.9 24.9 最大值 44.1 30.4 51.5 41.1 平均值 31.8 26.5 42.5 32.2 变异系数 0.11 0.7 0.10 0.10 γ/(kN·m−3) 最小值 17.7 18.7 16.9 17.6 最大值 19.7 20.1 18.4 19.4 平均值 18.9 19.4 17.7 18.5 变异系数 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 e 最小值 0.72 0.64 1.00 0.70 最大值 1.08 0.85 1.44 1.21 平均值 0.91 0.75 1.20 0.91 变异系数 0.10 0.07 0.11 0.10 IP 最小值 10.13 6.21 15.00 10.40 最大值 20.26 9.92 23.80 20.30 平均值 14.62 8.73 19.44 14.66 变异系数 0.16 0.09 0.11 0.18 IL 最小值 0.47 0.33 0.84 0.58 最大值 1.25 0.93 1.29 1.27 平均值 0.82 0.63 1.06 0.91 变异系数 0.23 0.19 0.10 0.16 表 9 抗剪强度指标统计
Table 9. Statistics of shear strength index
指标 统计项目 黏性土
(③1)粉土
(③2)淤泥质土
(③3)粉质黏土
(③4)c直快/kPa 最小值 8.84 4.00 6.00 − 最大值 23.28 14.00 12.00 − 平均值 14.38 9.58 9.29 − 变异系数 0.27 0.27 0.28 − φ直快/(°) 最小值 9.25 26.00 10.00 − 最大值 21.36 35.70 15.50 − 平均值 13.83 31.52 11.87 − 变异系数 0.19 0.10 0.17 − c固快/kPa 最小值 10.38 6.95 8.00 9.00 最大值 22.41 15.18 15.00 16.00 平均值 15.48 10.45 11.14 11.50 变异系数 0.22 0.23 0.22 0.23 φ固快/(°) 最小值 11.53 29.22 12.00 14.00 最大值 24.47 36.75 16.00 24.00 平均值 16.81 32.92 13.50 18.53 变异系数 0.19 0.08 0.11 0.18 表 10 地基承载力成果
Table 10. Results of foundation bearing capacity
研究方法 黏性土 (③1) 粉土(③2) 淤泥质土(③3) 粉质黏土(③4) 物性法 f0/kPa 135.87 194.55 87.58 152.03 原位法 静探法 f0/kPa 78.68 168.40 88.20 108.03 标贯法 f0/kPa 104.98 173.10 − 110.00 十字板法 fk/kPa 65.97 − − 98.00 理论法 公式(1) fa/kPa 113.43 115.80 82.10 131.18 公式(2) fk/kPa 107.15 144.75 70.97 125.82 经验法 公式(1) f0/kPa 129.50 162.80 105.00 141.90 公式(2) fk/kPa 113.50 143.10 100.48 115.73 注:f0、fa、fk分别为承载力基本值、特征值、标准值。 表 11 压缩及标贯指标统计表
Table 11. Statistics of compression and standard penetration test index
指标 统计项目 黏性土
(③1)粉土
(③2)淤泥质土
(③3)粉质黏土
(③4)a/MPa−1 最小值 0.22 0.10 0.49 0.17 最大值 0.70 0.21 1.08 0.80 平均值 0.46 0.15 0.77 0.44 变异系数 0.24 0.18 0.20 0.27 Es1-2/MPa 最小值 2.60 8.30 2.10 2.50 最大值 7.30 16.00 3.60 7.20 平均值 4.30 11.90 2.90 4.50 变异系数 0.23 0.16 0.13 0.21 N/击 最小值 1.20 4.30 1.00 2.00 最大值 4.80 10.30 2.50 7.00 平均值 2.90 7.20 1.70 4.10 变异系数 0.28 0.23 0.25 0.25 -
[1] 尹永川. 新近沉积粘性土的压缩模量与标准贯入试验锤击数的关系[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2002,29(1):68. [YIN Yongchuan. Relationship between the compressive modulus of newly deposited cohesive soil and the number of hammer blows in the standard penetration test[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2002,29(1):68. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2002.01.021
[2] 袁仁茂, 孙宏伟, 马凤山, 等. 北京平原区新近沉积土基本工程地质特性分析[J]. 第四纪研究,2005,25(1):93 − 99. [YUAN Renmao, SUN Hongwei, MA Fengshan, et al. Physicochemical and geotechnical characteristics of the recently deposited soil in Beijing plain region[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2005,25(1):93 − 99. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2005.01.013
[3] 马玉杰. 对北京地区新近沉积土的判别认识[J]. 岩土工程技术,2011,25(4):187 − 191. [MA Yujie. Understanding of the recently deposited soil in beijing area[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique,2011,25(4):187 − 191. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2011.04.006
[4] 王芸生, 王恒周, 赖万章, 等. 论渤海湾西岸的再造与变迁[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1980,7(5):20 − 23. [WANG Yunsheng, WANG Hengzhou, LAI Wanzhang, et al. On the reconstruction and changes of the west coast of Bohai Bay[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,1980,7(5):20 − 23. (in Chinese)
[5] 段永侯. 渤海海岸带变迁及其环境地质效应[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2000,27(3):1 − 5. [DUAN Yonghou. Changes of the Bohai sea coastal zone and its environmental geological effects[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2000,27(3):1 − 5. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2000.03.001
[6] 天津市城乡建设委员会. 天津市建筑地基基础设计规范: TBJ1—88[S]. 天津, 1988.
Tianjin Urban and Rural Construction Commission. Tianjin city building foundation design code: TBJ1—88[S]. Tianjin, 1988.(in Chinese)
[7] 张景恒, 刘家铮. 天津市区浅层地基土的工程性质特征研究[R]. 天津: 天津市勘察院, 1989.
ZHANG Jingheng, LIU Jiazheng, et al. Research on engineering characteristics of shallow foundation soil in Tianjin city[R]. Tianjin: Tianjin Institute of Geotechnical Investigation Surveying, 1989. (in Chinese)
[8] 天津市城乡建设委员会. 天津市岩土工程技术规范: DB/T29—20—2017[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2000.
Tianjin Urban and Rural Construction Commission. Tianjin Technical code for geotechnical engineering: DB/T29—20—2017[S]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
[9] 周玉明, 吴永红, 赵志峰, 等. 天津市区标准地层的建立及工程特性研究[R]. 天津: 天津市勘察院, 2007.
ZHOU Yunming, WU Yonghong, ZHAO Zhifeng, et al. Study on the establishment and engineering characteristics of standard strata in Tianjin Urban area[R]. Tianjin: Tianjin Institute of Geotechnical Investigation Surveying, 2007.(in Chinese)
[10] 天津市建设管理委员会. 天津市地基土层序划分技术规程: DB/T29—191[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009.
Tianjin Construction Management Commission. Technical specification for division of subsoil sequence in Tianjin: DB/T29—191[S]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[11] 天津市地质矿产局. 天津市地质环境图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004: 13-21.
Tianjin Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Atlas of geological environment of Tianjin[M].Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004: 13- 21. (in Chinese)
[12] 天津市地质调查院. 天津城市地质调查成果[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009.
Tianjin Geological Survey Institute. Results of Tianjin urban geological survey[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009. (in Chinese)
[13] 天津市地质资料馆. 天津滨海新区地质资料二次开发成果图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011.
Tianjin Geological Archive. Atlas of secondary development results of geological data in Tianjin Binhai New Area[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011. (in Chinese)
[14] 王海峰, 裴艳东, 刘会敏, 等. 渤海湾全新世牡蛎礁: 时空分布和海面变化标志点[J]. 地质通报,2011,30(9):1396 − 1404. [WANG Haifeng, PEI Yandong, LIU Huimin, et al. Holocene oyster reefs: spatial and temporal distribution and sea level indicators in Bohai Bay[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2011,30(9):1396 − 1404. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.008
[15] 王宏, 李凤林, 范昌福, 等. 环渤海海岸带14C数据集(Ⅰ)[J]. 第四纪研究,2004,24(6):601 − 613. [WANG Hong, LI Fenglin, FAN Changfu, et al. The 14C database (Ⅰ) on the circum-Bohai sea-Coast[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2004,24(6):601 − 613. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.06.001
[16] 王宏, 范昌福. 环渤海海岸带14C数据集(Ⅱ)[J]. 第四纪研究,2005,25(2):141 − 156. [WANG Hong, FAN Changfu. The 14C database (Ⅱ) on the circum-Bohai sea-Coast[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2005,25(2):141 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2005.02.003
[17] 赵希涛, 张景文, 焦文强, 等. 渤海湾西岸的贝壳堤[J]. 科学通报,1980,25(6):279 − 281. [ZHAO Xitao, ZHANG Jingwen, JIAO Wenqiang, et al. Shell bank on the west coast of Bohai Bay[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,1980,25(6):279 − 281. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/csb1980-25-6-279
[18] 庄振业, 许卫东, 李学伦. 渤海南岸6000年来的岸线演变[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报,1991,21(2):99 − 110. [ZHUANG Zhenye, XU Weidong, LI Xuelun. The coastline evolution on the south Coast of the Bohai sea since 6 k a B.P[J]. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao,1991,21(2):99 − 110. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: