An experimental study of the creep characteristics of loess landslide sliding zone soil with different water content
-
摘要:
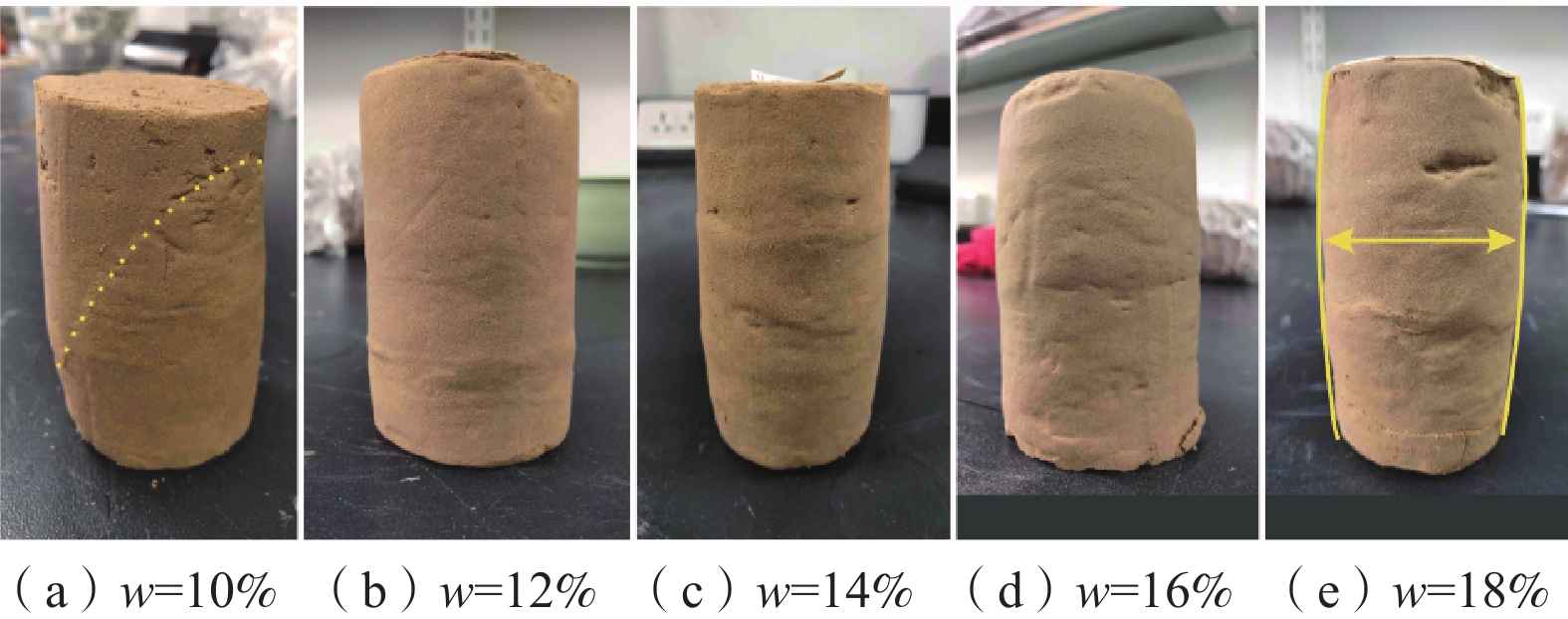
黄土斜坡在受到降雨、人工灌溉、河流水浸润等作用后容易发生蠕变,最终发生滑坡,有时甚至会造成灾难性事故。以往研究中对不同含水率下黄土滑坡滑带土的蠕变性质研究较少,更缺乏定量化的规律分析。以榆林市色草湾村黄土滑坡滑带土为例,进行了一系列三轴蠕变试验,得到了黄土不同含水率下(w=10%、12%、14%、16%、18%,w表示含水率)的应力-应变-时间曲线与应力-应变等时曲线,分析了含水率对黄土蠕变特性的影响,并利用等时曲线法求取了黄土的长期强度,得出如下结论:(1)含水率越大,样品蠕变破坏所需的偏应力越小,轴向应变也越大,含水率增大后自由水厚度增大,土颗粒间胶结程度减小,且水膜会对土颗粒起润滑作用易于其错动滑移;(2)含水率越大,施加每级荷载后样品蠕变曲线达到稳定状态所需时间越长,水分的增加会使土体结构完整性降低,在应力的作用下土体内部结构调整相对缓慢,固结和蠕变过程中孔隙水压力消散需要的时间也越长;(3)通过分析黄土试样蠕变破坏表面形态发现,含水率较小时,蠕变破坏后的试样有明显的剪切破坏面,当试样含水率越大时,越容易发生横向鼓胀,表现出塑性破坏特征,表明含水率较大时,水的软化作用大于水对于土体的裂隙扩展作用;(4)引入了黄土长期强度折损率,揭示了不同含水率下黄土滑坡滑带土的长期强度与长期强度折损率的规律。研究成果可为黄土滑坡的长期稳定性分析提供参考依据。
Abstract:Loess slopes are often prone to creeping after being subjected to rainfall, artificial irrigation, river water infiltration, etc. Eventually a landslide occurred, even causing a catastrophic accident. There are few studies on the creep properties of loess landslide soil under different water content in the existing literature, and there is a lack of quantitative analysis of the law. A series of triaxial creep tests of sliding zone soil of loess landslide in the Secaowan Village, Yulin City have been carried. The stress-strain-time curves and isochronous stress-strain curves with different water contents (w=10%, 12%, 14%, 16%, 18%, w represents the water content) are obtained and the influence of water content on the creep characteristics of loess is analyzed as well. The long-term strength of loess is obtained by using the isochronous curve method. The research results show that (1) When the water content of the sample is larger, the deviator stress required for the creep failure of the sample is smaller, and the axial strain is larger. This phenomenon can be explained by the electric double layer theory as follows: The thickness of free water increases, the degree of cementation among soil particles decreases, and the water film will lubricate the soil particles and make them easy to slip. (2) When the water content of the sample is larger, the time required for the creep strain to reach a stable state after each level of load is applied is longer. This phenomenon can be explained as follows: The increase of loess moisture reduces the structural integrity of the soil, and the adjustment of the internal structure of the soil is relatively slow under the action of stress. Therefore, it takes a longer time for the pore water pressure to dissipate during consolidation and creep. (3) By analyzing the surface morphology of the creep failure of the loess sample, it is found that when the water content is small, the sample after the creep failure has an obvious shear failure surface. When the water content of the sample is larger, the lateral swelling is more likely to occur, showing the characteristics of plastic failure, and indicating that when the moisture content is larger, the softening effect of water is greater than the effect of water on the crack expansion of the soil. (4) The long-term strength loss rate of loess is introduced. It reveals the law of long-term strength and long-term strength loss rate of loess landslide soil under different water content. The research results can provide a reference for the long-term stability analysis of loess landslides.
-
Key words:
- loess landslide /
- sliding zone soil /
- creep /
- water content /
- long-term strength
-

-
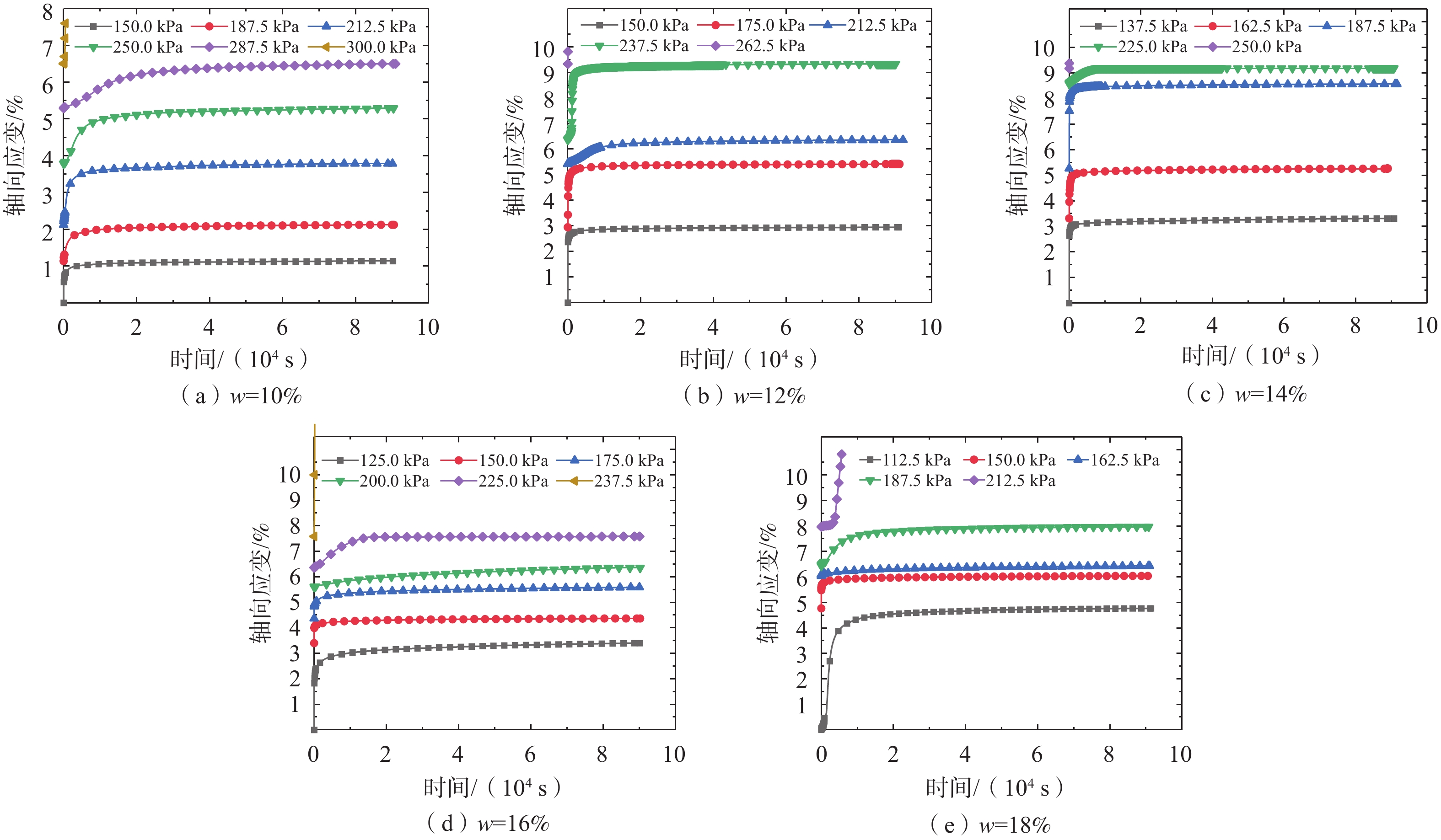
表 1 蠕变试验偏应力加载方案
Table 1. Deviator stress loading scheme for creep tests
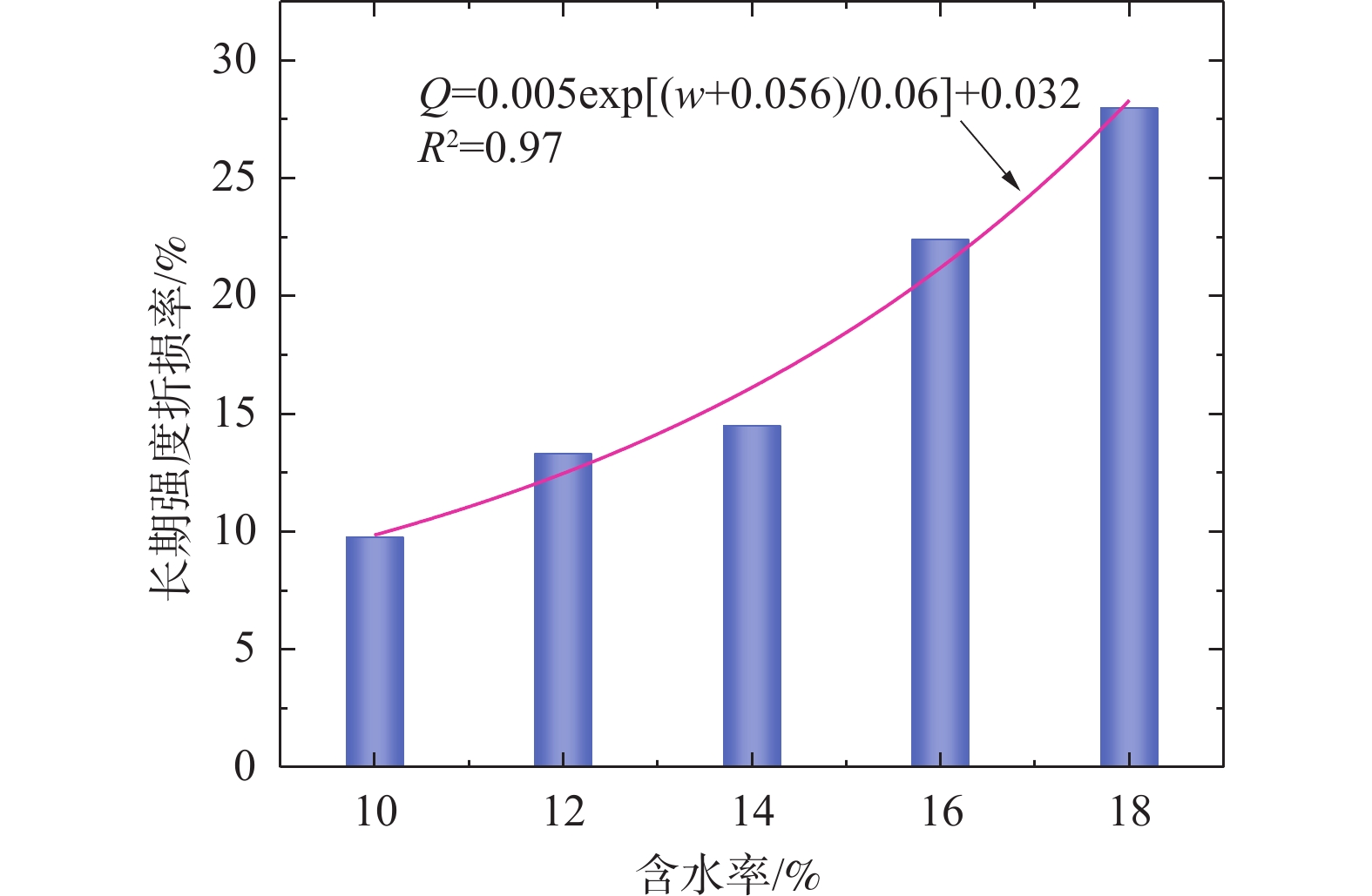
w/% q/kPa 10 150.0,187.5,212.5,250.0,287.5,300.0 12 150.0,175.0,212.5,237.5,262.5,287.5 14 137.5,162.5,187.5,225.0,250.0,262.5 16 125.0,150.0,175.0,200.0,225.0,237.5 18 112.5,150.0,162.5,187.5,212.5,225.0 表 2 黄土不同含水率下瞬时强度与长期强度
Table 2. Instantaneous strength and long-term strength of loess sample with different water content
w/% qf/kPa q'/kPa Q/% 10 312.5 282 9.8 12 300.0 260 13.3 14 275.0 235 14.5 16 250.0 194 22.4 18 237.5 171 28.0 -
[1] 刘东生. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985
LIU Dongsheng. Loess and environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985. (in Chinese)
[2] 龙建辉,郭文斌,李萍,等. 黄土滑坡滑带土的蠕变特性[J]. 岩土工程学报,2010,32(7):1023 − 1028. [LONG Jianhui,GUO Wenbin,LI Ping,et al. Creep property of soil in sliding zone of loess landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2010,32(7):1023 − 1028. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 许领,李宏杰,吴多贤. 黄土台缘滑坡地表水入渗问题分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2008,19(2):32 − 35. [XU Ling,LI Hongjie,WU Duoxian. Discussion on infiltration of surface water and their significance to terrace loess landslides[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2008,19(2):32 − 35. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2008.02.007
[4] 张茂省,李同录. 黄土滑坡诱发因素及其形成机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(4):530 − 540. [ZHANG Maosheng,LI Tonglu. Triggering factors and forming mechanism of loess landslides[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(4):530 − 540. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.014
[5] 王新刚,余宏明,胡斌,等. 节理控制的降雨入渗通道对黄土开挖边坡稳定性的影响[J]. 山地学报,2013,31(4):413 − 417. [WANG Xingang,YU Hongming,HU Bin,et al. Impact analysis of the joint control excavation loess slope’s stability under the influence of rainfall infiltration channel[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2013,31(4):413 − 417. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2013.04.005
[6] 段钊,张弘,唐皓,等. 泾河下游黄土台塬区侵蚀诱发滑坡机理[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(6):10 − 16. [DUAN Zhao,ZHANG Hong,TANG Hao,et al. Mechanism of erosion induced landslide in loess plateau area in the lower reaches of Jing River[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2019,38(6):10 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 张吉宏,段钊,唐皓. 蠕变对河流侧蚀型黄土滑坡影响的数值模拟[J]. 人民黄河,2020,42(2):142 − 146. [ZHANG Jihong,DUAN Zhao,TANG Hao. Numerical simulation of the effect of creep on loess landslide caused by lateral river erosion[J]. Yellow River,2020,42(2):142 − 146. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2020.02.030
[8] 彭建兵,林鸿州,王启耀,等. 黄土地质灾害研究中的关键问题与创新思路[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(4):684 − 691. [PENG Jianbing,LIN Hungchou,WANG Qiyao,et al. The critical issues and creative concepts in mitigation research of loess geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(4):684 − 691. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2014.04.014
[9] 葛苗苗,李宁,盛岱超,等. 水力耦合作用下非饱和压实黄土细观变形机制试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(9):2437 − 2448. [GE Miaomiao,LI Ning,SHENG Daichao,et al. Experimental investigation of microscopic deformation mechanism of unsaturated compacted loess under hydraulic coupling conditions[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(9):2437 − 2448. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2020.1784
[10] 王松鹤, 骆亚生, 董晓宏, 等. 黄土剪切蠕变特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(增刊1): 3088 − 3092
WANG Songhe, LUO Yasheng, DONG Xiaohong, et al. Experimental study of shear creep characteristics of loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(Sup1): 3088 − 3092. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 陈沛,王雁林,陈新建,等. 黄土-基岩滑坡滑带土蠕变本构模型研究[J]. 灾害学,2020,35(4):228 − 234. [CHEN Pei,WANG Yanlin,CHEN Xinjian,et al. Research on creep constitutive model of loess-basic landslide slip zone soil[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2020,35(4):228 − 234. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2020.04.042
[12] 魏建柄,刘卫斌. 非饱和土蠕变力学特性试验及经验模型研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):67 − 73. [WEI Jianbing,LIU Weibin. An experimental study of the creep mechanical properties of unsaturated soil and empirical models[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):67 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 慕焕东, 邓亚虹, 赫佳, 等. 基于分数阶导数理论的Q3黄土流变本构模型研究[J/OL]. 工程地质学报: 1 − 10. [2021-12-12]
MU Huandong, DENG Yahong, HAO Jia, et al. Study on rheological model of Q3 loess based on fractional derivative theory[J/OL]. Journal of Engineering Geology: 1 − 10. [2021-12-12]. https://doi. org/10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2020-125.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 王鹏程,骆亚生,胡连信,等. 重塑黄土三轴蠕变特性研究及模型分析[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(6):1627 − 1632. [WANG Pengcheng,LUO Yasheng,HU Lianxin,et al. Research on triaxial creep characteristics and models of remolded loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(6):1627 − 1632. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2015.06.014
[15] 王新刚,谷天峰,王家鼎. 基质吸力控制下的非饱和黄土三轴蠕变试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2017,44(4):57 − 61. [WANG Xingang,GU Tianfeng,WANG Jiading. Research on the triaxial creep test of unsaturated loess under the matric suction control[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(4):57 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 朱才辉,李玉波,兰开江,等. 黄土隧道地层蠕变效应对围岩压力的影响[J]. 工业建筑,2021,51(7):18 − 24. [ZHU Caihui,LI Yubo,LAN Kaijiang,et al. Creep effect of loess strata on surrounding rock pressure of tunnels[J]. Industrial Construction,2021,51(7):18 − 24. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.13204/j.gyjzg20072901
[17] 单帅,谢婉丽,朱荣森,等. 加卸荷条件下延安新区压实黄土蠕变特性研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境,2021,35(7):144 − 155. [SHAN Shuai,XIE Wanli,ZHU Rongsen,et al. Creep characteristics of compacted loess in Yan’an New District under loading and unloading conditions[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment,2021,35(7):144 − 155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 周静静,赵法锁,祝艳波,等. 低速缓动滑坡滑带土剪切蠕变特性[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(1):107 − 112. [ZHOU Jingjing,ZHAO Fasuo,ZHU Yanbo,et al. Shear creep properties for sliding-zone soil of the slow-moving landslides[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(1):107 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2020.01.17
[19] 周静静,赵法锁,袁湘秦,等. 滑带土蠕变过程及微观结构演化分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):115 − 121. [ZHOU Jingjing,ZHAO Fasuo,YUAN Xiangqin,et al. Creep process and the microstructural evolution of sliding-zone soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):115 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019010011
[20] 刘雄. 岩石流变学概论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994
LIU Xiong. Introduction to rock rheology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1994. (in Chinese)
[21] 叶为民,黄伟,陈宝,等. 双电层理论与高庙子膨润土的体变特征[J]. 岩土力学,2009,30(7):1899 − 1903. [YE Weimin,HUANG Wei,CHEN Bao,et al. Diffuse double layer theory and volume change behavior of densely compacted Gaomiaozi bentonite[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2009,30(7):1899 − 1903. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.07.004
[22] 骆亚生,谢定义,邵生俊,等. 非饱和黄土的结构变化特性[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2004,32(8):114 − 118. [LUO Yasheng,XIE Dingyi,SHAO Shengjun,et al. Variation characteristics of soil structure of unsaturated loess[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition),2004,32(8):114 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-9387.2004.08.026
[23] WANG X G,WANG J D,ZHAN H B,et al. Moisture content effect on the creep behavior of loess for the catastrophic Baqiao landslide[J]. CATENA,2020,187:104371. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2019.104371
[24] 沈明荣,谌洪菊,张清照. 基于蠕变试验的结构面长期强度确定方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2012,31(1):1 − 7. [SHEN Mingrong,CHEN Hongju,ZHANG Qingzhao. Method for determining long-term strength of discontinuity using shear creep test[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2012,31(1):1 − 7. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.01.001
-




 下载:
下载: