An analysis of the genesis and engineering influence of geothermal water in the Kangding tunnel site of the Sichuan-Xizang Railway
-
摘要:
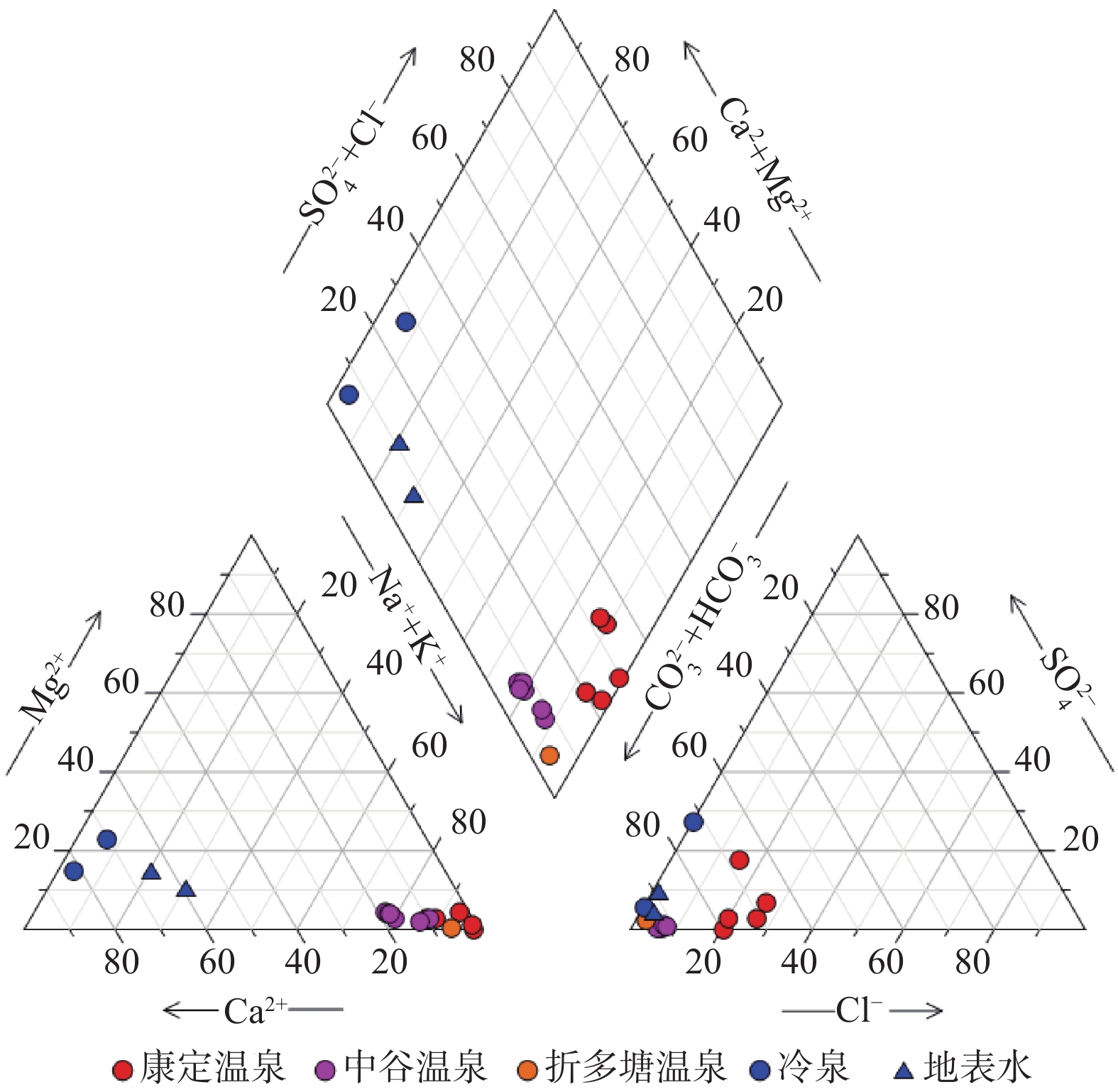
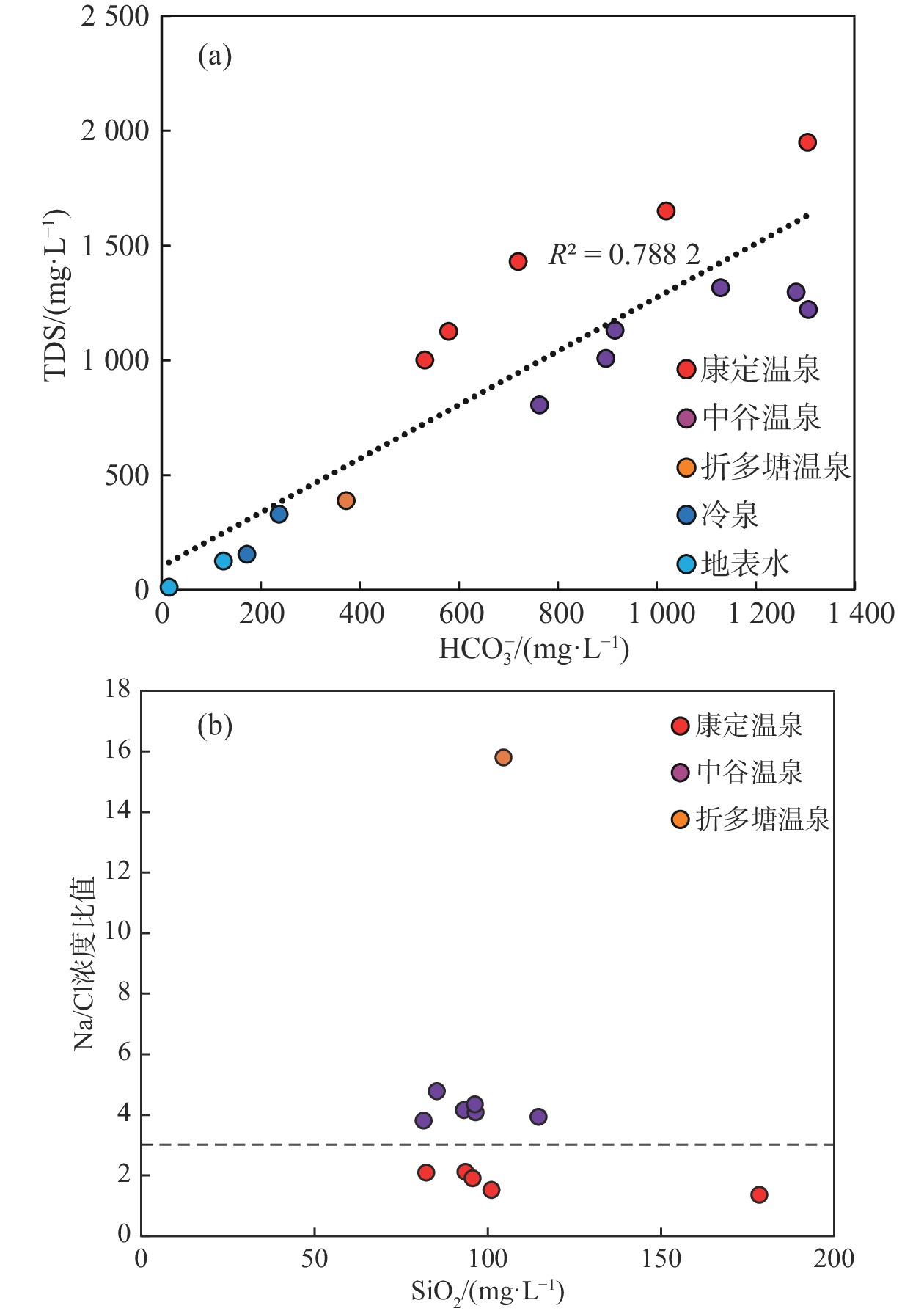
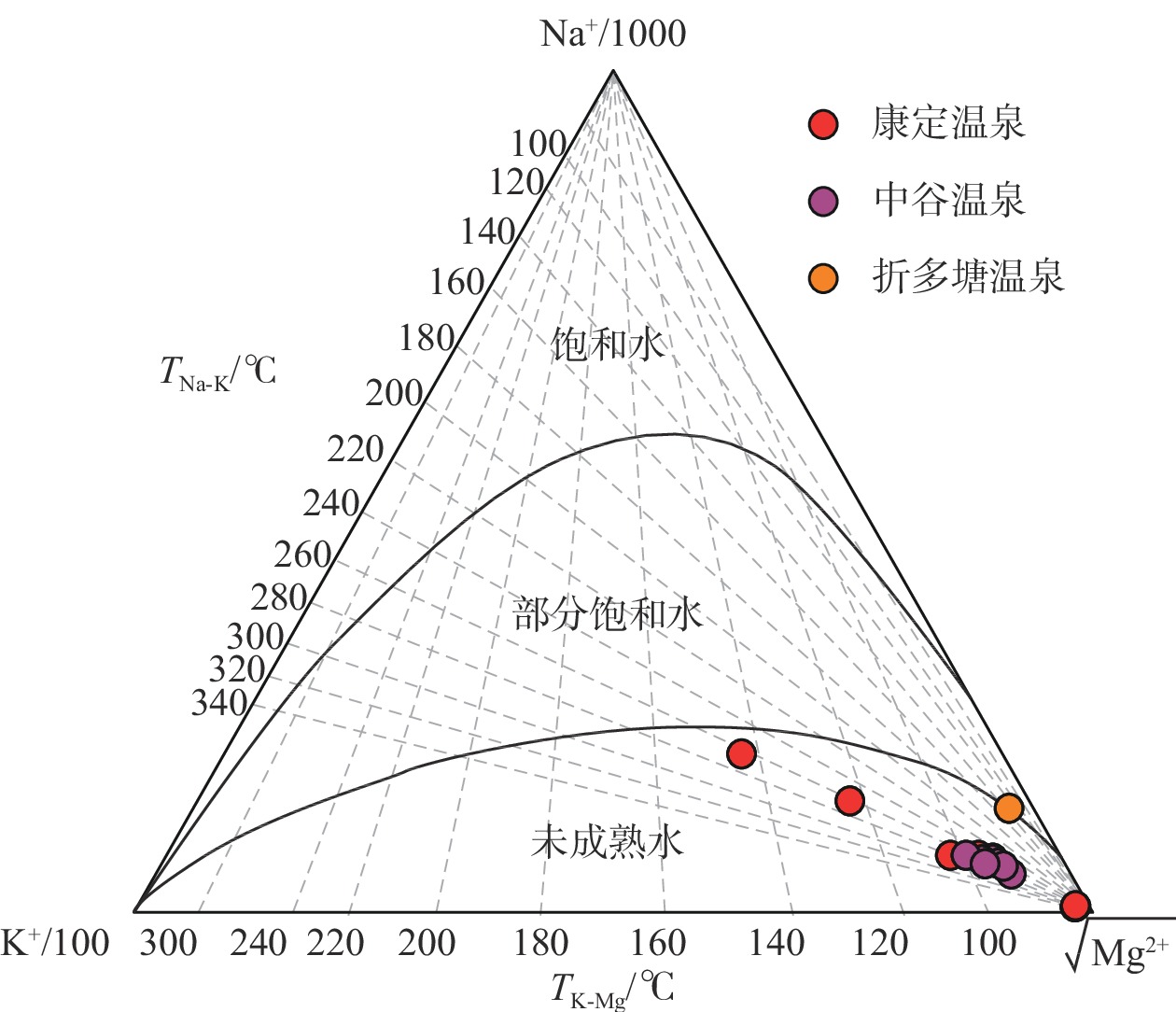
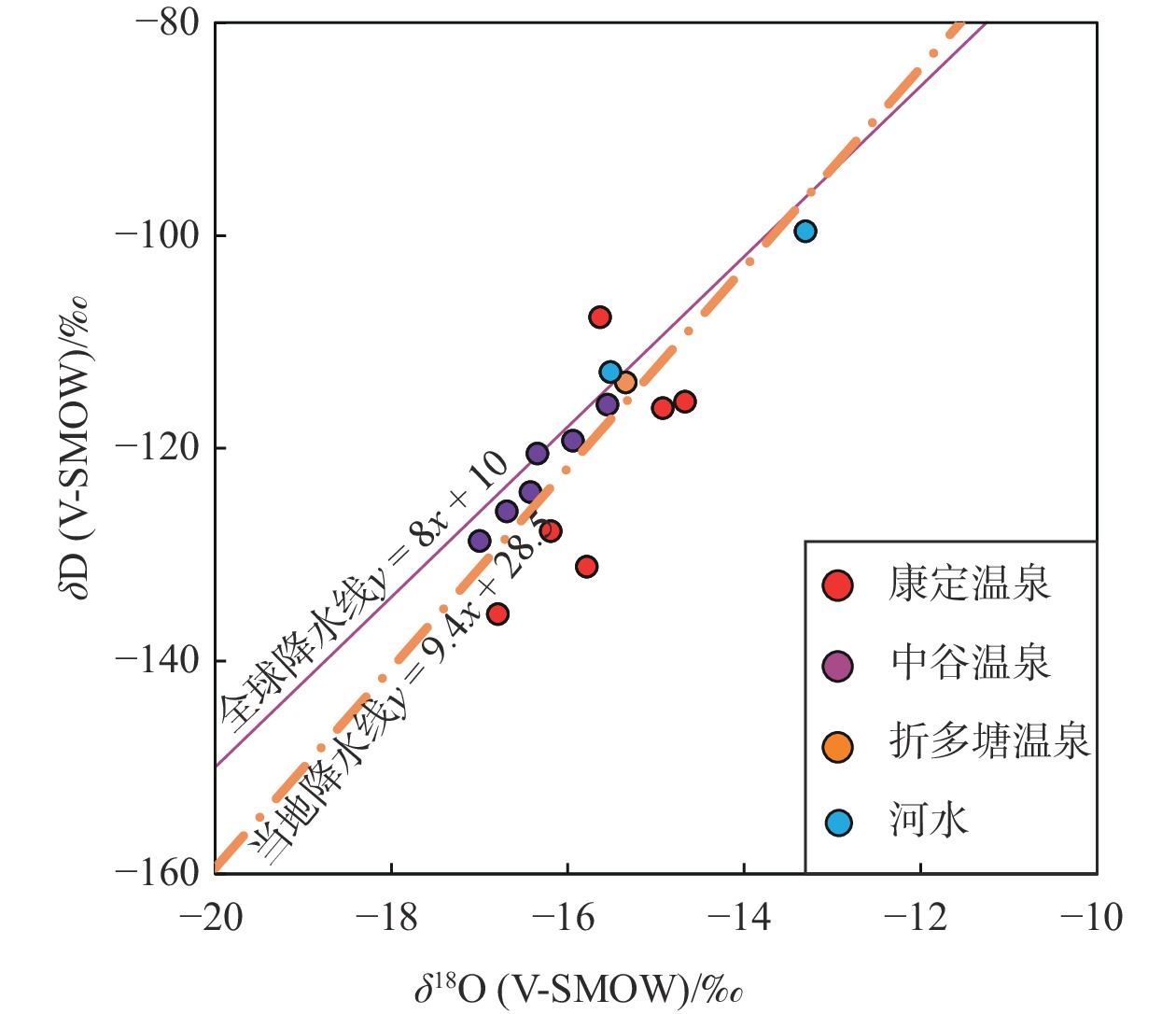
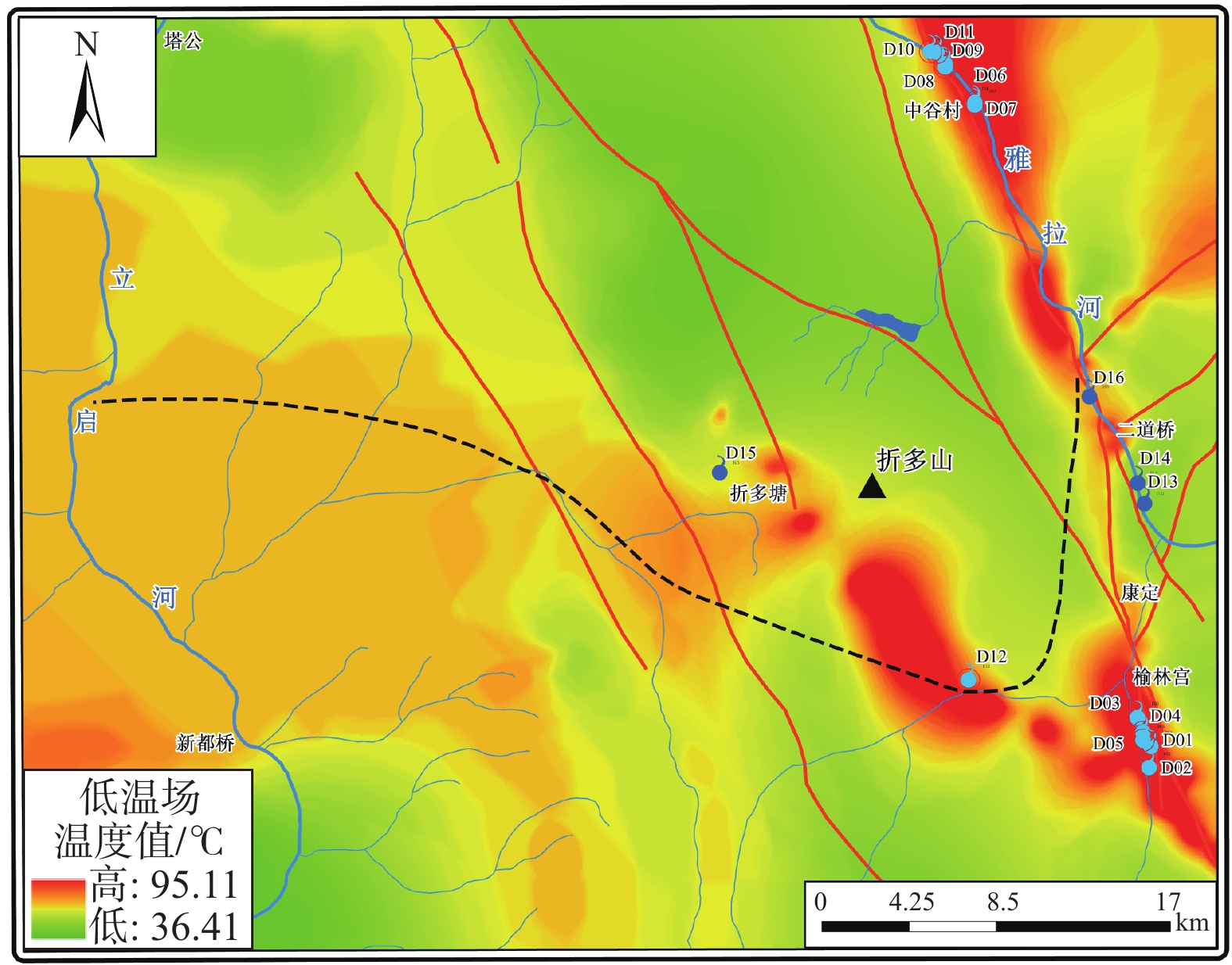
川藏铁路康定隧址区穿越鲜水河断裂带,属地热异常区,对铁路建设造成一定的热害威胁。采用野外调查、水化学分析和氢氧同位素测试等技术方法,开展了川藏铁路康定隧址区地热水成因研究。结果表明,康定隧址区地热水水化学类型主要为HCO3·Cl—Na和HCO3—Na型,聚集于折多塘、康定和中谷3个热水区。地热水均为未成熟水,热储温度为104~172 ℃,深部初始地热水温度为186~250 ℃,冷水混合比例为0.56~0.81。氢氧同位素显示地热水补给高程为3768~4926 m。在康定隧址区,地热水受到高海拔水源补给,主体断裂构造为导热构造,次级分支断裂和发育节理、裂隙的断层破碎带为导水构造,地热水形成后沿浅部断层破碎带出露形成温泉。FEFLOW数值模拟分析表明研究区100 m深度地温场温度为35.4~95.1 ℃,研究区内三个热水区之间存在低温通道。隧道建设时应重点关注康定热水区的高温水热灾害。
Abstract:The Kangding tunnel of the Sichuan-Xizang Railway crosses the Xianshuihe Fault Zone where geothermal abnormity occurs and is harmful for railway construction. This paper analyzes the genetic mechanism of geothermal waters through the integration of field survey, hydrochemical analysis and D-O isotopic experiments. The results show that HCO3·Cl—Na and HCO3—Na types are the main hydrochemical types of hot springs in the Kangding tunnel area, which exists in the Zheduotang, Kangding and Zhonggu geothermal areas. Geothermal waters are immature and the reservoir temperature ranges from 104 ℃ to 172 ℃. Deep initial geothermal waters display the reservoir temperature of 186−250 ℃ and are mixed by 56%−81% of cold water. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopes show that the recharge elevation of the geothermal water ranges from 3768 m to 4926 m. In the study area, geothermal waters are recharged by water source at high elevation. The main fault is the structure of thermal conductivity, and secondary faults and fracture zones are the channel of water migration. Geothermal waters arise and expose as hot springs on the land surface. Simulated geothermal field of 100 m has the temperatures of 35.4−95.1 ℃. Relatively low-temperature channel may be existed among three geothermal areas. High-temperature geohazard induced by geothermal water should be focused in the Kangding area during tunnel construction.
-
Key words:
- geothermal water /
- hydrogeochemistry /
- genetic model /
- engineering effect /
- Kangding tunnel area
-

-
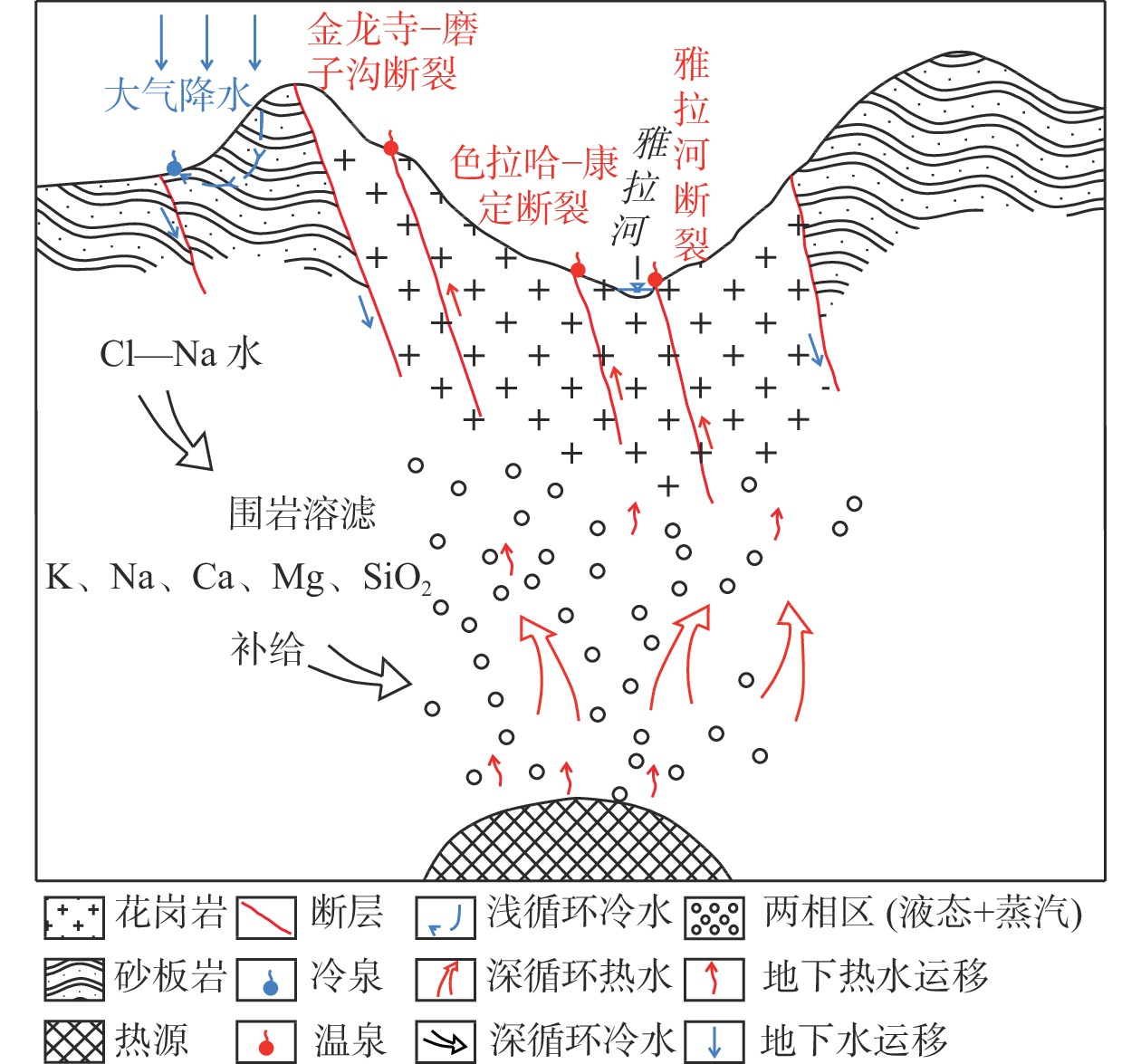
图 1 研究区地热地质图(根据文献[16]修改)
Figure 1.
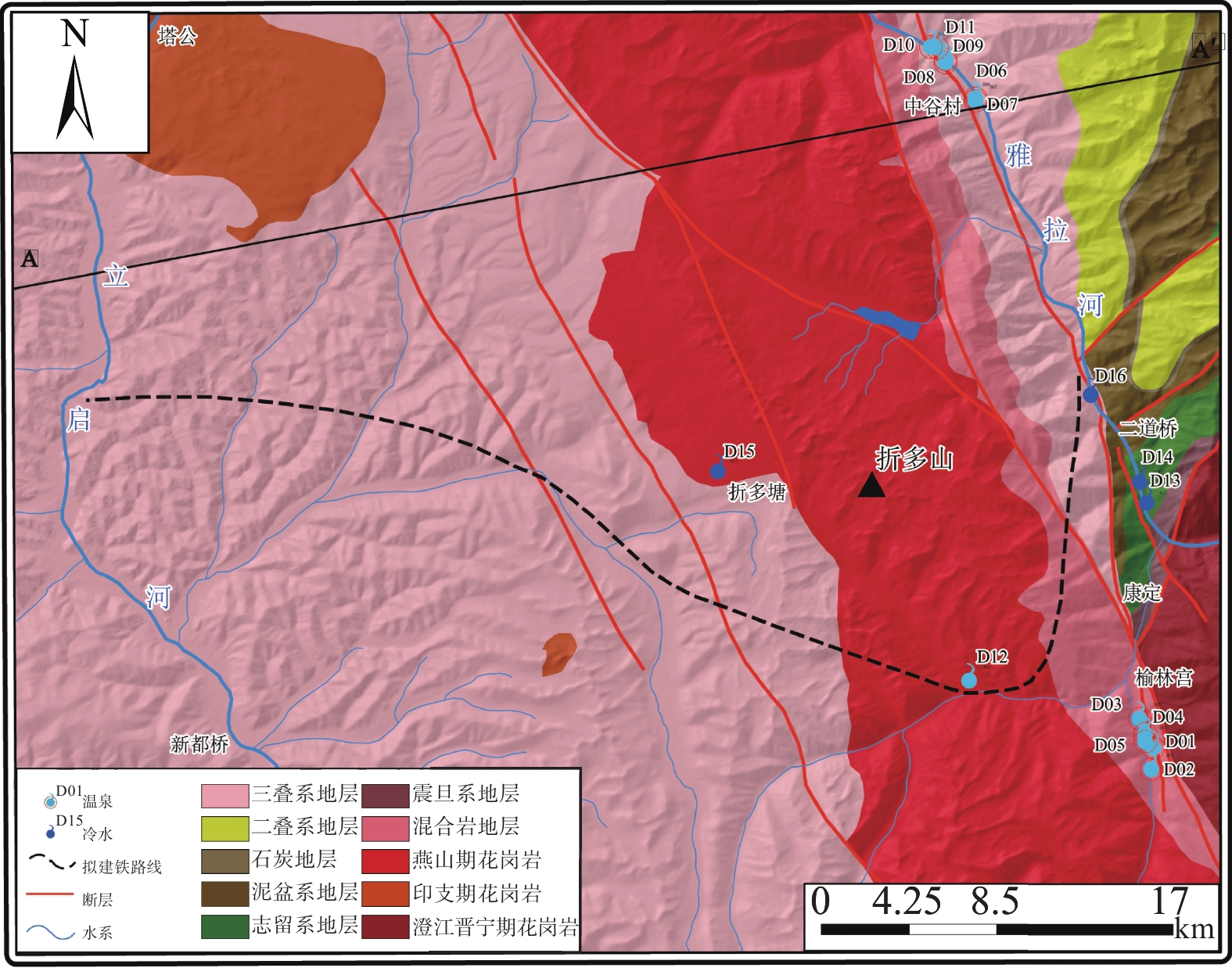
图 2 研究区剖面图(根据文献[16]修改)
Figure 2.
图 5 研究区地热水的Na-K-Mg三角图[17]
Figure 5.
表 1 研究区水样的水化学和同位素测试分析结果
Table 1. Hydrochemical and isotopic constituents of the water samples in the study area
编号 取样类型 位置 溶解性总固体 K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− 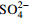

SiO2 离子平衡检验/% /(mg·L−1) D1 温泉水 榆林村白湾 1002.4 40.0 340.0 4.0 0.6 223.4 25.1 530.9 101.0 −1.5 D2 灌顶温泉 1430.8 55.0 400.0 40.1 14.6 294.3 75.8 720.0 178.3 0.6 D3 龙头沟温泉 1649.6 56.0 550.0 12.0 29.2 260.6 0.1 1019.0 93.5 7.7 D4 榆林村温泉 1949.7 75.0 650.0 7.0 7.3 340.4 46.4 1304.3 95.5 −1.8 D5 金家河坝温泉 1126.5 30.0 330.0 41.1 12.2 157.4 182.4 579.7 82.2 −0.2 D6 二道桥清泉村温泉 1147.1 12.0 74.0 320.6 30.4 46.1 11.5 1281.4 93.1 −2.5 D7 中谷热水塘1 1009.3 30.0 270.0 71.1 16.4 64.9 6.5 897.0 96.5 −0.3 D8 中谷热水塘2 1315.8 32.0 340.0 80.2 13.4 83.3 5.0 1128.8 114.5 −1.1 D9 亚拉乡1 1297.5 38.0 390.0 98.2 20.7 99.3 10.0 1281.4 96.2 0.2 D10 亚拉乡2 1222.0 36.0 370.0 90.2 21.3 85.1 2.9 1305.8 85.2 −2.0 D11 中谷大盖1 805.4 31.0 280.0 42.5 9.1 58.5 8.9 762.7 81.5 4.2 D12 中谷大盖2 1132.0 34.0 290.0 45.1 7.9 76.2 8.6 915.3 104.5 −4.3 D13 折多塘 388.9 2.1 140.0 9.0 0.6 8.9 8.7 372.2 52.0 −1.3 D14 冷泉水 清泉山庄北60 m 156.4 0.2 1.9 106.8 8.4 0.7 10.4 171.7 − −1.9 D15 二道桥 329.9 2.6 4.4 73.2 23.8 0.7 88.7 236.8 − −1.8 D16 地表水 折多山海子 13.0 0.1 1.4 9.8 0.5 0.5 0.7 14.2 − −0.2 D17 雅拉河水 127.2 1.4 8.6 31.2 7.2 1.8 13.3 124.3 10.3 −1.6 编号 取样类型 位置 温度/℃ pH 水化学类型 石英温标/℃ 硅焓方程法 δ18O/‰ δD/‰ δD补给高程/m 初始热水水温/℃ 冷水混合比 D1 温泉水 榆林村白湾 6.8 HCO3·Cl—Na 138 186 0.56 −16.8 −135.6 4926 D2 灌顶温泉 84 7.6 HCO3·Cl—Na 172 − − −14.7 −115.6 4097 D3 龙头沟温泉 81 8.7 HCO3·Cl—Na 133 198 0.63 −16.2 −127.8 4603 D4 榆林村温泉 70 8.4 HCO3·Cl—Na 135 210 0.71 −15.8 −131.1 4740 D5 金家河坝温泉 64 6.5 HCO3·Cl—Na 127 228 0.80 −14.9 −116.2 4122 D6 二道桥清泉村温泉 48 7.4 HCO3—Na 133 − − −15.6 −107.7 3768 D7 中谷热水塘1 40 6.9 HCO3—Na 135 250 0.81 −15.6 −115.9 4109 D8 中谷热水塘2 47 6.7 HCO3—Na 145 240 0.76 −15.9 −119.3 4251 D9 亚拉乡1 62 6.8 HCO3—Na 135 − − −16.7 −125.9 4524 D10 亚拉乡2 45 7.1 HCO3—Na 128 208 0.74 −17.0 −128.7 4641 D11 中谷大盖1 50 6.9 HCO3—Na 126 − − −16.4 −124.1 4450 D12 中谷大盖2 37 7.0 HCO3—Na 140 − − −16.3 −120.5 4300 D13 折多塘 46 7.8 HCO3—Na 104 190 0.81 −15.3 −113.8 4022 D14 冷泉水 清泉山庄北60 m 38 7.8 HCO3—Ca − − − − − − D15 二道桥 12 7.8 HCO3—Ca − − − − − − D16 地表水 折多山海子 12 7.3 HCO3—Ca − − − −15.6 −112.9 − D17 雅拉河水 − 8.1 HCO3—Ca − − − −13.3 −99.6 − -
[1] 唐晗晗, 郭良辉, 方圆. 青藏高原东南缘热流估算及与地震活动相关性分析[J]. 地球物理学报,2020,63(3):1056 − 1069. [TANG Hanhan, GUO Lianghui, FANG Yuan. Estimation of heat flow in southeastern margin of Xizang Plateau and its analysis of the correlation with earthquake activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2020,63(3):1056 − 1069. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg2019N0045
[2] 李晓, 王金金, 黄珣, 等. 鲜水河断裂带康定至道孚段热水化学与同位素特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2018,45(6):733 − 745. [LI Xiao, WANG Jinjin, HUANG Xun, et al. Chemical and isotopic characteristics of hot water in the Kangding-Daofu section of Xianshuihe fault zone, Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2018,45(6):733 − 745. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 张健, 李午阳, 唐显春, 等. 川西高温水热活动区的地热学分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学,2017,47(8):899 − 915. [ZHANG Jian, LI Wuyang, TANG Xianchun, et al. Geothermal data analysis at the high-temperature hydrothermal area in Western Sichuan[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2017,47(8):899 − 915. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] ZHANG J, LI W Y, TANG X C, et al. Geothermal data analysis at the high-temperature hydrothermal area in Western Sichuan[J]. Science China Earth Sciences,2017,60(8):1507 − 1521. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-9053-2
[5] TANG X C, ZHANG J, PANG Z H, et al. The eastern Xizang Plateau geothermal belt, Western China: Geology, geophysics, genesis, and hydrothermal system[J]. Tectonophysics,2017,717:433 − 448. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2017.08.035
[6] LI X, HUANG X, LIAO X, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and conceptual model of the geothermal waters in the Xianshuihe fault zone, southwestern China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2020,17(2):500. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17020500
[7] LI B, SHI Z M, WANG G C, et al. Earthquake-related hydrochemical changes in thermal springs in the Xianshuihe Fault zone, Western China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2019,579:124175. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124175
[8] QI J H, XU M, AN C J, et al. Characterizations of geothermal springs along the Moxi deep fault in the western Sichuan plateau, China[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors,2017,263:12 − 22. doi: 10.1016/j.pepi.2017.01.001
[9] ZHANG Y H, XU M, LI X, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and multivariate statistical analysis of natural water system: a case study in Kangding County, southwestern China[J]. Water,2018,10(1):80 − 96. doi: 10.3390/w10010080
[10] 卞跃跃, 赵丹. 四川康定地热田地下热水成因研究[J]. 地球学报,2018,39(4):491 − 497. [BIAN Yueyue, ZHAO Dan. Genesis of geothermal waters in the Kangding geothermal field, Sichuan Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2018,39(4):491 − 497. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2018.060401
[11] LUO J, PANG Z H, KONG Y K, et al. Geothermal potential evaluation and development prioritization based on geochemistry of geothermal waters from Kangding area, western Sichuan, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2017,76(9):1 − 24.
[12] GUO Q, PANG Z H, WANG Y C, et al. Fluid geochemistry and geothermometry applications of the Kangding high-temperature geothermal system in eastern Himalayas[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2017,81:63 − 75. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.03.007
[13] 张云辉. 鲜水河断裂康定-磨西段地热系统成因及开发利用研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018.
ZHANG Yunhui. Research on genesis and development of the geothermal system in the Kangding-moxi segment of the Xianshuihe fault[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] LI J X, YANG G, SAGOE G, et al. Major hydrogeochemical processes controlling the composition of geothermal waters in the Kangding geothermal field, western Sichuan Province[J]. Geothermics,2018,75:154 − 163. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.04.008
[15] LIU Q Q, SHI Y N, WEI D P, et al. Near-surface geothermal gradient observation and geothermal analyses in the Xianshuihe fault zone, eastern Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica - English Edition,2017,91(2):414 − 428. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.13108
[16] 梁信之, 谭庆鹄, 师常庆, 等. 1∶20万康定幅区域报告[R]. 成都: 四川省地质矿产局区域调查队, 1985.
LIANG Xinzhi, TAN Qinghu, SHI Changqing, et al. 1∶200 000 Kangding regional survey report[R]. Chengdu: Regional Geological Survey Party, Sichuan Bureau of Geological Exploration and Exploration of Mineral Resources, Sichuan, 1985.
[17] GIGGENBACH W F. Geothermal solute equilibria Derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1988,52(12):2749 − 2765. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(88)90143-3
[18] 史杰, 乃尉华, 李明, 等. 新疆曲曼高温地热田水文地球化学特征研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(3):165 − 172. [SHI Jie, NAI Weihua, LI Ming, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of high temperature geothermal field of the Quman geothermal field in Xinjiang[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(3):165 − 172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] FOURNIER R O. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems[J]. Geothermics,1977,5:41 − 50. doi: 10.1016/0375-6505(77)90007-4
[20] 李明辉, 袁建飞, 黄从俊, 等. 四川广安铜锣山背斜热储性质及地热成因模式[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):36 − 46. [LI Minghui, YUAN Jianfei, HUANG Congjun, et al. A study of the characteristics of geothermal reservoir and genesis of thermal groundwater in the Tongluoshan anticline near Guang’an in east Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):36 − 46. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] CRAIG H. Isotopic variations in meteoric waters[J]. Science,1961,133(3465):1702 − 1703. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
[22] 宋春林, 孙向阳, 王根绪. 贡嘎山亚高山降水稳定同位素特征及水汽来源研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2015,24(11):1860 − 1869. [SONG Chunlin, SUN Xiangyang, WANG Genxu. A study on precipitation stable isotopes characteristics and vapor sources of the subalpine Gongga mountain, China[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2015,24(11):1860 − 1869. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201511008
[23] 赵志宏, 徐浩然, 刘峰, 等. 川藏铁路折多山段隧道温度场与热害初步预测[J]. 现代地质,2021,35(1):180 − 187. [ZHAO Zhihong, XU Haoran, LIU Feng, et al. Preliminary prediction of temperature field and thermal damage in Zheduoshan region along Sichuan-Xizang Railway[J]. Geoscience,2021,35(1):180 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 何丽娟, 汪集旸. “大地热流”等地热学重要术语的概念与应用[J]. 中国科技术语,2021,23(3):3 − 9. [HE Lijuan, WANG Jiyang. Concept and application of some important terms in geothermics and geophysics such as terrestrial heat flow[J]. China Terminology,2021,23(3):3 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.12339/j.issn.1673-8578.2021.03.001
[25] 姜光政, 高堋, 饶松, 等. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第四版)[J]. 地球物理学报,2016,59(8):2892 − 2910. [JIANG Guangzheng, GAO Peng, RAO Song, et al. Compilation of heat flow data in the continental area of China(4th edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2016,59(8):2892 − 2910. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6038/cjg20160815
-



 下载:
下载: