Discussion on ecological water level threshold of groundwater in Baoding Plain area
-
摘要:
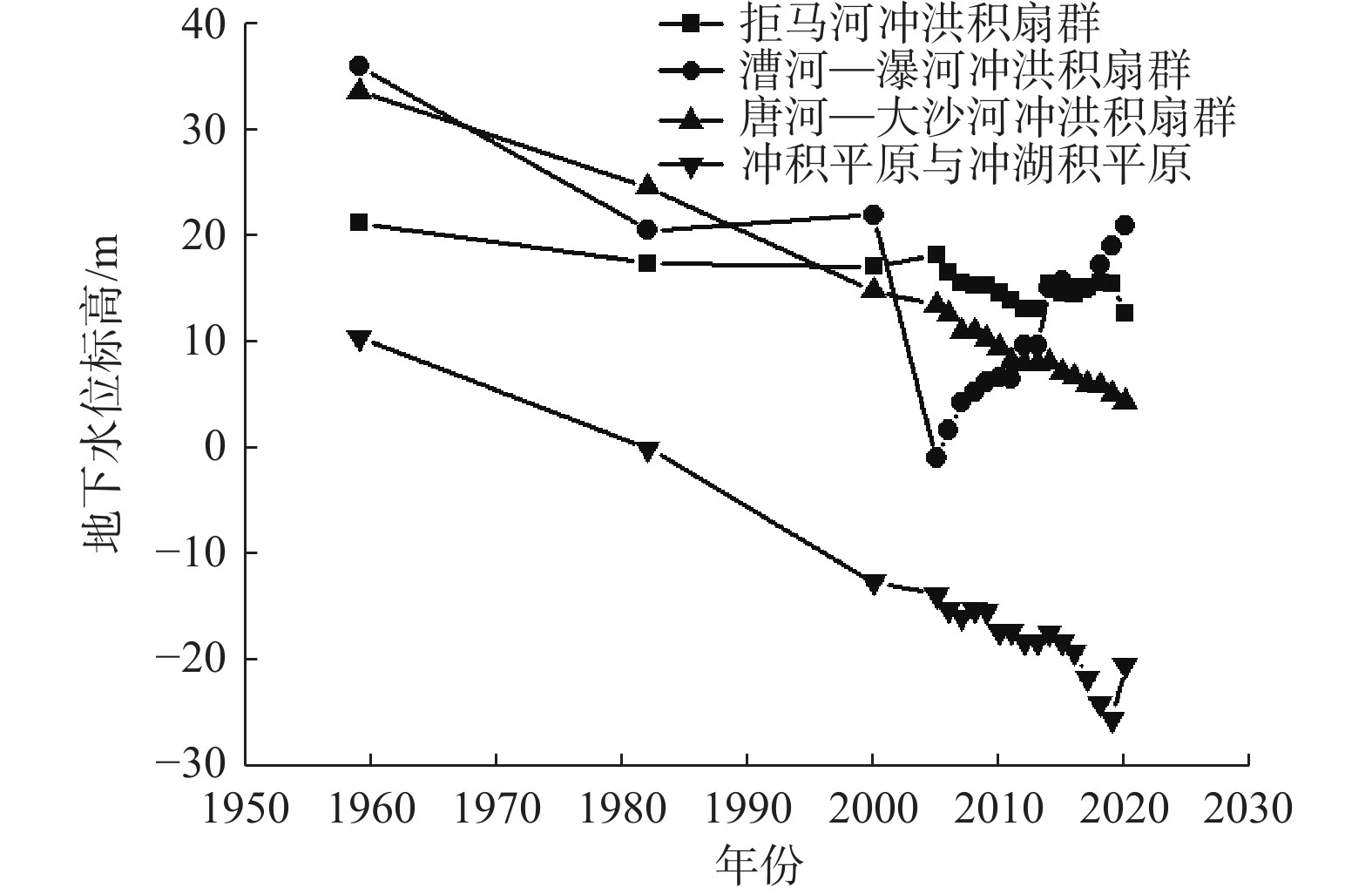
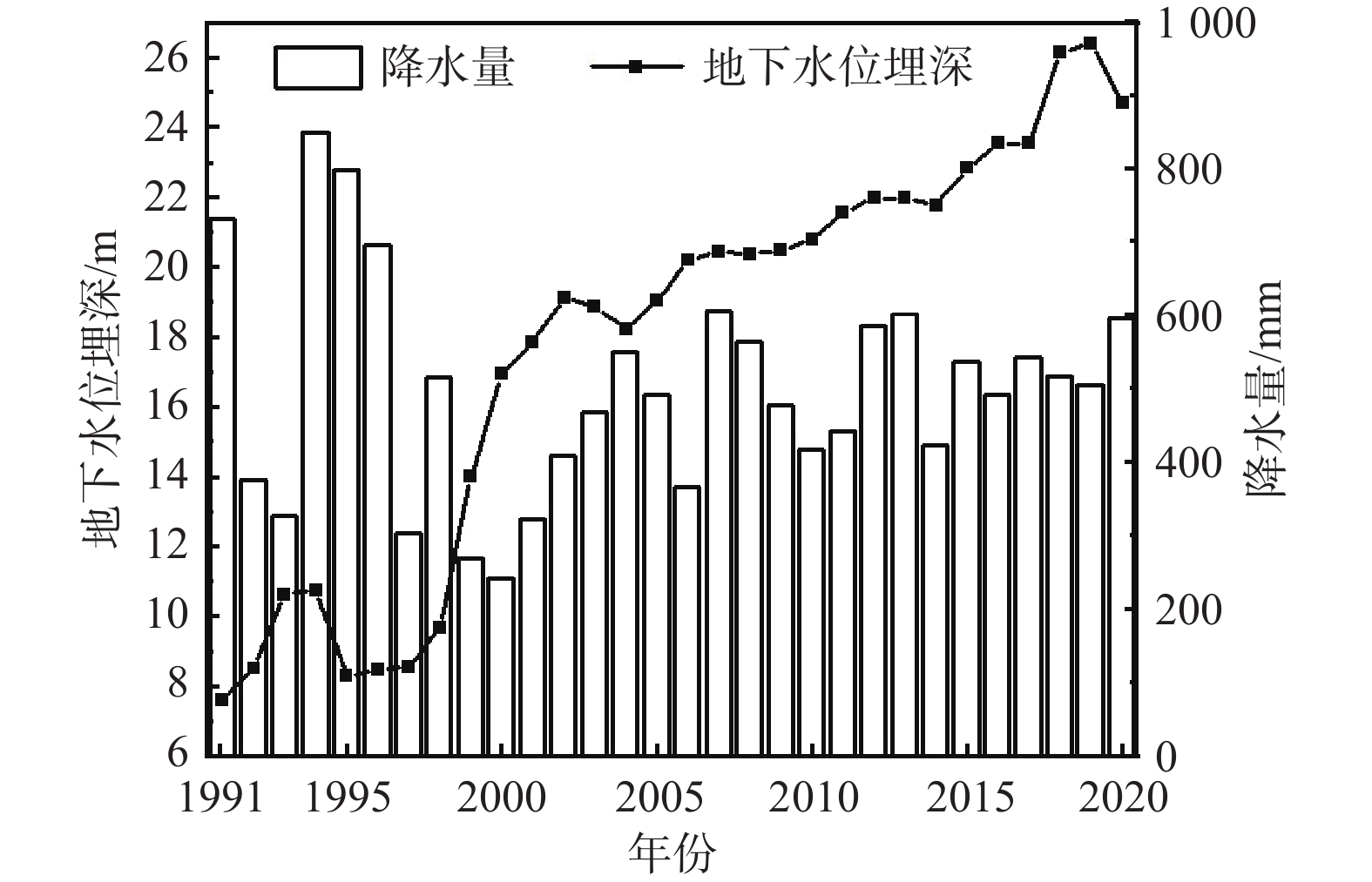
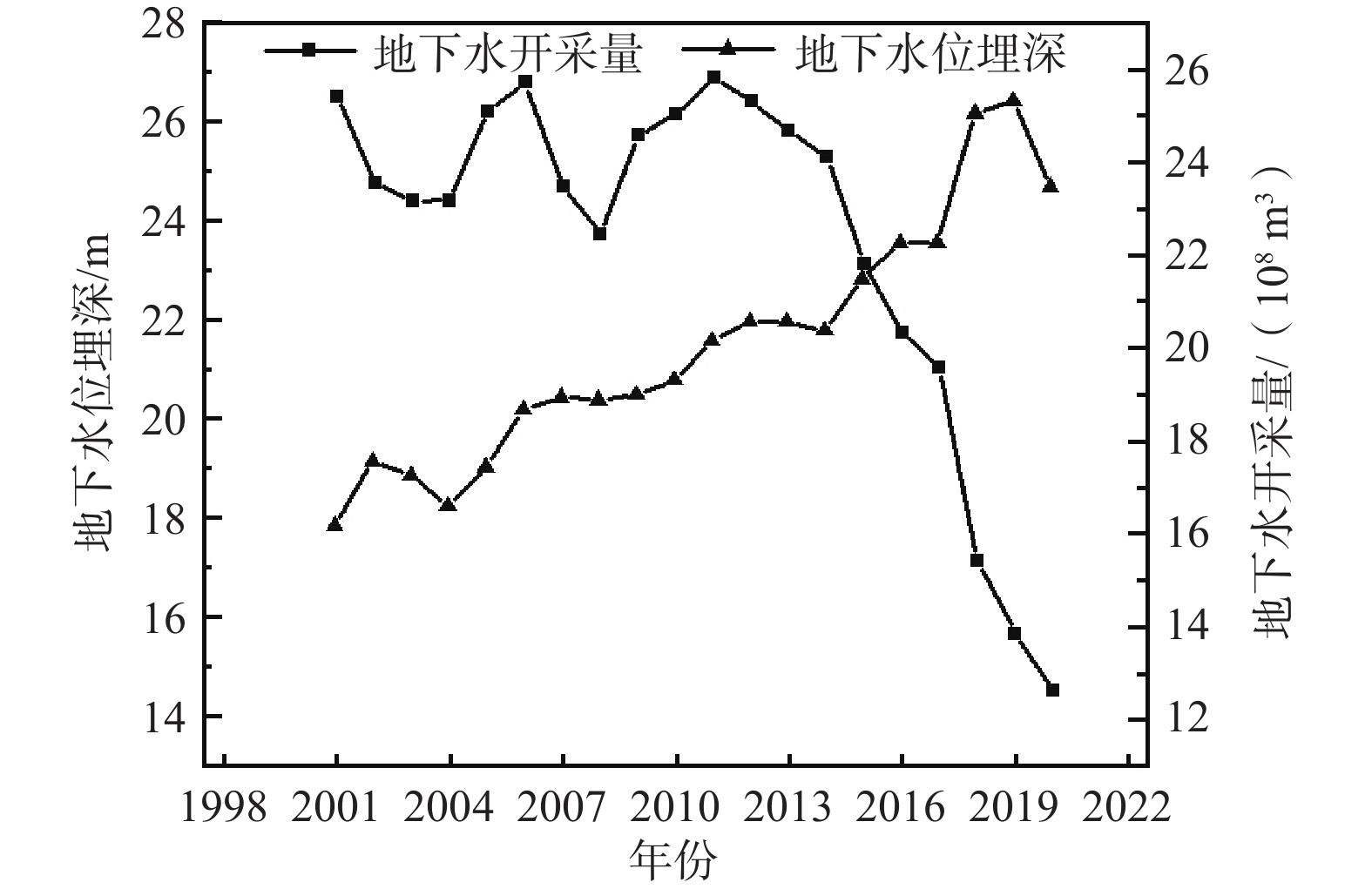
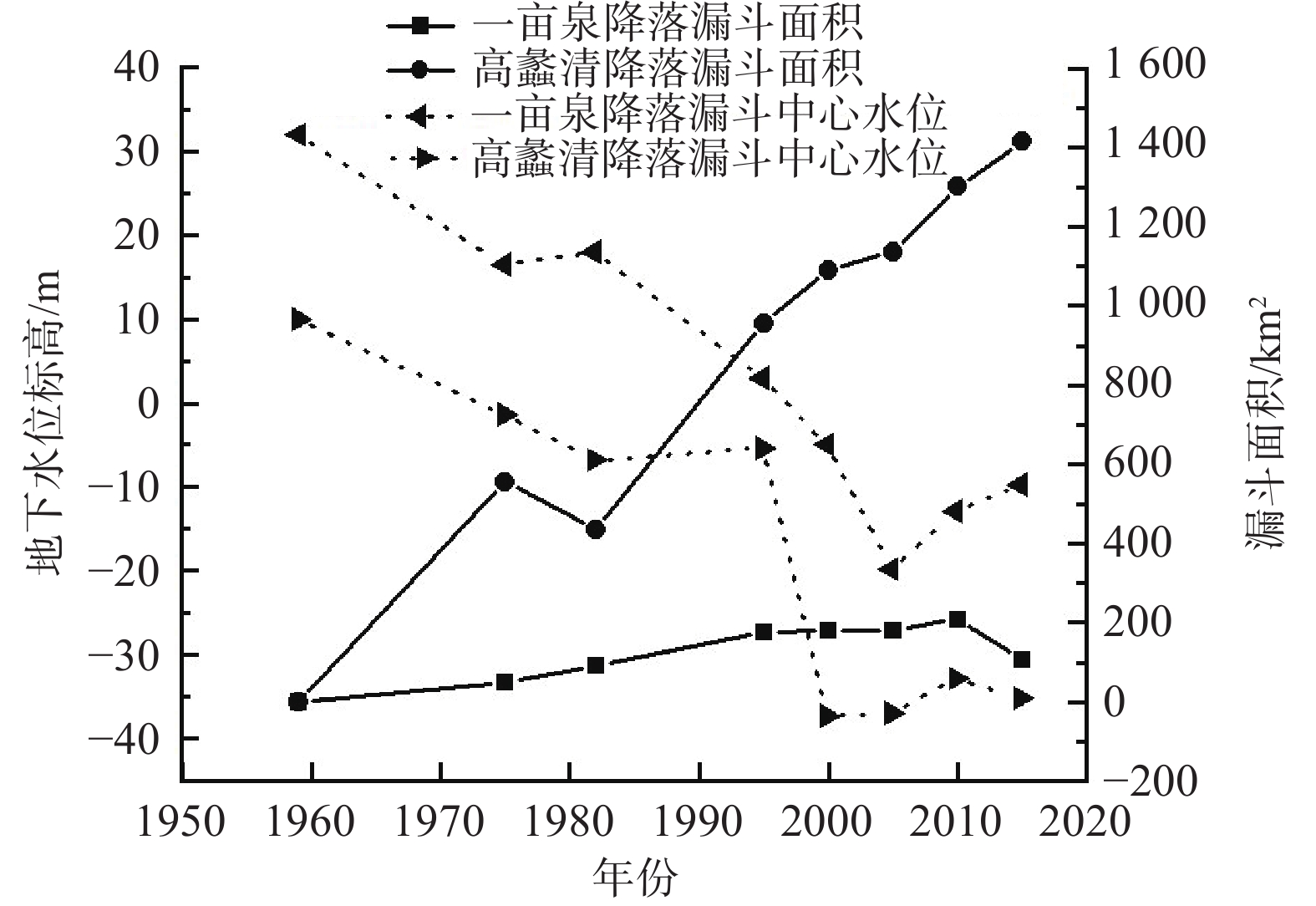
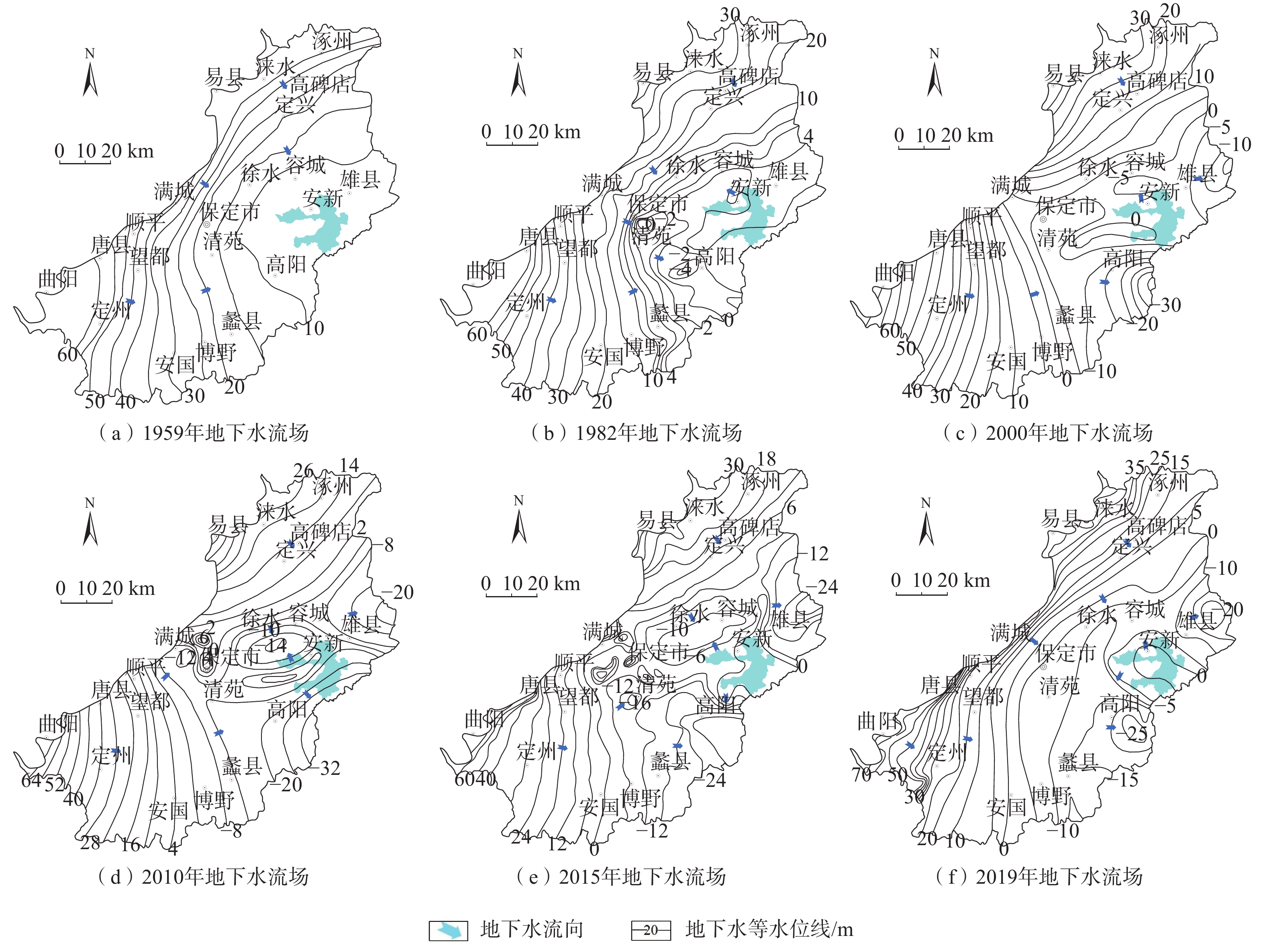
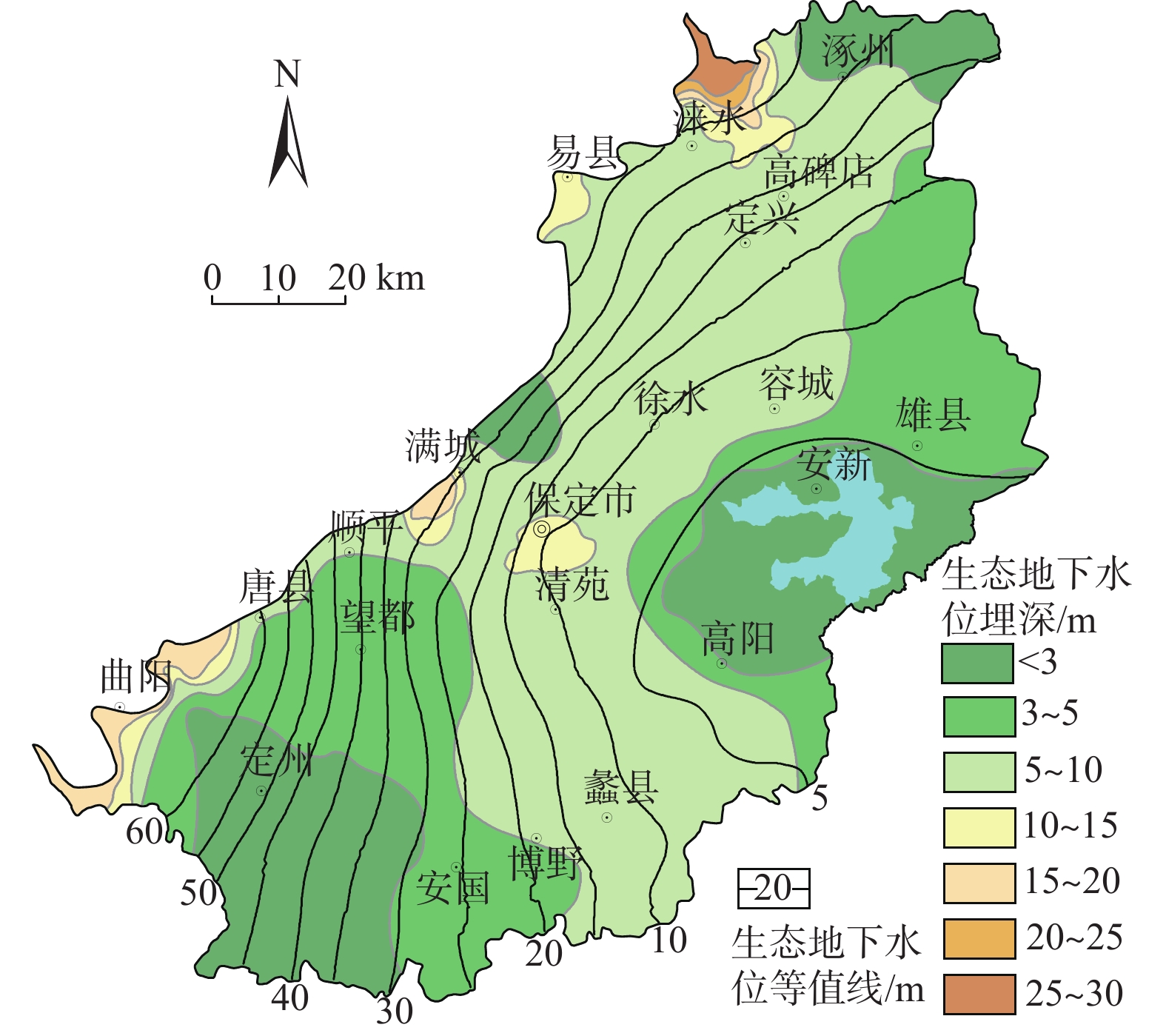
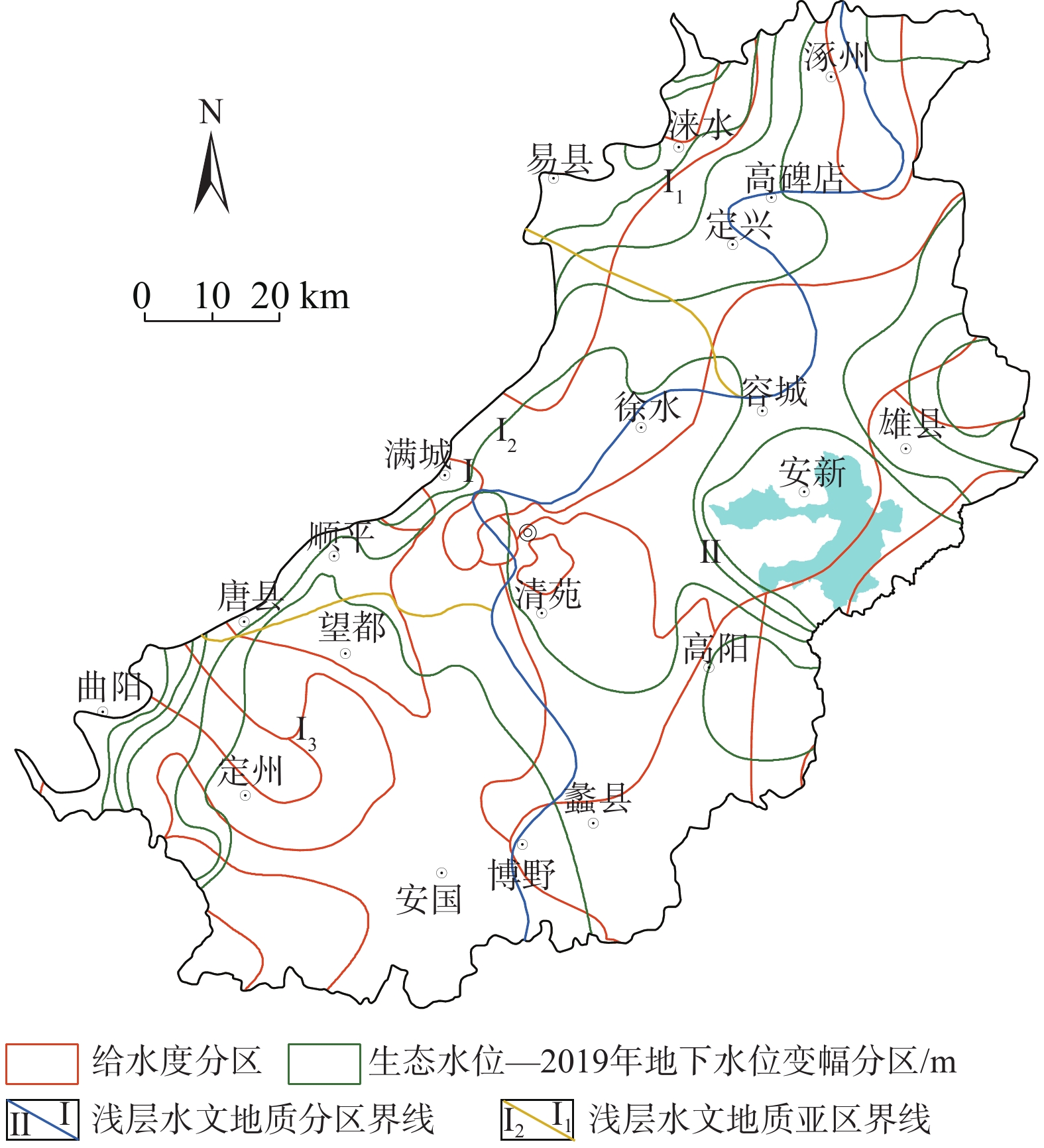
地下水具有重要的生态价值,地下水生态系统中的地下水位、水质和包气带含水率与含盐量的变化驱动着表生生态格局的演变,但目前对各变量的生态阈值研究尚处于起步阶段,理论与方法体系还不完善。以保定平原区为例,采用地下水位及地下水生态环境的历史回归法、GIS法、差分网格计算法等方法,从时空角度分析了地下水位变化的驱动力以及生态效应,在此基础上确定不同水文地质单元的生态水位阈值。研究表明:(1)20世纪50—60年代,研究区依赖于地下水的生态格局基本维持着天然状态;1959—2000年,地下水位持续下降,局部地段出现降落漏斗;2000—2008年,地下水位骤降,降落漏斗迅速扩张,地下水与地表水补排关系发生变异;2008年至今,部分区域地下水位逐渐上升。(2)研究区内山前地带地下水生态水位埋深为10~15 m,拒马河冲洪积扇群与漕河—瀑河冲洪积扇群为5~10 m,唐河—大沙河冲洪积扇群为3~5 m,冲积平原中定州—望都范围为3~5 m,保定市为10~15 m,其余均为5~10 m,冲湖积平原环淀区域小于3 m。(3)以确定的地下水生态水位为标准,初步估算研究区现状地下水位恢复至生态水位的需水量为57.14×108 m3。研究成果对恢复当地地下水生态环境格局有重要意义,对华北平原地下水生态水位的确定也具有借鉴意义。
Abstract:Groundwater is of important ecological value. The changes in groundwater level, water quality, water content and salt content in the unsaturated zone in groundwater ecosystems drive the evolution of supergene ecological pattern. So far, the research on the ecological threshold of each variable is still at the starting stage, and the theoretical and methodological system is not perfect. In this study the Baoding Plain is taken as an example, and the driving force and ecological effect of groundwater level changes are analyzed from the perspective of time and space by using the historical regression method, GIS method and difference grid calculation method of groundwater levels and groundwater ecological environments. On this basis, the ecological water level thresholds of different hydrogeological units are determined. The results show that: (1) In the 1950s-60s, the ecological pattern of the study area depending on groundwater basically maintained a natural state; from 1959 to 2000, the groundwater levels continued to decline, and the groundwater depression cones appeared in some areas. From 2000 to 2008, the groundwater levels dropped sharply, the groundwater depression cones expanded rapidly, and the recharge and discharge relationship between groundwater and surface water changed. Since 2008, groundwater levels have gradually increased in some regions. (2) The depth of groundwater ecological water level in the piedmont zone of the study area is 10–15 m deep, the Juma River alluvial fan group and Cao River-Pu River alluvial fan group are 5–10 m, the Tang-Dasha River alluvial fan group is 3–5 m, the Dingzhou-Wangdu area in the alluvial plain is 3–5 m, the city of Baoding is about 10–15 m, and the rest are 5–10 m. The area around the alluvial lacustrine plain is less than 3 m. (3) Taking the determined ecological groundwater level as the standard, it is preliminarily estimated that the water demand for restoring the current groundwater level to the ecological water level in the study area is 57.14×108 m3. The research results are of important significance for restoring the local groundwater ecological environment pattern and for determining the ecological groundwater level in the North China Plain.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- ecosystem /
- driving force /
- ecological groundwater level /
- Baoding Plain area
-

-
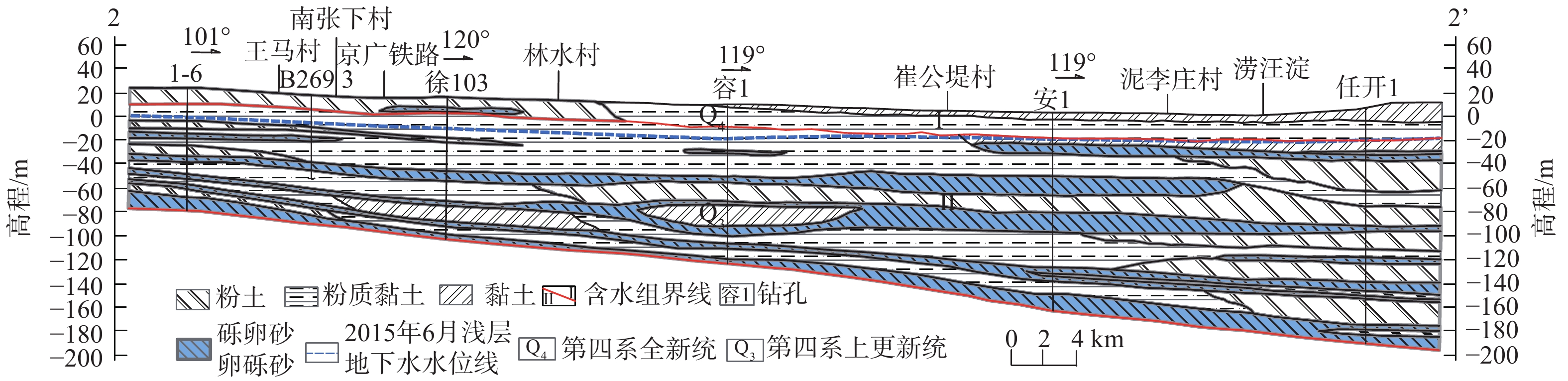
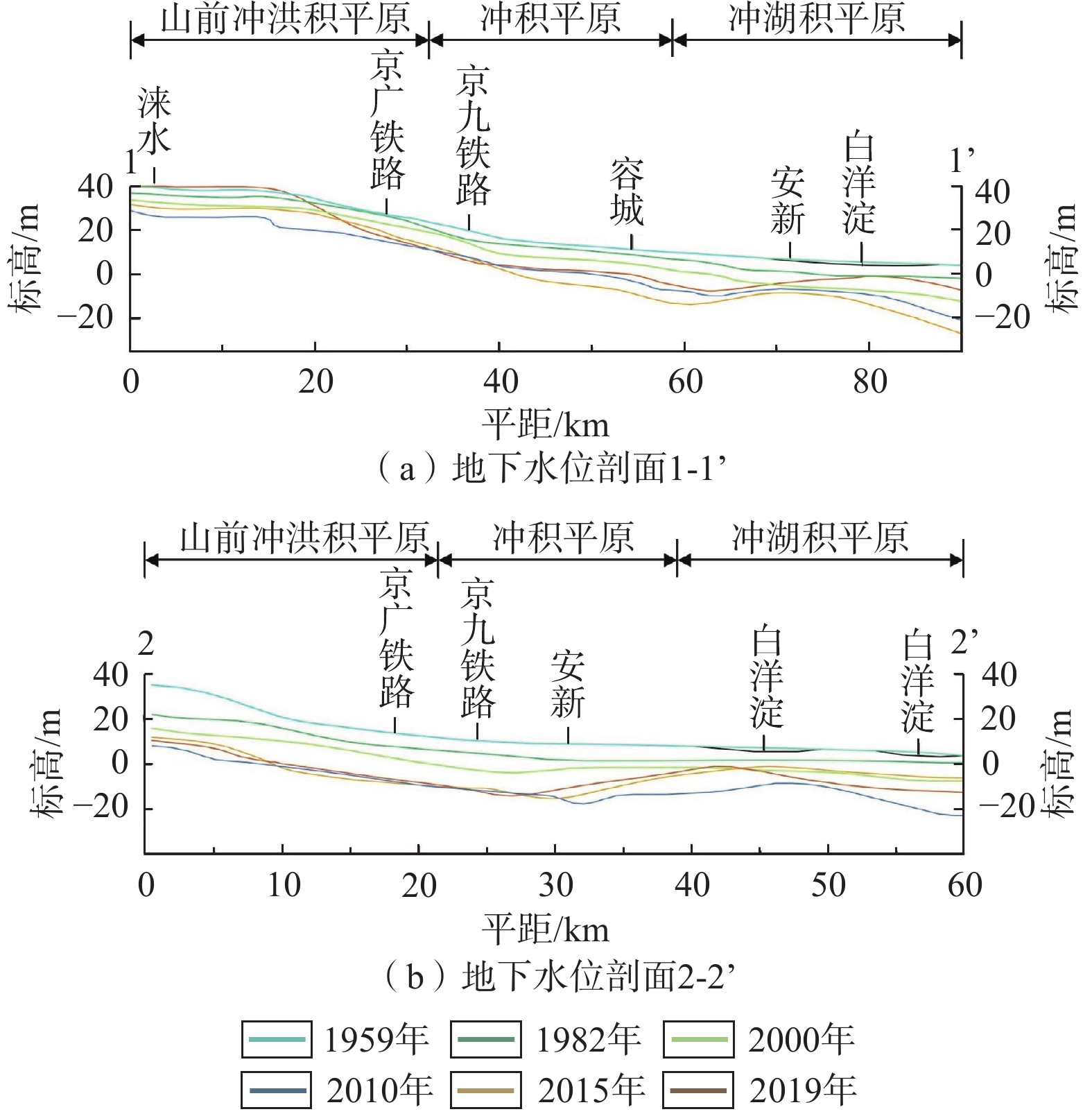
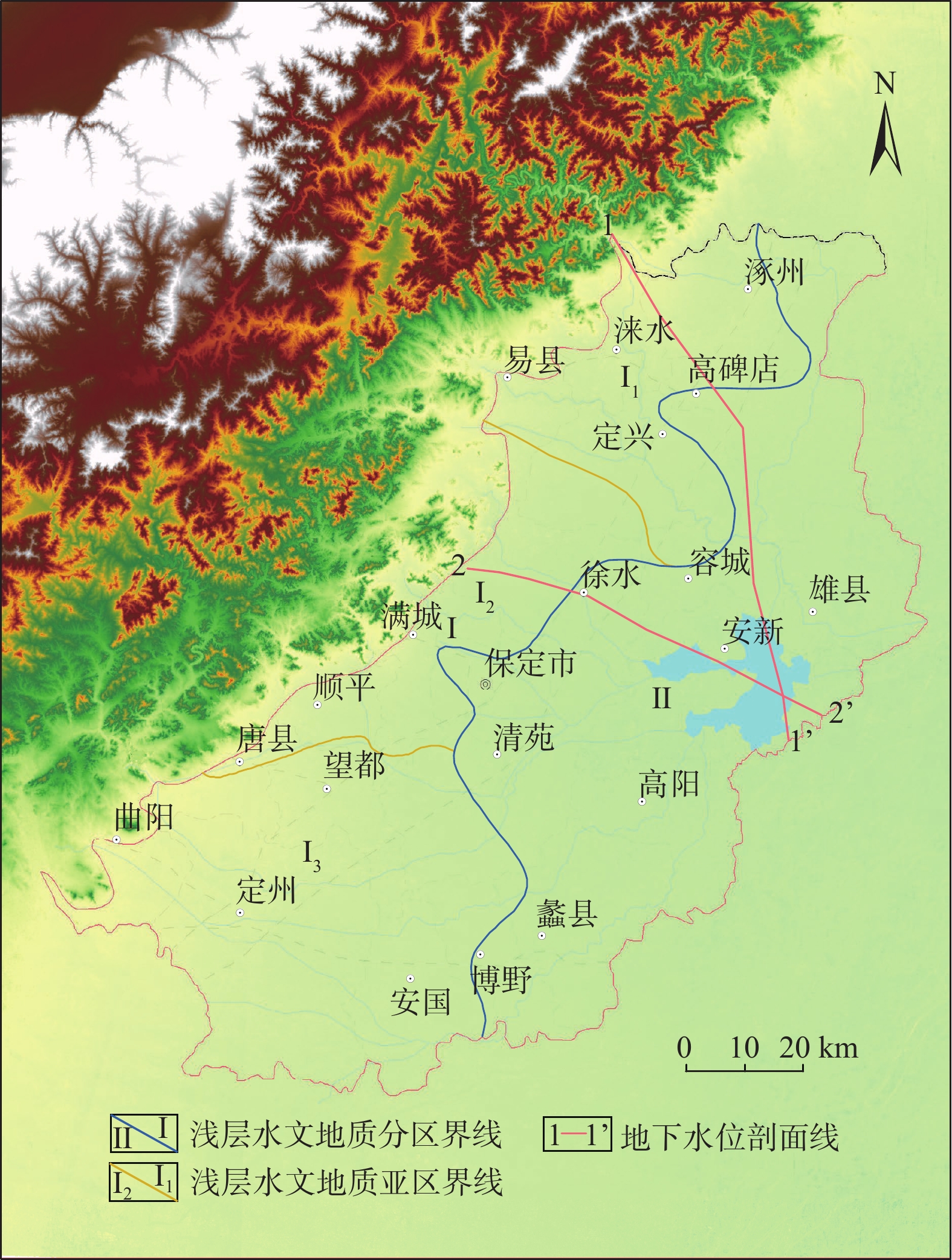
图 2 研究区2—2’水文地质剖面图(据文献[28]修改)
Figure 2.
表 1 浅层地下水生态补水量计算结果
Table 1. Calculation results of ecological recharge of shallow groundwater
水文地质单元 计算面积
/km2现状地下水位
/m地下水生态水位
/m水位变差
/m给水度 地下水生态补水量
/(108 m3)山前冲洪积平原(I) 拒马河冲洪积扇群(I1) 1 455.56 20.90 26.40 5.50 0.09 2.37 漕河—瀑河冲洪积扇群(I2) 1 250.32 10.10 26.20 16.10 0.09 5.50 唐河—大沙河冲洪积扇群(I3) 3 092.90 14.70 38.10 23.40 0.12 28.00 冲积平原+冲湖积平原(II) 4 790.33 −7.80 9.40 17.20 0.08 21.26 -
[1] 杨会峰, 曹文庚, 支传顺, 等. 近40年来华北平原地下水位演变研究及其超采治理建议[J]. 中国地质,2021,48(4):1142 − 1155. [YANG Huifeng, CAO Wengeng, ZHI Chuanshun, et al. Evolution of groundwater level in the North China Plain in the past 40 years and suggestions on its overexploitation treatment[J]. Geology in China,2021,48(4):1142 − 1155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 费宇红, 苗晋祥, 张兆吉, 等. 华北平原地下水降落漏斗演变及主导因素分析[J]. 资源科学,2009,31(3):394 − 399. [FEI Yuhong, MIAO Jinxiang, ZHANG Zhaoji, et al. Analysis on evolution of groundwater depression cones and its leading factors in North China Plain[J]. Resources Science,2009,31(3):394 − 399. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1007-7588.2009.03.007
[3] 郭海朋, 白晋斌, 张有全, 等. 华北平原典型地段地面沉降演化特征与机理研究[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(6):1115 − 1127. [GUO Haipeng, BAI Jinbin, ZHANG Youquan, et al. The evolution characteristics and mechanism of the land subsidence in typical areas of the North China Plain[J]. Geology in China,2017,44(6):1115 − 1127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 郭海朋, 李文鹏, 王丽亚, 等. 华北平原地下水位驱动下的地面沉降现状与研究展望[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(3):162 − 171. [GUO Haipeng, LI Wenpeng, WANG Liya, et al. Present situation and research prospects of the land subsidence driven by groundwater levels in the North China Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(3):162 − 171. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张光辉, 刘中培, 连英立, 等. 华北平原地下水演化地史特征与时空差异性研究[J]. 地球学报,2009,30(6):848 − 854. [ZHANG Guanghui, LIU Zhongpei, LIAN Yingli, et al. Geohistory characteristics and temporal-spatial diversity of groundwater evolution in North China Plain in Holocene[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2009,30(6):848 − 854. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2009.06.017
[6] 杨泽凡, 胡鹏, 赵勇, 等. 新区建设背景下白洋淀及入淀河流生态需水评价和保障措施研究[J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报,2018,6(6):563 − 570. [YANG Zefan, HU Peng, ZHAO Yong, et al. Study on ecological water demand and safeguard measures of Baiyangdian Lake and the upstream rivers under the background of Xiongan New Area[J]. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research,2018,6(6):563 − 570. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 翟新博. 塔里木河下游地下水恢复需水量探析[J]. 水利科学与寒区工程,2021,4(3):72 − 75. [ZHAI Xinbo. Analysis on groundwater restoration demandin the lower reaches of the Tarim River[J]. Hydro Science and Cold Zone Engineering,2021,4(3):72 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] LIU M, NIE Z L, CAO L, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on the ecological function of groundwater in the Shiyang River Watershed[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2021,9(4):326 − 340.
[9] 孙才志, 高颖, 朱正如. 基于生态水位约束的下辽河平原地下水生态需水量估算[J]. 生态学报,2013,33(5):1513 − 1523. [SUN Caizhi, GAO Ying, ZHU Zhengru. Estimation of ecological water demands based on ecological water table limitations in the lower reaches of the Liaohe River Plain, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2013,33(5):1513 − 1523. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.5846/stxb201206120844
[10] 吴明辉, 宁虎森, 王让会, 等. 克拉玛依地区减排林地下水动态变化及合理生态水位分析[J]. 水土保持通报,2010,30(4):129 − 133. [WU Minghui, NING Husen, WANG Ranghui, et al. Dynamic change of groundwater and reasonable ecological groundwater level in Karamay artificial carbon-dioxide-capture forest[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2010,30(4):129 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] DANG X Y, LU N, GU X F, et al. The relationship between groundwater and natural vegetation in Qaidam Basin[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering,2021,9(4):341 − 349.
[12] WANG W K, YANG Z Y, KONG J L, et al. Ecological impacts induced by groundwater and their thresholds in the arid areas in Northwest China[J]. Environmental Engineering and Management Journal,2013,12(7):1497 − 1507. doi: 10.30638/eemj.2013.184
[13] LIU F, SONG X F, YANG L H, et al. Predicting the impact of heavy groundwater pumping on groundwater and ecological environment in the Subei Lake Basin, Ordos Energy Base, Northwestern China[J]. Hydrology Research,2018,49(3/4):1156 − 1171.
[14] 杨泽元, 王文科, 黄金廷, 等. 陕北风沙滩地区生态安全地下水位埋深研究[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2006,34(8):67 − 74. [YANG Zeyuan, WANG Wenke, HUANG Jinting, et al. Research on buried depth of eco-safety about groundwater table in the blown-sand region of the Northern Shaanxi Province[J]. Journal of Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry (Natural Science Edition),2006,34(8):67 − 74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 王哲, 付宇, 朱静思,等. 华北典型河道地下水回补效果评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2021,51(3):843 − 853. [WANG Zhe, FU Yu, ZHU Jingsi, et al. Effect assessment on groundwater recharge for typical rivers in North China[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2021,51(3):843 − 853.
[16] 翟家齐, 董义阳, 祁生林, 等. 干旱区绿洲地下水生态水位阈值研究进展[J]. 水文,2021,41(1):7 − 14. [ZHAI Jiaqi, DONG Yiyang, QI Shenglin, et al. Advances in ecological groundwater level threshold in arid oasis regions[J]. Journal of China Hydrology,2021,41(1):7 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] ZHU Y H. Relationship of dominant herbaceous plant species and groundwater depth in Tongliao Plain, Northwestern China[J]. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research,2019,17(6):15363 − 15374.
[18] LI F W, WANG Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Modelling the response of vegetation restoration to changes in groundwater level, based on ecologically suitable groundwater depth[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2018,26(7):2189 − 2204. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1813-3
[19] 曹乐, 聂振龙, 刘敏, 等. 民勤绿洲天然植被生长与地下水埋深变化关系[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):25 − 33. [CAO Le, NIE Zhenlong, LIU Min, et al. Changes in natural vegetation growth and groundwater depth and their relationship in the Minqin oasis in the Shiyang River Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):25 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 党学亚, 卢娜, 顾小凡, 等. 柴达木盆地生态植被的地下水阈值[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(3):1 − 8. [DANG Xueya, LU Na, GU Xiaofan, et al. Groundwater threshold of ecological vegetation in Qaidam Basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(3):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] WANG Y, CHEN M J, YAN L, et al. Quantifying threshold water tables for ecological restoration in arid Northwestern China[J]. Groundwater,2020,58(1):132 − 142. doi: 10.1111/gwat.12934
[22] 汪勇, 陈敏建, 赵勇, 等. 基于生态圈层结构稳定的地下水位计算与调控[J]. 水科学进展,2021,32(4):597 − 607. [WANG Yong, CHEN Minjian, ZHAO Yong, et al. Calculation and regulation of groundwater level based on the stability of groundwater-dependent ecosystem[J]. Advances in Water Science,2021,32(4):597 − 607. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 尚海敏, 王文科, 段磊, 等. 天山北麓地下水基于生态水位的调控模拟分析[J]. 水土保持研究,2014,21(6):144 − 147. [SHANG Haimin, WANG Wenke, DUAN Lei, et al. Simulation on groundwater regulation based on ecological water table in the northern foot of Tianshan Mountain[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2014,21(6):144 − 147. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] LI X, ZHENG Y, SUN Z, et al. An integrated ecohydrological modeling approach to exploring the dynamic interaction between groundwater and phreatophytes[J]. Ecological Modelling,2017,356:127 − 140. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.04.017
[25] 陈敏建, 张秋霞, 汪勇, 等. 西辽河平原地下水补给植被的临界埋深[J]. 水科学进展,2019,30(1):24 − 33. [CHEN Minjian, ZHANG Qiuxia, WANG Yong, et al. Critical depth of recharge of the vegetation by groundwater in the West Liaohe Plain[J]. Advances in Water Science,2019,30(1):24 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] KAISER T, WEHRHAN M, WERNER A, et al. Regionalizing ecological moisture levels and groundwater levels in grassland areas using thermal remote sensing[J]. Grassland Science,2012,58(1):42 − 52. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-697X.2011.00240.x
[27] 张兆吉, 费宇红. 华北平原地下水可持续利用图集[M]. 北京: 中国地图出版社, 2009
ZHANG Zhaoji, FEI Yuhong. Atlas of groundwater sustainable utilization in North China Plain[M]. Beijing: Sino Maps Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[28] 田晓华, 冯创业, 张增勤, 等. 京津冀协同发展保定市平原区地质环境保障调查评价报告[R]. 石家庄: 河北省地矿局水文工程地质勘查院, 2017
TIAN Xiaohua, FENG Chuangye, ZHANG Zengqin, et al. Survey and evaluation report of geological environment protection in the plain area of Baoding City in the coordinated development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei[R]. Shijiazhuang: Hydrological Engineering Geological Survey Institute of Hebei Geology and Mineral Bureau, 2017. (in Chinese)
[29] 李林森. 白洋淀流域平原区地下水动力场演化及预测[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020
LI Linsen. Evolution and prediction of groundwater dynamic field in plain area of Baiyangdian Watershed[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 肖丽英. 海河流域地下水生态环境问题的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2004
XIAO Liying. Research on the problem of groundwater eco-environment in Haihe River Basin[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2004. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 孟素花, 费宇红, 张兆吉, 等. 华北平原地下水脆弱性演变及对埋深变化的响应[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2010,8(6):78 − 81. [MENG Suhua, FEI Yuhong, ZHANG Zhaoji, et al. Evolution features and respond to groundwater depth variation of groundwater vulnerability in North China Plain[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2010,8(6):78 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 廖梓龙, 马真臻, 程双虎, 等. 地下水控制性临界水位及确定方法[J]. 水利水电技术,2018,49(3):26 − 32. [LIAO Zilong, MA Zhenzhen, CHENG Shuanghu, et al. Dominant critical water level of groundwater and its determining method[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering,2018,49(3):26 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 盖美, 耿雅冬, 张鑫. 海河流域地下水生态水位研究[J]. 地域研究与开发,2005,24(1):119 − 124. [GAI Mei, GENG Yadong, ZHANG Xin. Research on groundwater ecology water level of Haihe River Basin[J]. Areal Research and Development,2005,24(1):119 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2005.01.027
[34] 张长春, 邵景力, 李慈君, 等. 华北平原地下水生态环境水位研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2003,33(3):323 − 326. [ZHANG Changchun, SHAO Jingli, LI Cijun, et al. A study on the ecological groundwater table in the North China Plain[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition),2003,33(3):323 − 326. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-



 下载:
下载: