A study of the early identification and risk assessment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu county
-
摘要:
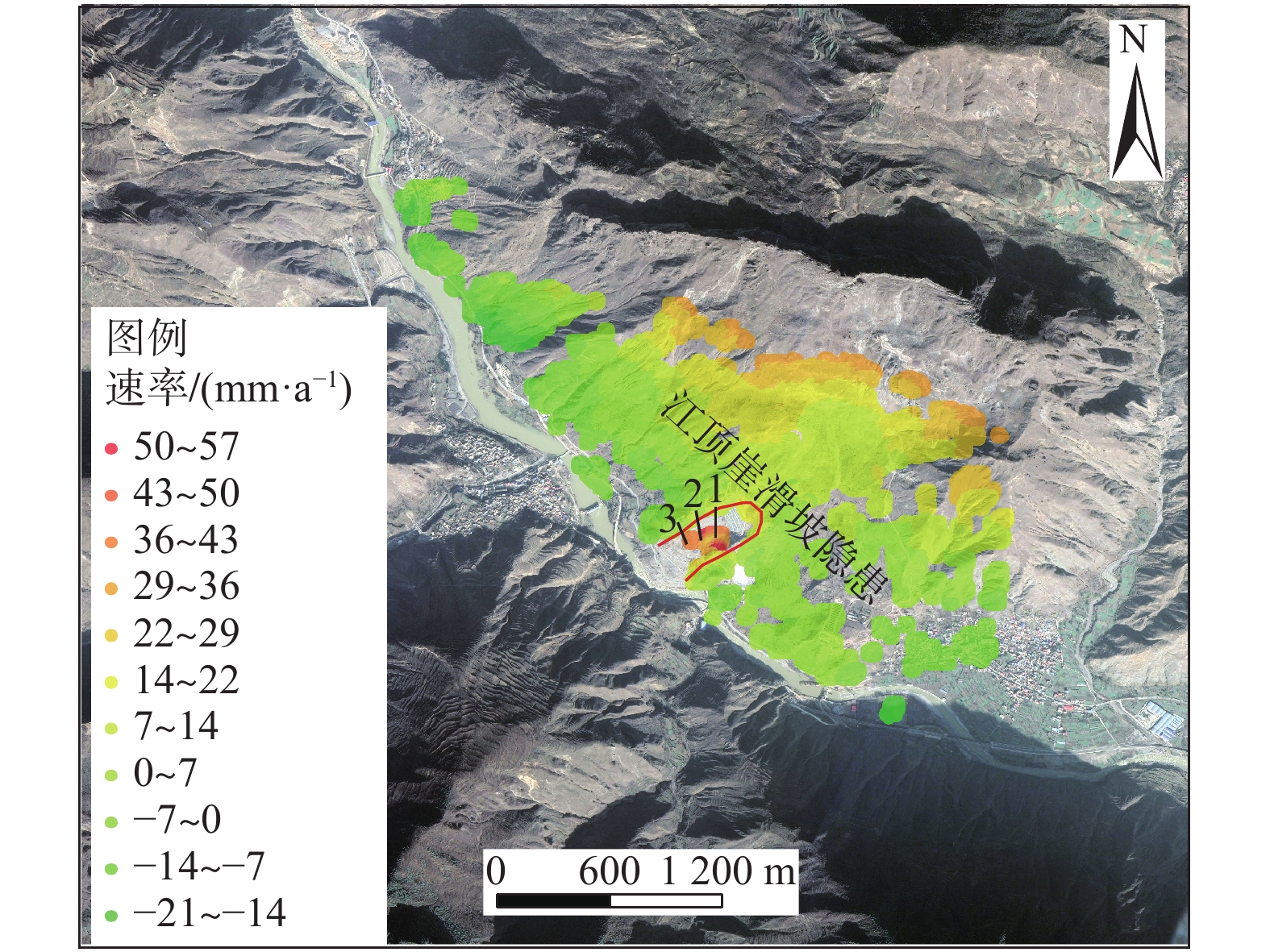
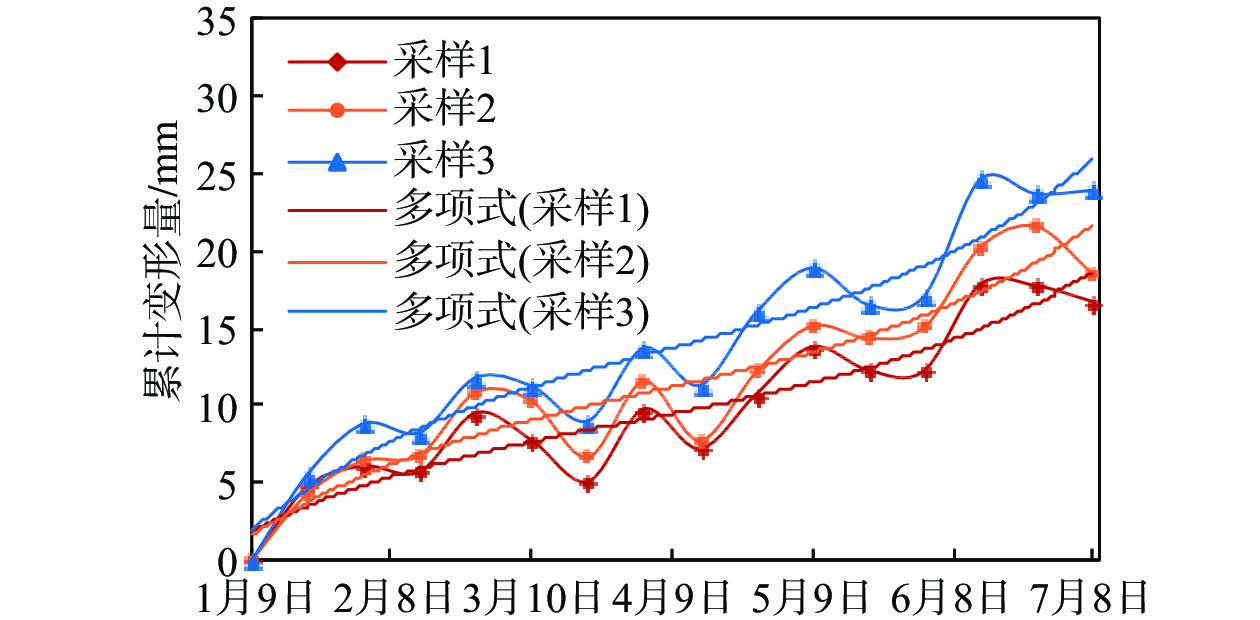
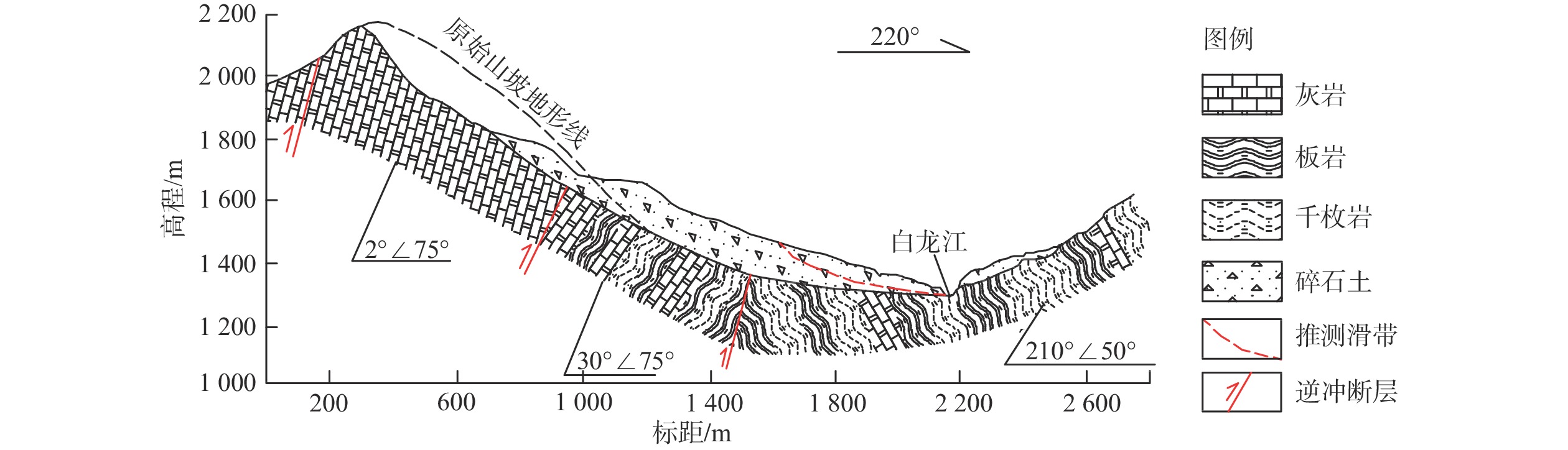
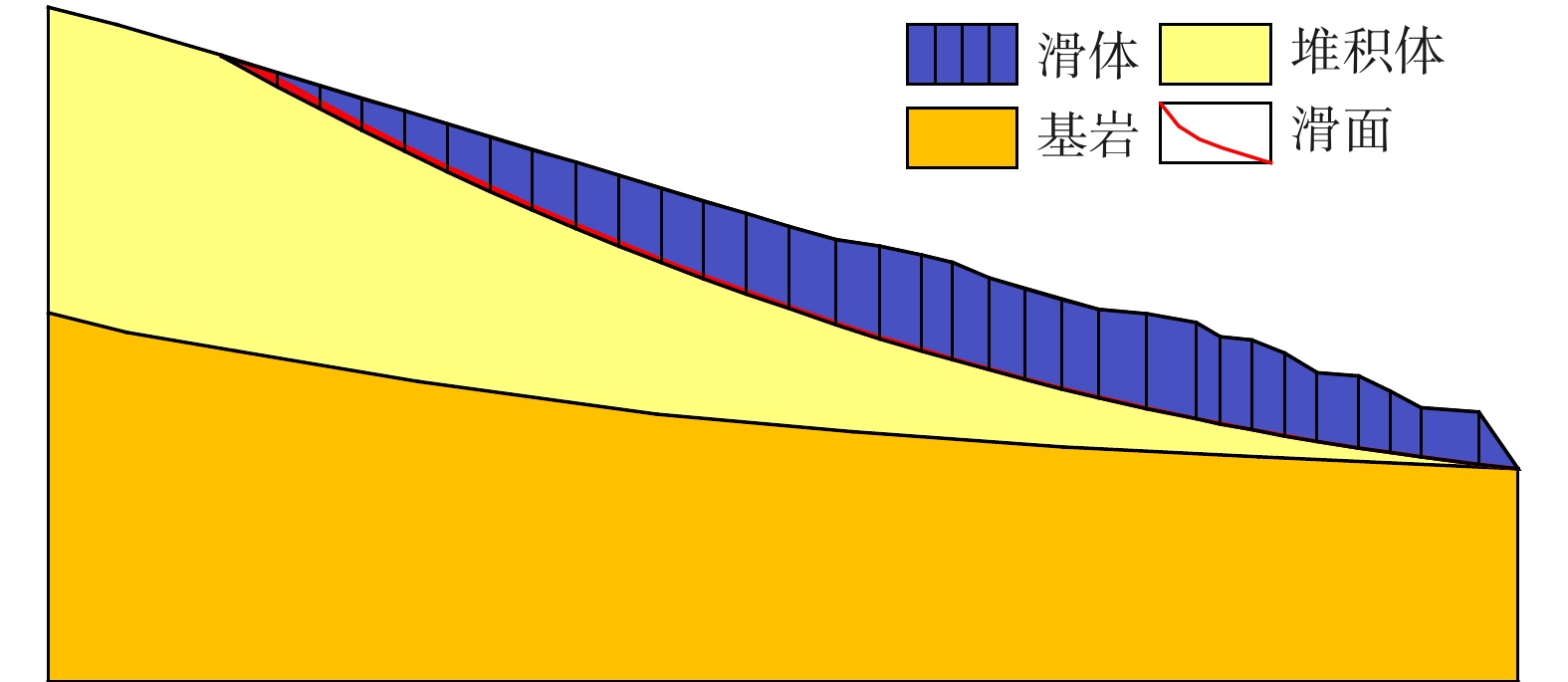
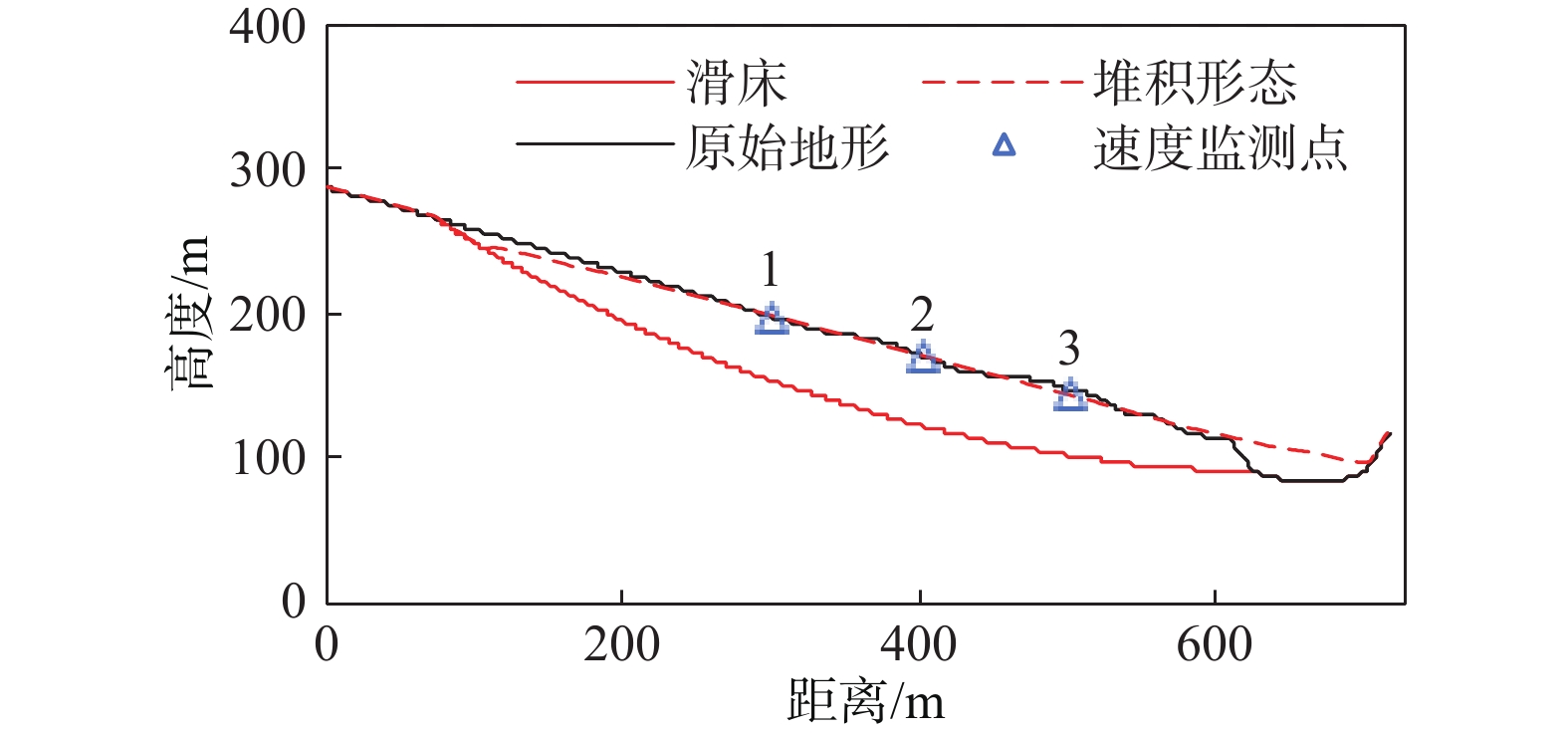
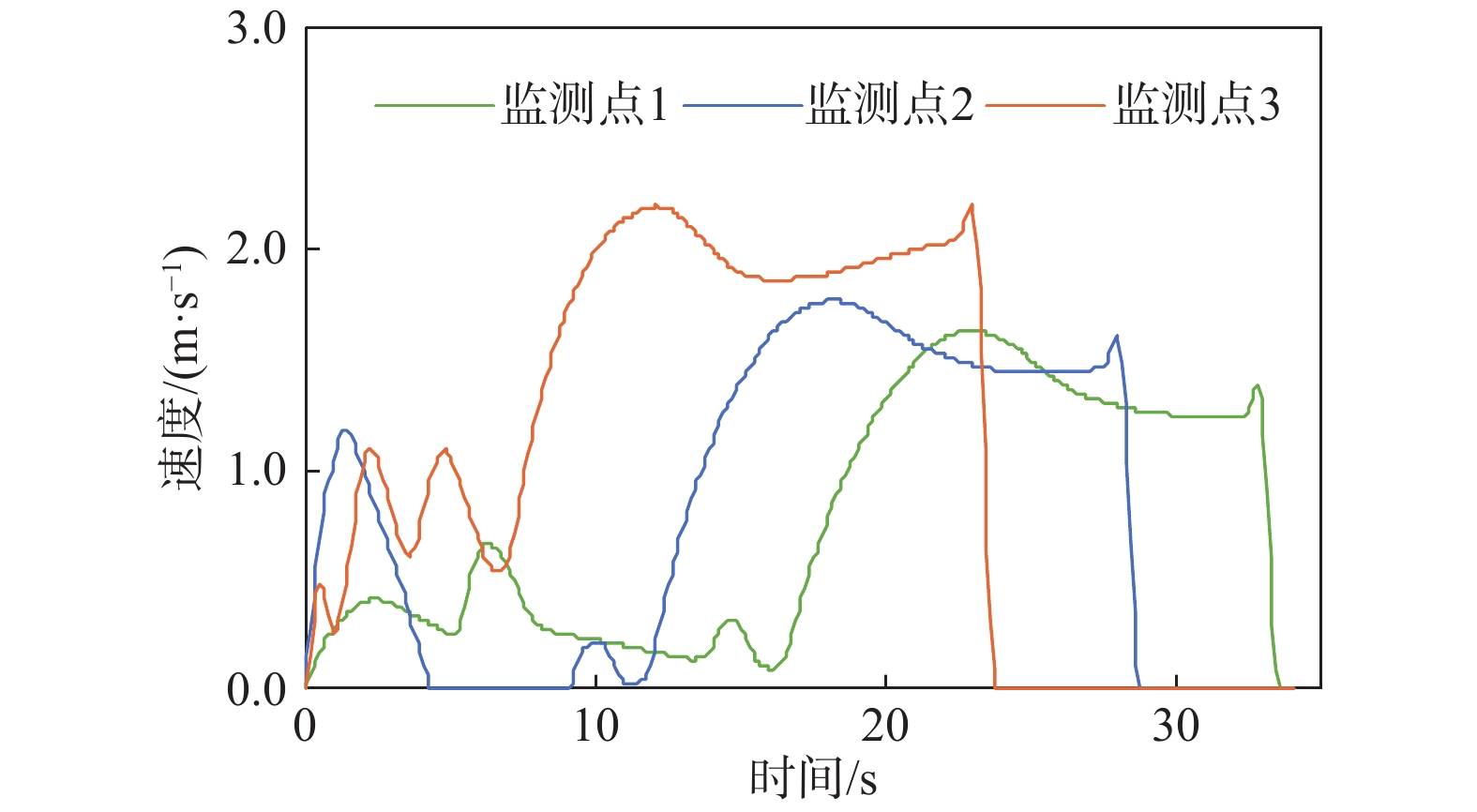
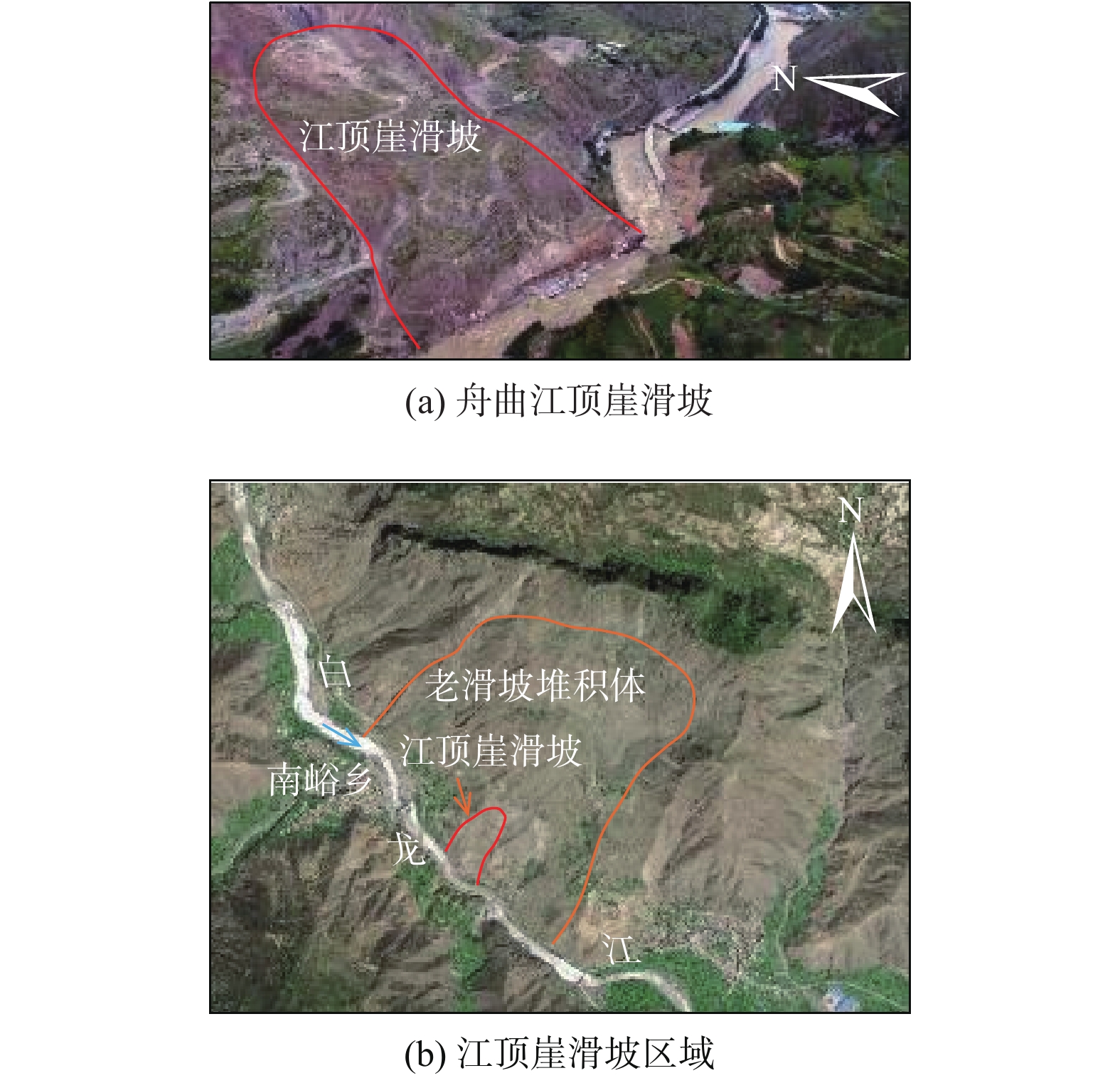
如何提前判识滑坡变形并对其进行早期风险评估已成为地质灾害防治领域的研究热点。文章以舟曲白龙江流域江顶崖堆积层滑坡为反分析案例,进行了滑坡变形早期判识及风险评估综合研究,提出了小基线集雷达干涉(SBAS-InSAR)技术解译分析、地质-力学联合分析、动力过程数值模拟分析三者相结合的滑坡变形早期判识与风险评估全流程分析模式。基于SBAS-InSAR技术解译能够准确地判识江顶崖滑坡的分布范围及早期形变特征,江顶崖滑坡的变形破坏模式为牵引式,滑坡体长度约680 m,宽度约210 m。基于早期识别信息,地质-力学联合分析表明:江顶崖滑坡为典型的老堆积层滑坡,前缘局部变形,破坏模式为牵引式,滑坡体平均厚度约35 m,滑床整体坡度较缓,失稳后运移速度不大。选取符合江顶崖滑坡体滑移摩擦特征的库伦摩擦模型,基于深度积分连续介质方程,分析计算滑坡体的动力学过程,结果表明:滑坡体滑移速度不大,最大值约为2.2 m/s,运动方式表现为推挤白龙江河道,堵江可能性较小,并且江顶崖滑坡体前缘错动完成后,该滑坡体滑移速度从前缘到后缘快速降为0,表现为牵引式运动特征。本次分析结果与实际相符,吻合度较高,采取的综合分析方法及研究模式可用于舟曲白龙江沿岸类似滑坡的早期判识及风险评估。
Abstract:How to identify deformed landslides in advance and conduct early risk assessments on them has become a research hotspot in the field of geological disaster prevention and control. In response to the above problems, the Jiangdingya landslide in the Bailong River Basin in Zhouqu is taken as a back analysis case, and a comprehensive study of the early identification and risk assessment of the landslide is carried out. In this paper, a full-process analysis method is proposed, which combine the small baseline subset interferometric synthetic aperture radar (SBAS-InSAR) technology interpretation, geo-mechanical analysis and dynamic process simulation. The research results show that the SABS-InSAR technology interpretation can effectively identify the range of the Jiangdingya landslide and its early deformation. It may be preliminarily determined that the failure mode of the Jiangdingya landslide is trailed and the plane characteristics of the landslide body is generally about 680 m in length and 210 m in width. Based on the early identification information and through geo-mechanical analysis, it is finally identified that the instability problem of the Jiangdingya landslide is a typical deformation problem of the front edge of the old accumulation layer landslide. The failure mode is the traction slip failure, the average thickness of the landslide body is in about 35 m, the overall slope of the sliding bed is relatively slow, and the moving speed is not large after instability. On the basis of the above analyses, a Coulomb friction model that conformed to the sliding friction characteristics of the Jiangdingya landslide body is selected. Based on the depth integral continuum equation, the dynamic process of the Jiangdingya landslide body is calculated and the speed of the landslide body is monitored. In terms of velocity monitoring curves and accumulation pattern, the sliding velocity of the landslide body is not large, the maximum value is about 2.2 m/s, the overall performance is pushing the Bailong River channel, and the possibility of blocking the river is relatively small. In addition, when the displacement of the front edge of the Jiangdingya landslide body is completed, the speed of the landslide body from the front edge to the rear edge quickly drope to zero, and the movement process is characterized by the traction movement. The analysis results of the Jiangdingya landslide in this paper are consistent with the actual event of the Jiangdingya landslide. The comprehensive analysis method and research model can provide a good reference for the early identification and risk assessment of similar landslides in the Bailong River Basin in Zhouqu county.
-

-
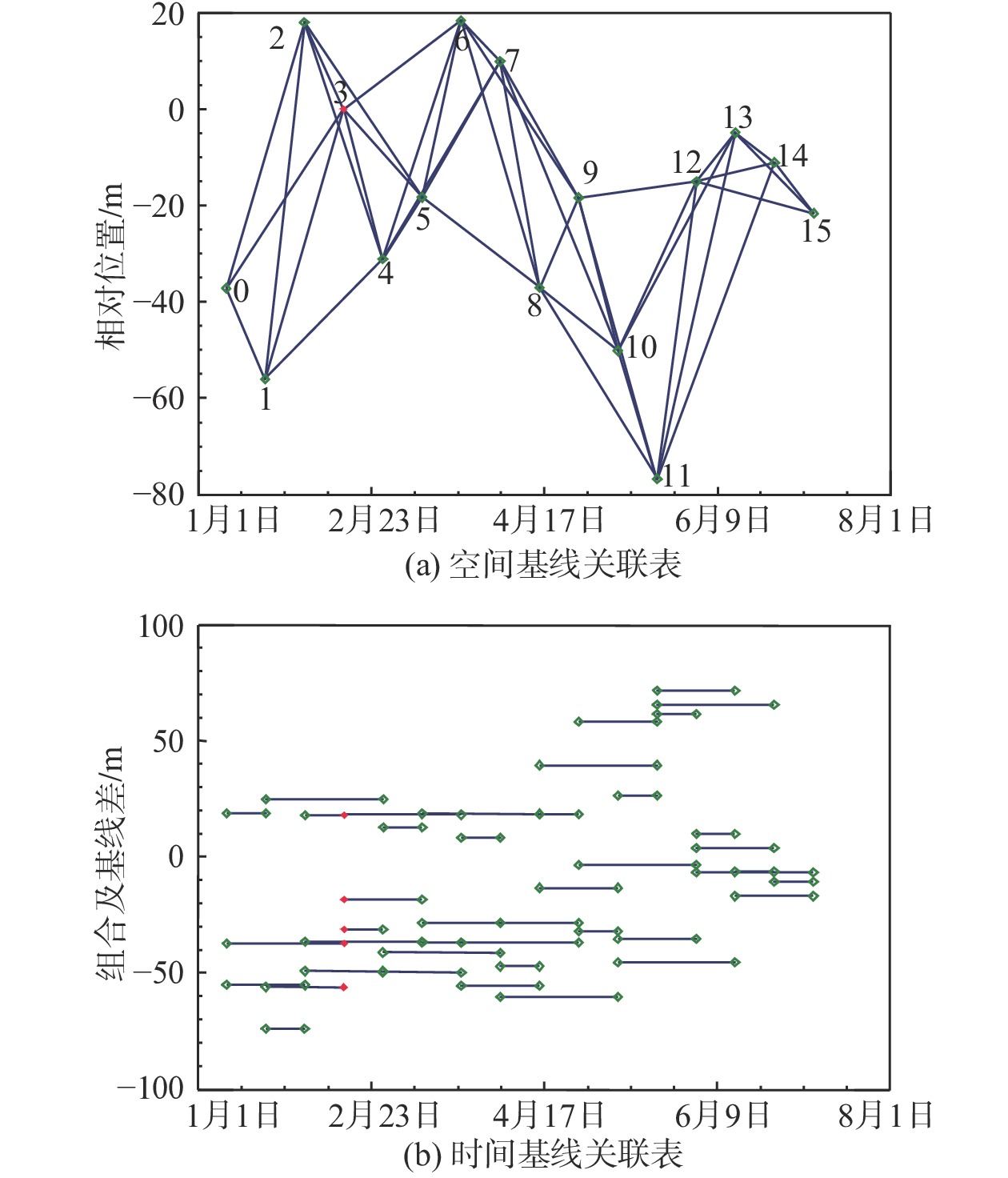
表 1 哨兵-1影像数据和ALOS PALSAR地形数据信息
Table 1. Information of Sentinel-1A images and ALOS PALSAR topography data
数据 参数 属性 哨兵-1A 类型 SLC 图像模式 IW 波段及波长/cm C, 5.5 入射角/(°) 43.3 轨道 升轨 方位向分辨率/m 20 距离向分辨率/m 5 极化方式 同向垂直极化(VV) ALOS PALSAR 观测模式 单极化(FBS) 地形数据分辨率/m 12.5 表 2 滑坡体物质物理力学性质
Table 2. Physical and mechanical properties of the landslide body
土体 密度/(kg·m−3) 摩擦角/(°) 黏聚力/kPa 状态 滑坡体 2100 16 10 饱和 -
[1] COSTANTINI M, FERRETTI A, MINATI F, et al. Analysis of surface deformations over the whole Italian territory by interferometric processing of ERS, Envisat and COSMO-SkyMed radar data[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2017,202:250 − 275. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2017.07.017
[2] DONG J, ZHANG L, LI M H, et al. Measuring precursory movements of the recent Xinmo landslide in Mao County, China with Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 PALSAR-2 datasets[J]. Landslides,2018,15(1):135 − 144. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0914-8
[3] 陆会燕, 李为乐, 许强, 等. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(9):1342 − 1354. [LU Huiyan, LI Weile, XU Qiang, et al. Early detection of landslides in the upstream and downstream areas of the Baige landslide, the Jinsha river based on optical remote sensing and InSAR technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(9):1342 − 1354. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957 − 966. [XU Qiang, DONG Xiujun, LI Weile. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957 − 966. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 李世海, 刘天苹, 刘晓宇. 论滑坡稳定性分析方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(增刊2):3309 − 3324. [LI Shihai, LIU Tianping, LIU Xiaoyu. Analysis method for landslide stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(Sup2):3309 − 3324. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 饶鸿, 王金淑, 赵志明, 等. 基于有限元软件自定义本构模型的膨胀土边坡降雨入渗分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):154 − 162. [RAO Hong, WANG Jinshu, ZHAO Zhiming, et al. An analysis of rainfall infiltration of expansive soil slope based on the finite element software custom constitutive model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):154 − 162. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 殷跃平, 王文沛. 高位远程滑坡动力侵蚀犁切计算模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(8):1513 − 1521. [YIN Yueping, WANG Wenpei. A dynamic erosion plowing model of long Run-out landslides initialized at high locations[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(8):1513 − 1521. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] HAN X D, CHEN J P, XU P H, et al. A well-balanced numerical scheme for debris flow Run-out prediction in Xiaojia Gully considering different hydrological designs[J]. Landslides,2017,14(6):2105 − 2114. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0850-7
[9] 刘广煜, 徐文杰, 佟彬, 等. 基于块体离散元的高速远程滑坡灾害动力学研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2019,38(8):1557 − 1566. [LIU Guangyu, XU Wenjie, TONG Bin, et al. Study on dynamics of high-speed and long Run-out landslide hazards based on block discrete element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2019,38(8):1557 − 1566. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 张卫雄, 翟向华, 丁保艳, 等. 甘肃舟曲江顶崖滑坡成因分析与综合治理措施[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(5):7 − 14. [ZHANG Weixiong, ZHAI Xianghua, DING Baoyan, et al. Causative analysis and comprehensive treatment of the jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(5):7 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] BERARDINO P, FORNARO G, LANARI R, et al. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2002,40(11):2375 − 2383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2002.803792
[12] 许才军, 何平, 温扬茂, 等. InSAR技术及应用研究进展[J]. 测绘地理信息,2015,40(2):1 − 9. [XU Caijun, HE Ping, WEN Yangmao, et al. Recent advances InSAR interferometry and its applications[J]. Journal of Geomatics,2015,40(2):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] CHEN D H, CHEN H E, ZHANG W, et al. Characteristics of the residual surface deformation of multiple abandoned mined-out areas based on a field investigation and SBAS-InSAR: a case study in Jilin, China[J]. Remote Sensing,2020,12(22):3752. doi: 10.3390/rs12223752
[14] 亓星, 朱星, 许强, 等. 基于斋藤模型的滑坡临滑时间预报方法改进及应用[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(4):832 − 839. [QI Xing, ZHU Xing, XU Qiang, et al. Improvement and application of landslide proximity time prediction method based on saito model[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(4):832 − 839. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 钟昌茂, 邱恩喜, 魏永幸, 等. 基于桩体抗剪强度的复合地基路堤稳定性分析方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(5):100 − 107. [ZHONG Changmao, QIU Enxi, WEI Yongxing, et al. Stability analysis method for the composite foundation embankment based on pile shear strength[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(5):100 − 107. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 王开喜, 张鹏. 舟曲白龙江城区段防洪堤设计水力学计算[J]. 甘肃水利水电技术,2010,46(12):41 − 43. [WANG Kaixi, ZHANG Peng. Hydraulic calculation of flood protection embankment design in city section of Bailong river in Zhouqu[J]. Gansu Water Conservancy and Hydropower Technology,2010,46(12):41 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] AN H, KIM M, LEE G, et al. Estimation of the area of sediment deposition by debris flow using a physical-based modeling approach[J]. Quaternary International,2019,503:59 − 69. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2018.09.049
[18] HUNGR O. Simplified models of spreading flow of dry granular material[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2008,45(8):1156 − 1168. doi: 10.1139/T08-059
-



 下载:
下载: