An analysis of spatio-temporal characteristics and influencing factors of surface evapotranspiration in the Yinchuan Plain based on MOD16 data
-
摘要:
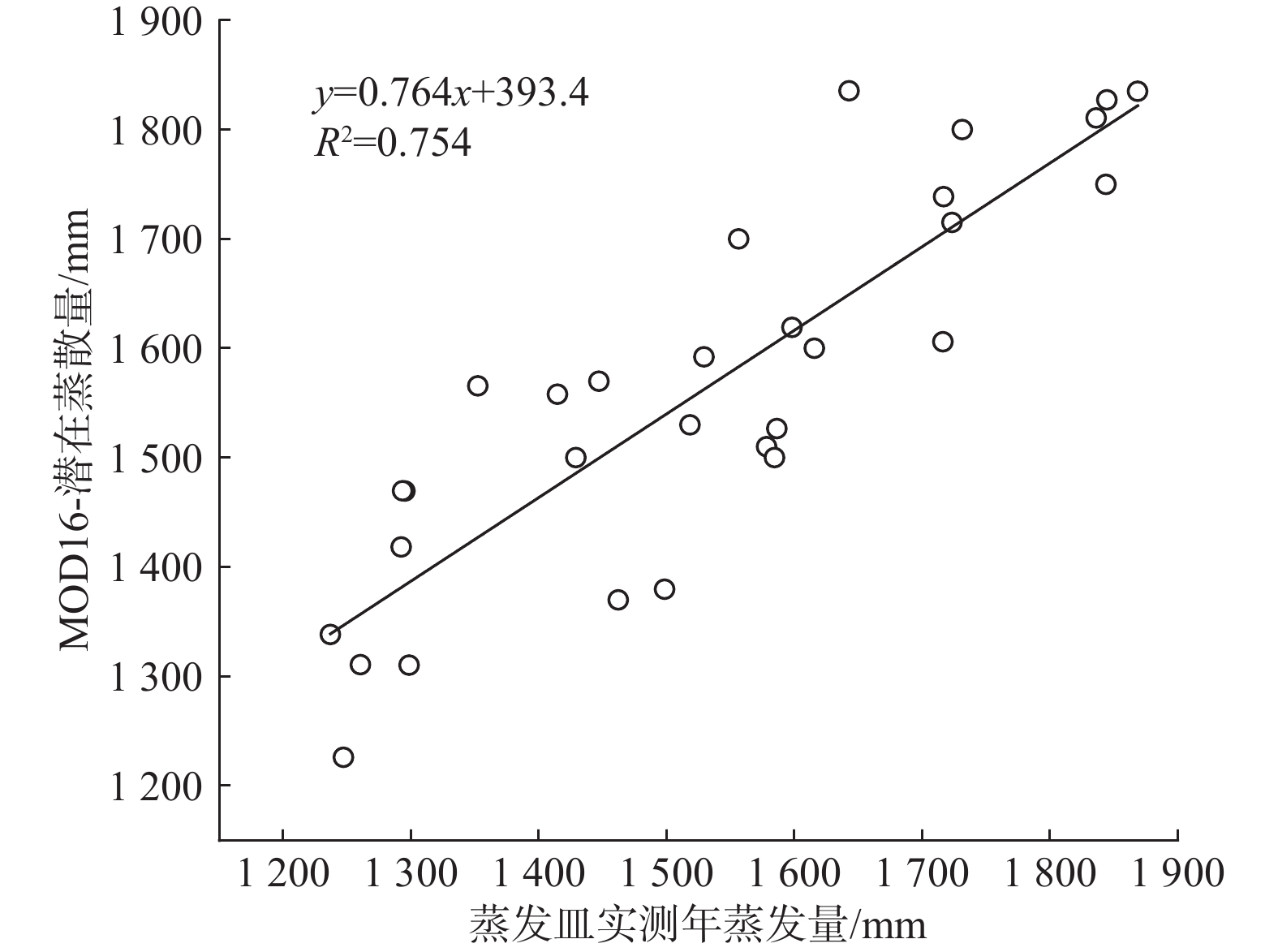
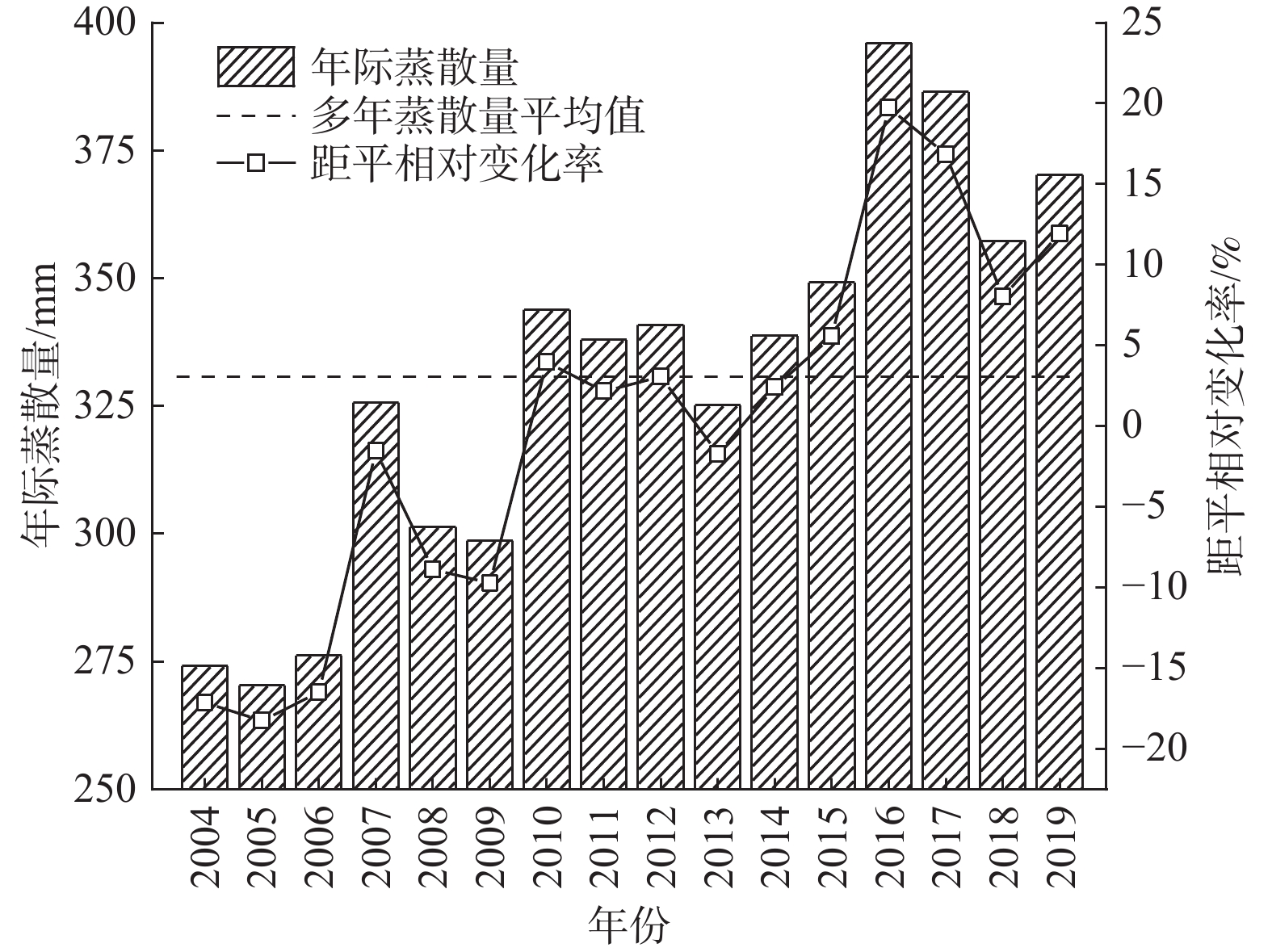
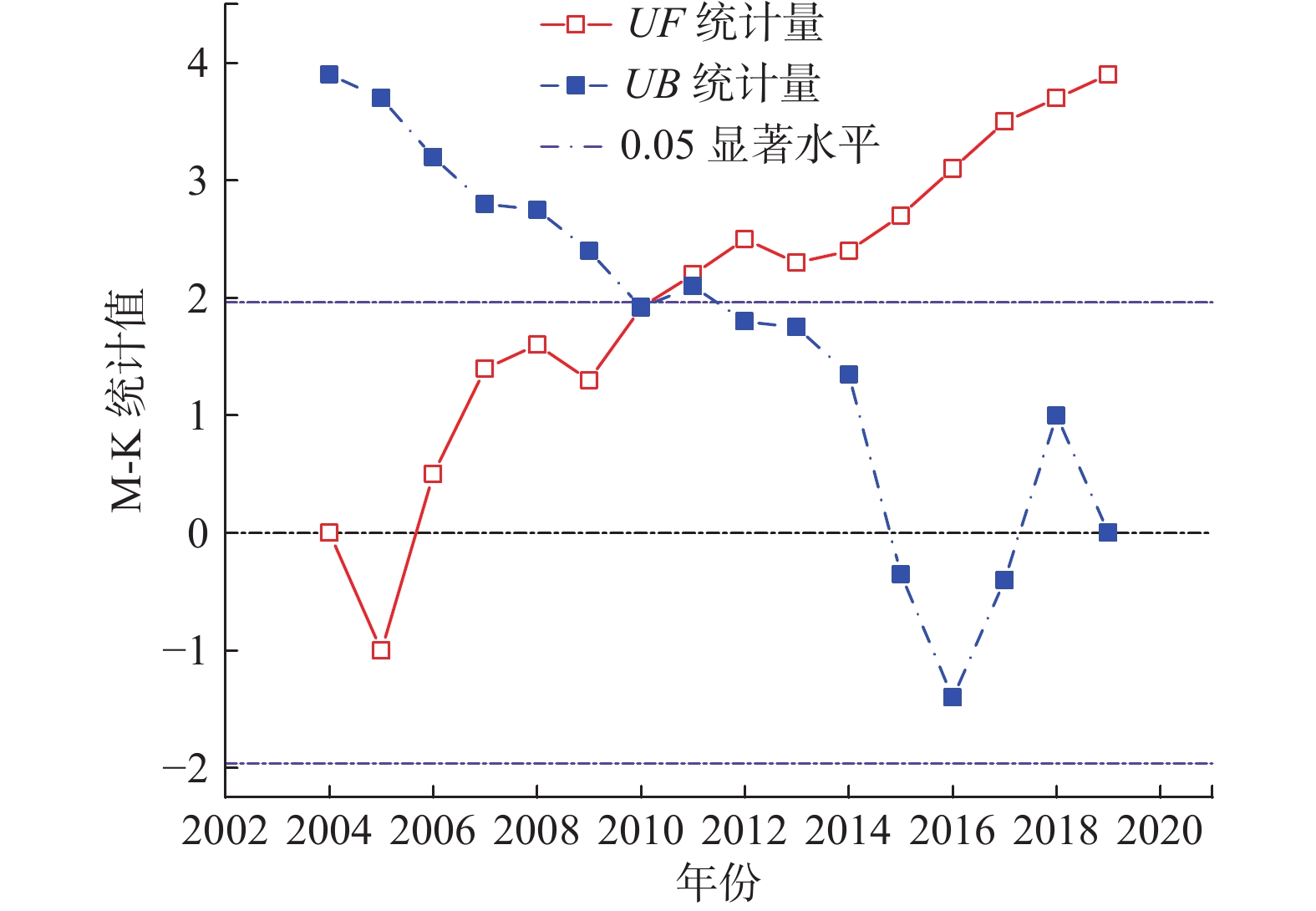
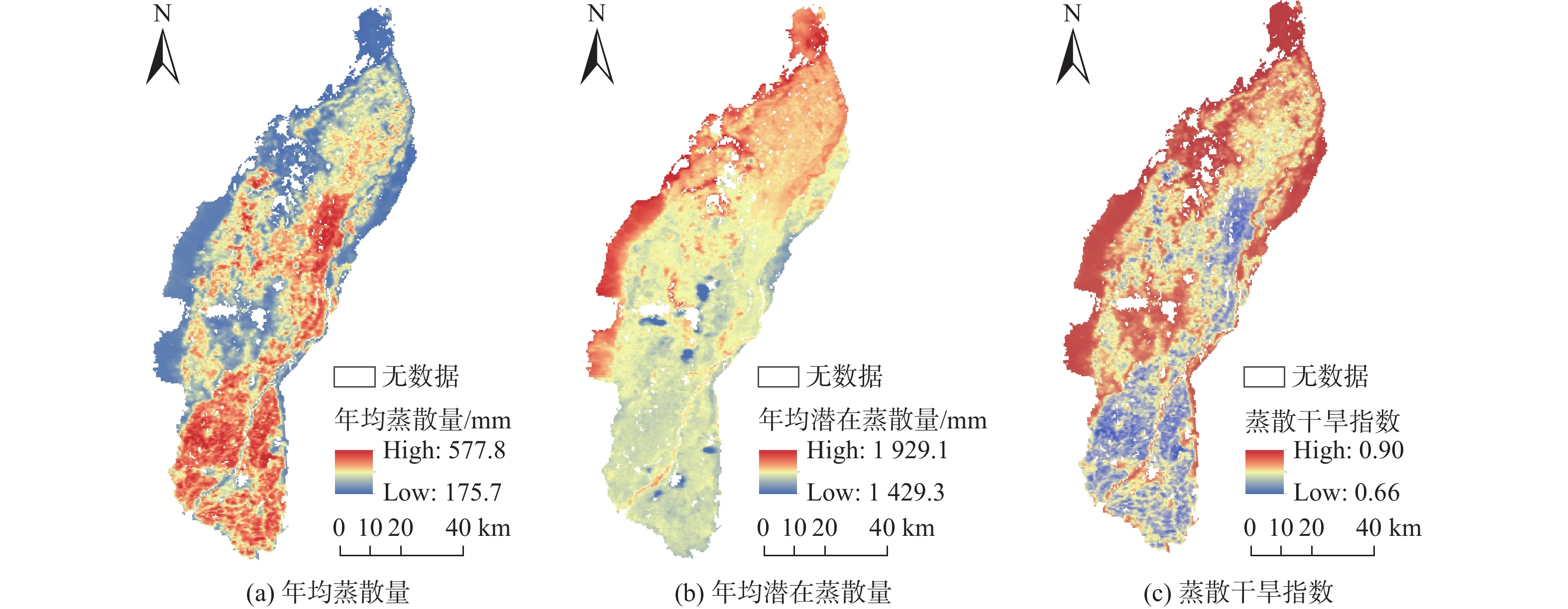
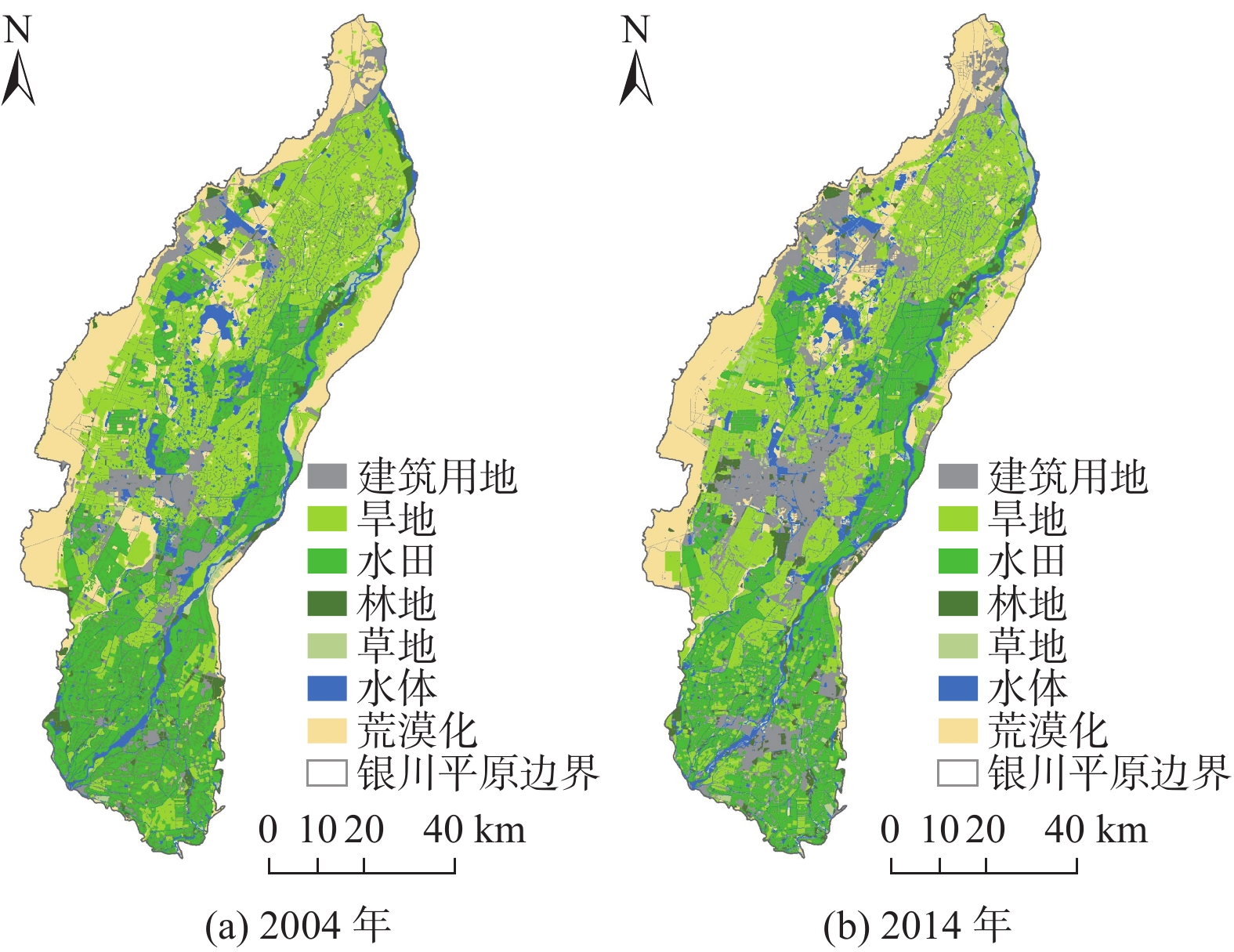
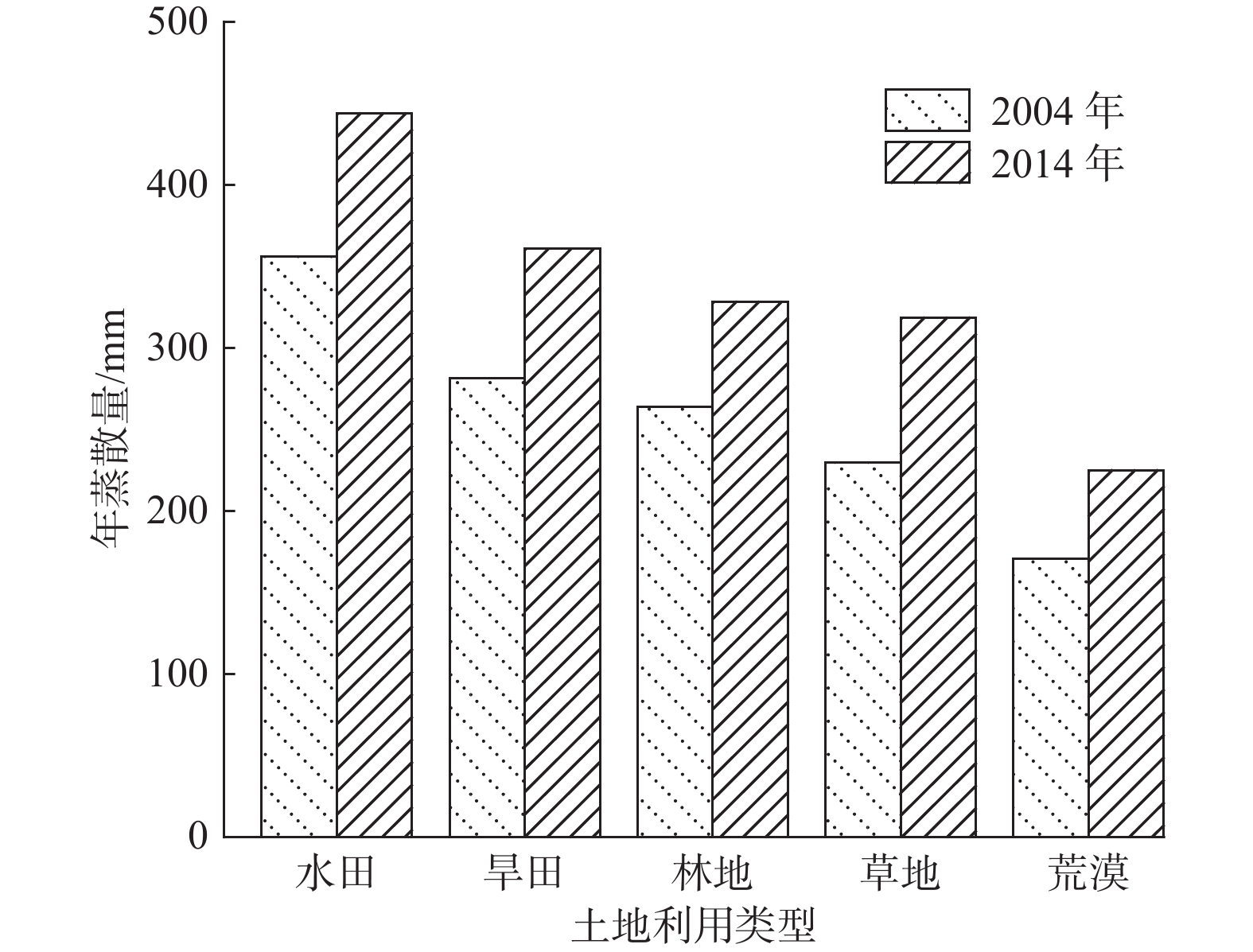
地表蒸散发是陆地水文循环的重要组成部分,分析蒸散量时空变化特征是深入了解干旱区水文过程的基础。由于银川平原缺乏区域尺度实际蒸散量的长期观测,很难得到长时间序列蒸散量的时空变化特征。基于MOD16A3地表蒸散量数据及研究区内气象站点实测数据,采用Theil Sen Median趋势度分析、MK突变检验及CA-Markov模型等方法,从时间与空间的角度分析2004—2019年银川平原地表蒸散量的变化特征及影响因素,预测2024年地表蒸散量的发展趋势。研究结果表明:2004—2019年银川平原蒸散量年际波动总体是增加趋势,MK突变检验结果显示2010年是蒸散量时序数据的突变点;银川平原实际蒸散量与潜在蒸散量空间分布格局、变化趋势均存在明显的差异性,蒸散量在近16年呈增加趋势,潜在蒸散量呈减少趋势,符合干旱区蒸散发互补相关理论。采用CA-Markov模型对2024年银川平原地表蒸散量未来发展趋势进行预测,模拟结果显示在未来5年银川平原蒸散量仍呈增加趋势;蒸散量的时空变化受气候与人类活动的共同影响,蒸散量与气温、降水、日照时数呈正相关,与相对湿度呈负相关,土地利用结构影响年蒸散量的空间格局,呈现出水田>旱田>林地>草地>荒漠的规律。
-
关键词:
- MOD16 /
- 蒸散发 /
- Theil-Sen Median趋势度 /
- CA-Markov模型 /
- 银川平原
Abstract:Surface evapotranspiration is an important part of terrestrial hydrological cycle, and the analysis of spatio-temporal variation characteristics of evapotranspiration is the basis of in-depth understanding of hydrological processes in arid areas. Due to the lack of long-term observations of actual regional evapotranspiration in the Yinchuan Plain, it is difficult to obtain the spatio-temporal variation characteristics of long-term series evapotranspiration. Based on the MOD16A3 surface evapotranspiration data and the measured data of meteorological stations in the study area, this paper analyzes the variation characteristics and influencing factors of surface evapotranspiration in the Yinchuan Plain from the perspective of time and space by using the methods of Theil Sen median trend analysis, MK mutation test and CA-Markov model, and predicts the development trend of surface evapotranspiration in the next five years. The results show that from 2004 to 2019, the interannual variation trend of evapotranspiration in the Yinchuan Plain is increasing, and the MK mutation test results show that the year of 2010 is the mutation point of evapotranspiration time series data. There are obvious differences in spatial distribution pattern and change trend between the actual evapotranspiration (ET) and potential evapotranspiration (PET) in the Yinchuan Plain. Actual evapotranspiration shows an increasing trend in recent 16 years, and potential evapotranspiration shows a decreasing trend, which conforms to the theory of complementary evapotranspiration in arid areas. The future development trend of surface evapotranspiration in the Yinchuan Plain in 2024 is predicted with the CA-Markov model. The simulation results show that the evapotranspiration will still increase in the next five years. The spatio-temporal variation of evapotranspiration is affected by climate and human activities. Evapotranspiration is positively correlated with temperature, precipitation and sunshine hours, and is negatively correlated with relative humidity. Land use structure affects annual evapotranspiration. The results also show the rule: Evapotranspiration of paddy field > dry land > woodland > grassland > desert.
-
Key words:
- MOD16 /
- evapotranspiration /
- Theil Sen median trend /
- CA-Markov model /
- Yinchuan Plain
-

-
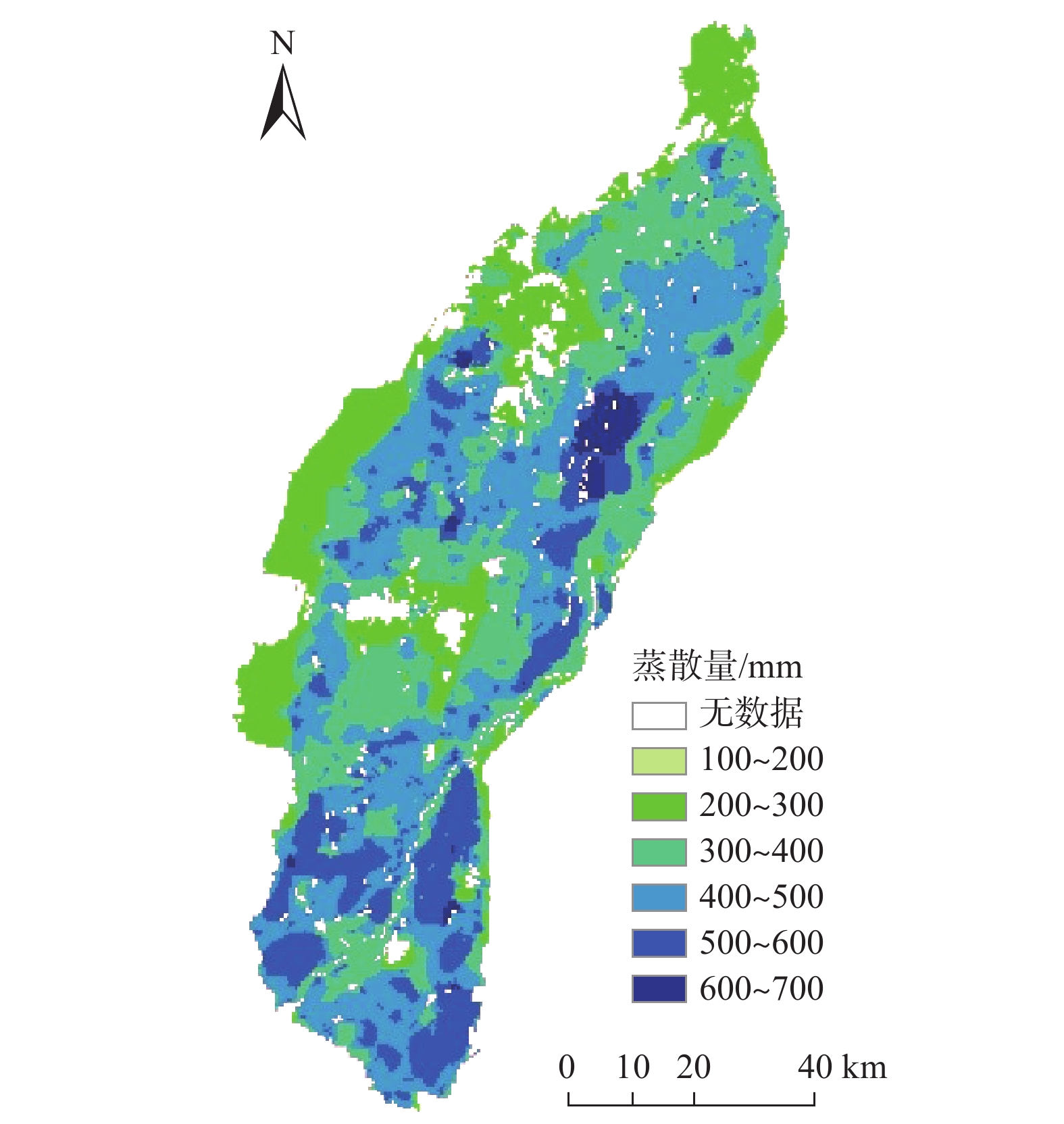
表 1 银川平原蒸散量、潜在蒸散量变化趋势及显著性统计
Table 1. Change trend and significance of evapotranspiration and potential evapotranspiration in the Yinchuan Plain
变化趋势 显著性面积占比/% 总计/% 不显著 弱显著 显著 极显著 蒸散量 增加 7.69 2.69 7.09 75.49 92.96 减少 4.41 0.81 1.09 0.73 7.04 潜在蒸散量 增加 0.13 0 0 0 0.13 减少 3.98 6.1 36.12 53.68 99.87 表 2 银川平原蒸散量等级面积占比
Table 2. Proportion of the evapotranspiration grade area in the Yinchuan Plain
蒸散量等级/
mm面积占比/% 2004年
实际值2009年
实际值2014年
实际值2019年
实际值2024年
预测值100~200 27.83 19.79 7.05 0.09 0 200~300 33.56 32.21 31.33 29.45 19.03 300~400 28.36 33.49 32.22 31.36 31.65 400~500 9.94 14.07 23.19 28.25 32.75 500~600 0.31 0.42 6.12 10.02 14.69 600~700 0 0 0 0.80 1.78 表 3 银川平原蒸散量与气象因子相关关系
Table 3. Correlation between evapotranspiration and meteorological factors in the Yinchuan Plain
气象因子 气温 降水 日照时数 相对湿度 相关系数 0.910 0.905 0.768 −0.746 -
[1] TIAN F, QIU G Y, YANG Y H, et al. Estimation of evapotranspiration and its partition based on an extended three-temperature model and MODIS products[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2013,498:210 − 220. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.06.038
[2] CHEN Y, XIA J Z, LIANG S L, et al. Comparison of satellite-based evapotranspiration models over terrestrial ecosystems in China[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2014,140(1):279 − 293.
[3] 王军, 李和平, 鹿海员. 基于遥感技术的区域蒸散发计算方法综述[J]. 节水灌溉,2016(8):195 − 199. [WANG Jun, LI Heping, LU Haiyuan. Review of regional evapotranspiration estimation models basing on the remote sensing[J]. Water Saving Irrigation,2016(8):195 − 199. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] RODELL M, HOUSER P R, JAMBOR U, et al. The global land data assimilation system[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society,2004,85(3):381 − 394. doi: 10.1175/BAMS-85-3-381
[5] MIRALLES D, HOLMES T, DE JEU R, et al.Global land-surface evaporation estimated from satellite-based observations[M].Geneva: World Meteorological Orgnization, 2008.
[6] SENAY G B, BOHMS S, SINGH R K, et al. Operational evapotranspiration mapping using remote sensing and weather datasets: a new parameterization for the SSEB approach[J]. JAWRA Journal of the American Water Resources Association,2013,49(3):577 − 591. doi: 10.1111/jawr.12057
[7] MU Q Z, ZHAO M S, RUNNING S W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2011,115(8):1781 − 1800. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.02.019
[8] DZIKITI S, JOVANOVIC N Z, BUGAN R D, et al. Comparison of two remote sensing models for estimating evapotranspiration: algorithm evaluation and application in seasonally arid ecosystems in South Africa[J]. Journal of Arid Land,2019,11(4):495 − 512. doi: 10.1007/s40333-019-0098-2
[9] HASSAN A, ISMAIL S S, ELMOUSTAFA A, et al. Evaluating evaporation rate from high Aswan Dam Reservoir using RS and GIS techniques[J]. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science,2018,21(3):285 − 293. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrs.2017.10.001
[10] 何慧娟, 卓静, 董金芳, 等. 基于MOD16监测陕西省地表蒸散变化[J]. 干旱区地理,2015,38(5):960 − 967. [HE Huijuan, ZHUO Jing, DONG Jinfang, et al. Surveying variations of evapotranspiration in Shaanxi Province Using MOD16 products[J]. Arid Land Geography,2015,38(5):960 − 967. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] WOOD E F, SU H B, MCCABE M, et al. Estimating evaporation from satellite remote sensing[C]//2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Proceedings (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37477). Toulouse, France. IEEE, 2003: 1163-1165.
[12] 孙玉芳. 基于遥感监测指数模型的银川平原土壤盐渍化动态研究[J]. 地下水,2019,41(5):80 − 82. [SUN Yufang. Study on soil salinization dynamics in Yinchuan plain based on remote sensing monitoring index model[J]. Ground Water,2019,41(5):80 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 袁丽华, 蒋卫国, 申文明, 等. 2000—2010年黄河流域植被覆盖的时空变化[J]. 生态学报,2013,33(24):7798 − 7806. [YUAN Lihua, JIANG Weiguo, SHEN Wenming, et al. The spatio-temporal variations of vegetation cover in the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2010[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2013,33(24):7798 − 7806. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] THEIL H. A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis[C]//Advanced Studies in Theoretical and Applied Econometrics. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 1992: 345-381.
[15] TIAN Q, WANG Q, ZHAN C, et al. Analysis of climate change in the coastal zone of Eastern China, against the background of global climate change over the last fifty years: case study of Shandong peninsula, China[J]. International Journal of Geosciences,2012,3(2):379 − 390. doi: 10.4236/ijg.2012.32042
[16] 张明明. 2000—2015年中国干旱半干旱区蒸散发时空变化及其影响因素分析[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019.
ZHANG Mingming. Analysis of the temporal and spatial variation of evapotranspiration and its driving factors in arid and semi-arid region of China from 2000 to 2015[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 温媛媛, 赵军, 王炎强, 等. 基于MOD16的山西省地表蒸散发时空变化特征分析[J]. 地理科学进展,2020,39(2):255 − 264. [WEN Yuanyuan, ZHAO Jun, WANG Yanqiang, et al. Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of surface evapotranspiration in Shanxi Province based on MOD16[J]. Progress in Geography,2020,39(2):255 − 264. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.02.007
[18] 王丽霞, 张珈玮, 张双成, 等. 基于CA-Markov模型的陕西省植被覆盖模拟及预测[J]. 安徽农业科学,2020,48(4):53 − 56. [WANG Lixia, ZHANG Jiawei, ZHANG Shuangcheng, et al. Simulation and prediction of vegetation coverage in Shaanxi Province based on CA-Markov model[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(4):53 − 56. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] BOUCHET R J. Évapotranspiration potentielle et évaporation sous abri[C]//Biometeorology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1962: 540-545.
[20] 邵小路, 姚凤梅, 张佳华, 等. 基于蒸散干旱指数的华北地区干旱研究[J]. 气象,2013,39(9):1154 − 1162. [SHAO Xiaolu, YAO Fengmei, ZHANG Jiahua, et al. Analysis of drought in North China based on evapotranspiration drought index[J]. Meteorological Monthly,2013,39(9):1154 − 1162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 薛阳, 金晓媚, 朱晓倩. 宁夏沿黄经济区蒸散量变化特征及水均衡方法验证[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(3):27 − 32. [Xue Yang, Jin Xiaomei, Zhu Xiaoqian. Variation of evapotranspiration of Ningxia Yellow River economic zone and the validation using water budget method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(3):27 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: