Effects of the pile buried pipe parameters on the thermal-mechanical coupling characteristics of energy pile under the groundwater seepage
-
摘要:
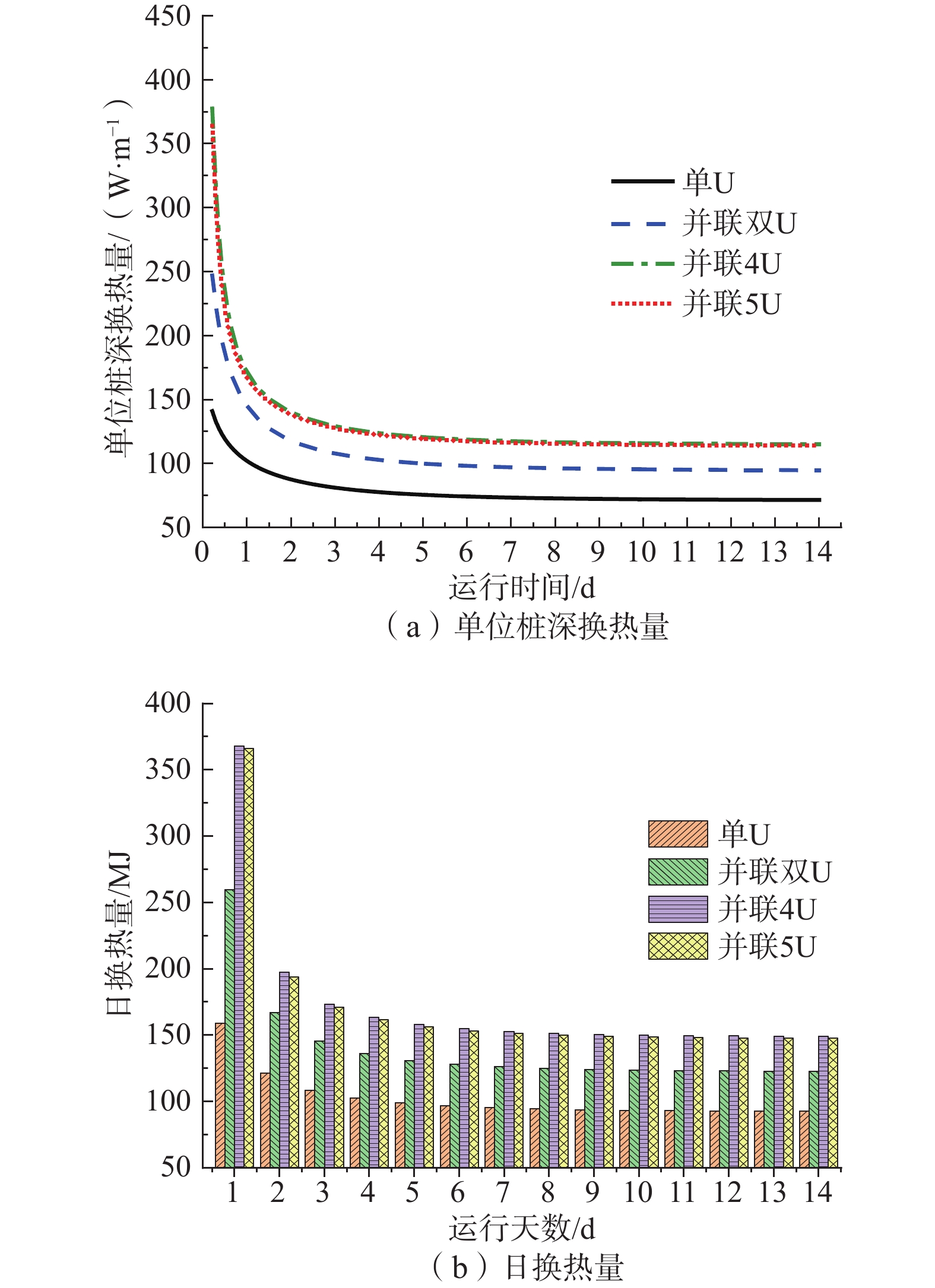
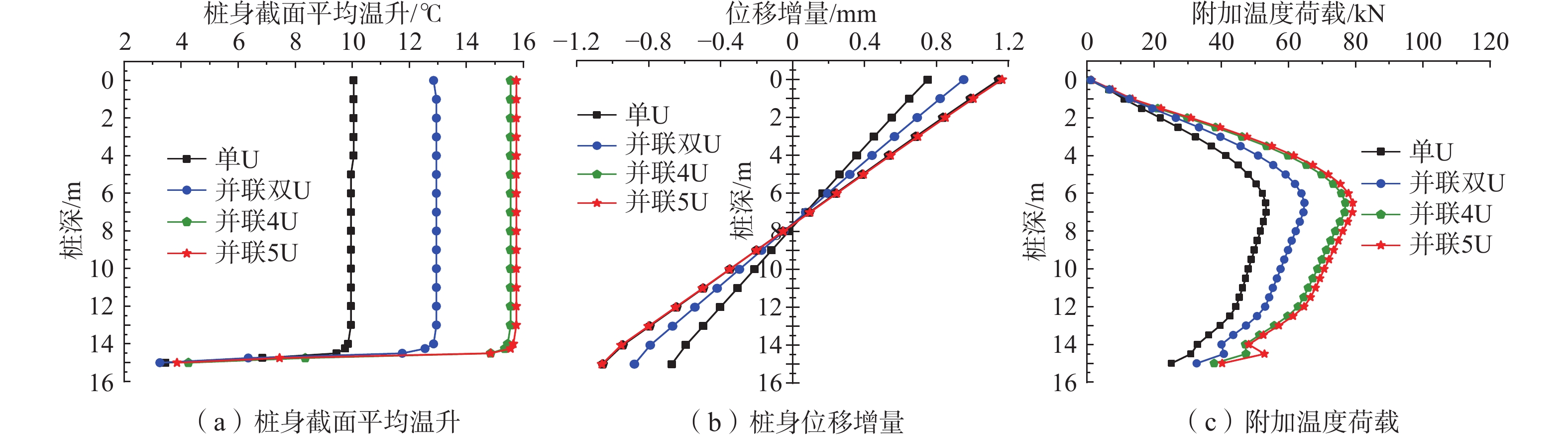
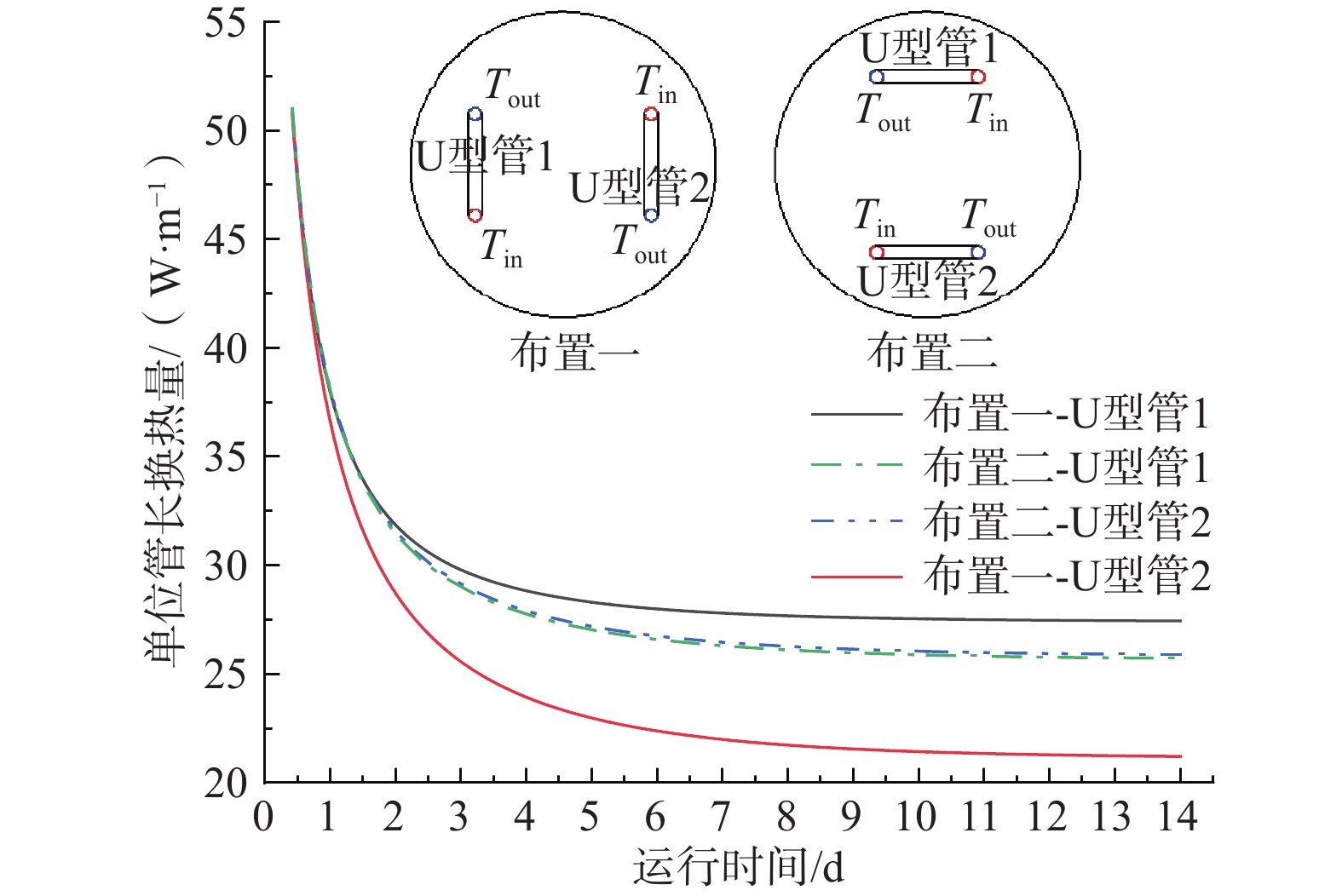
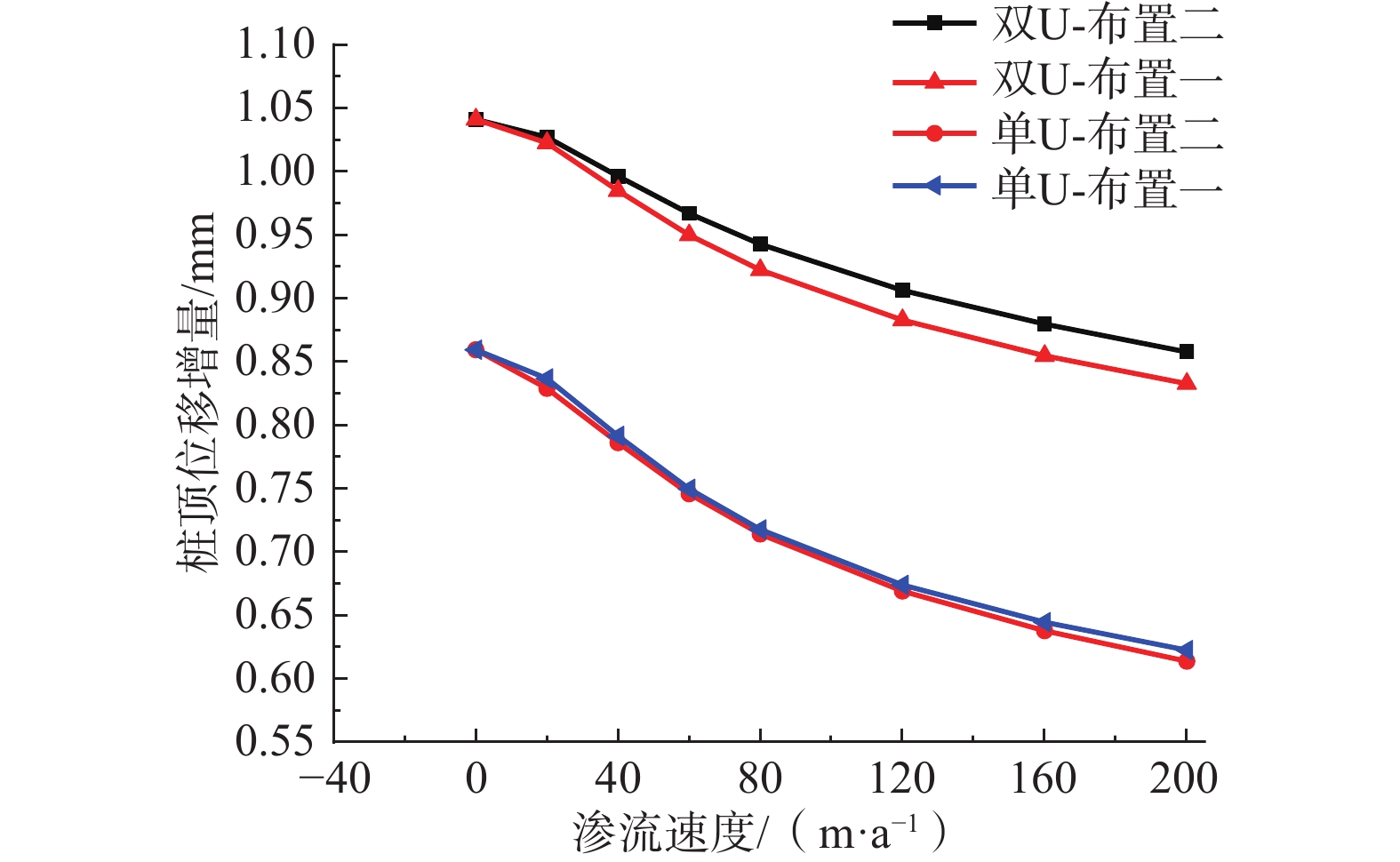
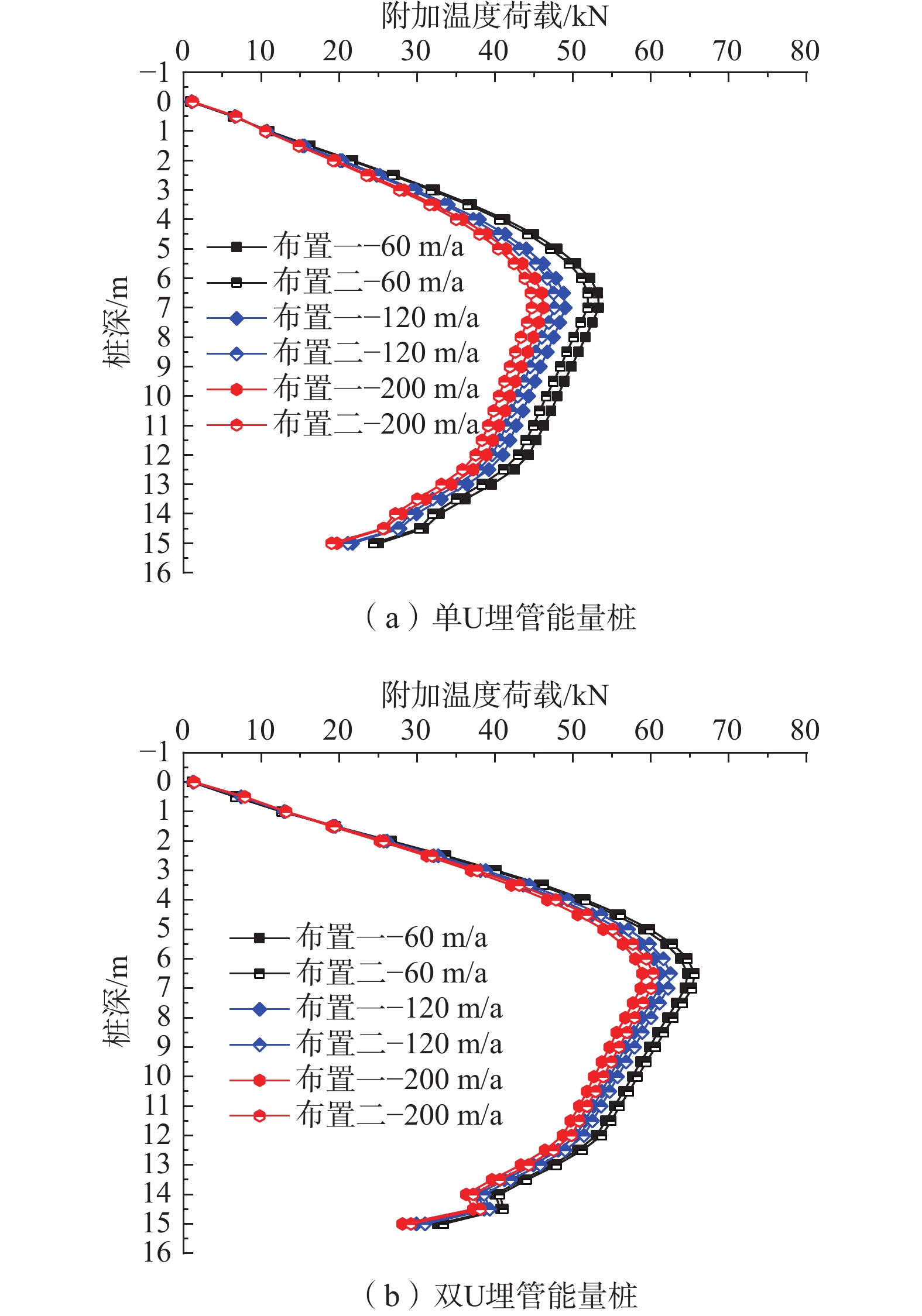
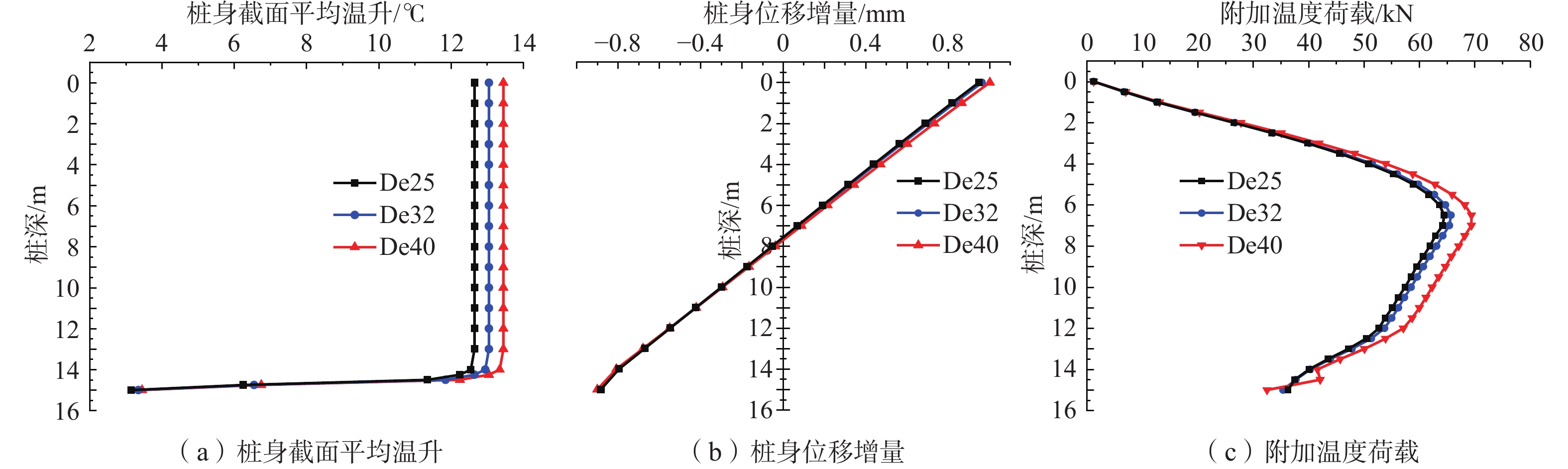
为获得地下水渗流作用下桩埋管参数对能量桩热-力耦合特性的影响,建立了不同埋管参数的能量桩数值模型,分析了桩埋管数量、埋管布置形式、埋管管径对单位桩深换热量、日换热量、桩截面平均温升、桩身位移增量及桩身附加温度荷载的影响。结果表明:增加埋管数量可以增大能量桩换热量,但也会加剧桩内不同埋管间的热干扰,导致换热性能下降及桩身位移和附加温度荷载的增加;渗流下桩埋管的布置形式对其换热性能有显著影响,而对桩的力学特性影响较小,且渗流速度越大,2种布置形式对应的能量桩换热量差异逐渐增加,桩顶位移增量与桩身附加温度荷载逐渐减少;增加埋管管径可以提高能量桩的换热量,但也会加大桩身和桩周土壤温升,导致桩身位移和附加温度荷载增大。研究结论对于渗流作用下能量桩的优化设计与高效运行具有一定的指导意义。
Abstract:In order to examine the influences of buried pipe parameters on the thermal-mechanical coupling characteristics of energy piles under the groundwater seepage, the numerical models of energy piles with different buried pipe parameters are established. The influences of the buried pipe number, layout of buried pipe, and diameter of buried pipe on the heat exchange rate per pile depth, daily heat exchange amount, pile body average temperature rises, displacement increment, and additional temperature load are investigated. The results show that the increasing number of buried pipes can improve the heat transfer of energy pile, but also increase the thermal interference between different buried pipes in the pile, resulting in the decrease of heat transfer performance and the increase of pile displacement and additional temperature load. Under the groundwater seepage, the layout of buried pipes has a significant effect on the heat transfer performance, but has little effect on the mechanical properties of the pile. Moreover, with the increasing seepage velocity, the difference of heat transfer rates of the energy piles corresponding to two layouts increases gradually, and the pile top displacement increment and the pile additional temperature load decrease gradually. The increasing diameter of buried pipe can improve the heat transfer of energy pile, but it will also increase the temperature rise of the pile and the soil around the pile, leading to the increase of pile displacement and additional temperature load. The research results can provide guidance for the optimal design and efficient operation of energy pile under seepage action.
-

-
表 1 模拟计算条件
Table 1. Calculated conditions for simulation
参数 数值 U型管内/外径/mm 25/32 U型管导热系数/(W·m−1·K−1) 0.48 U型管密度/(kg·m−3) 1200 U型管比热容/(J·kg−1·K−1) 2300 混凝土密度/(kg·m−3) 2500 混凝土导热系数/(W·m−1·K−1) 2.3 混凝土比热容/(J·kg−1·K−1) 960 土壤固体成分密度/(kg·m−3) 1800 土壤固体成分比热容/(J·kg−1·K−1) 1600 土壤固体成分导热系数/(W·m−1·K−1) 1.7 土壤孔隙率 0.4 循环流体密度/(kg·m−3) 1000 循环流体导热系数/(W·m−1·K−1) 0.67 循环流体比热容/(J·kg−1·K−1) 4216 土壤压缩模量/MPa 35 土壤泊松比 0.3 土壤黏聚力/kPa 20 土壤内摩擦角/(°) 30 混凝土压缩模量/MPa 30000 混凝土泊松比 0.2 表 2 不同桩埋管布置形式下能量桩的力学特性
Table 2. Mechanical properties of energy pile for different buried pipe layouts
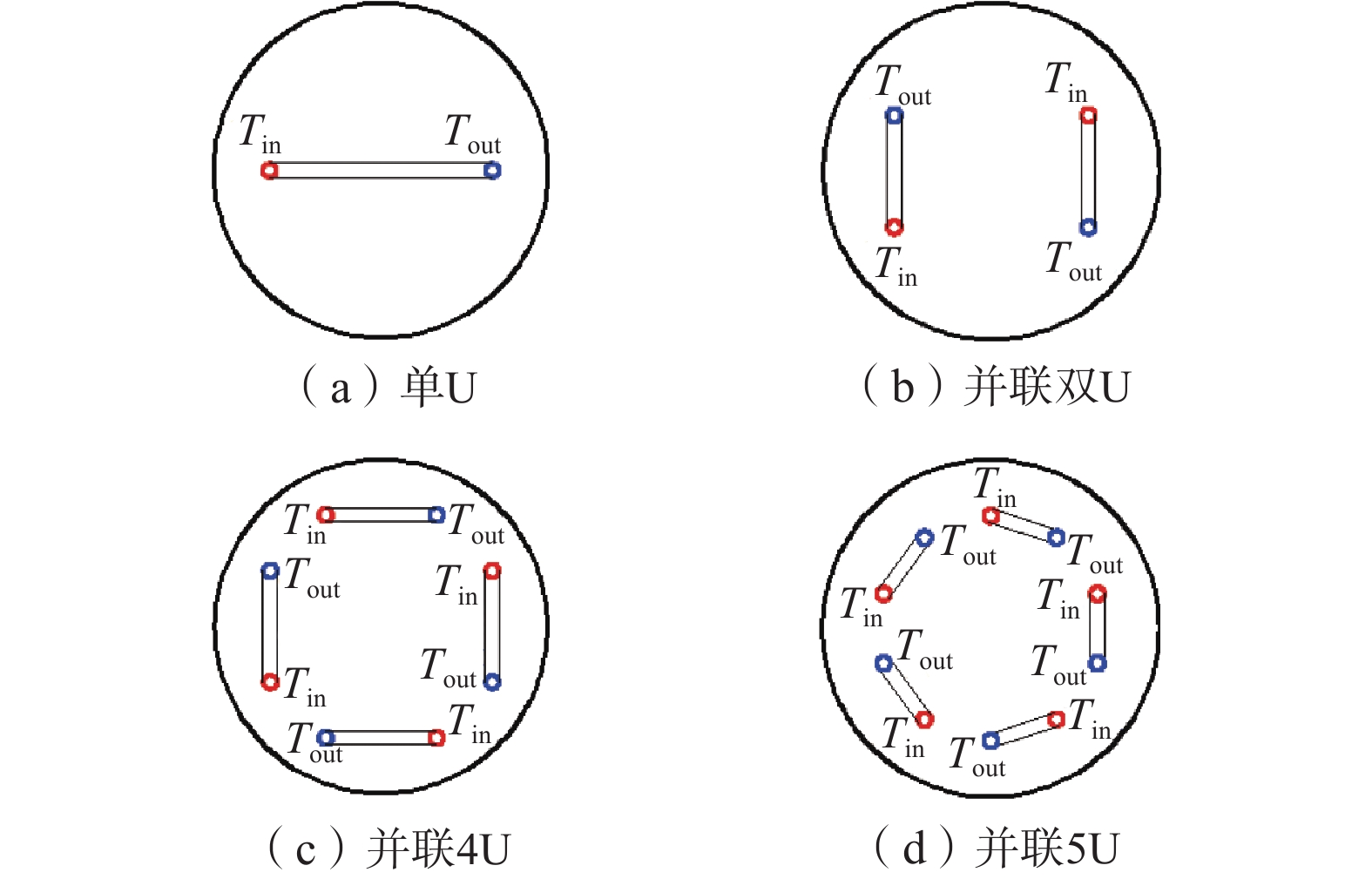
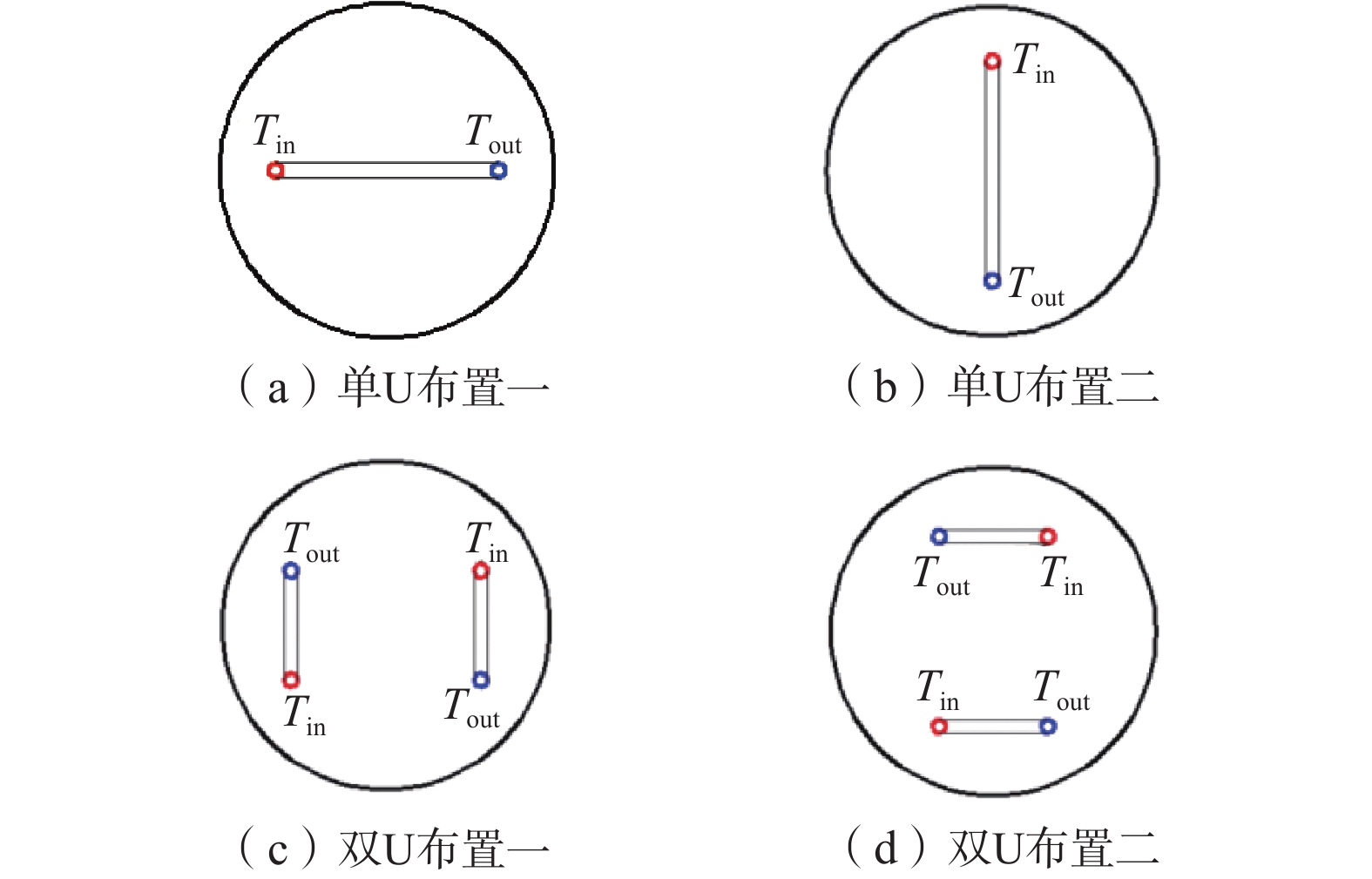
桩埋管形式 布置形式 桩顶位移增量/mm 最大附加温度荷载/kN 单U 布置一 0.75 53.3 布置二 0.74 51.9 双U 布置一 0.95 64.7 布置二 0.97 65.6 -
[1] 金光, 张之强, 吴暄, 等. 严寒地区地源热泵地埋管周围土壤冻结影响因素的实验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(6):164 − 168. [JIN Guang, ZHANG Zhiqiang, WU Xuan, et al. Experimental study on influencing factors of soil freezing around ground source heat pump buried pipe in cold region[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(6):164 − 168. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] WANG Z J, ZHANG R H, FANG P F, et al. Analysis of an energy pile enduring cyclic temperature loads[J]. Geotechnical Research,2019,6(3):227 − 233. doi: 10.1680/jgere.18.00043
[3] 杨涛, 刘律智, 花永盛. 冷-热循环下能量桩热-力学特性的数值模拟[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2019,39(4):585 − 591. [YANG Tao, LIU Lvzhi, HUA Yongsheng. Numerical simulation of thermo-mechanical behaviour of energy pile subjected to cooling-heating cycle[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2019,39(4):585 − 591. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 吴冠中, 张丹, 程健, 等. 不同埋管形式的预制能量管桩热响应试验研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2019,39(4):615 − 621. [WU Guanzhong, ZHANG Dan, CHENG Jian, et al. Thermal response tests on PHC energy piles with different configuration of heat exchange loop[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2019,39(4):615 − 621. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 常虹, 李洋, 李宗效. 不同埋管形式对混凝土能量桩受力特性的数值模拟研究[J]. 吉林建筑大学学报,2021,38(1):27 − 33. [CHANG Hong, LI Yang, LI Zongxiao. Numerical simulation study on mechanical characteristics of concrete energy pile under different buried pipe forms[J]. Journal of Jilin Jianzhu University,2021,38(1):27 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0185.2021.01.005
[6] 赵蕾, 高林, 张爽, 等. 不同埋管形式能量桩换热性能与承载性能的对比研究[J]. 安全与环境学报,2020,20(1):81 − 90. [ZHAO Lei, GAO Lin, ZHANG Shuang, et al. Exploration of the thermo-mechanical features of energy piles in regard to the different types of buried pipes[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment,2020,20(1):81 − 90. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王成龙, 刘汉龙, 孔纲强, 等. 不同埋管形式下能量桩热力学特性模型试验研究[J]. 工程力学,2017,34(1):85 − 91. [WANG Chenglong, LIU Hanlong, KONG Gangqiang, et al. Model tests on thermal mechanical behaviour of energy piles influenced with heat exchangers types[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2017,34(1):85 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2015.05.0455
[8] PARK S, LEE S, LEE D, et al. Effect of thermal interference on energy piles considering various configurations of heat exchangers[J]. Energy and Buildings,2019,199:381 − 401. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2019.07.008
[9] PARK S, LEE S, OH K, et al. Engineering chart for thermal performance of cast-in-place energy pile considering thermal resistance[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2018,130:899 − 921. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.065
[10] GO G H, LEE S R, YOON S, KANG H. Design of spiral coil PHC energy pile considering effective borehole thermal resistance and groundwater advection effects[J]. Applied Energy,2014,125:165 − 178. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.059
[11] YOU S, CHENG X H, YU C L, et al. Effects of groundwater flow on the heat transfer performance of energy piles:Experimental and numerical analysis[J]. Energy and Buildings,2017,155:249 − 259. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.09.023
[12] WANG D Q, LU L, ZHANG W K, et al. Numerical and analytical analysis of groundwater influence on the pile geothermal heat exchanger with cast-in spiral coils[J]. Applied Energy,2015,160:705 − 714. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.04.037
[13] ZHANG W K, YANG H X, FANG L, et al. Study on heat transfer of pile foundation ground heat exchanger with three-dimensional groundwater seepage[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2017,105:58 − 66. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.09.066
[14] GO G H, LEE S R, KANG H B, et al. A novel hybrid design algorithm for spiral coil energy piles that considers groundwater advection[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2015,78:196 − 208. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.12.060
[15] YOU T, YANG H X. Influences of different factors on the three-dimensional heat transfer of spiral-coil energy pile group with seepage[J]. International Journal of Low-Carbon Technologies,2020,15:458 − 470. doi: 10.1093/ijlct/ctaa006
[16] CHEN F, MAO J F, CHEN S Y, et al. Efficiency analysis of utilizing phase change materials as grout for a vertical U-tube heat exchanger coupled ground source heat pump system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2018,130:698 − 709. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.11.062
[17] ANSYS Fluent Inc. ANSYS fluent user's guide[M]. Canonsburg, PA: [s.n.], 2013.
[18] 杨卫波, 杨彬彬, 汪峰. 相变混凝土能量桩热-力学特性的数值模拟与试验验证[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(2):268 − 277. [YANG Weibo, YANG Binbin, WANG Feng. Numerical simulation and experimental validation of the thermo-mechanical characteristics of phase change concrete energy pile[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2021,37(2):268 − 277. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 张来军. 渗流场下能量桩换热及热-力耦合特性的理论和实验研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2021.
ZHANG Laijun. Theoretical and experimental study on heat transfer and thermo-mechanical coupling characteristics of energy piles under seepage field[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-




 下载:
下载: