An exploration on investigation and mapping of ground substrate in Ruyi River Basin, Bashang Plateau, Chengde City
-
摘要:
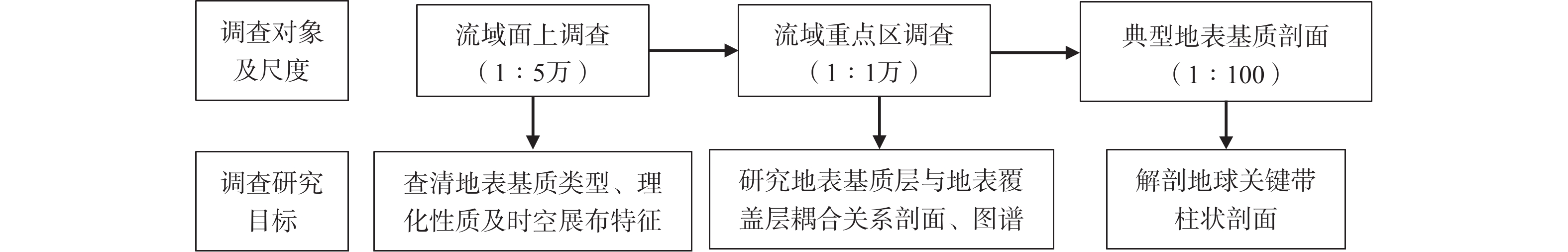
地表基质调查与编图是当前自然资源调查监测体系中的全新领域,但如何开展还缺乏统一的行动指南。在总结地球关键带理论和地表基质调查研究现状的基础上,充分借鉴区域地质、工程地质、第四纪地质、水文地质、环境地质等调查与编图表达方式,以承德坝上高原如意河流域为研究区,探索建立了基于地球关键带理论的地表基质调查与图件编制方法。基于野外调查结果,将如意河流域划分为玄武岩、安山岩、凝灰岩、流纹岩、冲洪积砂砾石、残坡积砂砾石、风积沙、湖积淤泥和沼积淤泥等9种地表基质类型,研究了不同类型地表基质的分布特征、调查和监测指标,编制了风积沙厚度空间分布图、地表基质与地表覆盖层耦合关系图和地表基质层图。地表基质厚度空间分布图可展布不同类型地表基质厚度的空间分布特征,地表基质与地表覆盖层耦合关系图可直观刻画地表基质的剖面结构特征和理化性质对地表覆盖生态要素的约束作用,地表基质图能系统地反映地表基质与地表覆盖层的结构、展布、特征和耦合关系。地表基质系列图件是岩-土-水-生等地球关键带多圈层交互作用在地质图上的反映。该研究可为在全国范围开展地表基质调查与编图提供参考。
Abstract:The investigation and mapping of ground substrate is a whole new field of natural resources survey and monitoring system in the current situation, which has not been evolved into a unified guideline on action. In this paper, based on the summarization of the current situation of the Earth’s critical zone theory and ground substrate survey, fully drawing on the investigation methods and map expression styles of regional geology, engineering geology, Quaternary geology, hydrogeology, environmental geology, etc., and taking Ruyi River Basin in Bashang Plateau of Chengde City as the research area, we establish the method of the investigation and mapping of ground substrate based on the theory of the Earth’s critical zone. Based on the field investigation results, the ground substrate in Ruyi River Basin can be divided into nine types as follows: basalt, andesite, tuff, rhyolite, alluvial-proluvial gravel, eluvial-proluvial gravel, aeolian sand, lacustrine silt and marsh silt. The distribution characteristics as well as the investigation and monitoring indicators in different types of ground substrates are also studied. The spatial distribution map of aeolian sand thickness, coupling relationship profile between the ground substrate and the ground covered layer, and ground substrate map are drew. The spatial distribution map of ground substrate thickness can show the spatial distribution characteristics of the thickness of different types of surface substrate layers. The coupling relationship profile of ground substrate and surface covered layer can directly describe the constraint of the profile structural characteristics and physical and chemical properties of ground substrate on the ecological elements of the covered layer. The ground substrate map can systematically reflect the structure, distribution, characteristics and coupling relationship between ground substrate and ground covered layer. The series maps of ground substrate are the reflection of the interaction of multiple cycles in the Earth’s critical zone, such as the rock, the soil, the water, and the organism. The results of this study can provide references for the nationwide investigation and mapping of the ground substrate.
-
Key words:
- ground substrate /
- surface covered layer /
- mapping /
- Ruyi River Basin /
- Bashang Plateau
-

-
表 1 如意河流域地表基质分类特征、调查和监测指标
Table 1. Classification characteristics, survey and monitoring indicators of ground substrate in Ruyi River Basin
地表基质
三级分类分布情况及特征描述 调查指标 监测指标 玄武岩 呈面状分布于流域的上中游,在韭菜顶至
神仙洞一片分布集中,坡度大于20°岩性、颜色、产状、
结构面类型、结构面密度、
坚硬程度、风化程度、
结构类型、完整程度等含水率、渗透性等 安山岩 零星分布,面积较小 凝灰岩 分布面积较大,在韭菜顶一带沿如意河河道两岸分布,
一般上部发育一层厚度为30 cm左右的灰色森林土流纹岩 出露面积较小,范围较集中 冲洪积
砂砾石主要分布在如意河干支流两岸,沿河流两岸呈带状分布,
其中砾质以中砾、细砾为主,砂土以细砂、粉砂为主,
上部发育草甸土和风沙土颜色、砾径、砾石含量、
磨圆度、分选性等含水率、渗透性等 残坡积
砂砾石出露较分散,呈条带状或透镜状分布,在玄武岩基质、
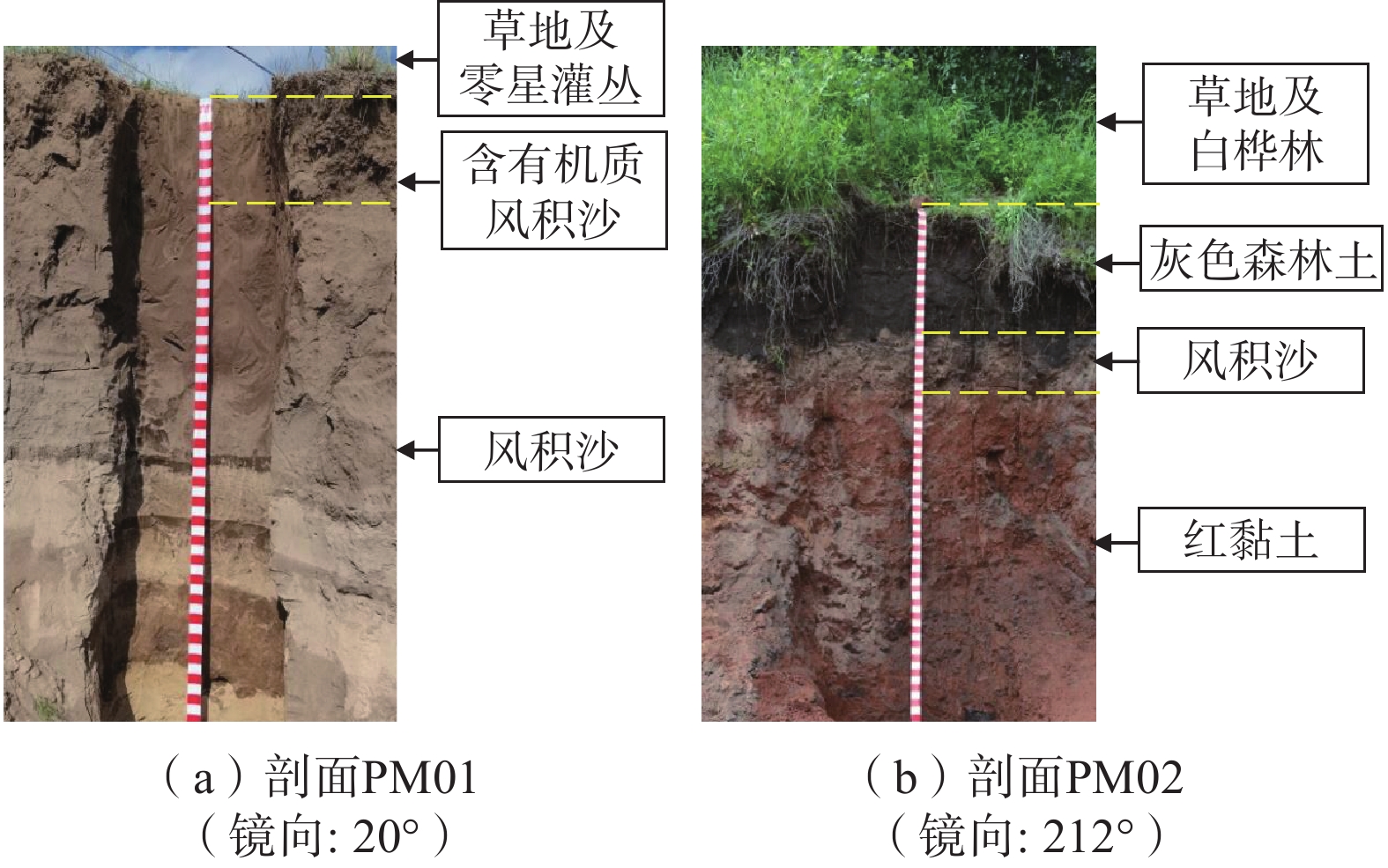
风积沙层中零星分布风积沙 分布范围最广,呈片状分布,集中分布在如意河流域中下游,
上部一般有25 cm左右的含有机质风积沙,土壤养分含量较低质地、颜色、粒径、
成土母质、厚度、
结构类型等含水率、温度、电导率、有机碳、酸碱度、各种有益和有害元素含量等 湖积淤泥 分布在月亮湖等几个湖泊底部 颜色、气味、水深、
水动力条件等酸碱度、重金属和有机污染物类型、含量、活性等 沼积淤泥 主要分布在月亮湖南部、如意河源头一片,为沼泽草地和沼泽地 -
[1] ZHANG Ganlin,SONG Xiaodong,WU Kening. A classification scheme for Earth’s critical zones and its application in China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2021,64(10):1709 − 1720. doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9798-2
[2] HOLBROOK W S,MARCON V,BACON A R,et al. Links between physical and chemical weathering inferred from a 65-m-deep borehole through Earth’s critical zone[J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9(1):4495. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40819-9
[3] BANWART S A,NIKOLAIDIS N P,ZHU Yongguan,et al. Soil functions:Connecting Earth’s critical zone[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,2019,47:333 − 359. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-063016-020544
[4] GIARDINO J R, HOUSER C. Principles and dynamics of the critical zone[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2015.
[5] 马腾,沈帅,邓娅敏,等. 流域地球关键带调查理论方法—以长江中游江汉平原为例[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(12):4498 − 4511. [MA Teng,SHEN Shuai,DENG Yamin,et al. Theoretical approaches of survey on Earth’s critical zone in basin:An example from Jianghan Plain,central Yangtze River[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(12):4498 − 4511. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 李金发. 认清经济新形势 顺应改革新趋势:加快中国地质调查工作的调整与改革[J]. 中国地质调查,2016,3(1):1 − 6. [LI Jinfa. Recognizing the new economic situation and adapting to the new trend of reform-speeding up the adjustment and reform of geological survey in China[J]. Geological Survey of China,2016,3(1):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王京彬,卫晓锋,张会琼,等. 基于地质建造的生态地质调查方法—以河北省承德市国家生态文明示范区综合地质调查为例[J]. 中国地质,2020,47(6):1611 − 1624. [WANG Jingbin,WEI Xiaofeng,ZHANG Huiqiong,et al. The eco-geological survey based on geological formation,exemplified by integrated geological survey of National Ecological Civilization Demonstration Area in Chengde City,Hebei Province[J]. Geology in China,2020,47(6):1611 − 1624. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12029/gc20200601
[8] 自然资源部. 自然资源调查监测体系构建总体方案[Z/OL] . (2020-01-17)[2021-12-10]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-01/18/content_5470398.html.
Ministry of Natural Resources. Generalscheme for construction of natural resources survey and monitoring system[Z/OL]. (2020-01-17)[2021-12-10]. (in Chinese)
[9] 自然资源部. 自然资源部办公厅印发《地表基质分类方案(试行)》的通知[Z/OL]. (2020-12-22)[2021-12-10]. http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202012/t20201222_2596025.html.2020
Ministry of Natural Resources. Notice of the general office of the ministry of natural resources printing and distributing the ground cover layer classification scheme(trial)[Z/OL]. (2020-12-22)[2021-12-10] (in Chinese with English Abstract)
[10] 殷志强,秦小光,张蜀冀,等. 地表基质分类及调查初步研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):8 − 14. [YIN Zhiqiang,QIN Xiaoguang,ZHANG Shuji,et al. Preliminary study on classification and investigation of surface substrate[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):8 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 郝爱兵,殷志强,彭令,等. 学理与法理和管理相结合的自然资源分类刍议[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):1 − 7. [HAO Aibing,YIN Zhiqiang,PENG Ling,et al. A discussion of the classification of natural resources based on the combination of academic-legal principles and management[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 殷志强, 邵海, 庞菊梅, 等. 承德资源环境承载能力综合地质调查与评价2021年延续报告[R]. 北京: 中国地质环境监测院, 2020
YIN Zhiqiang, SHAO Hai, PANG Jumei, et al. Continuation report of comprehensive geological survey and evaluation of Chengde resources and environment carrying capacity in 2021[R]. Beijing: China Institute of Geo-Environment Monitoring, 2020. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
[13] 朱永官,李刚,张甘霖,等. 土壤安全:从地球关键带到生态系统服务[J]. 地理学报,2015,70(12):1859 − 1869. [ZHU Yongguan,LI Gang,ZHANG Ganlin,et al. Soil security:From Earth’s critical zone to ecosystem services[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2015,70(12):1859 − 1869. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11821/dlxb201512001
[14] 张月丛, 成福伟, 张娜, 等. 承德生态恢复与居民福祉[M]. 北京: 经济管理出版社, 2020
ZHANG Yuecong, CHENG Fuwei, ZHANG Na, et al. Ecological restoration and residents’ welfare in Chengde[M]. Beijing: Economic Management Press, 2020. (in Chinese with English Abstract)
[15] 孙厚云,卫晓锋,孙晓明,等. 御道口汉诺坝玄武岩偏硅酸矿泉水形成机制及其地质建造制约[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(11):4236 − 4253. [SUN Houyun,WEI Xiaofeng,SUN Xiaoming,et al. Formation mechanism and geological construction constraints of metasilicate mineral water in Yudaokou,Hannuoba basalt area[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(11):4236 − 4253. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 卫晓锋,王京彬,孙厚云,等. 基于地质建造探索承德市土地利用优化路径[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):15 − 25. [WEI Xiaofeng,WANG Jingbin,SUN Houyun,et al. Exploration of land use optimization path based on geological formation in Chengde City[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):15 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 侯红星,张蜀冀,鲁敏,等. 自然资源地表基质层调查技术方法新经验—以保定地区地表基质层调查为例[J]. 西北地质,2021,54(3):277 − 288. [HOU Hongxing,ZHANG Shuji,LU Min,et al. Technology and method of the ground substrate layer survey of natural resources:Taking Baoding area as an example[J]. Northwestern Geology,2021,54(3):277 − 288. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 李响,周效华,相振群,等. 地表基质调查的工作思路刍议—以海南岛为例[J]. 地质通报,2023,42(1):68 − 75. [LI Xiang,ZHOU Xiaohua,XIANG Zhenqun,et al. Discussion on the contents of ground substrate investigation and the index system of elements and attributes[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2023,42(1):68 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 中国地质调查局. 地质调查支撑自然资源综合调查总体设计(2021—2030年)[M]. 2021
China Geological Survey. The overall design of comprehensive survey of natural resources supported by geological survey(2021-2030)[M]. 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 李俊琦,马腾,邓娅敏,等. 江汉平原地球关键带监测网建设进展[J]. 中国地质调查,2019,6(5):115 − 123. [LI Junqi,MA Teng,DENG Yamin,et al. Progresses on monitoring network construction of Earth’s critical zone in Jianghan Plain[J]. Geological Survey of China,2019,6(5):115 − 123. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 侯红星,葛良胜,孙肖,等. 地表基质调查内容及要素-属性指标体系探讨[J]. 自然科学,2021,9(4):433 − 442. [HOU Hongxing,GE Liangsheng,SUN Xiao,et al. Discussion on the contents of ground substrate investigation and the index system of elements and attributes[J]. Open Journal of Nature Science,2021,9(4):433 − 442. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12677/OJNS.2021.94049
[22] 白超琨,侯红星,付宪军,等. 综合物探方法在河北保定地区地表基质层试点调查中的应用[J]. 自然科学,2021,9(4):414 − 425. [BAI Chaokun,HOU Hongxing,FU Xianjun,et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical method to ground substrate layer pilot survey in the area of Hebei Baoding[J]. Open Journal of Nature Science,2021,9(4):414 − 425. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12677/OJNS.2021.94047
[23] 石建省,马荣,马震. 区域地球多圈层交互带调查探索研究[J]. 地球学报,2019,40(6):767 − 780. [SHI Jiansheng,MA Rong,MA Zhen. Regional investigation of the Earth’s critical zone[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2019,40(6):767 − 780. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2019.061801
-




 下载:
下载: