Transformation characteristics of the large-flow river and groundwater in the fault zone in the glacier-covered area of Bomi in Xizang
-
摘要:
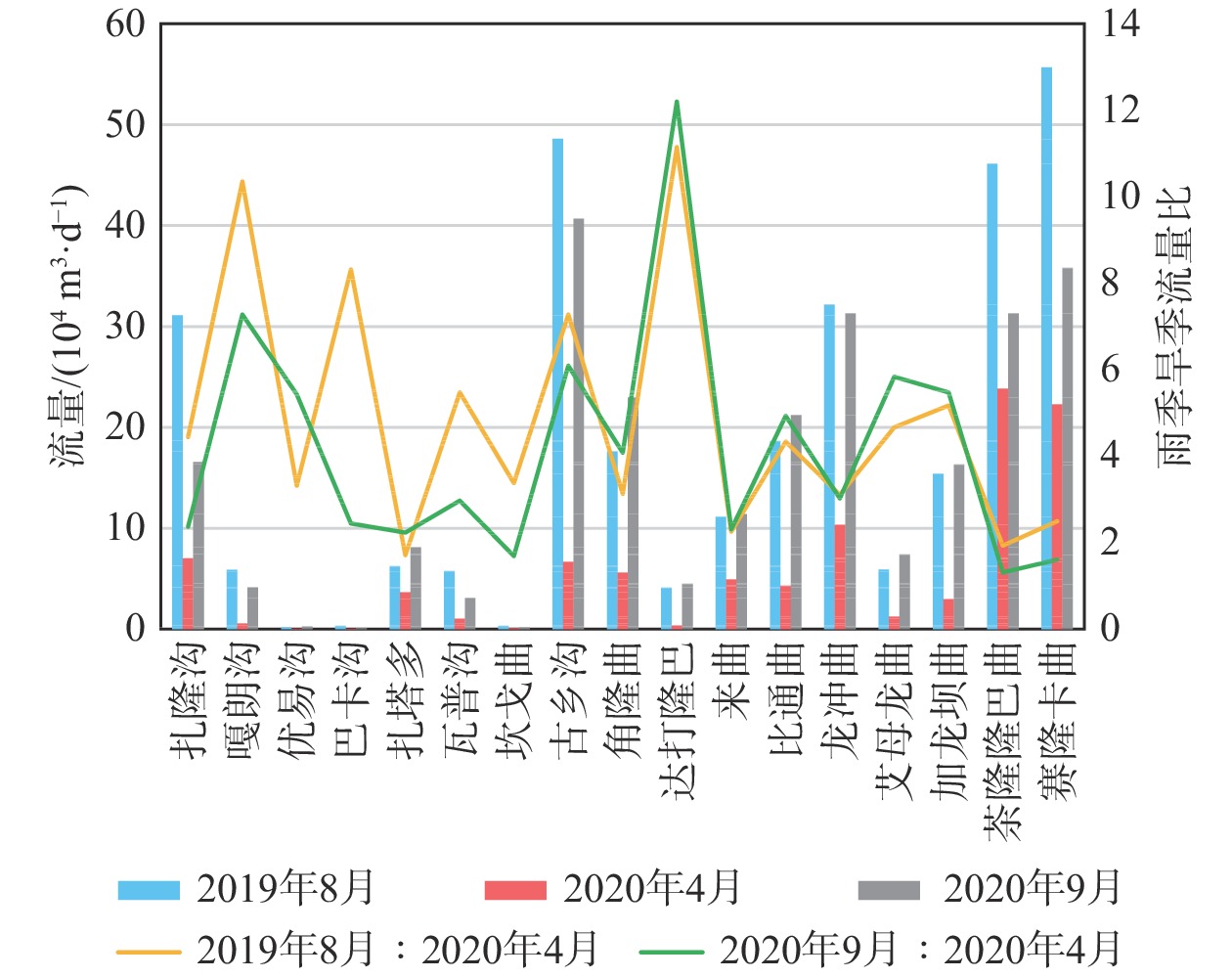
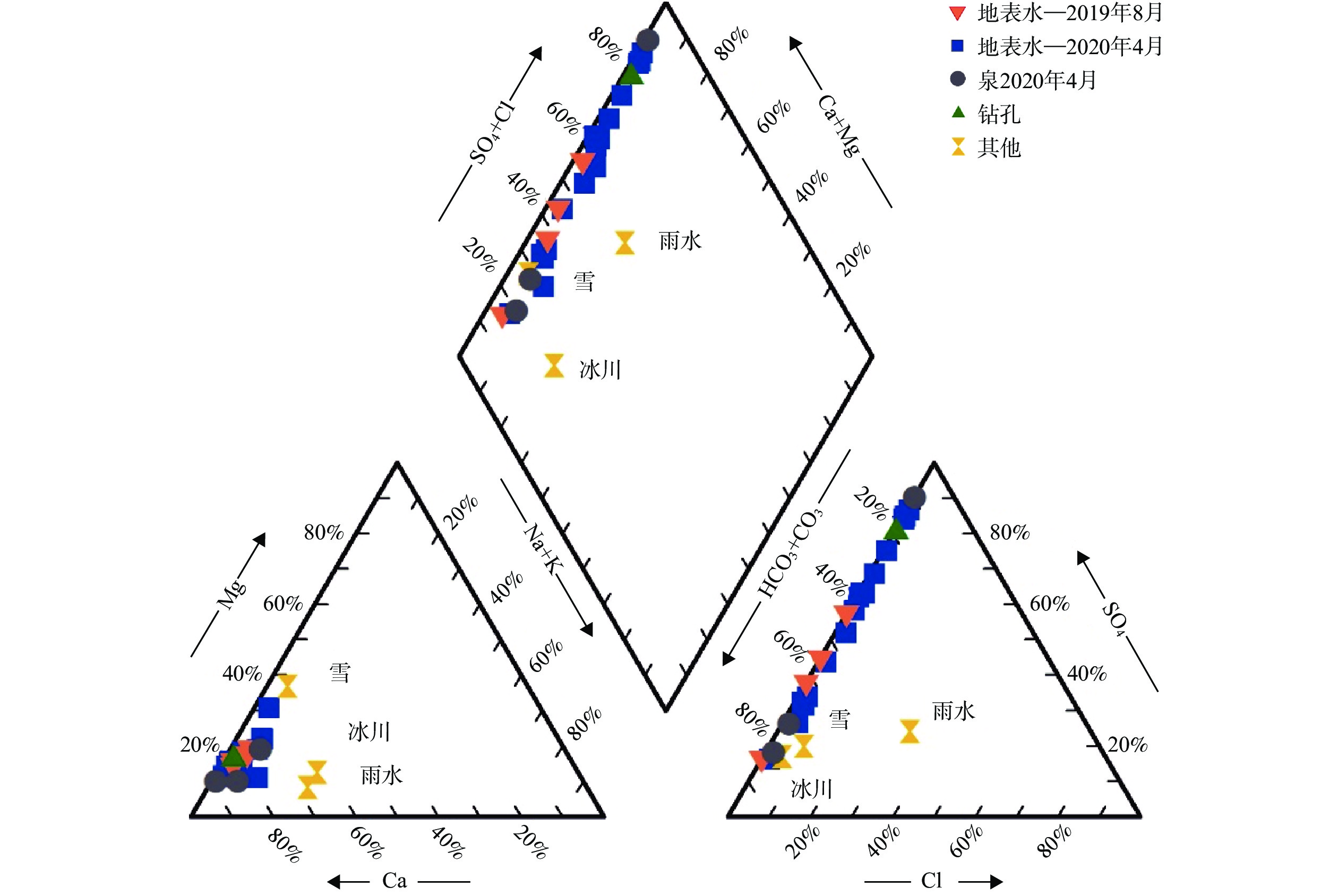
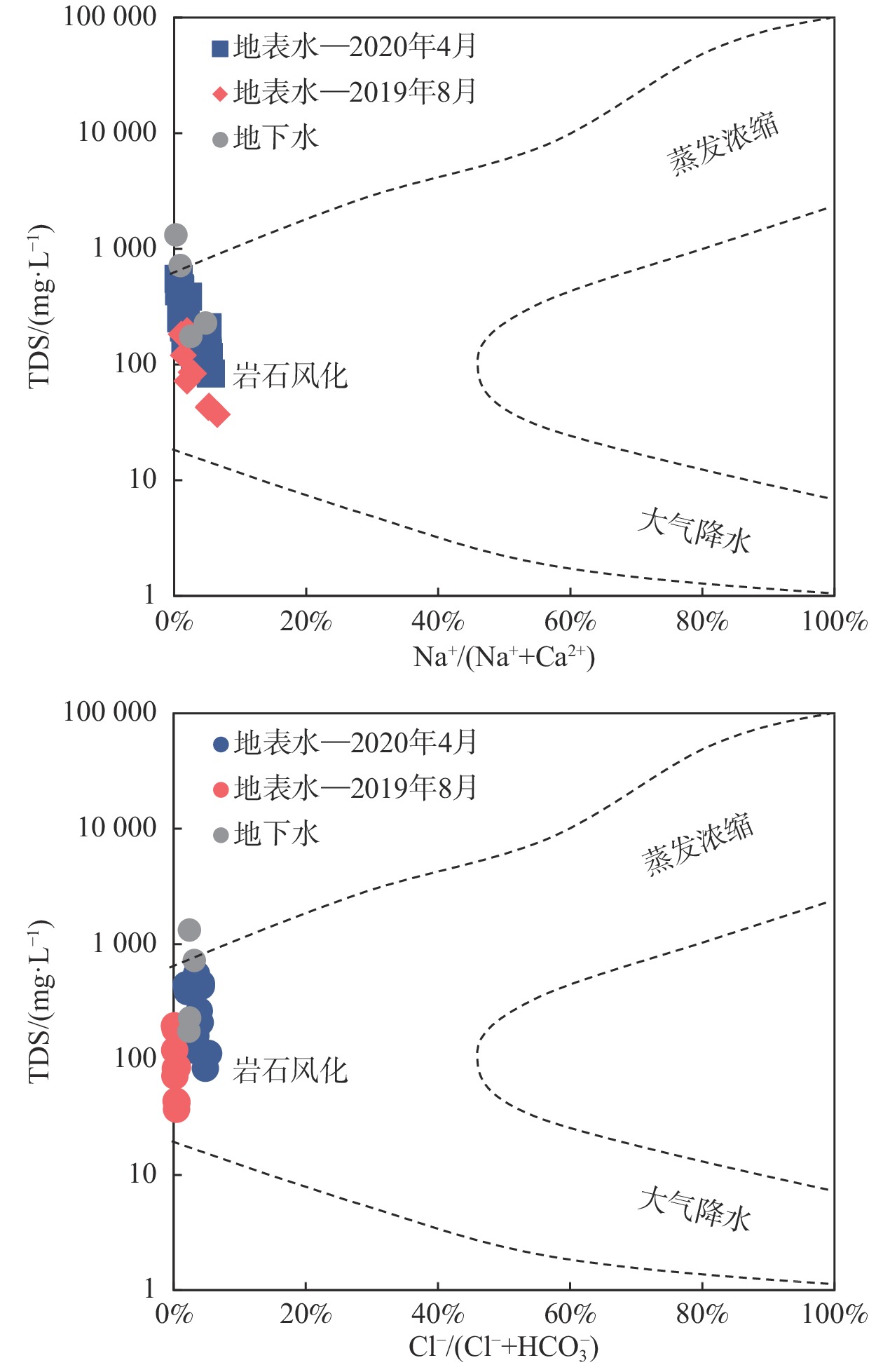
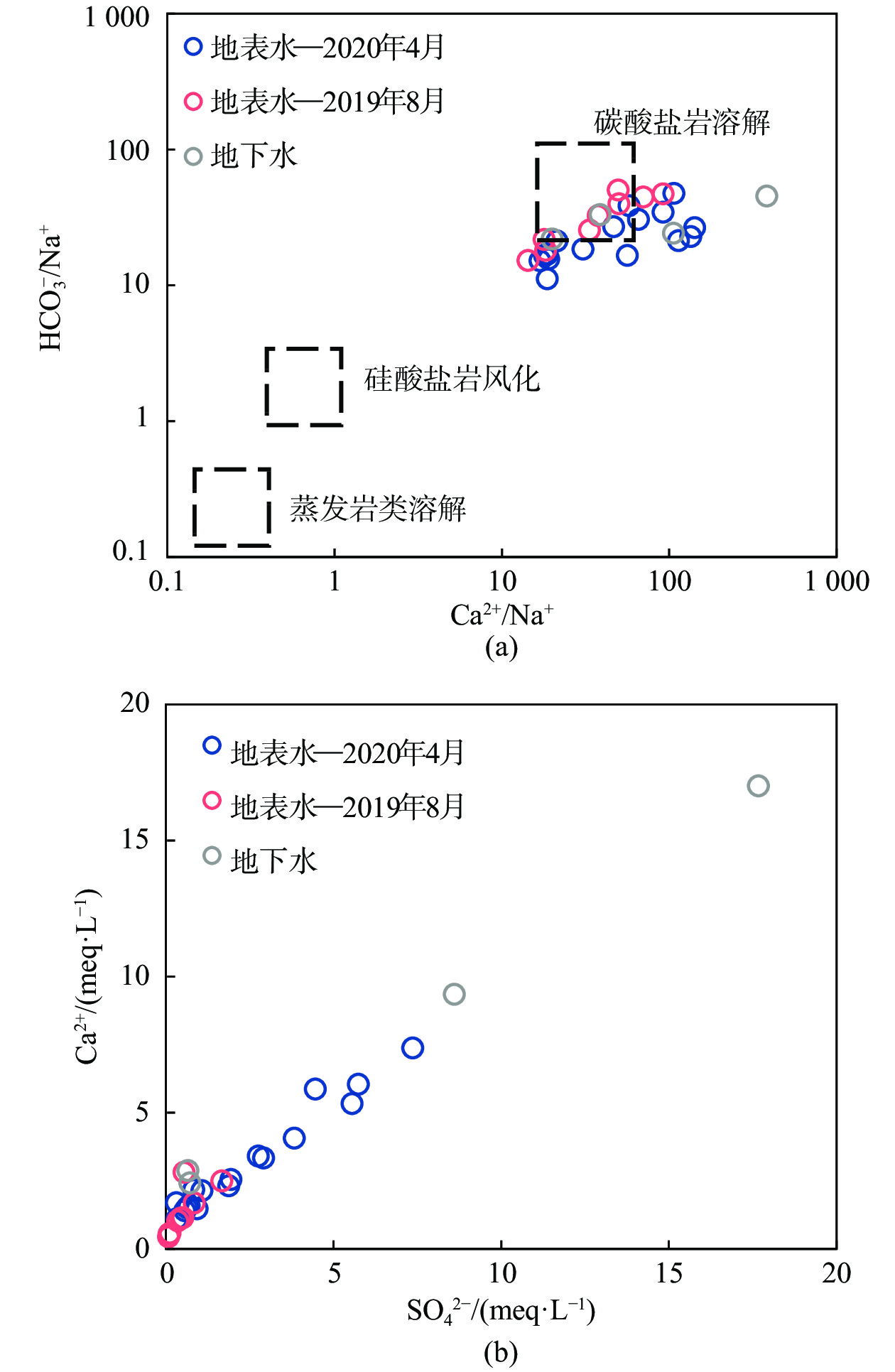
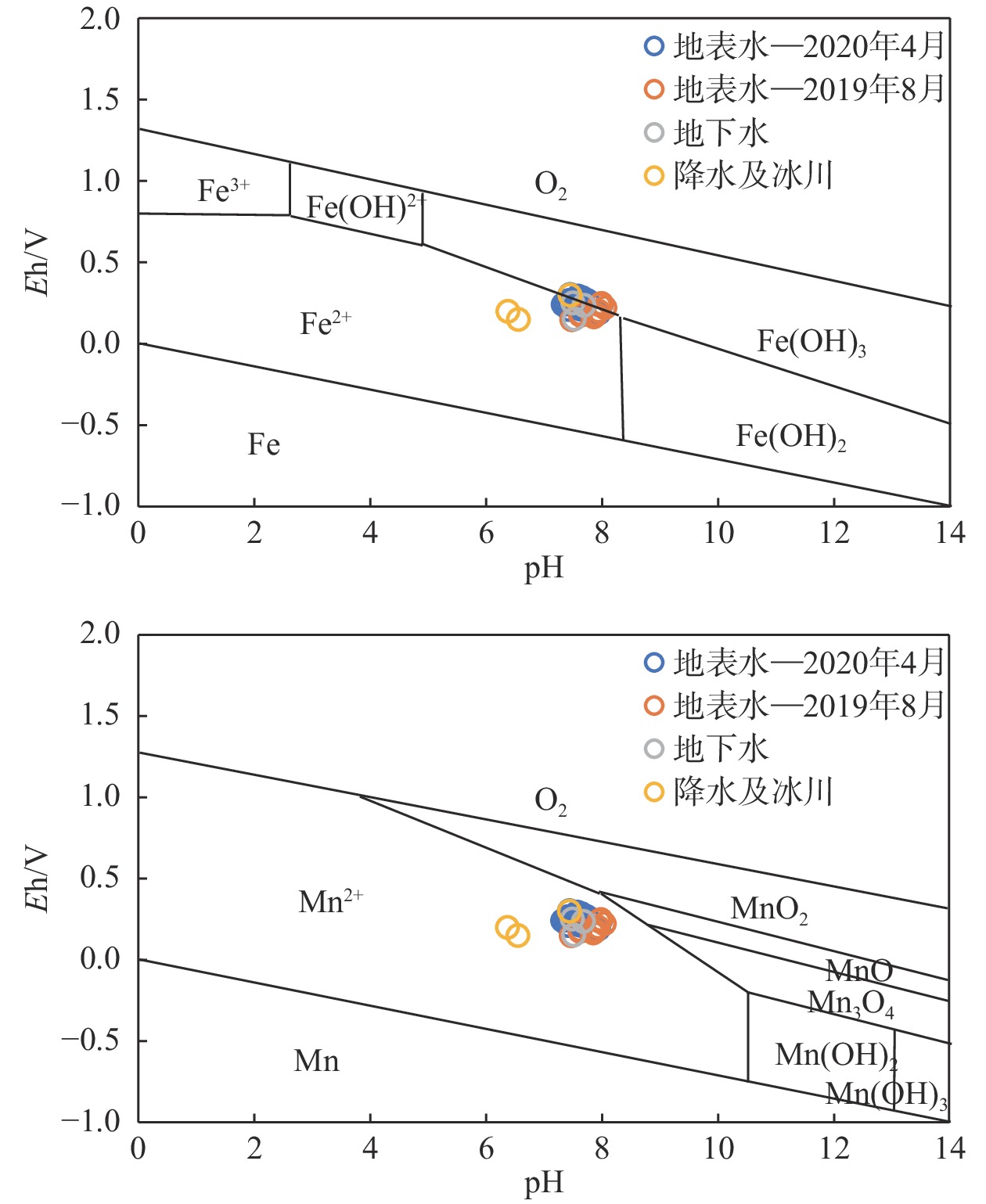
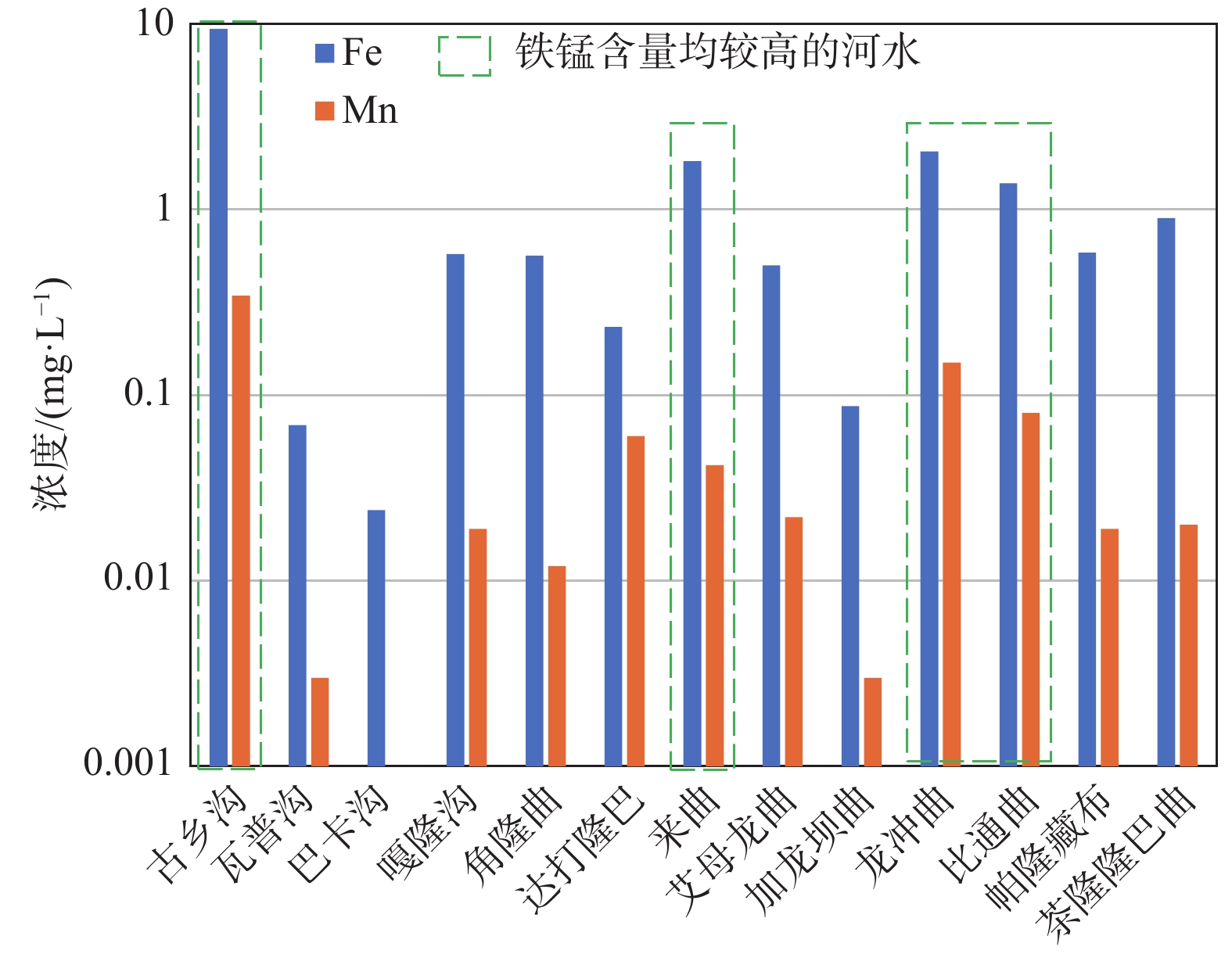
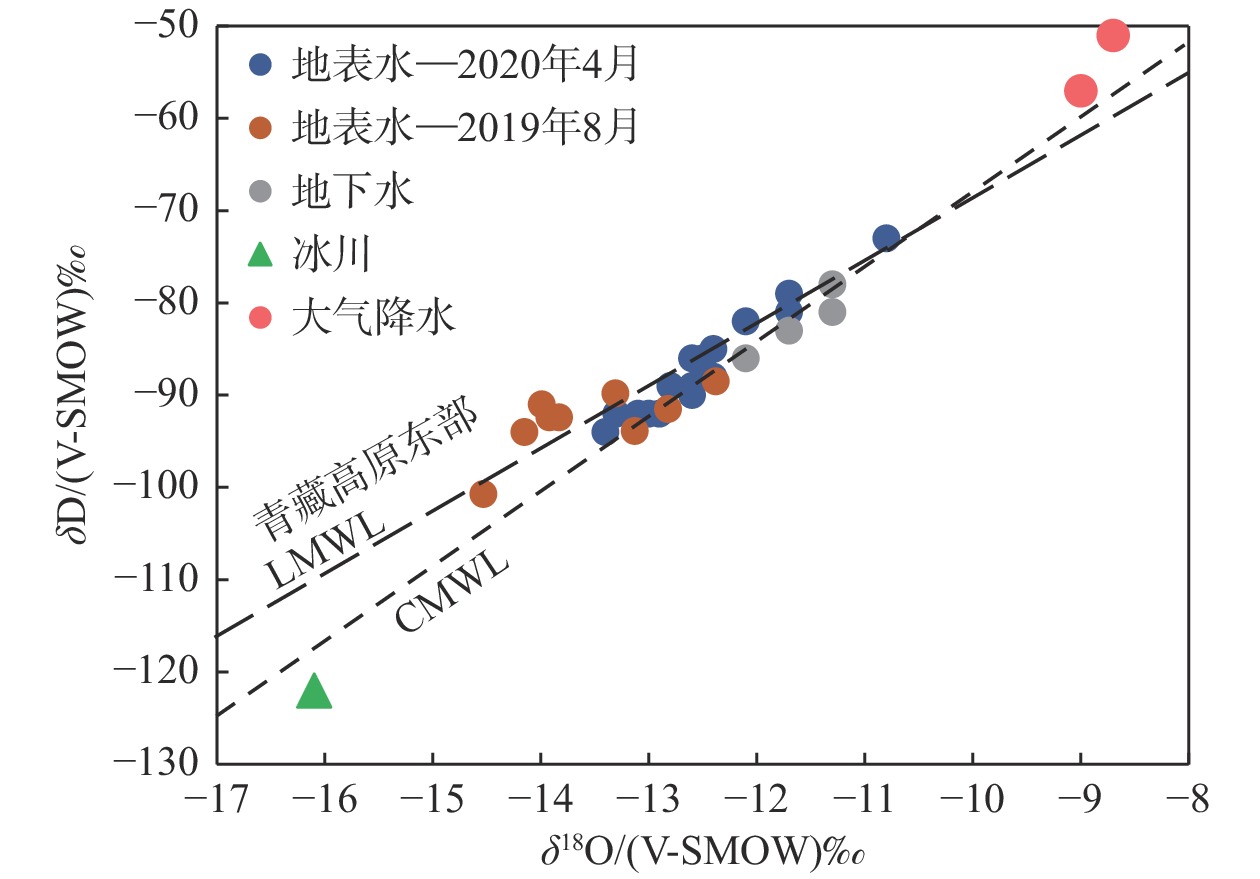
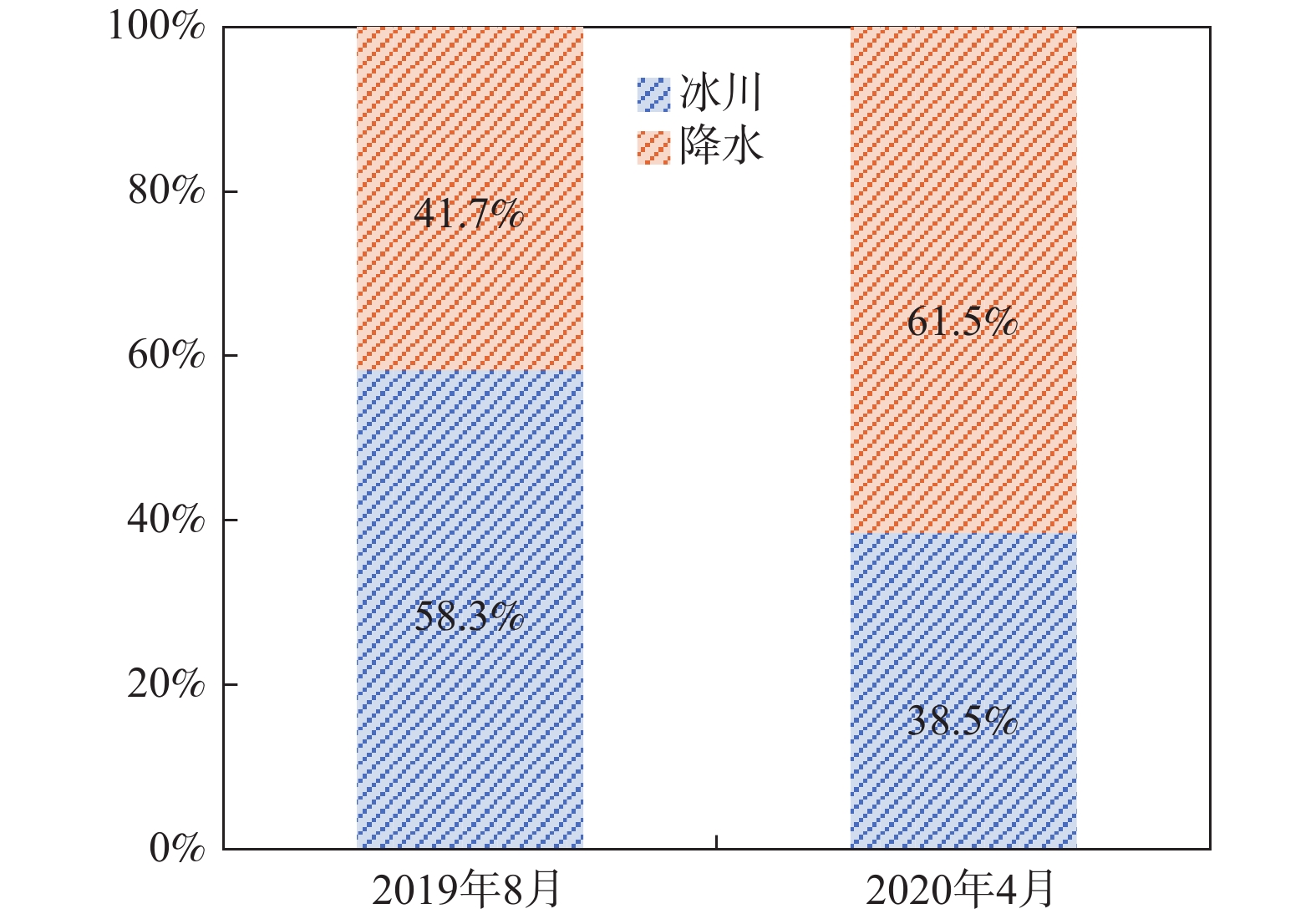
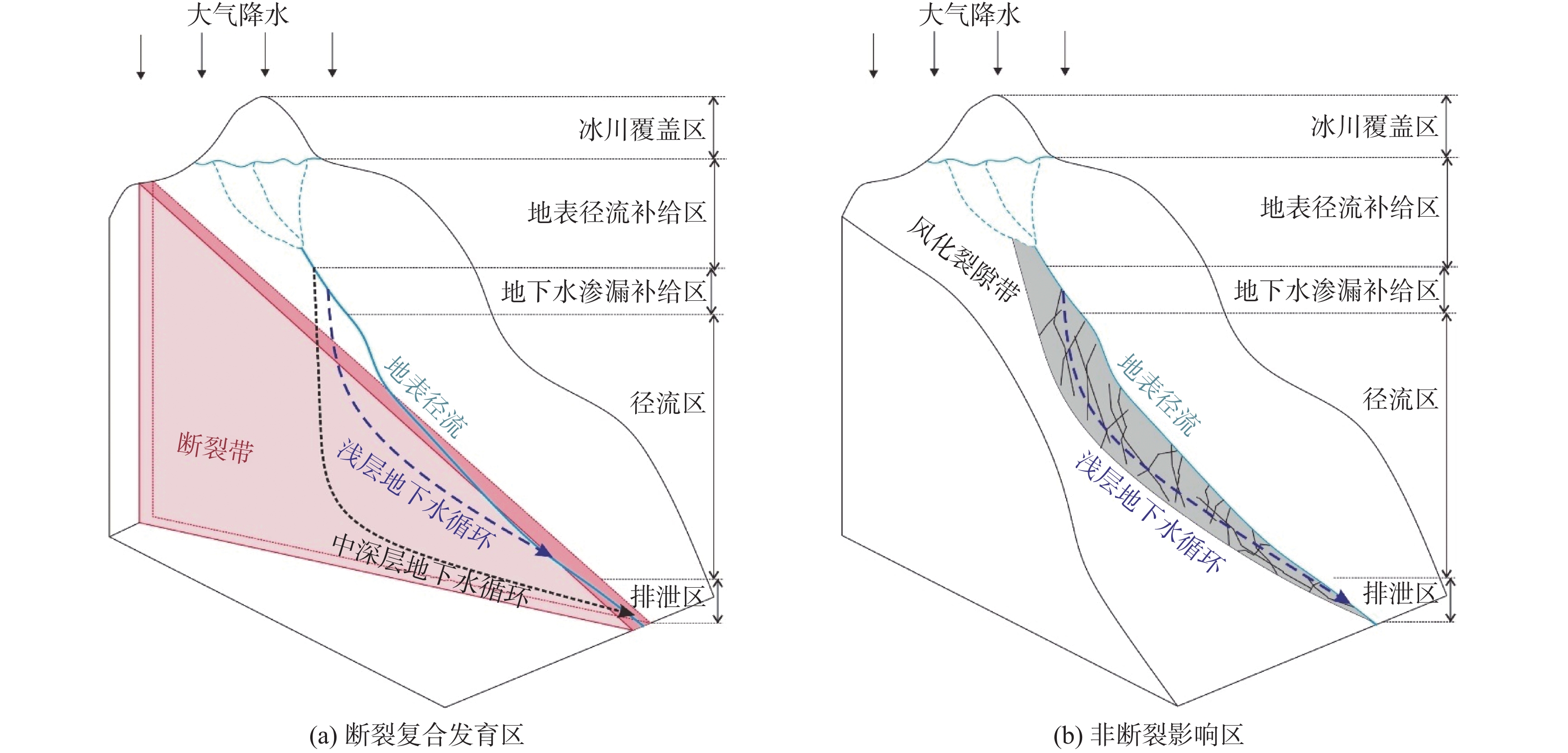
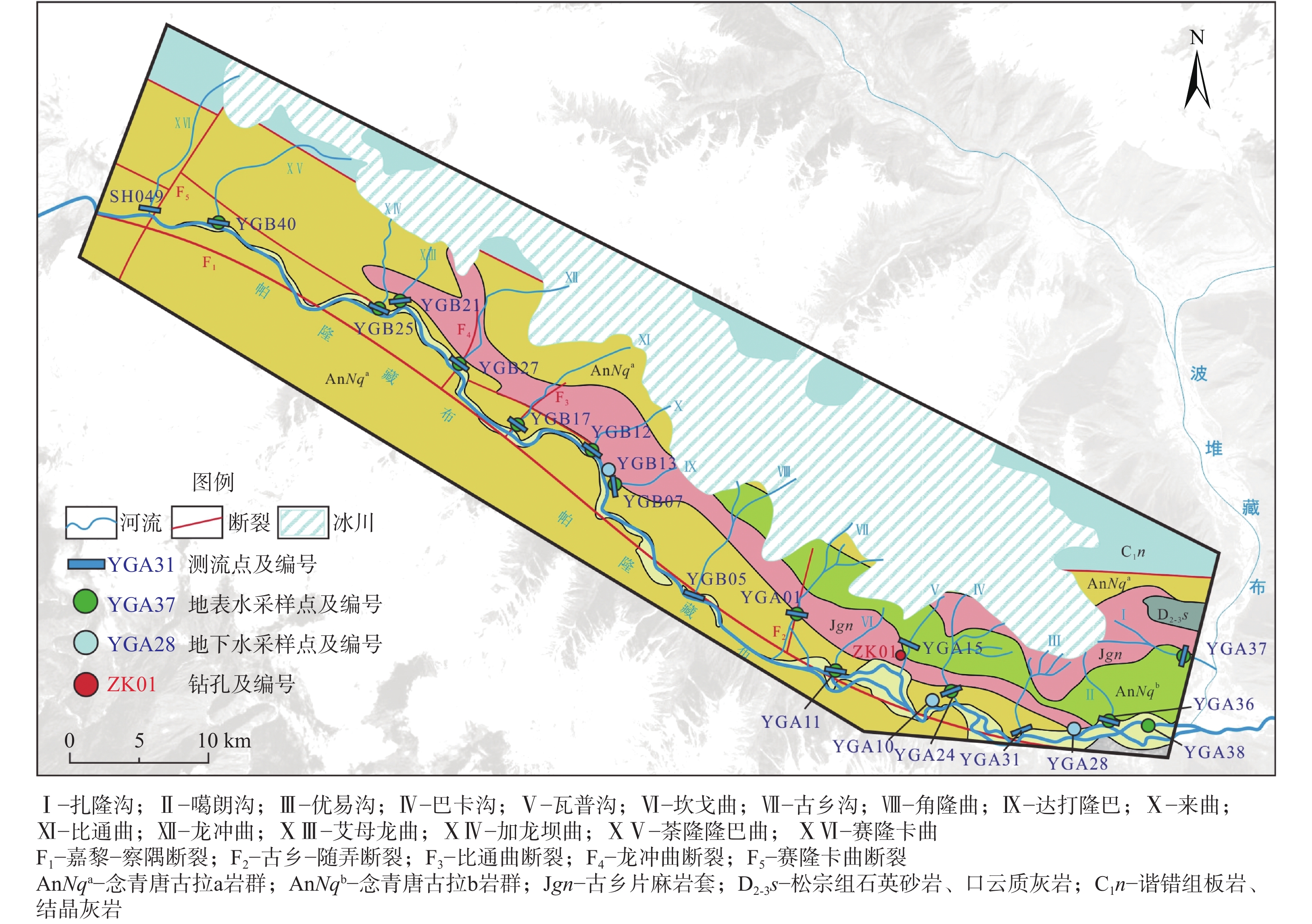
川藏铁路波密段穿越冰川覆盖区,分布多条与断裂复合发育的大型河流,水量丰富,可与断裂共同构成构造高压涌水突泥灾害风险源。本文通过多期测流和对大气降水、冰川、河流和地下水水化学、同位素特征分析,研究了大型河流的流量变化特征和地表水与断裂带裂隙水的转化关系。结果表明:西藏波密冰川覆盖区河水主要接受冰川融水和大气降水补给。雨季河水的δ18O和δD值小于旱季,说明河水雨季和旱季的补给源结构不同。旱季气温低,以大气降水补给为主;雨季冰川融水量陡增,为主要补给源。断裂影响范围内的古乡沟、比通曲和龙冲曲河水流量较大,均超过4×104 m3/d,但年内流量波动幅度小于非断裂带影响范围的河流。河流可渗漏补给断裂带水。浅层循环断裂带水年龄5~10 a,中深层断裂带水年龄超过4000 a,水岩作用较充分。非断裂带影响范围的河流与基岩风化裂隙水存在较密切的水力联系和较频繁的相互转化。研究成果可为青藏高原东部冰川覆盖区铁路隧道高压涌水突泥灾害的早期识别和灾害防范措施制定提供参考。
Abstract:The Bomi section of the Sichuan-Xizang Railway passes through the glacier-covered area where multiple large-scale river compounded with faults occur. The river water is abundant, leading to a tectonic high-pressure water inrush and mud outburst disaster risk source. This paper studies the flow characteristics of large-scale river and the transformation relationship between surface water and tectonic fissure water through flow measurement and analysis of precipitation, glacier melting water, river water and groundwater hydrochemistry, isotopic characteristics, and hydrogeochemical processes. The results show that the river water in Bomi glacier covered area in Xizang is mainly supplied by glacier melting water and precipitation. In rainy season, the values of δ 18O and δ D are less than those in dry season, indicating that the structure of water-supply source is different. During the dry season, the main source of replenishment is precipitation due to the low temperature, and in the rainy season the amount of glacier melting increases sharply, which becomes the main source of recharge. The discharge of rivers Guxianggou, Bitongqu and Longchongqu, which are compounded with the fault, is larger than 4×104 m3/d. However, the annual flow fluctuation is less than that of the rivers in the non-fault zone. The river water could supply the fault zone water, forming shallow circulation groundwater of 5−10 a and medium and deep circulation groundwater of more than 4000 a. There is a close hydraulic connection and frequent mutual transformation between the river and bedrock weathering fissure water in the non-fault zone. The research results can provide references for the early identification of high-pressure water and mud inrush disasters in tunnels and the formulation of disaster prevention measures in the glacier-covered area of the eastern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau.
-

-
表 1 水样主要水化学指标值
Table 1. Concentration statistics of the main hydrochemical indexes of water samples
样品分类 项目 pH TDS K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− 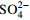

/(mg·L−1) 地表水—
2020年
4月最大值 7.99 551.00 5.16 2.84 147.40 23.07 1.75 353.50 158.50 最小值 7.33 84.00 1.29 0.85 21.95 1.88 1.40 15.19 53.84 平均值 7.57 248.53 2.65 1.53 62.65 7.79 1.69 118.35 85.86 标准差 0.18 143.92 1.08 0.58 37.50 5.21 0.13 102.28 27.91 中位数 7.57 210.00 2.24 1.36 46.16 6.65 1.75 90.23 83.75 变异系数 0.02 0.58 0.41 0.38 0.60 0.67 0.08 0.86 0.33 地表水—
2019年
8月最大值 8.05 196.17 4.39 1.30 56.20 8.69 0.20 80.31 173.20 最小值 7.48 37.09 0.40 0.47 8.62 0.98 0.05 4.29 27.83 平均值 7.83 96.18 1.64 0.72 26.20 3.46 0.09 25.15 64.26 标准差 0.19 55.89 1.15 0.22 16.10 2.26 0.04 22.53 41.16 中位数 7.90 83.82 1.45 0.69 22.30 3.06 0.08 21.67 52.57 变异系数 0.02 0.58 0.70 0.31 0.61 0.65 0.45 0.90 0.64 地下水 最大值 7.69 1325.00 6.28 3.30 340.00 23.04 2.79 848.60 191.40 最小值 7.50 176.00 4.69 1.02 48.23 3.51 1.75 32.03 122.60 平均值 7.58 612.50 5.62 1.94 158.11 14.59 2.18 332.11 142.25 标准差 0.08 462.82 0.58 0.86 118.45 8.55 0.45 336.14 28.48 中位数 7.57 474.50 5.76 1.73 122.11 15.90 2.10 223.91 127.50 变异系数 0.01 0.76 0.10 0.44 0.75 0.59 0.21 1.01 0.20 降水及
冰川最大值 7.45 67.37 0.55 5.24 12.57 1.59 1.75 8.50 53.78 最小值 6.38 10.63 0.39 0.10 1.07 0.08 1.40 1.41 6.52 平均值 6.80 36.02 0.49 1.85 5.93 1.06 1.52 4.75 31.07 标准差 0.47 23.54 0.07 2.40 4.86 0.69 0.16 2.91 19.34 中位数 6.56 30.07 0.54 0.21 4.15 1.51 1.40 4.33 32.90 变异系数 0.07 0.65 0.15 1.30 0.82 0.65 0.11 0.61 0.62 表 2 样品年代半定量对应表
Table 2. Half quantitive corresponding table between content and age
样品类型及编号 氚含量/TU 半定量年龄* 分类 泉-YGA10 6.2±0.9 5~10 a 浅循环地下水 泉-YGA28 4.1±0.8 5~10 a 浅循环地下水 泉-YGA34 3.9±0.8 1952年前补给与
5~10 a补给混合水浅循环地下水 钻孔样品 2.9±0.7 4640 a 中深循环地下水 地表水-YGA01 5.9±0.9 − 河水与地下水混合 地表水-YGB17 7.0±0.9 − 河水与地下水混合 地表水-YGB30 8.5±1.2 − 河水与地下水混合 注:*钻孔样品为14C测定的表现年龄。 -
[1] LI C S, DING J F, LIAO Y K, et al. Analysis on environmental impact factors of tunnel karst dynamics system in typical areas[C]//Groundwater chemical kinetics and fractal characteristics of karst tunnel. Singapore: Springer Singapore, 2020: 15-49.
[2] 李利平, 朱宇泽, 周宗青, 等. 隧道突涌水灾害防突厚度计算方法及适用性评价[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(增刊1):41 − 50. [LI Liping, ZHU Yuze, ZHOU Zongqing, et al. Calculation methods of rock thickness for preventing water inrush in tunnels and their applicability evaluation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(Sup1):41 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 李术才, 许振浩, 黄鑫, 等. 隧道突水突泥致灾构造分类、地质判识、孕灾模式与典型案例分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(5):1041 − 1069. [LI Shucai, XU Zhenhao, HUANG Xin, et al. Classification, geological identification, hazard mode and typical case studies of hazard-causing structures for water and mud inrush in tunnels[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(5):1041 − 1069. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 白明洲, 许兆义, 王连俊, 等. 深埋隧道岩溶突水灾害的地质条件研究[J]. 铁道工程学报,2006,23(3):21 − 24. [BAI Mingzhou, XU Zhaoyi, WANG Lianjun, et al. Research on the geological condition of karst water bursting disaster in the course of tunnel caving[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2006,23(3):21 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2006.03.006
[5] 徐则民, 黄润秋, 罗杏春. 特长岩溶隧道涌水预测的系统辨识方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2002,29(4):50 − 54. [XU Zemin, HUANG Runqiu, LUO Xingchun. Identification of karst water system in long tunnel[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2002,29(4):50 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2002.04.015
[6] 马士伟. 岩溶隧道涌突水地质灾害破坏机理与预警技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国铁道科学研究院, 2011.
MA Shiwei. Study on mechanism of inrush water geological hazard and warning technology of karst tunnel[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Railway Sciences, 2011.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 李术才, 王康, 李利平, 等. 岩溶隧道突水灾害形成机理及发展趋势[J]. 力学学报,2017,49(1):22 − 30. [LI Shucai, WANG Kang, LI Liping, et al. Mechanical mechanism and development trend of water-inrush disasters in karst tunnels[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2017,49(1):22 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-16-345
[8] 高波, 王军朝, 张佳佳, 等. 帕隆藏布流域(波密-索通)典型冰碛物-崩滑型物源冰川泥石流发育特征分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2018,18(19):176 − 182. [GAO Bo, WANG Junchao, ZHANG Jiajia, et al. Analysis of the development characteristics of typical glacial debris flow that has materials source of moraine and colluvial or slide deposits in the Parlung River (Bomi-Suotong)[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2018,18(19):176 − 182. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2018.19.027
[9] 赵聪, 梁京涛, 王军朝, 等. 帕隆藏布流域(波密-然乌段)冰川动态变化遥感分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2019,19(21):56 − 62. [ZHAO Cong, LIANG Jingtao, WANG Junchao, et al. Remote sensing analysis of glacier dynamic changes in Parlung Zangbo river[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2019,19(21):56 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.21.009
[10] 邓桃, 姚令侃, 黄艺丹, 等. 海洋型冰川塑造地貌特征与铁路选线程式[J]. 铁道标准设计,2021,65(1):28 − 33. [DENG Tao, YAO Lingkan, HUANG Yidan, et al. Landform characteristics of marine glaciers and railway route selection program[J]. Railway Standard Design,2021,65(1):28 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 刘宗香, 苏珍, 姚檀栋, 等. 青藏高原冰川资源及其分布特征[J]. 资源科学,2000,22(5):49 − 52. [LIU Zongxiang, SU Zhen, YAO Tandong, et al. Resources and distribution of glaciers on the Xizang Plateau[J]. Resources Science,2000,22(5):49 − 52. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2000.05.011
[12] 许君利, 刘时银, 张世强, 等. 塔里木盆地南缘喀拉米兰河克里雅河流内流区近30a来的冰川变化研究[J]. 冰川冻土,2006,28(3):312 − 318. [XU Junli, LIU Shiyin, ZHANG Shiqiang, et al. Glaciers fluctuations in the Karamilan-Keriya River watershed in the past 30 years[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2006,28(3):312 − 318. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2006.03.002
[13] 罗锋. 川藏铁路某冰川泥石流桥梁安全净空高度研究[J]. 铁道标准设计,2021,65(7):92 − 97. [LUO Feng. Case study on the safe clearance height of bridge project crossing a glacial debris flow of Sichuan-Xizang Railway[J]. Railway Standard Design,2021,65(7):92 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 郭长宝, 吴瑞安, 蒋良文, 等. 川藏铁路雅安—林芝段典型地质灾害与工程地质问题[J]. 现代地质,2021,35(1):1 − 17. [GUO Changbao, WU Rui’an, JIANG Liangwen, et al. Typical geohazards and engineering geological problems along the Ya’an-Linzhi section of the Sichuan-Xizang Railway, China[J]. Geoscience,2021,35(1):1 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] LI X Y, HE X B, KANG S C, et al. Diurnal dynamics of minor and trace elements in stream water draining Dongkemadi Glacier on the Xizang Plateau and its environmental implications[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2016,541:1104 − 1118. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.08.021
[16] 王利杰, 曾辰, 王冠星, 等. 西藏山南地区沉错湖泊与径流水化学特征及主控因素初探[J]. 干旱区地理,2017,40(4):737 − 745. [WANG Lijie, ZENG Chen, WANG Guanxing, et al. Chemical characteristics and impact factors of the Drem-tso Lake and supplying runoff in the Southern Xizang[J]. Arid Land Geography,2017,40(4):737 − 745. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 孙英, 周金龙, 魏兴, 等. 巴楚县平原区地下水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 环境化学,2019,38(11):2601 − 2609. [SUN Ying, ZHOU Jinlong, WEI Xing, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and cause analysis of groundwater in the plain area of Bachu County[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2019,38(11):2601 − 2609. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] LI X Y, DING Y J, LIU Q, et al. Intense chemical weathering at glacial meltwater-dominated Hailuogou basin in the southeastern Xizang Plateau[J]. Water,2019,11(6):1209. doi: 10.3390/w11061209
[19] 李明月, 孙学军, 李胜楠, 等. 青藏高原及其周边地区冰川融水径流无机水化学特征研究进展[J]. 冰川冻土,2020,42(2):562 − 574. [LI Mingyue, SUN Xuejun, LI Shengnan, et al. Advances on inorganic hydrochemistry of glacial meltwater runoff in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and its surrounding areas[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2020,42(2):562 − 574. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 王保弟, 王冬兵, 唐渊, 等. 川藏铁路交通廊带地质图及说明书(1∶250000)[R]. 成都: 中国地质调查局成都地质调查中心, 2019.
WANG Baodi, WANG Dongbing, TANG Yuan, et al. Geological map and manual of Sichuan-Xizang Railway traffic corridor (1∶250000)[R]. Chengdu: Chengdu Center of China Geological Survey, 2019. (in Chinese)
[21] 张小文, 何江涛, 黄冠星. 石家庄地区浅层地下水铁锰分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 地学前缘,2021,28(4):206 − 218. [ZHANG Xiaowen, HE Jiangtao, HUANG Guanxing. Distribution characteristics and cause analysis of iron and manganese in shallow groundwater in Shijiazhuang area[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2021,28(4):206 − 218. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.7.4
[22] KHOZYEM H, HAMDAN A, TANTAWY A A, et al. Distribution and origin of iron and manganese in groundwater: case study, Balat-Teneida area, El-Dakhla Basin, Egypt[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2019,12(16):1 − 16.
[23] 余东, 周金龙, 陈劲松, 等. 新疆喀什地区高铁锰地下水空间分布特征及成因分析[J]. 环境化学,2020,39(11):3235 − 3245. [YU Dong, ZHOU Jinlong, CHEN Jinsong, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and genesis of groundwater with high iron and manganese content in Kashi Prefecture, Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry,2020,39(11):3235 − 3245. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2020032401
[24] 黄冠星, 孙继朝, 荆继红, 等. 珠江三角洲地区地下水铁的分布特征及其成因[J]. 中国地质,2008,35(3):531 − 538. [HUANG Guanxing, SUN Jichao, JING Jihong, et al. Distribution and origin of iron in groundwater of the Zhujiang delta[J]. Geology in China,2008,35(3):531 − 538. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2008.03.018
[25] 李维杰, 王建力, 王家录. 西南地区不同地形降水稳定同位素特征及其水汽来源[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2018,27(5):1132 − 1142. [LI Weijie, WANG Jianli, WANG Jialu. Characteristics of the stable isotopes in precipitation and the source of water vapor in different terrain in the southwest region[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin,2018,27(5):1132 − 1142. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201805020
[26] 杨楠, 苏春利, 曾邯斌, 等. 基于水化学和氢氧同位素的兴隆县地下水演化过程研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(6):160 − 168. [YANG Nan, SU Chunli, ZENG Hanfu, et al. Evolutional processes of groundwater in Xinglong County based on hydrochemistry and hydrogen and oxygen isotopes[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(6):160 − 168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 张春潮, 侯新伟, 李向全, 等. 三姑泉域岩溶地下水水化学特征及形成演化机制[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):62 − 71. [ZHANG Chunchao, HOU Xingwei, LI Xiangquan, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution mechanism of karst groundwater in the catchment area of the Sangu Spring[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):62 − 71. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 高旭波, 向绚丽, 侯保俊, 等. 水化学−稳定同位素技术在岩溶水文地质研究中的应用[J]. 中国岩溶,2020,39(5):629 − 636. [GAO Xubo, XIANG Xuanli, HOU Baojun, et al. Application of hydrochemistry coupled with stable isotopes in the study of Karst water hydrogeology[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2020,39(5):629 − 636. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] CLARK I D, FRITZ P. Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology[M]. New York: Lewis Publishers, 1999.
-



 下载:
下载: