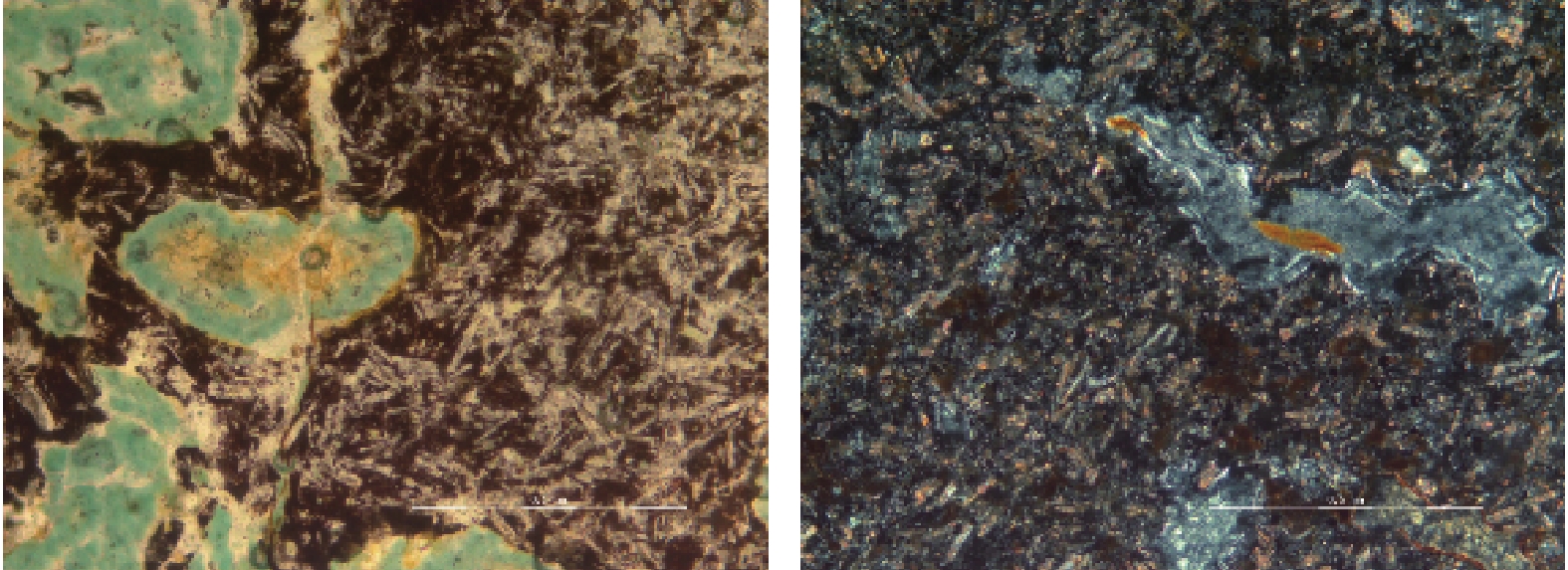
Water-rock /soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province
-
摘要:
滑坡体水-岩(土)作用是一种复杂的物理化学综合作用,影响坡体的稳定性,但关于目前水-岩(土)相互作用对地质灾害发生方面的影响研究仍较为薄弱。以贵州省鸡场滑坡为研究对象,分析滑坡区岩土体矿物组成和化学成分特征,结合区域内基岩裂隙水、大气降水的成分变化,利用主成分分析方法,研究鸡场滑坡水-岩(土)作用过程,并分析水岩演化作用对滑坡稳定性的影响。结果表明:(1)滑体内玄武岩的风化过程是一种机械破碎-矿物蚀变耦合的水-岩相互作用,发生在“微观-细观-宏观”3种尺度上;(2)选取前3个因子Z1、Z2、Z3(分别占总方差的49.365%、27.135%、15.092%)分析地下水的化学特征,主因子Z1反映了玄武岩原生矿物的溶蚀作用对地下水化学成分的控制作用,主因子Z2反映了地下水的蒸发作用与SiO2溶解度随pH变化的矿物沉淀作用,主因子Z3反映了地下水与岩(土)体间存在离子交换作用且主参与离子为Mg2+和K+;(3)水岩作用产物主要为伊利石、蒙皂石、绿泥石等黏土矿物,使得岩体结构面内黏土矿物含量增加,岩体劣化损伤,对滑带的形成及滑坡的解体产生重要影响。由此研究说明滑坡地下水与岩土体相互作用的主要过程能被主成分分析结果充分反映。
Abstract:The water-rock/soil interaction of a landslide is a complex physical and chemical synthesis, which seriously affects the stability of the slope. Research on the water-rock/soil interaction of a landslide on the occurrence of geological disasters is relatively weak. This article takes the Jichang landslide as the research object, analyzes the characteristics of the mineral composition and chemical composition of the rock and soil in the landslide area, combines the compositional changes of bedrock fissure water and atmospheric precipitation in the area, and uses the principal component analysis method to study the water-rock of the Jichang landslide The process of action and the influence of water and rock evolution on the stability of landslides are analyzed. The results show that: (1) The weathering process of basalt in the sliding body is a water-rock interaction coupled by mechanical crushing-mineral alteration, occurring on “micro-micro-macro” three scales. (2) The first three factors, accounting for 49.365%, 27.135%, and 15.092% of the total variance, respectively, are selected to analyze the chemical characteristics of groundwater. The main factor Z1 reflects the control effect of the dissolution of basalt primary minerals on the chemical composition of the groundwater, the main factor Z2 reflects the evaporation of groundwater and the precipitation of minerals in which the solubility of SiO2 changes with pH, and the main factor Z3 reflects the ion exchange between groundwater and rock (soil) with the main participating ions being Mg2+ and K+. (3) The products of water-rock interaction are mainly clay minerals such as illite, smectite and chlorite, which increase the content of clay minerals in the structural plane of the rock mass, deteriorate and damage the rock mass, significantly influcing the formation of slip zones and the disintegration of landslides. The results of principal component analysis of groundwater can reflect the main process of interaction between landslide groundwater and rock/soil.
-

-
表 1 鸡场滑坡内岩土体X-矿物衍射分析结果
Table 1. Analysis results of X-mineral diffraction of rock and soil mass in Jichang landslide
样品 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 辉石/% 9.6 20.3 10.4 — 31.2 石英/% 9.3 2.6 3.2 16.7 3.4 钾长石/% 2.7 2.6 3.4 1.8 2.5 斜长石/% 16.2 47.2 41.0 8.8 31.8 磷灰石/% 1.8 2.4 2.2 3.0 2.0 钛铁矿/% 3.6 3.3 4.1 5.0 3.2 磁铁矿/% 5.7 1.1 6.2 1.3 — 褐铁矿/% 3.5 2.5 1.3 10.7 9.1 伊利石/% 9.5 0.9 12.7 3.2 0.8 蒙皂石/% 32.3 2.7 13.5 33.7 4.2 绿泥石/% 5.7 14.3 2.0 15.8 11.8 注:结果均为质量占比;“—”表示无此成分。R1代表滑坡后壁基岩裂隙水出露处结构面夹层土,R2代表裂隙水出露处较致密的杏仁状玄武岩,R3代表滑坡后壁出露的肉眼可见较松散的灰绿色蚀变杏仁状磁化玄武岩,R4代表堆积体玄武岩中有“石夹土”现象的外圈强风化部分,R5代表内部弱风化部分。 表 2 鸡场滑坡内岩土体元素分析结果
Table 2. Analysis results of rock and soil elements in Jichang landslide
样品 R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 Na2O/% 0.16 2.77 0.89 — 1.17 MgO/% 3.23 4.47 3.25 1.90 3.67 Al2O3/% 14.71 13.58 15.19 17.79 13.68 SiO2/% 43.79 44.46 47.87 36.89 44.96 P2O5/% 0.75 1.00 0.92 1.22 0.82 SO3/% 1.63 1.45 1.17 0.37 1.66 K2O/% 3.66 0.73 4.85 2.08 2.07 CaO/% 3.37 5.92 3.1 0.54 8.03 TiO2/% 2.15 2.11 2.44 3.62 2.51 V2O5/% 0.09 0.09 0.06 0.13 0.09 Cr2O3/% 0.01 0.02 — 0.01 0.04 MnO/% 0.26 0.24 0.08 0.24 0.30 FeO/% 5.55 10.99 4.51 3.71 12.41 Fe2O3/% 13.88 8.49 10.83 22.00 5.88 LOI/% 6.74 3.69 4.86 9.49 2.71 注:结果均为质量占比;“—”表示无此成分。 表 3 贵州省鸡场滑坡地下水及雨水化学成分分析结果
Table 3. Major ions of groundwater in the Jichang landslide
样品编号 质量浓度/(mg·L−1) pH SiO2 Mg2+ Ca2+ Na+ K+ Cl− 

TDS 雨水1 1.01 0.78 2.86 0.10 0.16 1.34 — 10.08 10.31 6.0 雨水2 1.28 — 2.70 0.10 1.11 0.68 — 10.08 10.44 4.9 试样3 33.53 0.96 2.70 1.06 1.23 0.23 0.85 16.37 15.21 6.9 试样4 22.53 1.59 6.61 1.28 0.24 0.4 1.12 27.71 25.73 6.8 试样5 17.53 1.27 5.16 1.69 0.15 0.23 5.11 21.41 26.04 6.6 试样6 18.53 1.36 6.35 1.44 — 0.13 3.57 25.19 27.77 7.1 试样7 19.87 1.24 5.87 0.58 0.50 0.38 4.87 25.19 22.51 6.4 试样8 21.20 1.18 6.35 0.96 0.18 0.36 5.56 25.19 29.08 6.8 试样9 18.87 1.26 6.03 0.96 0.27 0.42 6.35 25.19 28.39 6.6 试样10 3.28 — 7.94 1.64 0.14 0.24 6.79 31.49 31.92 6.9 试样11 10.88 1.55 15.87 3.85 0.38 0.83 8.21 62.97 63.91 7.1 注:(1)雨水1与雨水2均为8月3日在滑坡附近所接雨水,其余试样为滑坡体上基岩裂隙水;(2)滑坡体中基岩裂隙水取样时间均为8月4日,取样点如图3中所示。 表 4 鸡场滑坡地下水化学成分间的相关系数矩阵
Table 4. Correlation matrices of the major ions of groundwater in the Jichang landslide
因子 SiO2 Mg2+ Ca2+ Na+ K+ Cl− 

SiO2 1 0.624 −0.083 0.086 0.181 −0.613 0.019 0.024 Mg2+ 1 0.390 0.419 −0.356 −0.126 0.255 0.429 Ca2+ 1 0.915 −0.347 0.037 0.759 0.992 Na+ 1 −0.244 −0.116 0.683 0.933 K+ 1 0.017 −0.465 −0.282 Cl− 1 −0.288 −0.027 
1 0.756 
1 表 5 鸡场滑坡地下水化学成分主成分分析结果
Table 5. Results of the principal component analysis ofgroundwater in the Touzhai landslide
主因子 Z1 Z2 Z3 SiO2 0.138 0.960 0.039 Mg2+ 0.561 0.514 −0.422 Ca2+ 0.947 −0.241 0.145 Na+ 0.920 −0.059 0.245 K+ −0.472 0.169 0.799 Cl− −0.171 −0.743 −0.167 
0.842 −0.057 0.030 
0.955 −0.144 0.202 特征值 3.949 1.851 1.226 方差贡献率/% 49.365 27.135 15.092 累积贡献率/% 49.356 76.500 91.592 -
[1] 徐则民,黄润秋,唐正光. 硅酸盐矿物溶解动力学及其对滑坡研究的意义[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(9):1479 − 1491. [XU Zemin,HUANG Runqiu,TANG Zhengguang. Kinetics of silicate mineral dissolution and its implications for landslide studies[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(9):1479 − 1491. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.09.004
[2] LASAGA A C. Chemical kinetics of water-rock interactions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,1984,89(Sup6):4009 − 4025. doi: 10.1029/JB089iB06p04009
[3] SHUZUI Haruo. Process of slip-surface development and formation of slip-surface clay in landslides in Tertiary volcanic rocks,Japan[J]. Engineering Geology,2001,61(4):199 − 220. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00025-4
[4] WEN Baoping,AYDIN A. Mechanism of a rainfall-induced slide-debris flow:Constraints from microstructure of its slip zone[J]. Engineering Geology,2005,78(1/2):69 − 88.
[5] 易连兴. 西南岩溶山区复合水动力场滑坡影响模式:以关岭县大寨滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):43 − 50. [YI Lianxing. Impact model of landslide with complex hydrodynamic field in karst mountain areas of Southwest China:A case study of the Dazhai landslide in Guanling County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 严春杰, 唐辉明, 陈洁渝, 等. 三峡库区典型滑坡滑带土微结构和物质组分研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2002, 23(增刊1): 23 − 26
YAN Chunjie, TANG Huiming, CHEN Jieyu, et al. Studies of soil microstructures and compositions of slipping zone in reservior district of Three Gorges Profect[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2002, 23(Sup 1): 23 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 江洎洧,项伟,曾雯,等. 三峡库区黄土坡临江滑坡体水岩(土)相互作用机理[J]. 岩土工程学报,2012,34(7):1209 − 1216. [JIANG Jiwei,XIANG Wei,ZENG Wen,et al. Water-rock(soil) interaction mechanism of Huangtupo riverside landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2012,34(7):1209 − 1216. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 周翠英,邓毅梅,谭祥韶,等. 软岩在饱水过程中水溶液化学成分变化规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(22):3813 − 3817. [ZHOU Cuiying,DENG Yimei,TAN Xiangshao,et al. Testing study on variation regularities of solution components in saturation of soft rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004,23(22):3813 − 3817. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.22.015
[9] 孙德安,李培,高游,等. 红黏土浸水变形特性试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(5):74 − 78. [SUN Dean,Li Pei,Gao You,et al. An experimental study of deformation characteristics of lateritic clay due to wetting[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(5):74 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 刘立才,郑凡东,李炳华,等. 南水北调水源在密怀顺水源地回灌的地下水水质变化试验[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(4):18 − 22. [LIU Licai,ZHENG Fandong,LI Binghua,et al. Experiment of groundwater quality change for simulating the South-to-North water into the Mihuaishun aquifer[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(4):18 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 郑光,许强,刘秀伟,等. 2019年7月23日贵州水城县鸡场镇滑坡-碎屑流特征与成因机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(3):541 − 556. [ZHENG Guang,XU Qiang,LIU Xiuwei,et al. The Jichang landslide on July 23,2019 in Shuicheng,Guizhou:Characteristics and failure mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(3):541 − 556. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 王志兵,申林方,徐则民. 头寨滑坡地下水化学特征及其反映的水-岩(土)相互作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(1):111 − 116. [WANG Zhibing,SHEN Linfang,XU Zemin. Hydrochemical characteristics and their implication for the water-rock/soil interaction in the Touzhai landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(1):111 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 李志强,许强,李姝,等. 按主成分分析法研究黄土灌溉区水-岩(土)相互作用[J]. 科学技术与工程,2017,17(23):161 − 167. [LI Zhiqiang,XU Qiang,LI Shu,et al. Study on water-rock/soil interaction in loess irrigation area based on the principal component analysis[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2017,17(23):161 − 167. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.23.026
[14] 王志兵,徐则民. 头寨滑坡玄武岩腐岩的岩石化学和矿物学特征[J]. 矿物学报,2008,28(4):447 − 454. [WANG Zhibing,XU Zemin. Petrochemistry and mineralogy of basalt saprolite in Touzhai landslide[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2008,28(4):447 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2008.04.017
[15] 许强. 对地质灾害隐患早期识别相关问题的认识与思考[J]. 武汉大学学报·信息科学版,2020,45(11):1651 − 1659. [XU Qiang. Understanding and consideration of related issues in early identification of potential geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(11):1651 − 1659. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 沈钦华,王火焰,周健民,等. 含钾矿物中钾的释放及其与溶液环境中离子种类的关系[J]. 土壤,2009,41(6):862 − 868. [SHEN Qinhua,WANG Huoyan,ZHOU Jianmin,et al. Dynamic release of potassium from potassium bearing minerals as affected by ion species in solution[J]. Soils,2009,41(6):862 − 868. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 马水山,雷俊荣,张保军,等. 滑坡体水岩作用机制与变形机理研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,2005,22(5):37 − 39. [MA Shuishan,LEI Junrong,ZHANG Baojun,et al. Study on rock-water interaction and deformation mechanism of landslide[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2005,22(5):37 − 39. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5485.2005.05.011
[18] SOEDER D J. The Marcellus shale:Resources and reservations[J]. Eos,Transactions American Geophysical Union,2010,91(32):277 − 278. doi: 10.1029/2010EO320001
[19] 唐良琴,聂德新,任光明. 软弱夹层粘粒含量与抗剪强度参数的关系分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2003,14(2):58 − 62. [TANG Liangqin,NIE Dexin,REN Guangming. The relational analysis between the clay grain content and strength characteristics of weak intercalated layer[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2003,14(2):58 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] HERMANRUD C,VENSTAD J M,CARTWRIGHT J,et al. Consequences of water level drops for soft sediment deformation and vertical fluid leakage[J]. Mathematical Geosciences,2013,45(1):1 − 30. doi: 10.1007/s11004-012-9435-0
-



 下载:
下载: