An experimental study of the measuring hydration film thickness of clay particles with atomic force microscope probe
-
摘要:
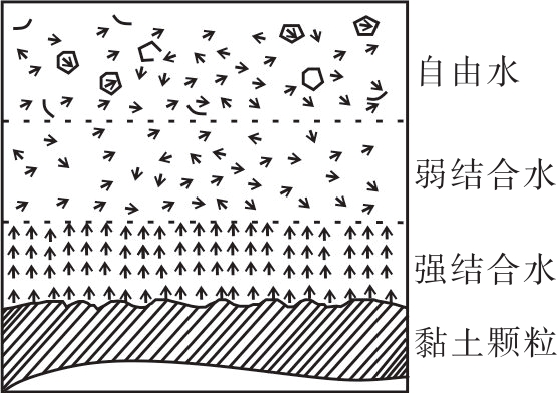
黏土颗粒水化膜厚度问题是泥质膨胀性岩土膨胀机制研究的理论基础。关于黏土颗粒水化膜厚度测试资料较为丰富,但通过原子力显微镜测试黏土颗粒水化膜厚度的研究成果还较为少见,且在测试方法方面尚不完善。基于3层水化膜结构模型和原子力显微镜测试技术,通过对蒙脱石粉末、泥岩粉末、泥岩岩片3种样品的测试研究,提出了水化膜厚度刺入式测试方法、粉末样和岩石样的制样方法、试验数据的统计处理方法。总结了水化膜厚度测试曲线自由水段、弱结合水段、强结合水段、黏土颗粒段的变化规律。通过和既有研究成果的对比分析,论证了原子力显微镜刺入测试黏土颗粒水化膜厚度的合理性与可行性。结合工程实践,探讨了定量化获取水化膜厚度在理解泥质膨胀性岩土膨胀机制方面的工程意义和理论价值。
Abstract:The thickness of hydration film of clay particles is the theoretical basis of swelling mechanism of argillaceous expansive rock and soil. There are abundant data on the measurement of clay particle hydration film thickness, but the study of the measurement of clay particle hydration film thickness by atomic force microscopy is relatively rare, and the test method is not perfect. Based on the three-layer hydration membrane structure model and atomic force microscope test technology, through the test and research on montmorillonite powder, mudstone powder and mudstone rock slice, this paper puts forward the measurement method of the thickness of the hydration film, the preparation method of powder sample and rock sample, and the statistical processing method of the test data. The variation rules of the free water section, weakly bound water section, strong bound water section and clay particle section of the hydration film thickness test curve are summarized. Through comparative analyses with the existing research results, the rationality and feasibility of the testing the thickness of the hydration film of clay particles by the atomic force microscope is demonstrated. Combined with engineering practice, the engineering significance and theoretical value of the quantitatively obtaining the hydration film thickness in understanding the swelling mechanism of the argillaceous expansive rock and soil are discussed.
-

-
图 1 黏土颗粒表面示意图[8]
Figure 1.
表 1 3种泥质样品主要测试结果
Table 1. Main test results of three kinds of mud samples
样品类型 强结合水膜/nm 弱结合水膜/nm 水膜总厚度/nm 备注 蒙脱石粉末 14.29 25.13 39.42 200目粉末 泥岩粉末 14.18 29.64 43.82 200目粉末 泥岩岩片 14.77 28.88 43.65 用10000目
砂纸打磨表 2 黏土颗粒水化膜厚度研究结果
Table 2. Results of the study of hydration film thickness of clay particle
表 3 泥质膨胀性岩土水化膨胀模型简表
Table 3. Simplified table of hydration-swelling model for the argillaceous expansive rock and soil
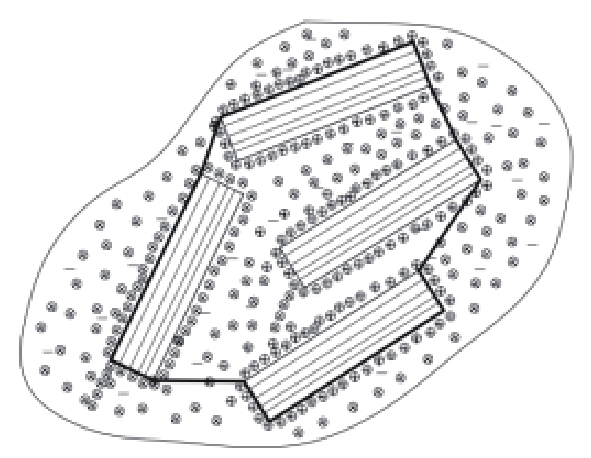
黏土矿物晶体 黏土颗粒水化膜 土样结构吸水膨胀模型 水化膜理论模型 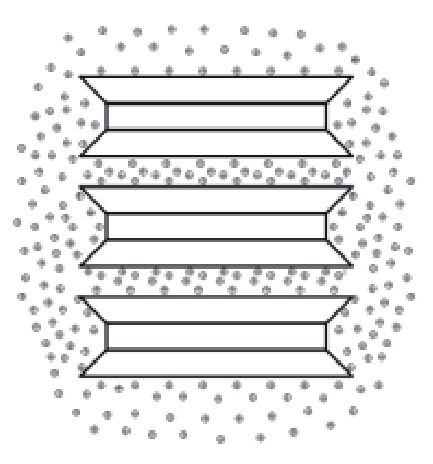

黏土矿物晶层之间被水分子
和交换性阳离子充填,改变
晶层间距。晶体周围被水化
的阴离子和阳离子包围黏土颗粒结构由黏土矿物晶
体(矩形部分)、水(圆点)和
空气组成,黏土颗粒表面形
成水化膜土体结构由土颗粒、水(黑色部分)
和空气组成,土颗粒之间的接触关
系及其形成的孔隙特征如上所示黏土颗粒表面的水化膜模型可以
分为4个部分,即黏土颗粒、强结
合水层、弱结合水层、自由水层表 4 膨胀参数与水化膜的联系
Table 4. Relationship between swelling parameters and hydration film
膨胀参数 基本含义 与水化膜的联系 自由膨胀率 黏土颗粒粉末自由分散状态下的最大吸水膨胀能力,是结合水膜厚度的最大变形表现 分散的土颗粒自由吸水形成水化膜,与其粒径大小密切相关 饱和吸水率 泥质膨胀岩岩块和岩粉自由吸水的最大吸水率,是泥质膨胀性岩石最大吸水能力的体现 岩块和岩粉结构性差别对结合水膜厚度有不同的影响 吸湿含水量 在一定的温度(25 ℃)和相对湿度(60%)条件下,膨胀土试样的吸附平衡含水率,是黏土试样自由吸附水分子的能力 黏土颗粒吸附水分子,在颗粒表面形成弱结合水膜,引起岩土体膨胀变形 蒙脱石含量 蒙脱石、伊利石、高岭石等亲水性黏土矿物含量是黏性土膨胀变形的物质基础,其中蒙脱石的膨胀性最强。蒙脱石含量越高,膨胀土产生吸水膨胀变形越大 蒙脱石形成结合水膜,是泥质膨胀性岩土吸水膨胀的微观机制 阳离子交换量 不同的黏土矿物,因晶格同晶替代、晶格边缘破损和裸露的氢氧基上氢的活性和数量上的差异及分散度的不同,使得不同的黏土矿物颗粒的阳离子交换量不同。一般以每百克土中含有多少毫克当量的交换性阳离子来表示 阳离子交换量大致反映了土中黏粒含量及矿物成分,在一定程度上反映了土中双电层的发育程度,可以近似地判断土的膨胀潜势 -
[1] 郭永春, 陈伟乐, 赵海涛. 膨胀土吸水过程的试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(4):108 − 112. [GUO Yongchun, CHEN Weile, ZHAO Haitao. Experimental research of water-uptake process of the expansive soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(4):108 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] [美]米切尔. 岩土工程土性分析原理[M]. 高国瑞, 等, 译. 南京: 南京工学院出版社, 1988: 105-116.
Mitchell J K. Fundamentals of soil behavior[M].GAO Guorui, et al, trs. Nanjing: Southeast University Press, 1988: 105-116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] [苏]奥西波夫. 粘土类土和岩石的强度与变形性能的本质[M]. 李生林, 张之一, 译. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985: 152-168.
В. И. Осипов. The essence of strength and deformation properties of clay-like soils and rocks[M]. LI Shenglin, ZHANG Zhiyi, trs. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1985: 152-168. (in Chinese)
[4] 李生林, 秦素娟, 薄遵昭, 等. 中国膨胀土工程地质研究[M]. 南京: 江苏科学技术出版社, 1992.
LI Shenglin, QIN Sujuan, BO Zhunzhao, et al. Studies on the engineering geology of expansive soils in China[M]. Nanjing: Phoenix Science Press, 1992. (in Chinese)
[5] 谭罗荣, 孔令伟. 特殊岩土工程土质学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.
TAN Luorong, KONG Lingwei. Soil science of special geotechnical engineering[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
[6] 高国瑞. 近代土质学[M]. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.
GAO Guorui. Neoteric soil geotechnology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013. (in Chinese)
[7] 赵梦怡. 膨胀土膨胀量理论计算方法及在土坡工程中的应用[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019.
ZHOU Mengyi. Theoretical calculation method of swelling capacity of expansive soil and its application in slope engineering[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] DROST-HANSEN W. Effects of vicinal water on colloidal stability and sedimentation processes[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,1977,58(2):251 − 262. doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(77)90142-4
[9] 吴伦. 基于原子力显微镜的煤粒表面水化膜和颗粒间相互作用力研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2015.
WU Lun. Study on hydration film on coal surface and interaction force between particles based on AFM[D]. Xuzhou, China University of Mining and Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载:


