Identification and time series monitoring of hidden dangers of geological hazards in the typical loess hilly regions
-
摘要:
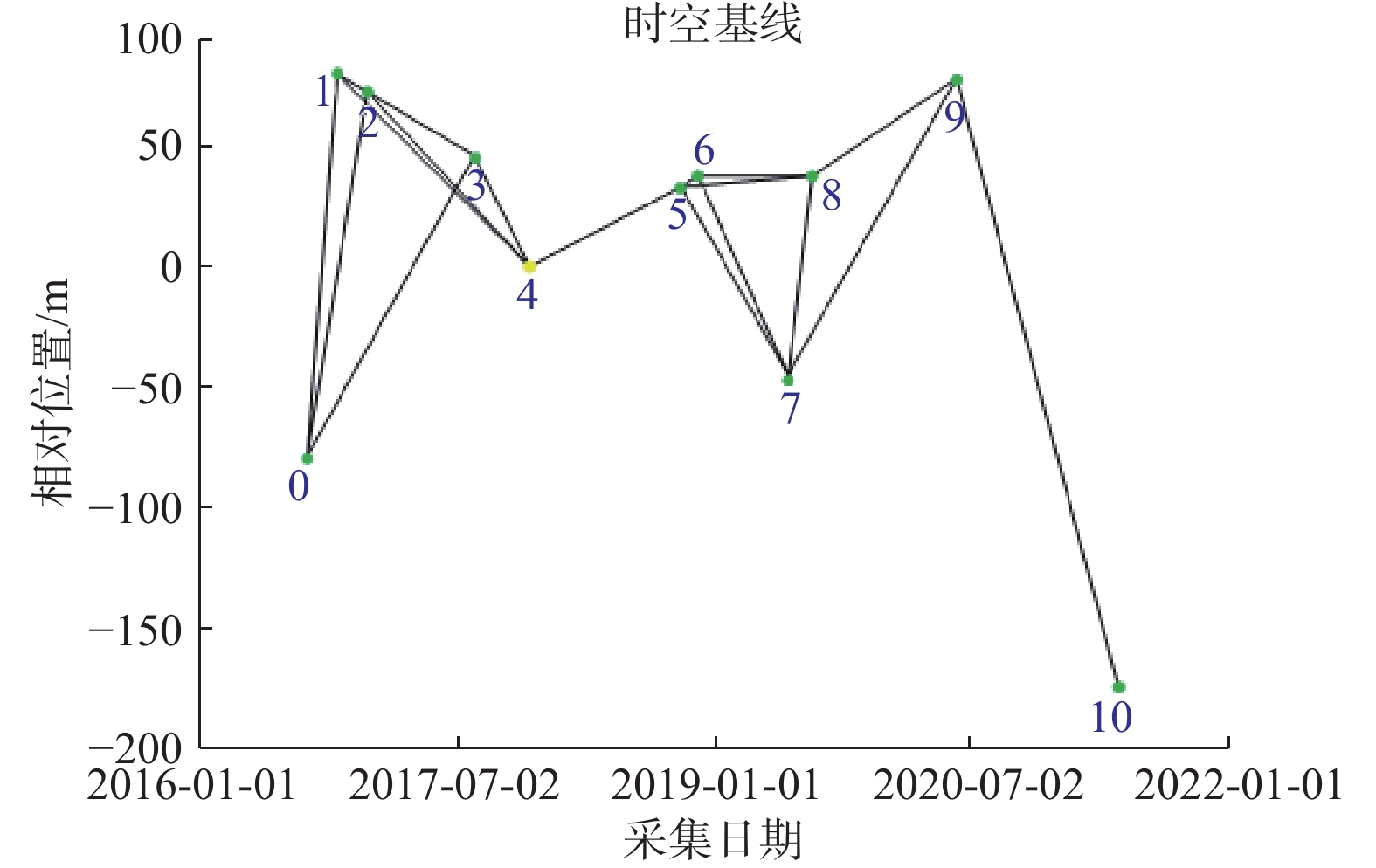
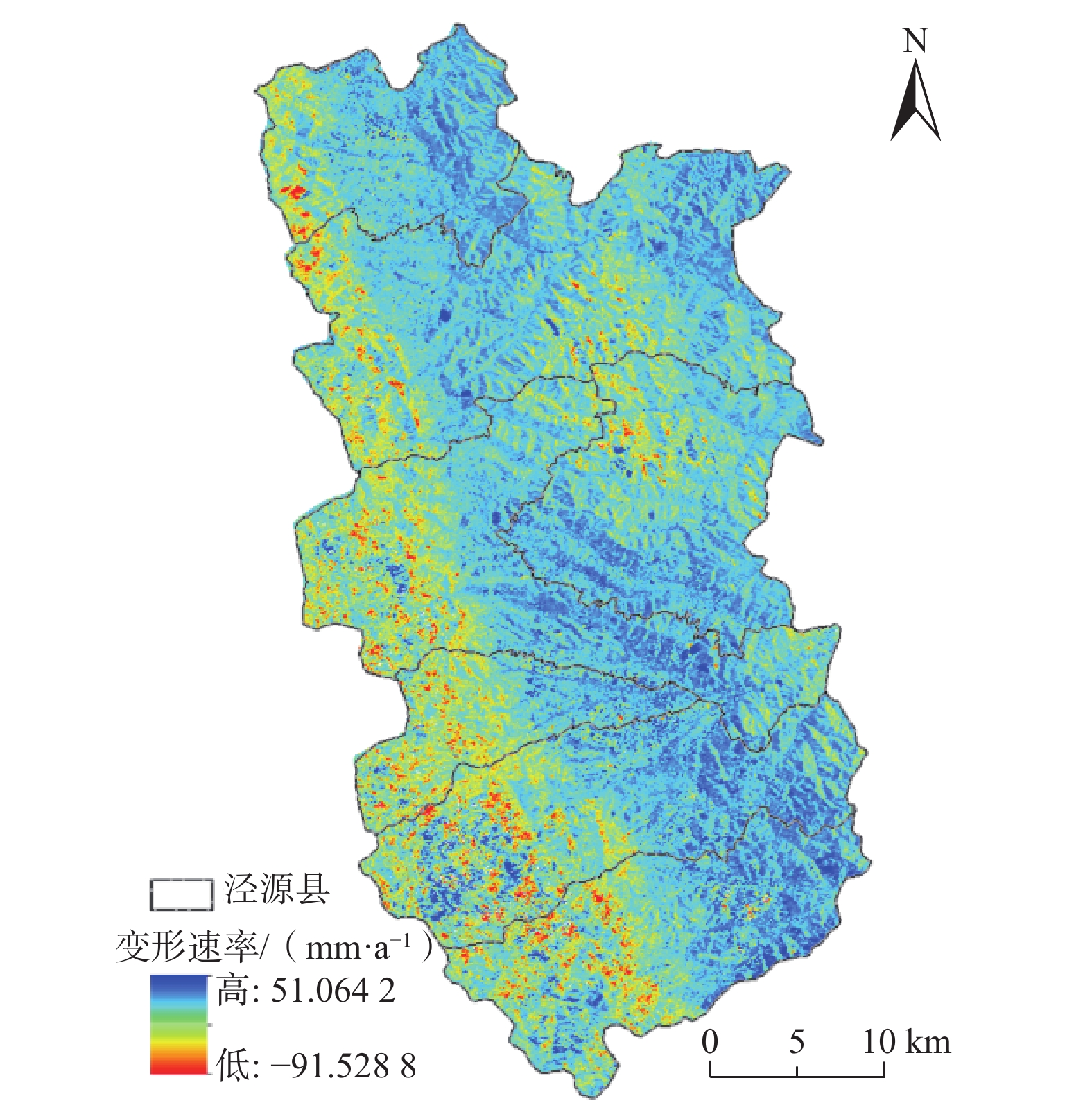
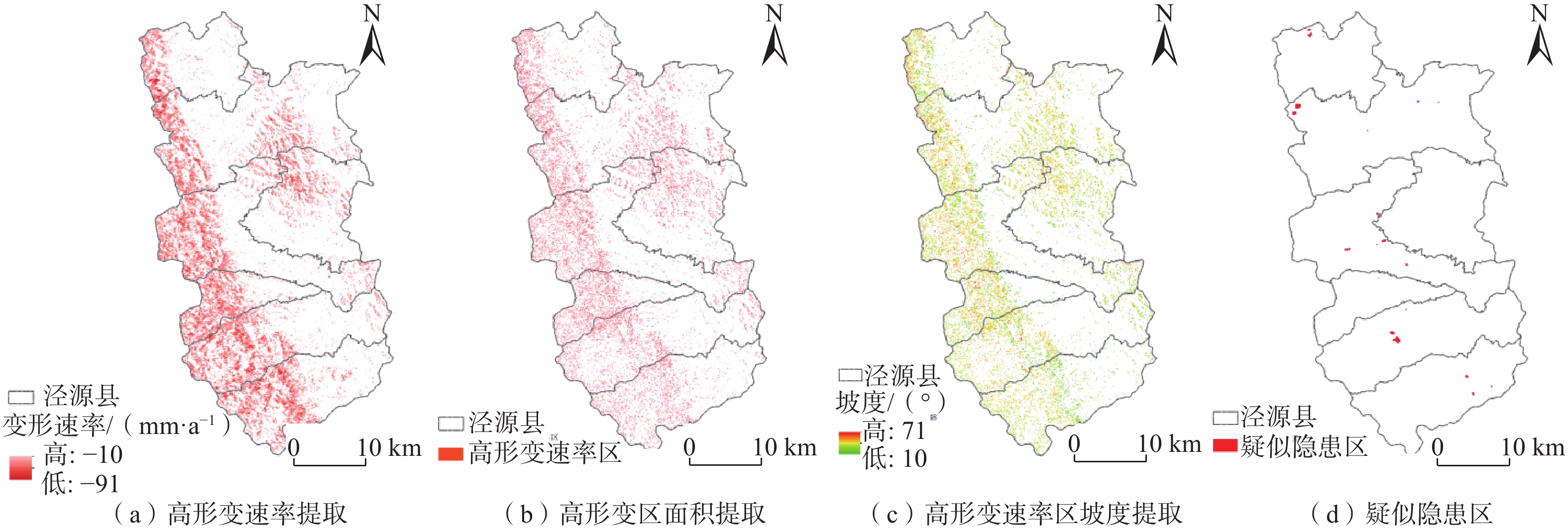
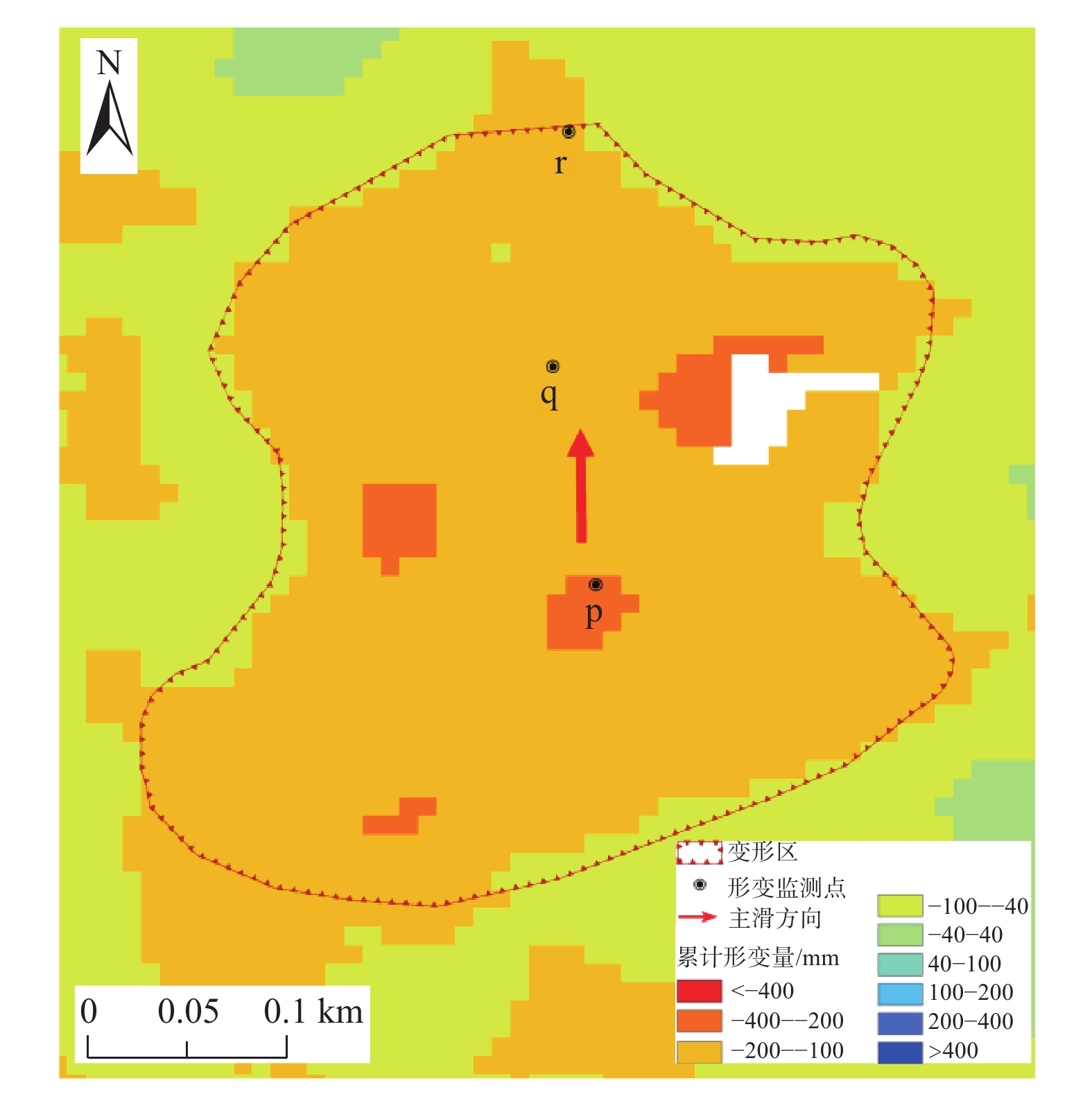
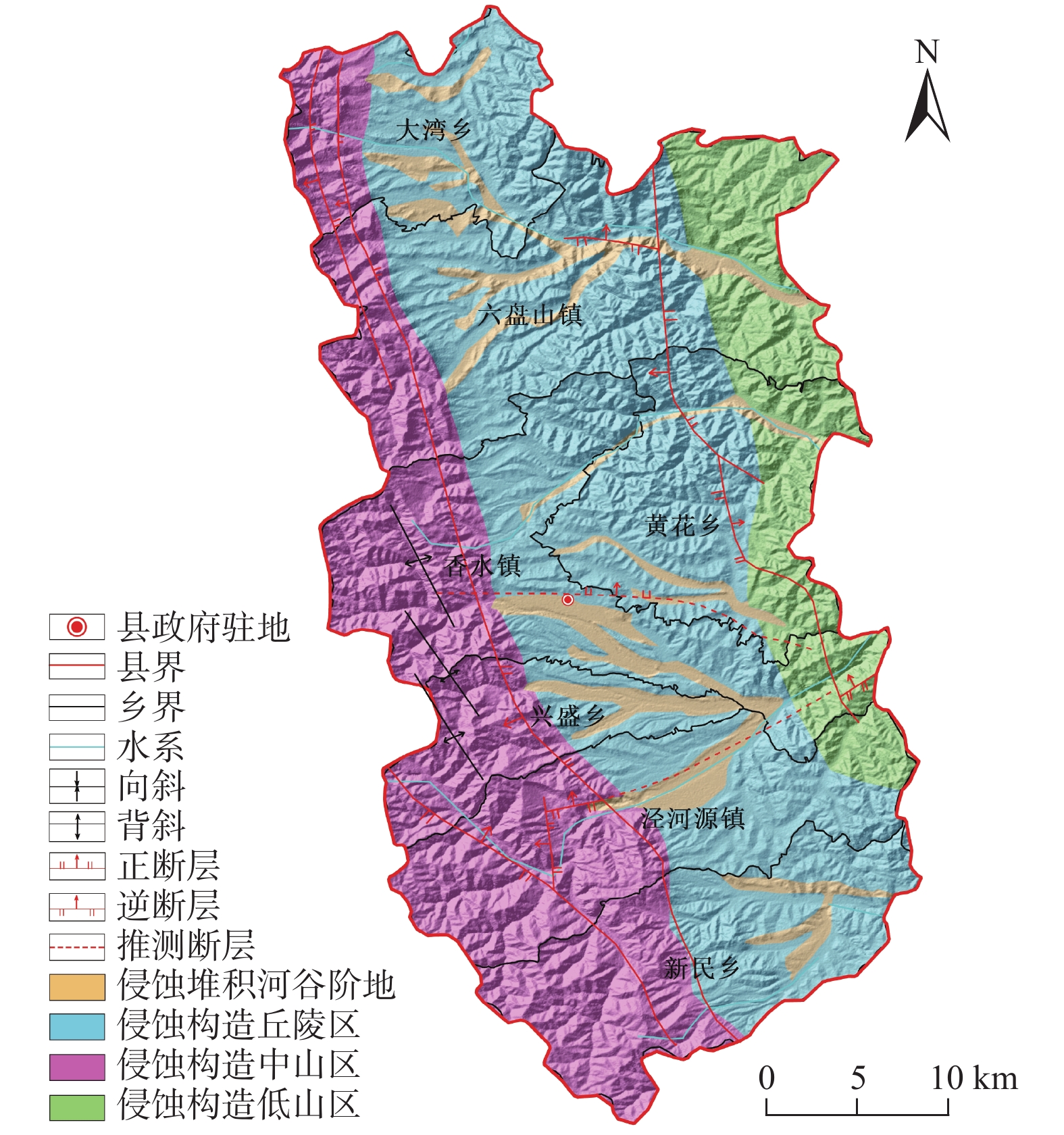
宁厦南部地区以黄土丘陵地貌为主,区内沟壑纵横,小型滑坡较为发育,地表形变监测难度大。为探索黄土丘陵区的地质灾害隐患识别方法,以宁夏回族自治区固原市泾源县为研究区,应用SBAS-InSAR技术对采集到的2016年7月—2021年5月的11期升轨L波段ALOS-2数据进行处理,得到形变速率结果。联合高分光学影像,根据形变速率、形变规模、坡度、形变区到承灾体的距离等因素进行综合分析,在泾源县共识别疑似隐患27处。经实地验证,其中22处形变迹象较明显、而且有明确的承灾体,确定为地质灾害隐患。对其中典型隐患点进行时序形变分析,发现这些区域在监测时间段内有持续显著的地表形变,最大沉降速率达到91.53 mm/a。结果表明:在黄土丘陵区,应用L波段SAR数据,采用SBAS-InSAR技术的地质灾害形变监测效果显著,联合高分辨率的光学影像数据、应用综合遥感识别的方法,在该地区地质灾害隐患识别的正确率较高,具有很好的适用性。未来可编程采集升、降轨结合的L波段数据、结合无人机LiDAR数据做更深入的研究,以进一步提高地质灾害隐患识别的准确率,为地质灾害精准防治做好技术支撑。
Abstract:The geomorphology of southern Ningxia is dominated by loess hills, with gullies and well-developed small landslides in the area, making surface deformation monitoring difficult. To explore the identification method of geological hazards in the loess hilly area, Jingyuan district in the city of Guyuan in Ningxia Huizu Zizhiqu is taken as the study area, and the SBAS-InSAR technology is applied to process a total of 11 periods of ascending L-band ALOS-2 data collected from July 2016 to May 2021 to obtain the deformation rate of the Jingyuan district. Combined with high-resolution optical images, a comprehensive analysis is carried out according to factors such as deformation rate, deformation scale, slope, and disaster-bearing body. A total of 27 suspected hidden dangers are identified. After field verification, 22 of them show obvious signs of deformation and have clear hazard-bearing bodies. The time-series deformation analysis of the typical hidden danger points shows that these areas have continuous and significant surface deformation during the monitoring period, and the maximum subsidence rate reaches 91.53 mm/a. The results show that the combined L-band SAR and high-definition optical image data and the application of the integrated remote sensing identification method are highly accurate and are of high applicability in the area. The next step is to collect L-band data on a combination of ascending and descending orbits and to conduct in-depth research on the basis of LiDAR data from drones in order to further improve the accuracy of geological hazard identification and to provide technical support for the precise prevention and control of geological hazards.
-

-
[1] 胡胜. 黄土高原滑坡空间格局及其对地貌演化的影响[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2019
HU Sheng. Spatial pattern of landslide in Loess Plateau and its influence on geomorphologic evolution[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] XIAO Lihan, ZHENG Rui, ZOU Rong. Coseismic slip distribution of the 2021 Mw7.4 Maduo,Qinghai earthquake estimated from InSAR and GPS measurements[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2022,33(4):885 − 891. doi: 10.1007/s12583-022-1637-x
[3] 刘沛源,常鸣,武彬彬,等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的成汶高速汶川段滑坡易发区选线研究[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(6):2048 − 2057. [LIU Peiyuan,CHANG Ming,WU Binbin,et al. Route selection of landslide prone area in Wenchuan section of Chengdu-Wenchuan expressway based on SBAS-InSAR[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(6):2048 − 2057. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.6.dqkx202206011
[4] GRAHAM L C. Synthetic interferometer radar for topographic mapping[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE,1974,62(6):763 − 768. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1974.9516
[5] MASSONNET D,ROSSI M,CARMONA C,et al. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry[J]. Nature,1993,364:138 − 142. doi: 10.1038/364138a0
[6] MASSONNET D,BRIOLE P,ARNAUD A. Deflation of Mount Etna monitored by spaceborne radar interferometry[J]. Nature,1995,375:567 − 570. doi: 10.1038/375567a0
[7] GABRIEL A K,GOLDSTEIN R M,ZEBKER H A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas:differential radar interferometry[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research,1989,94(B7):9183. doi: 10.1029/JB094iB07p09183
[8] XIA Ye, KAUFMANN H, GUO Xiaofang. Differential SAR interferometry using corner reflectors[C]//IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Toronto, Canada: IEEE, 2002: 1243-1246.
[9] 褚宏亮,邢顾莲,李昆仲,等. 基于地面三维激光扫描的三峡库区危岩体监测[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(4):124 − 132. [CHU Hongliang,XING Gulian,LI Kunzhong,et al. Monitoring of dangerous rock mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir area based on the terrestrial laser scanning method[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(4):124 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202008015
[10] 卫童瑶,殷跃平,高杨,等. 三峡库区巫山县塔坪H1滑坡变形机制[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):73 − 81. [WEI Tongyao,YIN Yueping,GAO Yang,et al. Deformation mechanism of the Taping H1 landslide in Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):73 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202003043
[11] 陆会燕,李为乐,许强,等. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(9):1342 − 1354. [LU Huiyan,LI Weile,XU Qiang,et al. Early detection of landslides in the upstream and downstream areas of the baige landslide,the Jinsha River based on optical remote sensing and InSAR technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(9):1342 − 1354. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] LIU Xiaojie,ZHAO Chaoying,ZHANG Qin,et al. Integration of Sentinel-1 and ALOS/PALSAR-2 SAR datasets for mapping active landslides along the Jinsha River corridor,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2021,284:106033. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106033
[13] 解明礼,赵建军,巨能攀,等. 多源数据滑坡时空演化规律研究—以黄泥坝子滑坡为例[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2020,45(6):923 − 932. [XIE Mingli,ZHAO Jianjun,JU Nengpan,et al. Research on temporal and spatial evolution of landslide based on multisource data:A case study of Huangnibazi landslide[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45(6):923 − 932. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 王志荣,吴玮江,周自强. 甘肃黄土台塬区农业过量灌溉引起的滑坡灾害[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2004,15(3):43 − 46. [WANG Zhirong,WU Weijiang,ZHOU Ziqiang. Landslide induced by over-irrigation in loess platform areas in Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2004,15(3):43 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2004.03.010
[15] 赵超英,刘晓杰,张勤,等. 甘肃黑方台黄土滑坡InSAR识别、监测与失稳模式研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):996 − 1007. [ZHAO Chaoying,LIU Xiaojie,ZHANG Qin,et al. Research on loess landslide identification,monitoring and failure mode with InSAR technique in Heifangtai,Gansu[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):996 − 1007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 许强,彭大雷,何朝阳,等. 突发型黄土滑坡监测预警理论方法研究—以甘肃黑方台为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(1):111 − 121. [XU Qiang,PENG Dalei,HE Chaoyang,et al. Theory and method of monitoring and early warning for sudden loess landslide:A case study at Heifangtai Terrace[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(1):111 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-038
[17] 刘陈伟,蒋亚楠,廖露,等. 黑方台主要形变区的SBAS-InSAR识别与分析[J]. 测绘科学,2022,47(5):56 − 65. [LIU Chenwei,JIANG Yanan,LIAO Lu,et al. Identification and analysis of the main deformation area of Heifangtai Platform with SBAS-InSAR[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping,2022,47(5):56 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16251/j.cnki.1009-2307.2022.05.008
[18] 刘希林,郭梨花. 泥石流易发区灾害可接受程度对比研究—以云南东川和甘肃舟曲为例[J]. 地理科学,2019,39(1):164 − 172. [LIU Xilin,GUO Lihua. Comparisons of the acceptability of debris flow disasters in the hazard-prone areas:Case studies in Dongchuan and Zhouqu[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2019,39(1):164 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.2019.01.019
[19] 薛强,张茂省. 延安淹土安滑坡监测预警及变形特征[J]. 西北地质,2018,51(2):220 − 226. [XUE Qiang,ZHANG Maosheng. Monitoring,early warning and deformation characteristics of Yantu’an landslide in Yan’an[J]. Northwestern Geology,2018,51(2):220 − 226. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2018.02.029
[20] 孙永亮. 宁夏泾源县矿山地质灾害分布特征及防治建议[J]. 世界有色金属,2022,19:229 − 231. [SUN Yongliang. Distribution characteristics and prevention suggestions of mine geological disasters in Jingyuan County, Ningxia[J]. World Nonferrous Metals,2022,19:229 − 231. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 朱建军,胡俊,李志伟,等. InSAR滑坡监测研究进展[J]. 测绘学报,2022,51(10):2001 − 2019. [ZHU Jianjun,HU Jun,LI Zhiwei,et al. Recent progress in landslide monitoring with InSAR[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2022,51(10):2001 − 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] BERARDINO P,FORNARO G,LANARI R,et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2002,40(11):2375 − 2383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792
[23] KURSAH M B,WANG Y,BAYOH H D,et al. A comparative study on the predictive ability of archived and SBAS-InSAR inventories for landslide susceptibility using frequency ratio model in Western Area,Sierra Leone[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2021,80(10):387. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09663-x
[24] 葛大庆,王艳,郭小方,等. 利用短基线差分干涉纹图集监测地表形变场[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2008,28(2):61 − 66. [GE Daqing,WANG Yan,GUO Xiaofang,et al. Surface deformation field monitoring by use of small-baseline differential interferograms stack[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2008,28(2):61 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5942.2008.02.011
[25] 聂成顺. 基于InSAR和光学遥感的会东县滑坡隐患识别研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021
NIE Chengshun. Recognition for potential landslides in Huidong County based on InSAR and optical remote sensing[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: